Samsung Foundry to Triple Production Capacity by 2026
Samsung said on Thursday that its foundry division will triple production capacity by 2026 in a bid to meet ever-growing demand for chips. To do so, Samsung Foundry will build at least one new fab and will also expand capacities at existing ones. The move will make Samsung Foundry considerably more competitive against both existing makers of semiconductors like TSMC as well as the newcomer, Intel Foundry Services.
"We plan to expand our capacity about three times by 2026 to meet customers' needs as much as possible by expanding capacity in Pyeongtaek as well as considering establishing a new plant in the U.S.," said Samsung executive Han Seung-hoon on the company's earnings conference call, reports Nikkei.
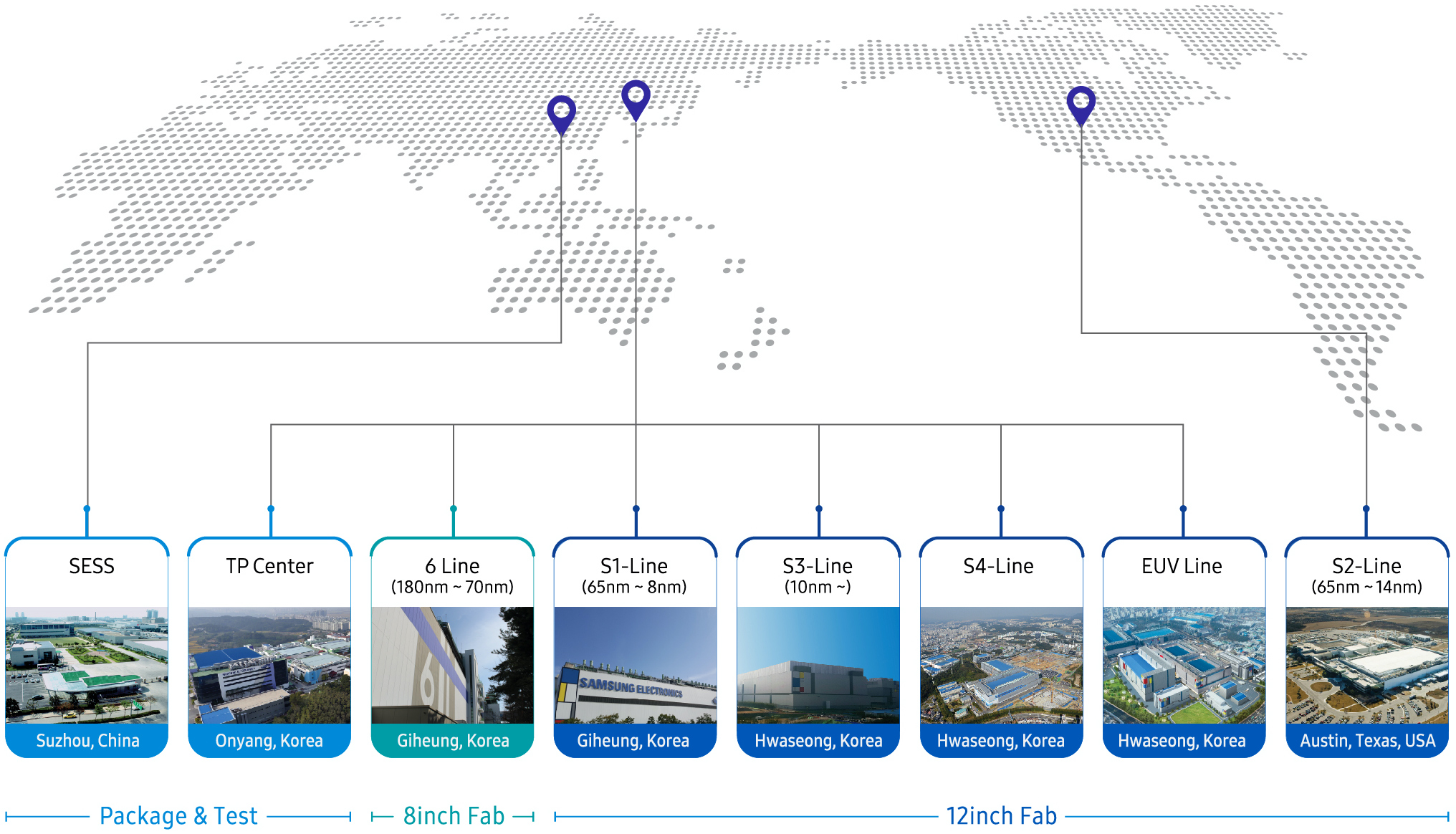
We're not sure what the "considering" refers to here, since Samsung Foundry is already set to build a brand-new fab in the U.S. It will also expand its S5 EUV fab near Hwaseong, South Korea. Meanwhile, the company has never disclosed actual capacities of its existing advanced and leading-edge fabs, so it's difficult to track what the "three times" promise actually means for those plants.
Samsung is the world's largest chipmaker by capacity. As of December, 2020, it had installed capacity of around 3.060 million 200-mm equivalent wafer starts per month, according to IC Insights. Yet most of its semiconductor production capacity is dedicated to DRAM and NAND memory. While Samsung Foundry is the world's No. 2 contract maker of chips by revenue (according to TrendForce), it is the world's No. 4 foundry by installed capacity (according to Counterpoint Research) largely because the company is focused primarily on leading-edge and advanced fabrication technologies.
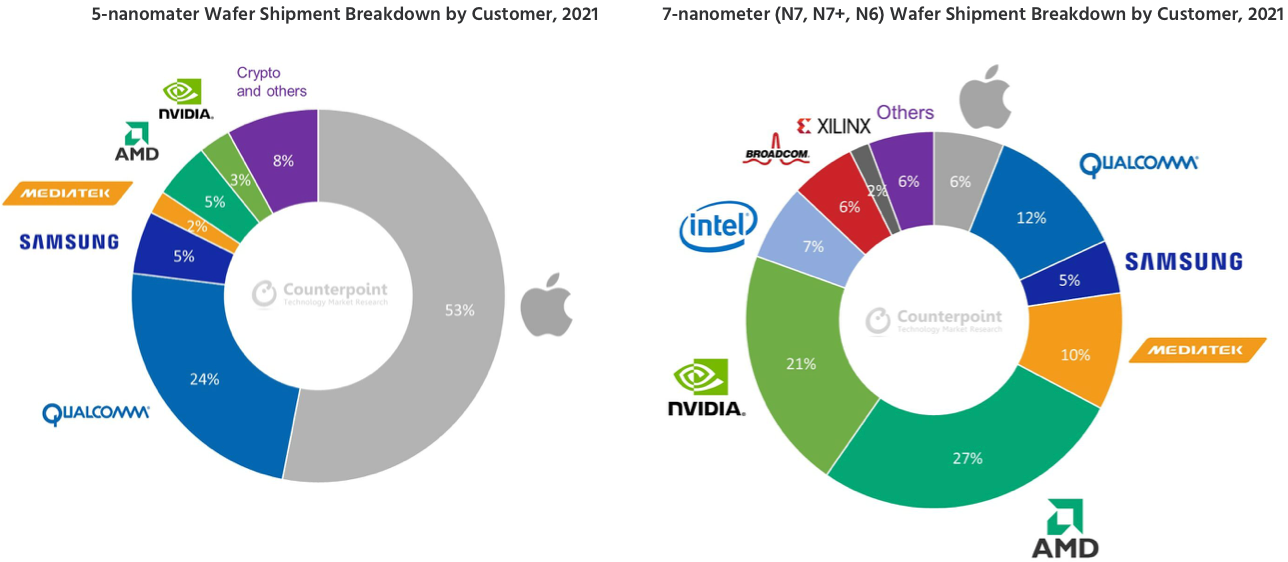
Demand for chips made using sophisticated and leading-edge fabrication processes is increasing as various emerging technologies require very capable processors. Counterpoint Research indicated earlier this year that at least seven companies would use a 5 nm-class technology in 2021, but this class of nodes is only available from TSMC and Samsung Foundry today. However, as Intel is now engaging in a foundry race, its leading-edge processes will soon be available to other fabless developers of chips and its Intel Foundry Services division will compete directly against TSMC and Samsung Foundry.
Boosting Samsung Foundry's capacity by three times by 2026 means that either the company expects demand from existing customers to triple in about four years, or to gain share from TSMC (and to not lose anything to Intel). Samsung Foundry has reasons to be optimistic here. It only served around 35 customers in 2017 (and by that time Apple ceased to be SF's main client), but now it serves over 100 clients, including Nvidia and Qualcomm. If Samsung Foundry continues to gain customers, it will clearly need additional capacity. Meanwhile, not all of Samsung Foundry's customers need leading-edge technologies, so while building new state-of-the-art fabs for 3GAA and subsequent generations (S5, S6) is important, the company will have to offer enough capacity for previous-generation nodes.
For example, Samsung Foundry could help increase capacity by adding more tools to its facilities that produce chips on mature processes that are still widely used to meet demand from its parent company Samsung Electronics. Yet, increasing mature capacities could mean a change of Samsung Foundry's business model, which focuses on premium nodes, so this may not be exactly the case here.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
In any case, with massive semiconductor-related CapEx spending that exceeds $100 billion set for the coming years, Samsung Semiconductor is definitely poised and ready to build new fabs and increase production capacity of its Samsung Foundry division.

Anton Shilov is a contributing writer at Tom’s Hardware. Over the past couple of decades, he has covered everything from CPUs and GPUs to supercomputers and from modern process technologies and latest fab tools to high-tech industry trends.