Windows Server 8 to Get a New File System: ReFS
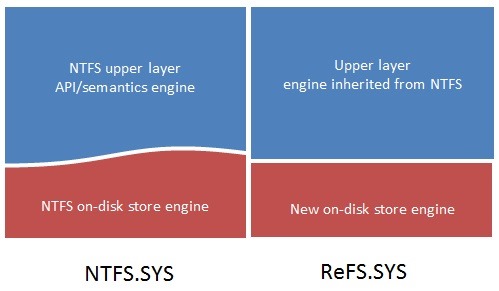
Microsoft will be introducing a new file system with Windows 8 Server, called ReFS, which is built on top of the existing NTFS, but will deliver new features for scale and prevent data corruption.
ReFS, short for Resilient File System, will initially debut with Windows 8 Server, but is expected to make its way through to Windows 8 client system to support the full feature set of Storage Spaces, which will allow users to create storage pools from multiple physical and virtual storage devices.
According to Microsoft, ReFS will be an always-online file system "for the next decade or more" that is architected for "extreme scale" with large volume, file and directory sizes, as well as data verification and auto-correction via checksums while maintaining compatibility with a "wide subset of widely adopted" NTFS features.
ReFS will support a maximum size of 4 PB per storage pool path and file lengths of up to 32,000 (unicode) characters, up to 2^64 (18,446,744,100,000,000,000 or about 18 quintillion) directories in a storage volume, and up to 2^64 files in a single directory. ReFS also supports, in theory, to a maximum volume size of 2^78 bytes, as Windows stack addressing is limited to 2^64 bytes, which translates to 16,384 PB. The file size limit is 2^64-1 bytes.
REFS's most critical feature, however, may be its ability to answer data corruption on-the-fly, as all ReFS metadata is check-summed across multiple volumes (in storage spaces environments), which enables the technology to detect disk corruptions. If the user chooses to activate file checksums (integrity streams) as well, ReFS will always give preference to the original file over the newer file. "This allocate-on-write technique ensures that pre-existing data is not lost due to the new write," wrote Surendra Verma, a development manager on Microsoft's Storage and File System team. "The checksum update is done atomically with the data write, so that if power is lost during the write, we always have a consistently verifiable version of the file available whereby corruptions can be detected authoritatively."
Just like NTFS, Microsoft will be testing and deploying ReFS in server environments initially. However, its feature may have true advantages in combined server-client environment, especially if we include cloud-computing services and storage pools. Expect ReFS to become available on your desktop and notebook PC in the foreseeable future as Verma noted that ReFS will be "the next massively deployed file system."
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.

Douglas Perry was a freelance writer for Tom's Hardware covering semiconductors, storage technology, quantum computing, and processor power delivery. He has authored several books and is currently an editor for The Oregonian/OregonLive.
-
nforce4max Does it support files with names greater than 256 characters long? I often have to rename files (web pages) that I download because their names being outrageously long that some are up to 384 characters long. Web masters should consider article numbers or a web page naming scheme that isn't a directory or a long title and directory -_-Reply
I wonder how much better win serv 8 is compared to 2003 and 2008 R2. -
hannibal Yep. Interesting to see if we see full implementation of this in win8 servicepack or in win9.Reply
In anyway nice upgrade, that will have greater impact later, when it is properly tested and allowed to use allso in boot sector.
-
freggo "file lengths of up to 32,000 (unicode) characters"Reply
Uh, am I missing something or is this a typo.
What is a 'file length' ?
Do they mean file NAME or Sector size ?
-
jcaulley_74 nforce4maxDoes it support files with names greater than 256 characters long? I often have to rename files (web pages) that I download because their names being outrageously long that some are up to 384 characters long.Reply
freggoUh, am I missing something or is this a typo.What is a 'file length' ?Do they mean file NAME or Sector size ?
"path and file (name) lengths of up to 32,000 (unicode) characters" -
jcaulley_74 Other relevant info from the ReFS blog:Reply
"Q) Can I boot from ReFS in Windows Server 8?
No, this is not implemented or supported.
Q) Can ReFS be used on removable media or drives?
No, this is not implemented or supported.
Q) What semantics or features of NTFS are no longer supported on ReFS?
The NTFS features we have chosen to not support in ReFS are: named streams, object IDs, short names, compression, file level encryption (EFS), user data transactions, sparse, hard-links, extended attributes, and quotas." -
jimmysmitty jcaulley_74Other relevant info from the ReFS blog:"Q) Can I boot from ReFS in Windows Server 8?No, this is not implemented or supported.Q) Can ReFS be used on removable media or drives?No, this is not implemented or supported.Q) What semantics or features of NTFS are no longer supported on ReFS?The NTFS features we have chosen to not support in ReFS are: named streams, object IDs, short names, compression, file level encryption (EFS), user data transactions, sparse, hard-links, extended attributes, and quotas."Reply
As with any new file system, it takes time to become adopted. NTFS was not fully adopted until late into XPs release, some people were still using FAT32.
Honestly though it looks interesting. Looks more geared towards servers, as NTFS does what we need for DT but maybe it will incorporate a few things from the now dead WINFS..... -
warezme Just curious, how is this done "atomically" , "The checksum update is done atomically..."? Will we be using quantum computing with windows 8?Reply -
ojas Looking at the changes they're making going from win 7 to 8...I'm getting a very strong feeling that Win 9 will turn out to be a master of all trades...great for power users, great for gamers, great for consumption devices and great for servers/enterprises...I mean, they'll have some teething troubles with Win 8 as they did with Vista, but they'll refine it in the end.Reply
Win 9 will hopefully spur Apple into make a better OS too...but i know they'll be happy with a blown up version of a mobile OS so hopefully Mac OS goes extinct...long live Winux! (or Lindows :P )