US Government Details Procedure In Revealing Security Vulnerabilities
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
The U.S. government has detailed the guidelines it follows on revealing security flaws to companies.
Unveiled in its Vulnerabilities Equities Policy, the White House delved into the specific set of rules it follows while working alongside various government agencies, such as the National Security Agency (NSA) and the Department of Homeland Security.
The VEP Charter touches on how the federal government handles the process that determines whether they should inform a company about a cyber security flaw found in its service or product. But the document also mentions how they may also withhold showing the vulnerability so it can be used for "operational or intelligence-gathering purposes".
In a blog post, White House cybersecurity coordinator Rob Joyce stressed the importance of transparency, with the release of the once-private rules being "important to establish confidence" in the government’s decision-making process.
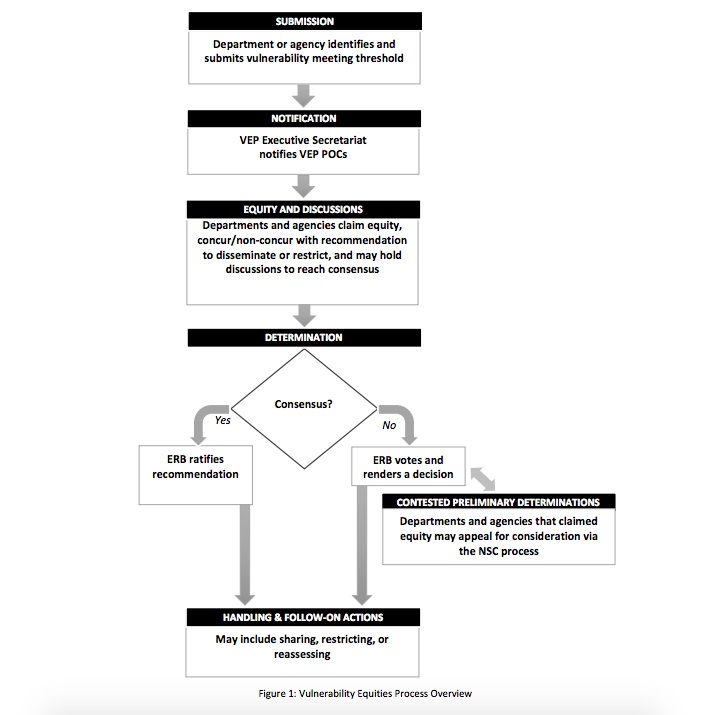
A flow chart in the charter details how the board starts the process with analyzing how dangerous the security flaw is, as well looking at the amount of potential damage that could be caused and how easy it is for the vulnerability to be exploited by hackers.
The agencies will also consider using the vulnerability for their own benefit, as well as assessing the risks involved with how the U.S.'s relationship with other countries and companies will be affected should it be revealed that the government had knowledge of the security defect.
The review occurs in the space of five days but is expedited if attacks because of vulnerability are already being used. The board then must come to a consensus on whether to reveal the security flaw to the company or not. Should the board decide to disclose the vulnerability, it must alert the company in seven business days. However, if the powers that be determine that the discovered flaw should be kept a secret, the board will annually review it until they have a change of heart or it becomes known to the public.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
The government has been criticized for keeping security exploits it's discovered a secret from an affected company. For example, a vulnerability that was being exploited by the NSA led to the WannaCry/WannaCrypt ransomware global outbreak, prompting Microsoft to condemn the government’s insistence in keeping certain security flaws to itself.

Zak Islam is a freelance writer focusing on security, networking, and general computing. His work also appears at Digital Trends and Tom's Guide.