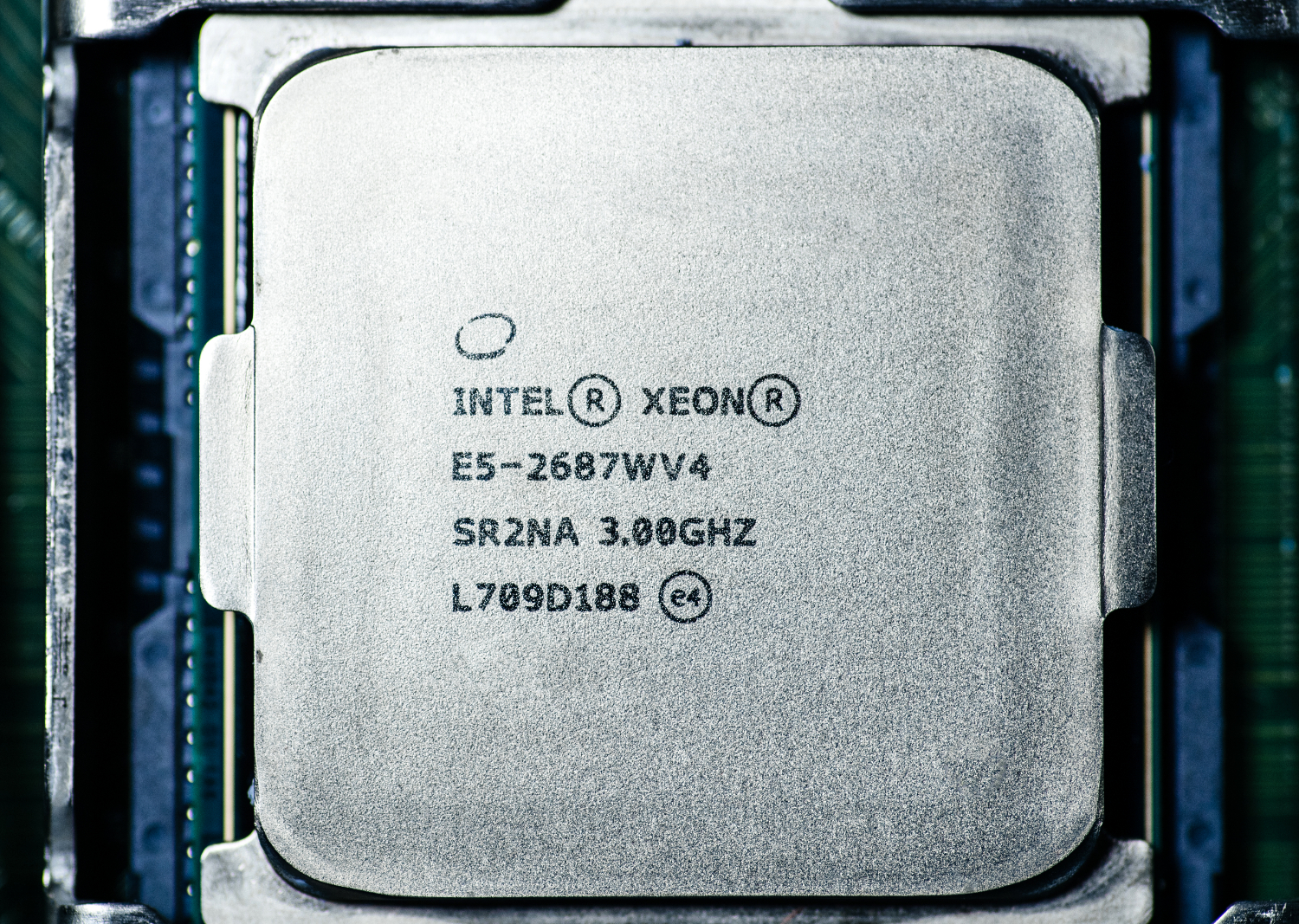
Xeon and Other Intel CPUs Hit by NetCAT Security Vulnerability, AMD Not Impacted
Researchers at Vrije University in Amsterdam revealed on Wednesday that Intel's server-grade processors suffer from a vulnerability, which they dubbed NetCAT. The vulnerability enables a side-channel attack that can infer what a CPU is working on and is said to rely on issues with two Intel technologies found primarily in the Xeon CPU line: Data-Direct I/O Technology (DDIO) and Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA). According to the researchers, AMD chips aren't impacted by the bug.
Intel said in a security bulletin that NetCAT affects Xeon E5, E7 and SP processors that support DDIO and RDMA. An underlying issue with DDIO--which has been enabled in Xeon processors by default since 2012--is what enables the side-channel attacks. Vrije University's researchers said that RDMA allows their exploit to "surgically control the relative memory location of network packets on the target server."
According to the researchers, the vulnerability means that untrusted devices on a network "can now leak sensitive data such as keystrokes in a SSH session from remote servers with no local access." Right now the only way to defend against these attacks would be to disable DDIO entirely, but the researchers said disabling RDMA could help, at least a little bit, for anyone unwilling to give up DDIO in their servers.
Intel said in its bulletin that Xeon users should "limit direct access from untrusted networks" and use "software modules resistant to timing attacks, using constant-time style code." The Vrije University researchers said those software modules wouldn't actually defend against NetCAT, however, and would only theoretically help with similar exploits in the future. So the most secure option remains disablement.
Vrije University's researchers disclosed NetCAT to Intel and the Dutch National Cyber Security Centre on June 23. They received a bounty for their report (they didn't specify the amount) and coordinated the vulnerability's disclosure with Intel. More information about NetCAT is available via this research paper; it's also been assigned the CVE identifier of CVE-2019-11184.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.

Nathaniel Mott is a freelance news and features writer for Tom's Hardware US, covering breaking news, security, and the silliest aspects of the tech industry.
-
PC Tailor Reply
You say that, they also have security flaws.Metal Messiah. said:Thank heavens, AMD CPUs are safe for now.
However I always take this with a bit of a pinch of salt, as ultimately, these flaws are being discovered by people being paid to find these flaws, and Intel still currently hold the mass market share, especially in commercial / business industry. So ultimately, its where you'd direct all of the funding and research of cyber security.
You'd also be directing a lot of that work into the working industry, which are still predominantly Intel.
I believe AMD will also have it's series of flaws, just there is less focus to find them. Not to say there is no focus, but less. -
Yeah, obviously I know AMD CPUs also have security flaws. I was just referring specifically to this NetCAT vulnerability.Reply
-
Keviny Oliveira Intel fail security again lol.Reply
a/myYDwUgView: https://imgur.com/gallery/myYDwUg -
jimmysmitty ReplyPC Tailor said:You say that, they also have security flaws.
However I always take this with a bit of a pinch of salt, as ultimately, these flaws are being discovered by people being paid to find these flaws, and Intel still currently hold the mass market share, especially in commercial / business industry. So ultimately, its where you'd direct all of the funding and research of cyber security.
You'd also be directing a lot of that work into the working industry, which are still predominantly Intel.
I believe AMD will also have it's series of flaws, just there is less focus to find them. Not to say there is no focus, but less.
Agreed. Flaws are more often found in major market holders as they will target them first. It is like when they said "CMacs don't get viruses" yet there have been a few, especially in recent times. It just takes time for these to be found.
That said my favorite part is this:
limit direct access from untrusted networks
ANY IT admin would have a network designed to already do this. This is an issue that will only be seen by people who do not secure their networks properly. -
PC Tailor Reply
What do you mean?! Macs DON'T get Viruses ! ;)jimmysmitty said:"CMacs don't get viruses" yet there have been a few, especially in recent times. It just takes time for these to be found.
No, because If I was a hacker trying to steal information, I'd definitely NOT go for the OS that holds around 80% of the market share :LOL:
Most of those security problems won't be aimed at the general home user anyway, if an advanced enough programmer wanted to do the research and exploit these, they wouldn't be desperate to get into Steve's from Liverpool home computer so they can look at his Ibiza photos. -
setx Do you really think that there is the same difference in interest in finding bugs in Intel to AMD CPUs as the difference in bugs found? I'm sure Intel wouldn't mind paying for flaws found in AMD and maybe even more than in Intel (no matter officially or not).Reply
Also, why just talk about AMD? Is there less interest in finding bugs in ARM? Do they have less market share or their market segments are less interesting? No they aren't.
The truth is Intel on deserved 1'st place of all major CPU vendors. -
TJ Hooker Reply
Look at where ARM CPUs are used compared to x86 CPUs are used. What do you think is a more appealing target, cell phones or data centers? And Intel still has the vast majority of data centre market share.setx said:Do you really think that there is the same difference in interest in finding bugs in Intel to AMD CPUs as the difference in bugs found? I'm sure Intel wouldn't mind paying for flaws found in AMD and maybe even more than in Intel (no matter officially or not).
Also, why just talk about AMD? Is there less interest in finding bugs in ARM? Do they have less market share or their market segments are less interesting? No they aren't.
Edit: Well this is embarrassing, as pointed out below I forgot about the huge embedded market for ARM. -
setx Reply
I think that all those embedded devices are way, way more appealing target than data centers. Because data centers will just roll out update next week and security hole is mitigated while majority of embedded devices won't have any updates until they are decommissioned several years later.TJ Hooker said:Look at where ARM CPUs are used compared to x86 CPUs are used. What do you think is a more appealing target, cell phones or data centers? And Intel still has the vast majority of data centre market share.