Tom's Hardware Verdict
Featuring a 2MP camera, a Pico and all the trimmings, this kit adds workable person and object detection to your Raspberry Pi Pico.
Pros
- +
+ Simple instructions
- +
+ Quick results
- +
+ Compatible with many boards
Cons
- -
Needs C/C++ knowledge
- -
Lens is unprotected
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
When we think of machine learning and artificial intelligence we instantly think of large data centers with massive computational power. But the Raspberry Pi Pico is capable of machine learning via TinyML, developed for microcontrollers. With the $40 Uctronics TinyML Learning Kit, we can easily add computer vision to our projects.
Compatible with many different microcontrollers, such as those from Arduino, the Uctronics TinyML Learning Kitincludes an Arducam Mini 2MP Plus Camera which has been used for some time with other microcontrollers, but with the power of the Raspberry Pi Pico we see much better performance for machine learning, an almost 10x increase compared to an Arduino.
We put the Uctronics TinyML Learning Kit on the bench and learned more about what this kit can offer.
Design and Use of the Uctronics TinyML Learning Kit
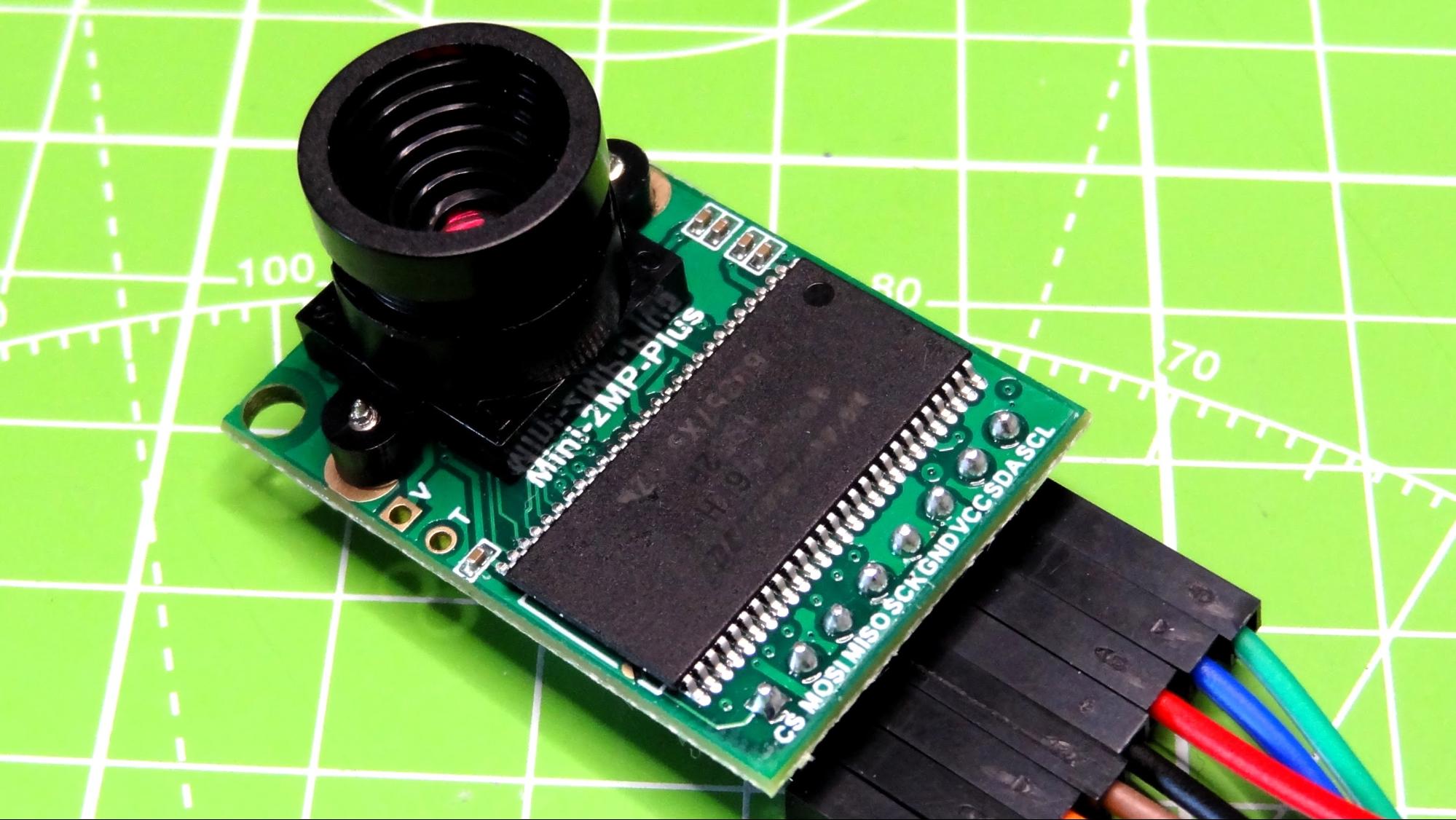
Measuring just 0.78 x 1.34 inches (20 x 34.1 mm) the focus of the kit is the Arducam 2MP Plus, a camera which is based on the OV2640, a 2MP camera which can be used with microcontrollers and computers via a SPI (data stream and commands) and I2C (sensor configuration) protocols.
This camera is not limited to just being used on the included Raspberry Pi Pico; it can also be used with Arduino and ESP32 based boards. A 2MP resolution may not sound like much, but for computer vision and machine learning it is plenty when we consider that our image will only be 320 x 320 pixels. The camera lens is contained in an M12 mount and the lens is interchangeable with other M12 lenses, available separately.
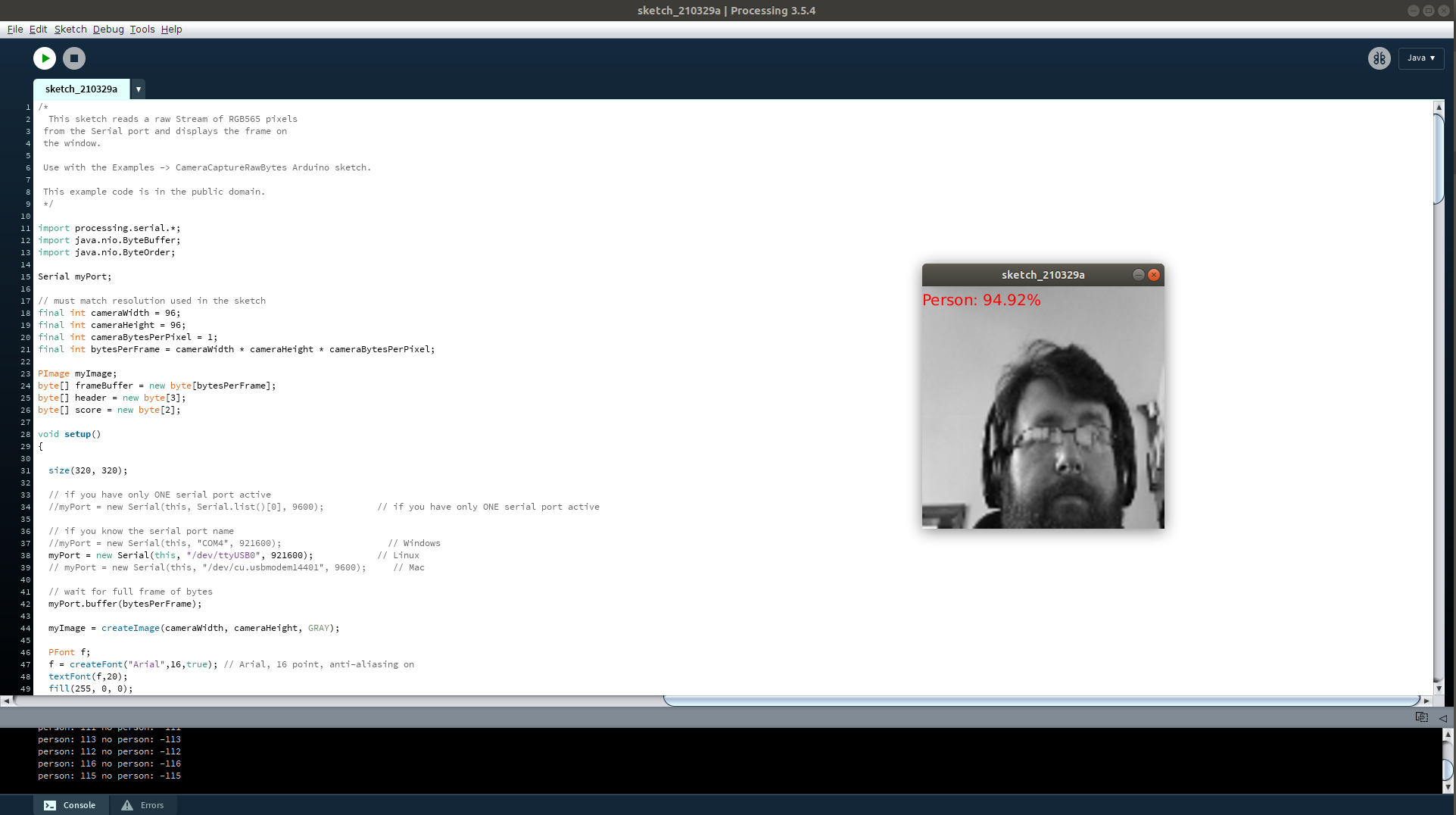
Connecting the camera to the Raspberry Pi Pico, or other RP2040 is a piece of cake thanks to the included jumper wires. The online resources clearly show the GPIO pins that we should use to connect the camera to the Pico and show the GPIO pins for the included CP2102 USB to TTL adaptor which is used to send video data from the Pico to an application, which in our review was a person detection script running Processing, a programming interface similar to the Arduino IDE but geared towards the visual arts.
After flashing a pre-made UF2 project, written in C/C++ to our Raspberry Pi Pico, we then installed the Processing IDE and the corresponding code to receive the image data and display on our desktop. If you are a MicroPython fan, then right now there are no MicroPython libraries for TensorFLow Lite for the Raspberry Pi Pico, but Arducam is working on supporting this. The Arducam Mini 2MP Plus Camera can also be used to take simple images and it has a community supported MicroPython library to simplify the process.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
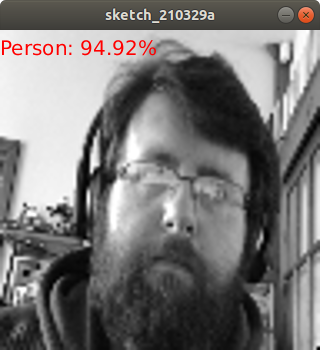
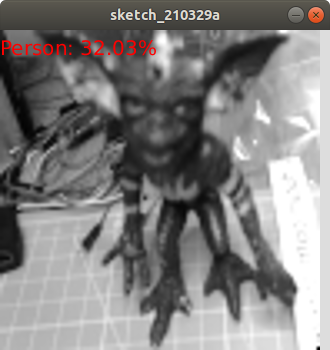
A camera connected to a Raspberry Pi Pico is cool, but machine learning is much cooler. Tiny Machine Learning (TinyML), is a version of TensorFlow developed for use on microcontrollers that almost always have less computational power than a full computer. Microcontrollers such as those from Arduino, Espressif (ESP32) and now Raspberry Pi are capable of being trained to identify objects, patterns or respond to external inputs from microphones, sensors etc.
Arducam claims that using the OV2640 camera with the Raspberry Pi Pico we can process at 1 FPS, which may not sound like much but the equivalent project running on an Arduino is 1 frame every 18 seconds. So the Pico is clearly the better board for TinyML on a budget. Arducam provides a Github repository containing a series of TinyML demos available as raw C code for customization and compilation on your machine. Should you wish to jump straight into using the demos, there are pre-compiled versions saved as UF2 files ready for use on the Pico.
What Projects Can We Use The Uctronics TinyML Learning KitFor?
The Uctronics TinyML Learning Kit is designed for TinyML and so it is geared towards projects that require just enough processing power to add computer vision and artificial intelligence to a project. Using the camera as an input, we can give a robot “sight” and, using different models, we can train the robot to search for objects or persons.
Want to watch for intruders in a room and send alerts to your devices via the Internet? Well the Arducam camera and our guide to getting your Raspberry Pi Pico online will enable just this.
Bottom Line
The Uctronics TinyML Learning Kit is great fun, but to get the best from it, you really need to know your C/C++, until the MicroPython library is ready for release that is. If you are already familiar with machine learning then chances are that this is no stumbling block for you.
The Arducam Mini 2MP Plus Camera is incredibly easy to assemble, with clear instructions and a well documented GitHub repository and with a little time even a novice programmer could get great results.

Les Pounder is an associate editor at Tom's Hardware. He is a creative technologist and for seven years has created projects to educate and inspire minds both young and old. He has worked with the Raspberry Pi Foundation to write and deliver their teacher training program "Picademy".