Corsair SF750 PSU Review: A Tiny Power Factory
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Transient Response Tests, Ripple Measurements and EMC Pre-Compliance Testing
Advanced Transient Response Tests
For details on our transient response testing, please click here.
In the real world, power supplies are always working with loads that change. It's of immense importance, then, for the PSU to keep its rails within the ATX specification's defined ranges. The smaller the deviations, the more stable your PC will be.
We should note that the ATX spec requires capacitive loading during the transient rests, but in our methodology we chose to apply the worst case scenario with no extra capacitance on the rails.
Advanced Transient Response at 20 Percent – 200ms
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 12.031V | 11.875V | 1.30% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.067V | 4.964V | 2.03% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.359V | 3.261V | 2.92% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.023V | 4.964V | 1.17% | Pass |
Advanced Transient Response at 20 Percent – 20ms
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 12.027V | 11.783V | 2.03% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.066V | 4.948V | 2.33% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.357V | 3.240V | 3.49% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.023V | 4.969V | 1.08% | Pass |
Advanced Transient Response at 20 Percent – 1ms
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 12.030V | 11.854V | 1.46% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.066V | 4.949V | 2.31% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.358V | 3.252V | 3.16% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.023V | 4.979V | 0.88% | Pass |
Advanced Transient Response at 50 Percent – 200ms
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 12.022V | 11.948V | 0.62% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.062V | 4.953V | 2.15% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.353V | 3.250V | 3.07% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.006V | 4.947V | 1.18% | Pass |
Advanced Transient Response at 50 Percent – 20ms
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 12.019V | 11.763V | 2.13% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.064V | 4.947V | 2.31% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.358V | 3.270V | 2.62% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.035V | 4.990V | 0.89% | Pass |
Advanced Transient Response at 50 Percent – 1ms
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 12.021V | 11.930V | 0.76% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.062V | 4.944V | 2.33% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.352V | 3.231V | 3.61% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.006V | 4.956V | 1.00% | Pass |
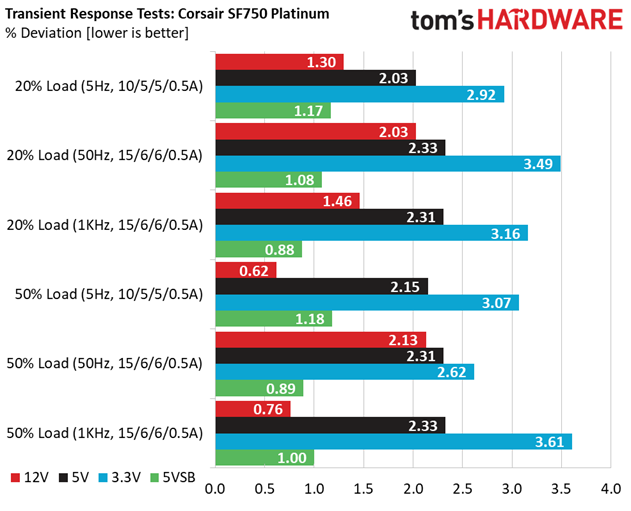
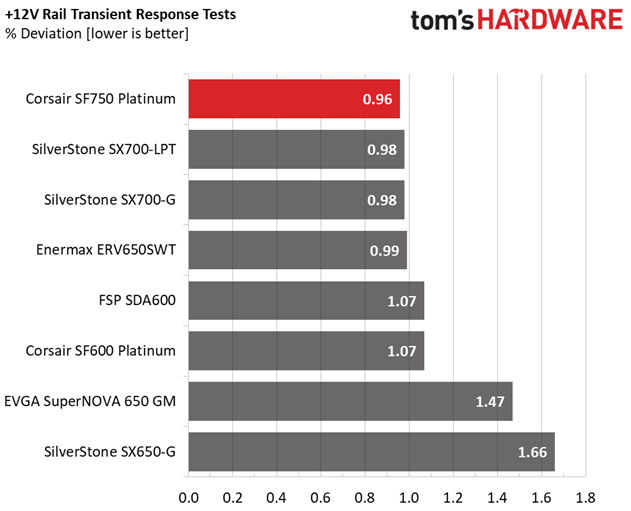
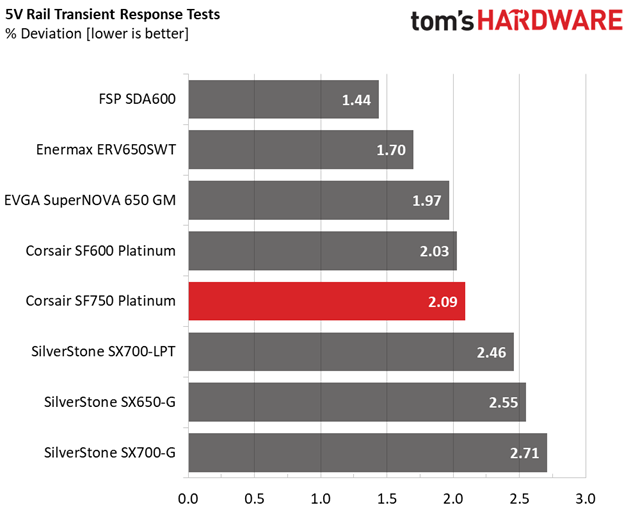
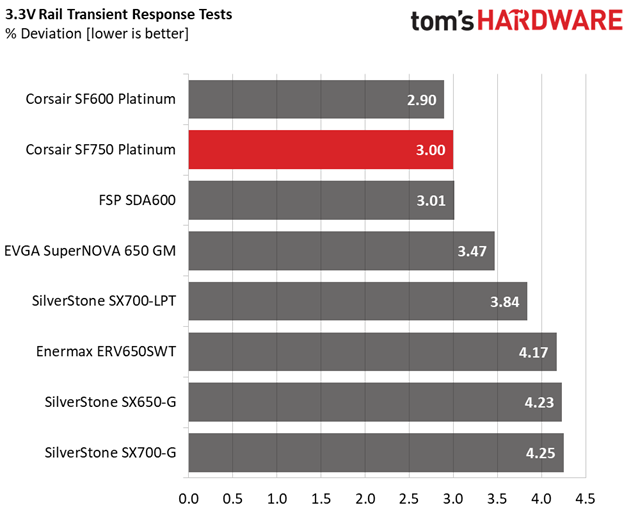
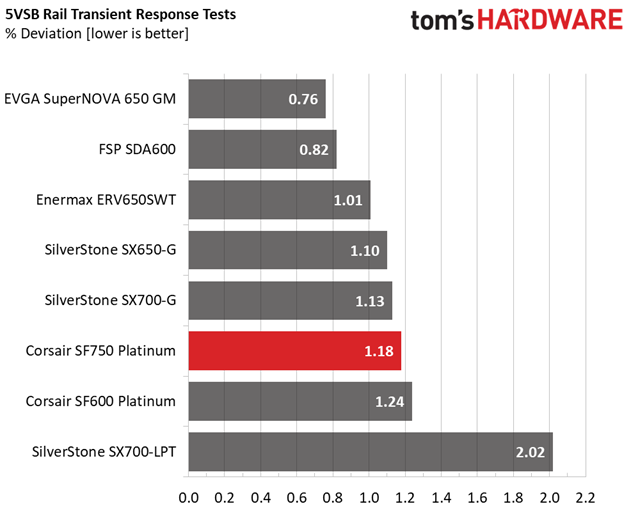
The +12V rail performs fantastic, and this is the most important among all since it handles the majority of components. The minor rails have low deviations as well.
Turn-On Transient Tests
In the next set of tests, we measure the PSU's response in simpler transient load scenarios—during its power-on phase. Ideally, we don't want to see any voltage overshoots or spikes since those put a lot of stress on the DC-DC converters of installed components.
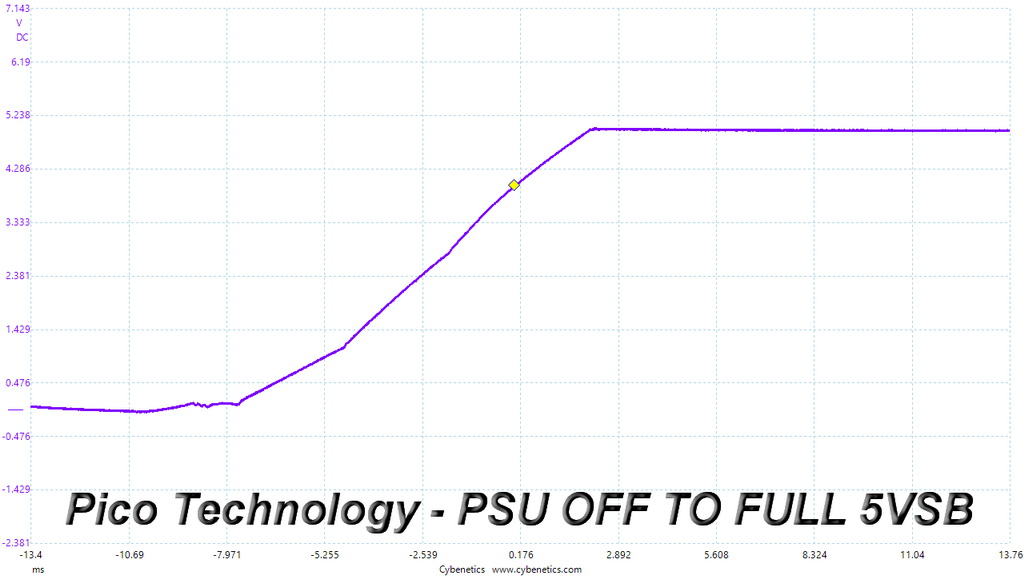
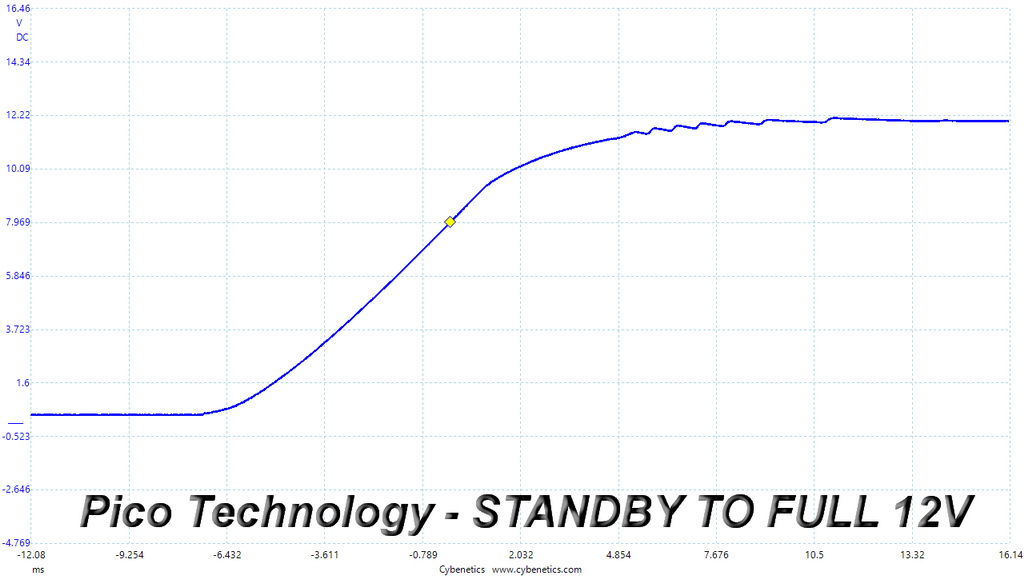
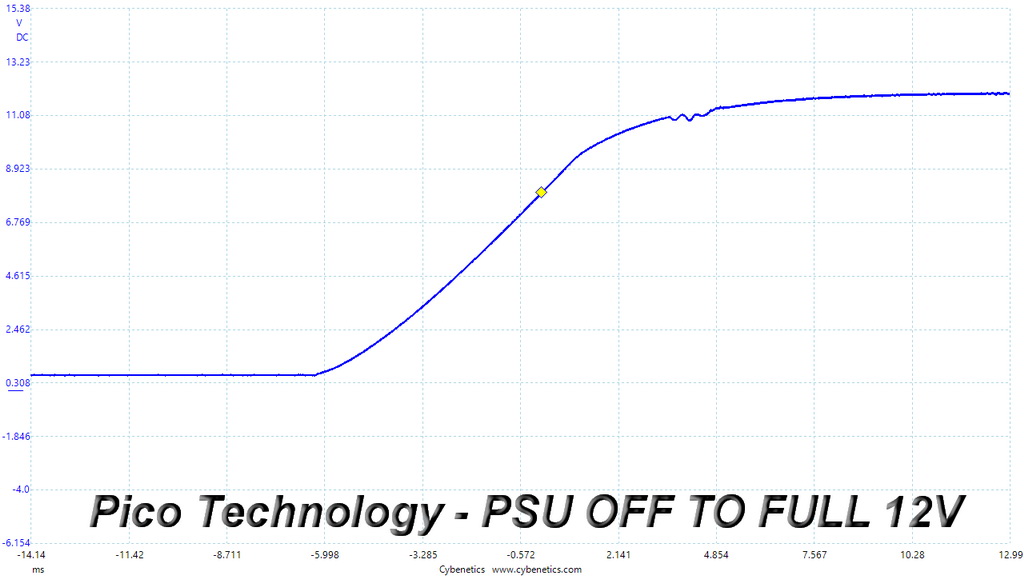
Very good results here. We only notice some waves in the +12V rail's slopes, which however are pretty small.
Ripple Measurements
Ripple represents the AC fluctuations (periodic) and noise (random) found in the PSU's DC rails. This phenomenon significantly decreases the capacitors' life span because it causes them to run hotter. A 10°C increase can cut into a cap's useful life by 50 percent. Ripple also plays an important role in overall system stability, especially when overclocking is involved.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
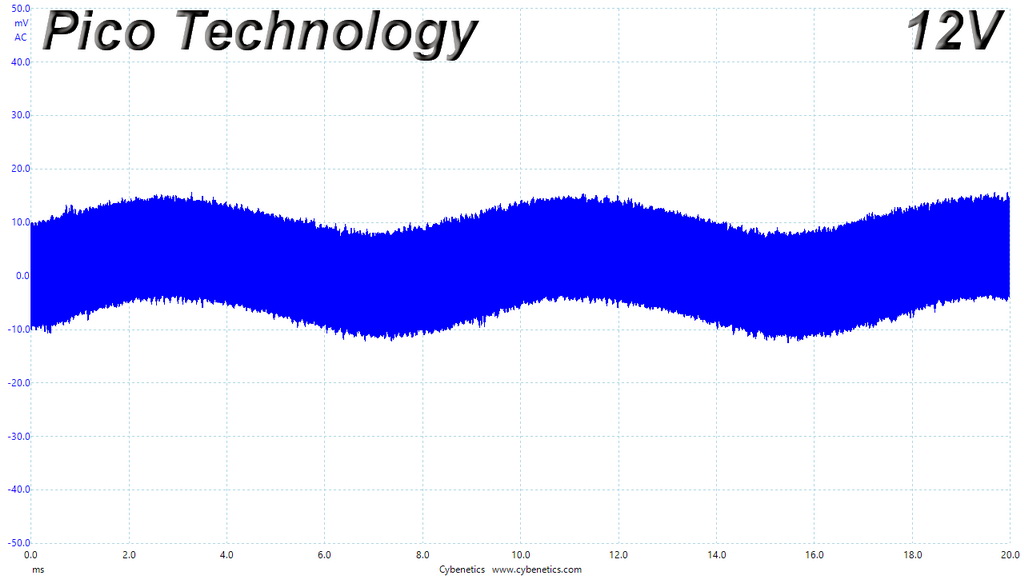
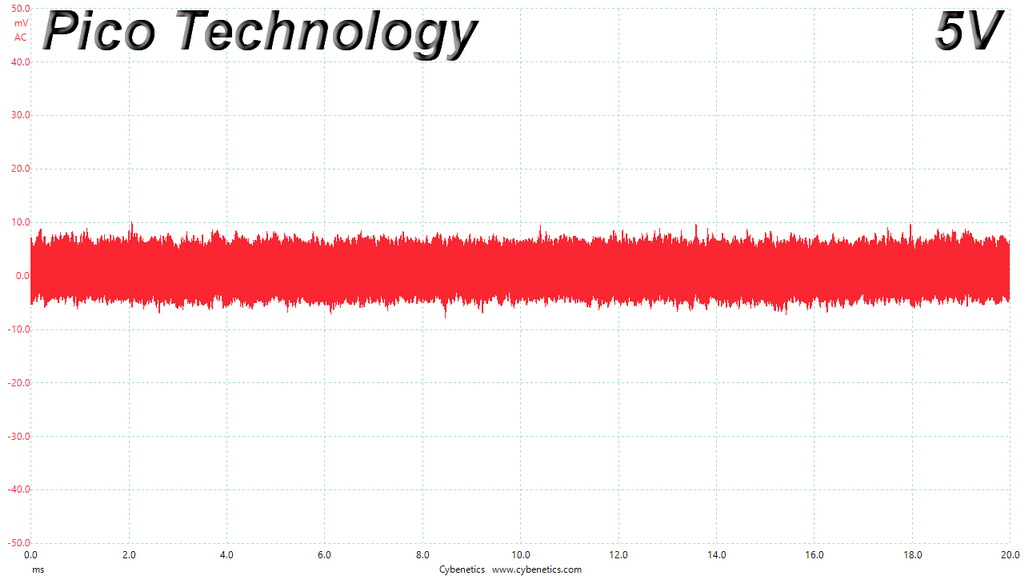
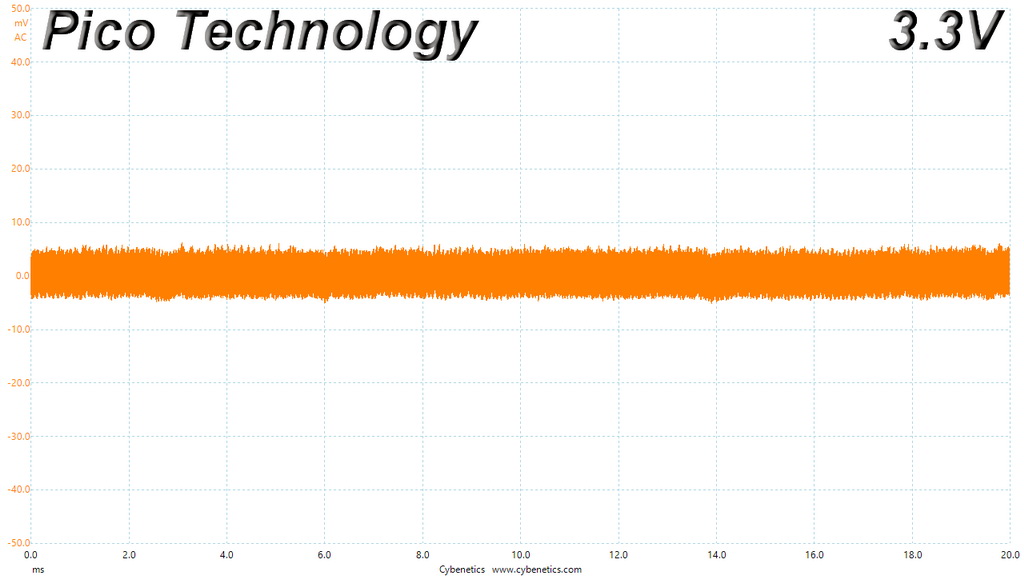
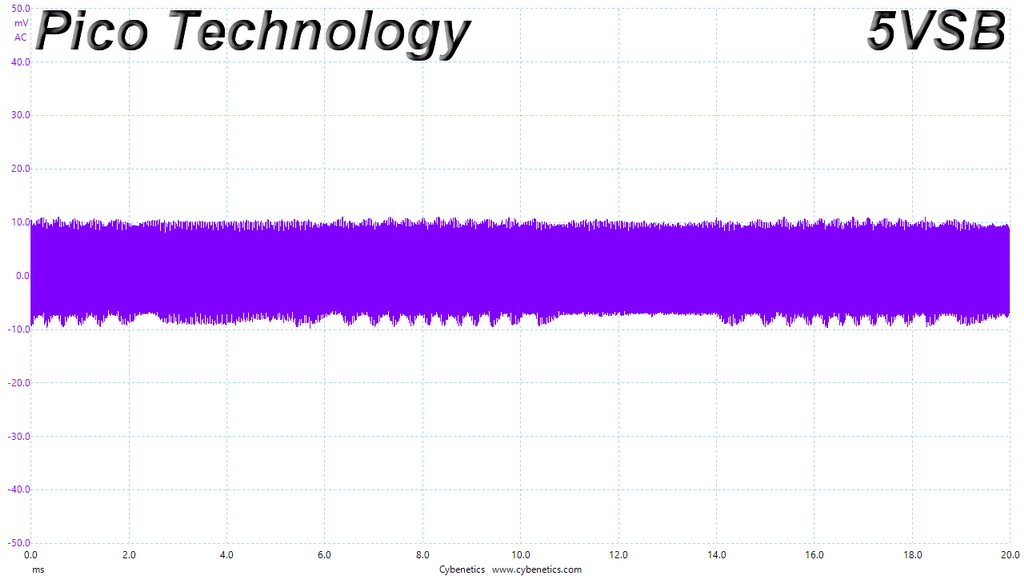
The ripple limits, according to the ATX specification, are 120mV (+12V) and 50mV (5V, 3.3V, and 5VSB).
| Test | 12V | 5V | 3.3V | 5VSB | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% Load | 11.3 mV | 11.3 mV | 5.4 mV | 7.0 mV | Pass |
| 20% Load | 11.4 mV | 11.4 mV | 6.3 mV | 8.1 mV | Pass |
| 30% Load | 8.7 mV | 13.4 mV | 8.5 mV | 8.9 mV | Pass |
| 40% Load | 11.5 mV | 13.3 mV | 8.4 mV | 9.6 mV | Pass |
| 50% Load | 13.4 mV | 15.5 mV | 9.8 mV | 10.5 mV | Pass |
| 60% Load | 15.5 mV | 15.1 mV | 10.9 mV | 12.1 mV | Pass |
| 70% Load | 17.6 mV | 17.1 mV | 11.9 mV | 14.4 mV | Pass |
| 80% Load | 20.5 mV | 17.5 mV | 13.5 mV | 16.6 mV | Pass |
| 90% Load | 22.4 mV | 17.9 mV | 14.5 mV | 18.8 mV | Pass |
| 100% Load | 29.5 mV | 20.2 mV | 16.7 mV | 20.9 mV | Pass |
| 110% Load | 32.5 mV | 21.3 mV | 17.7 mV | 23.3 mV | Pass |
| Crossload 1 | 17.3 mV | 18.0 mV | 15.5 mV | 16.7 mV | Pass |
| Crossload 2 | 29.4 mV | 18.5 mV | 11.6 mV | 21.6 mV | Pass |
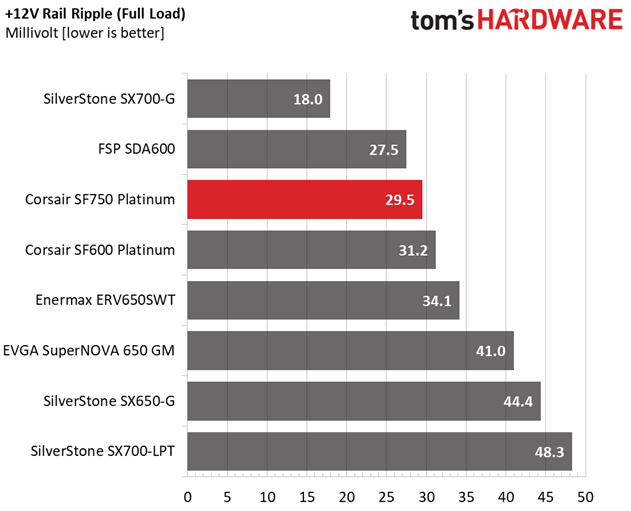
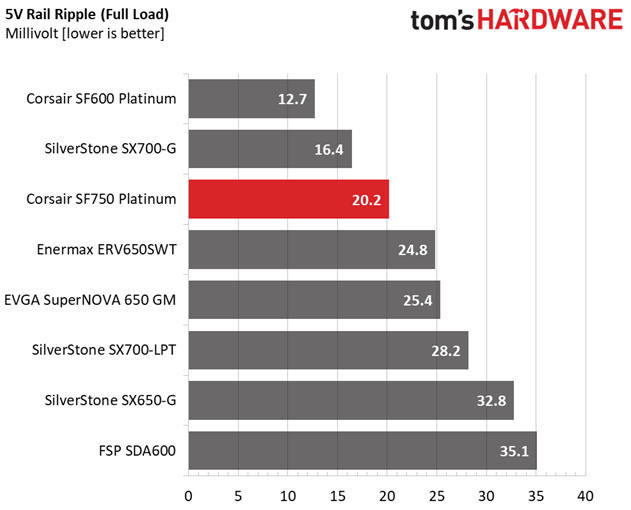
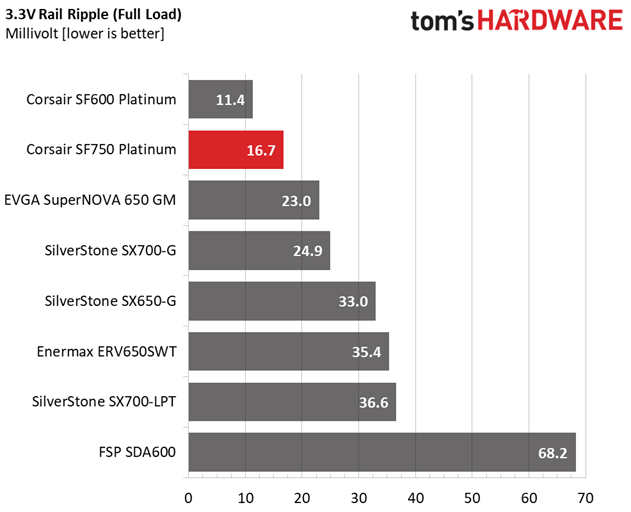
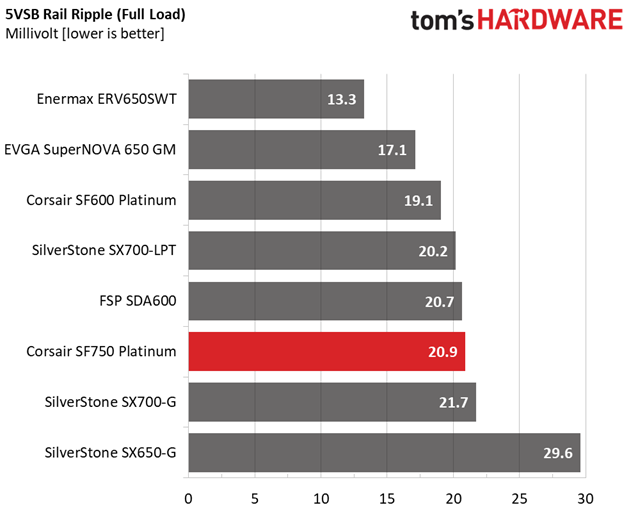
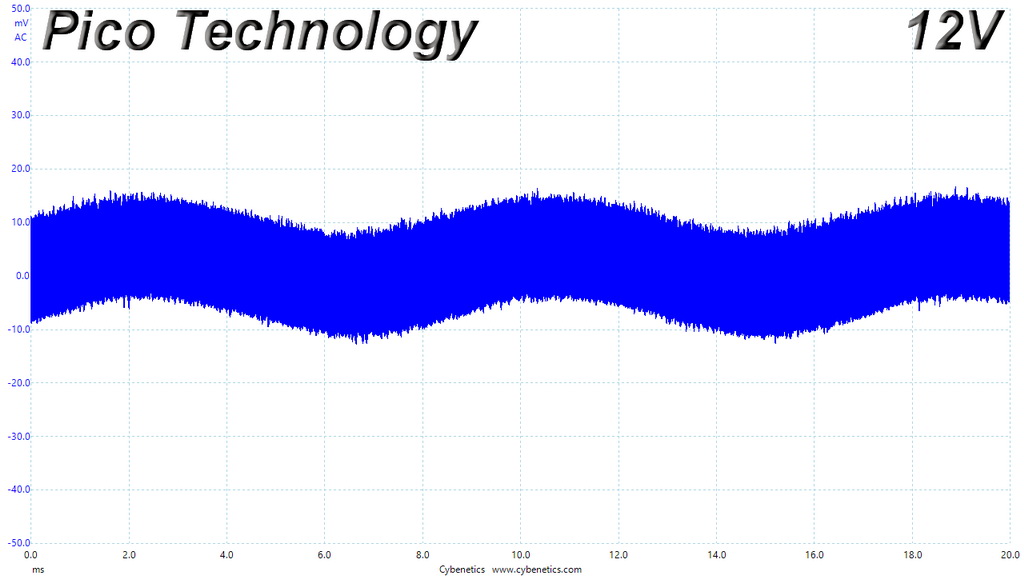
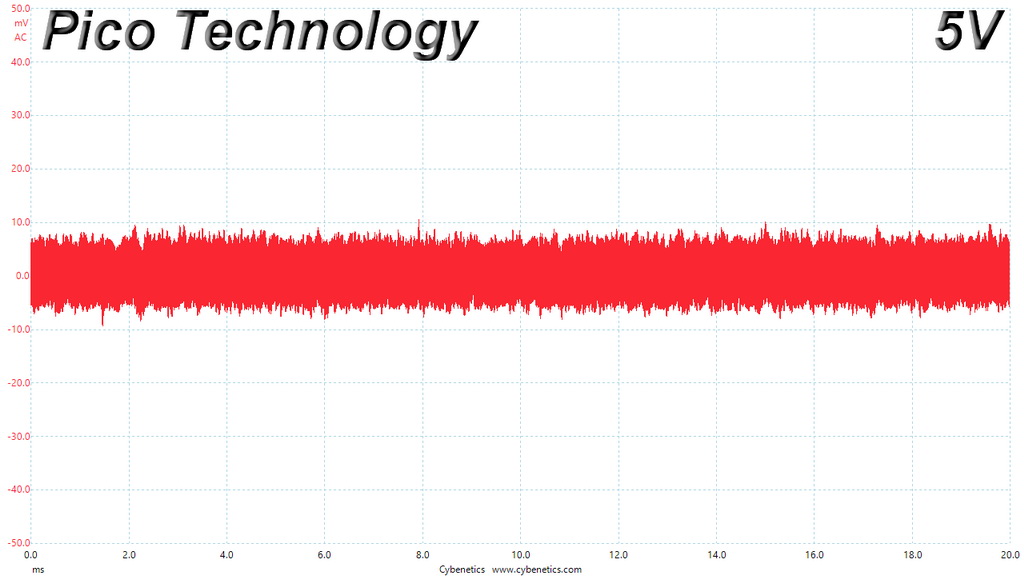
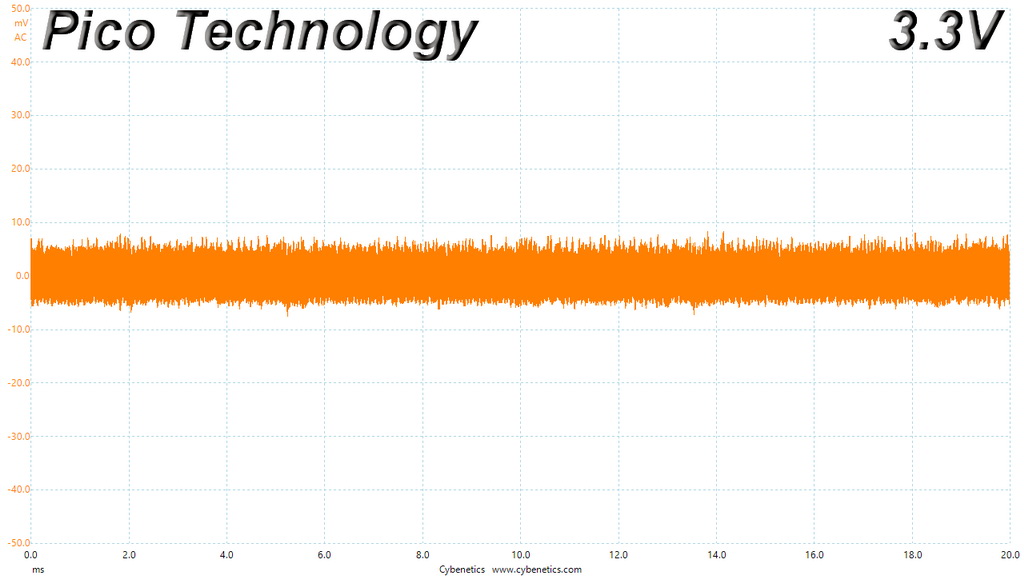
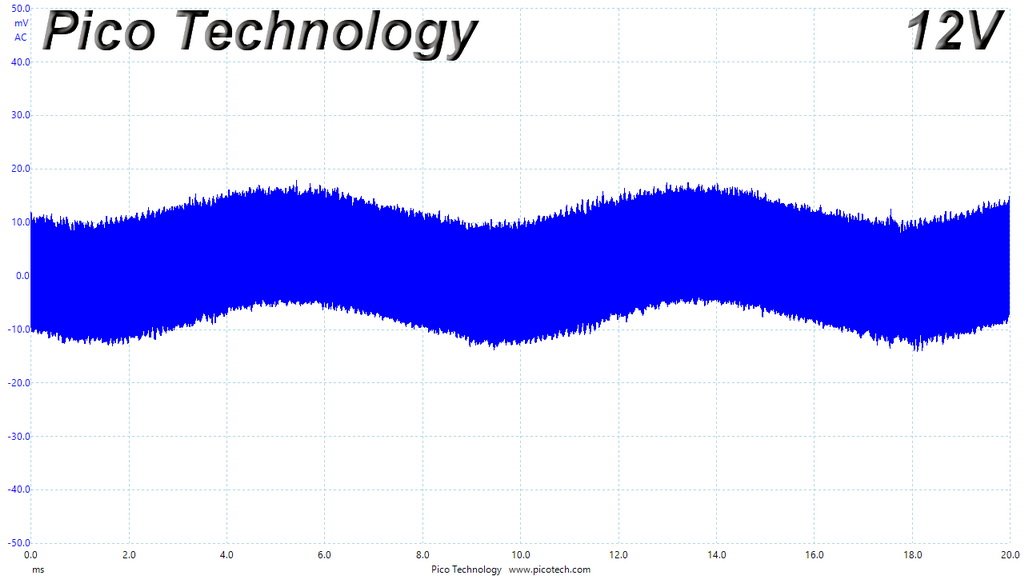
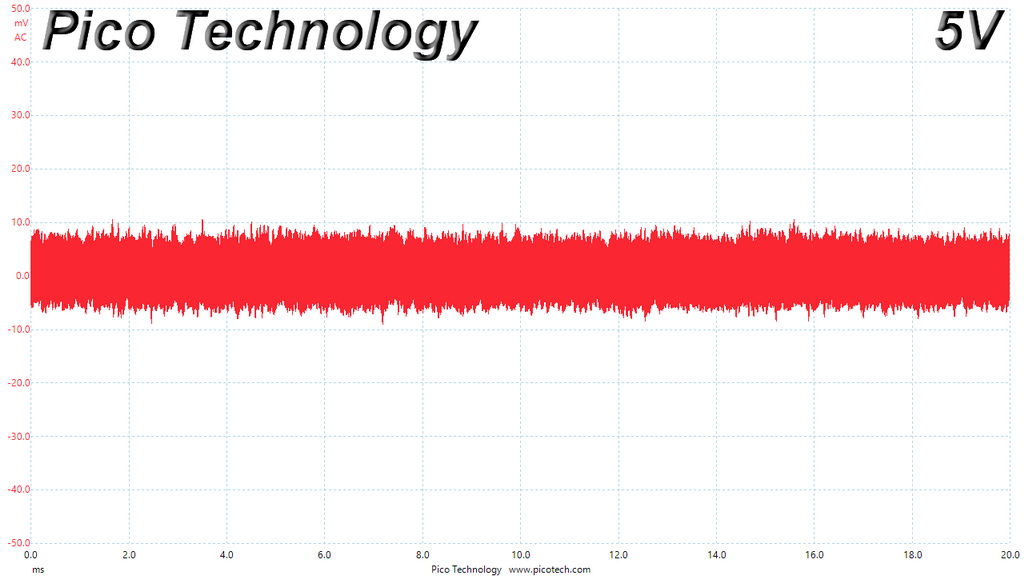
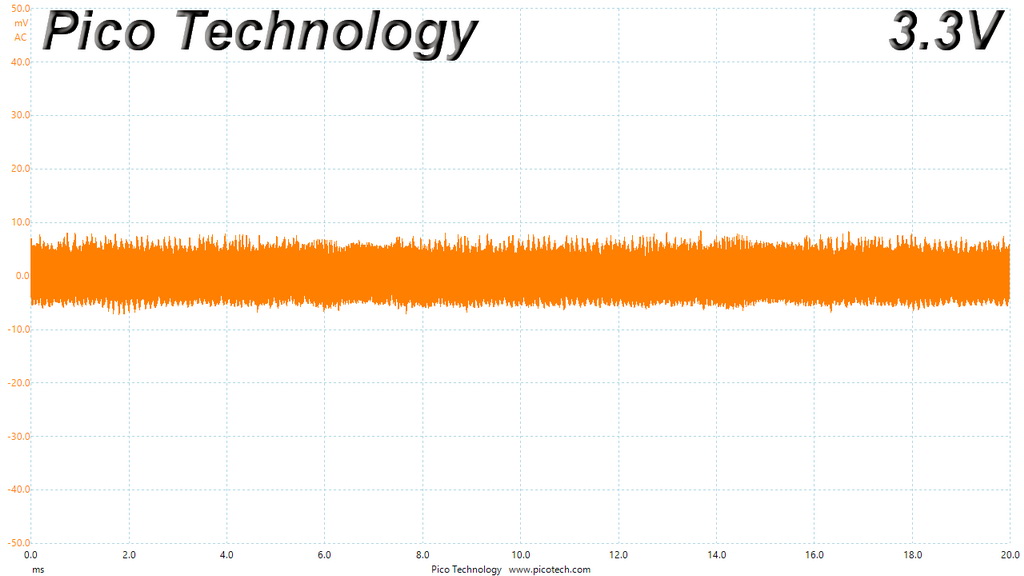
The ripple suppression is very good on all rails and the most impressive part is that this is achieved without any extra filtering caps on the cables.
Ripple At Full Load
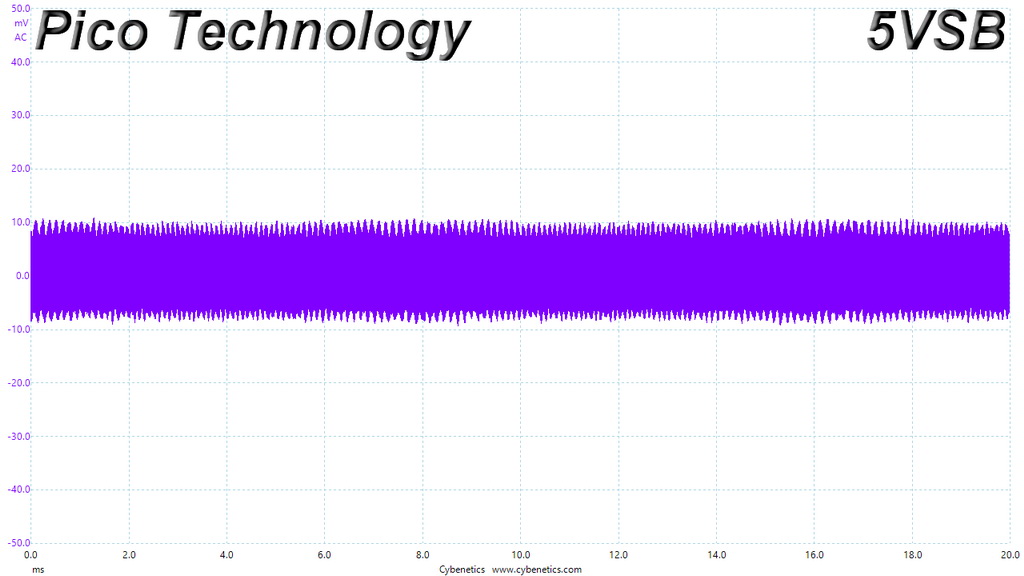
Ripple At 110% Load
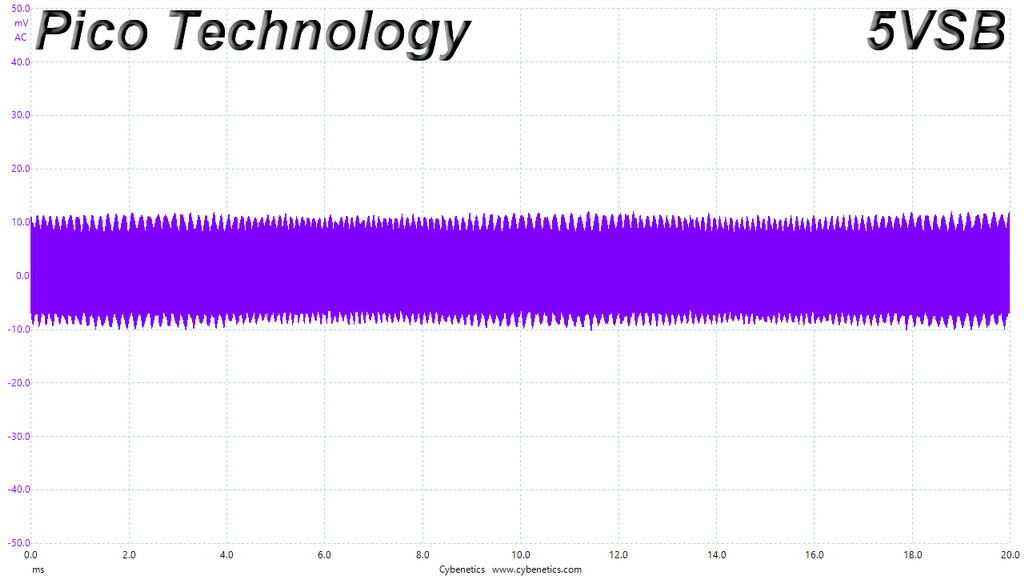
Ripple At Cross-Load 1
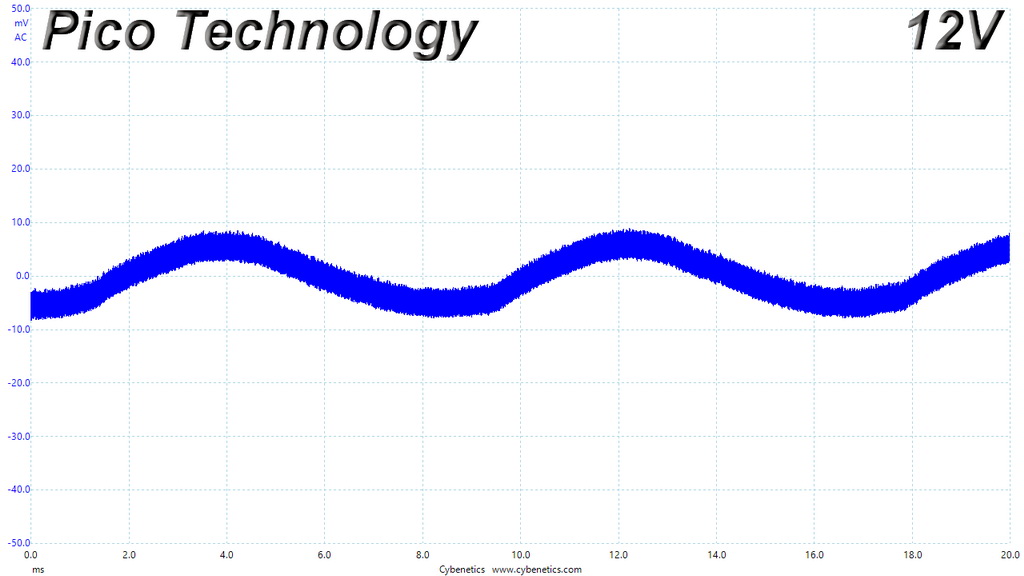
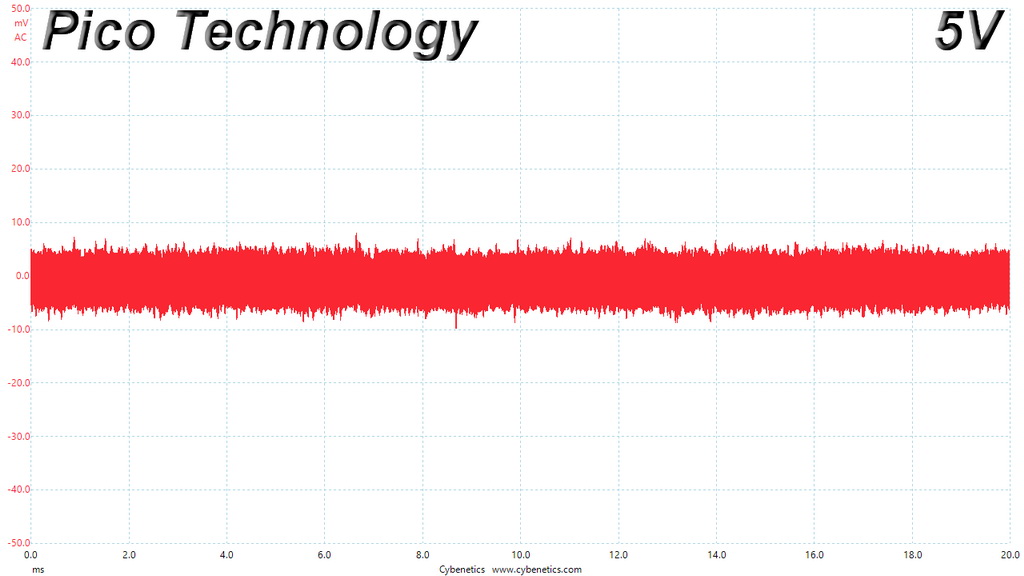
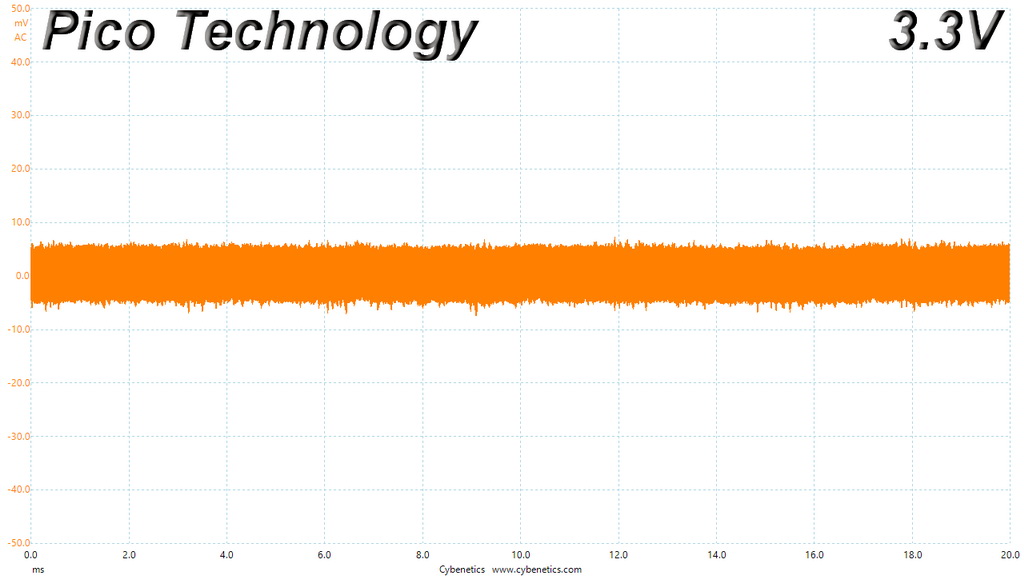
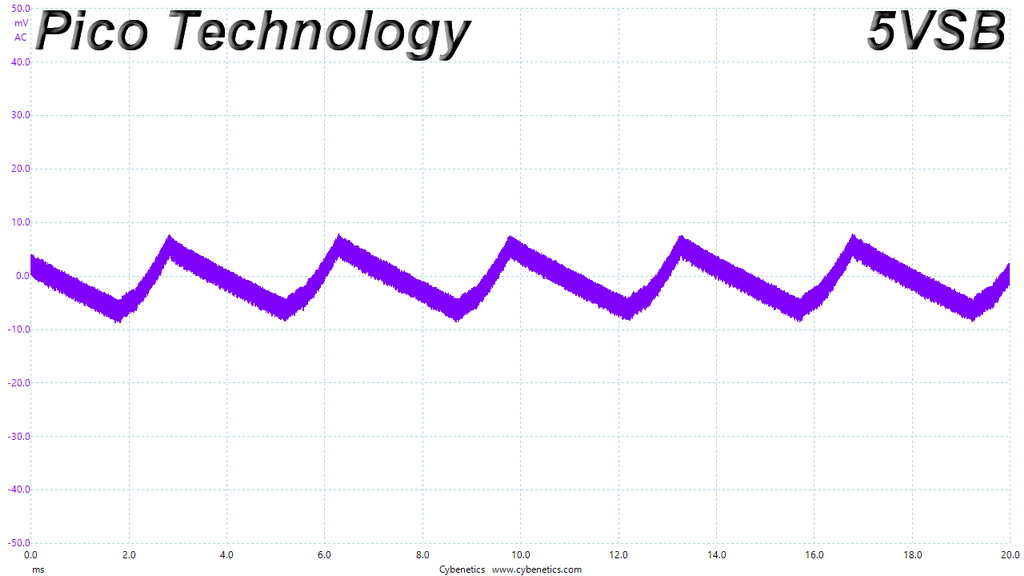
Ripple At Cross-Load 2
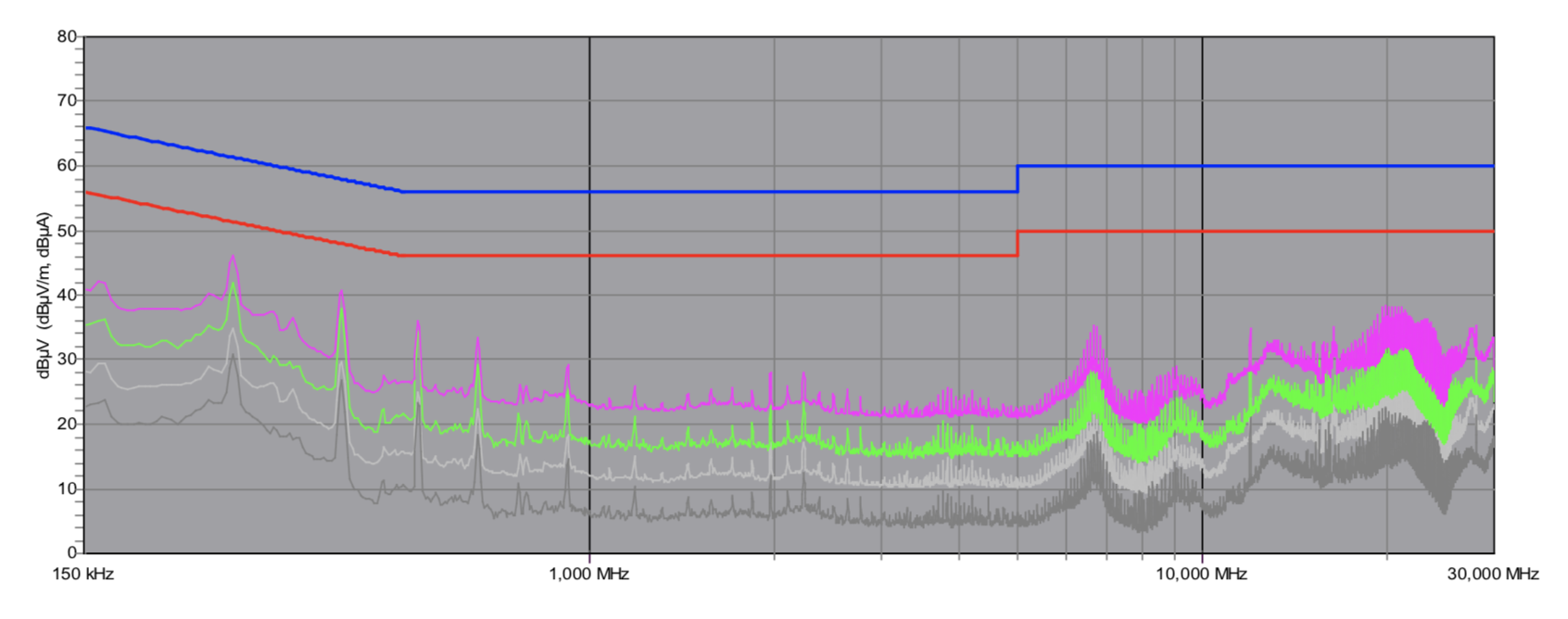
EMC Pre-Compliance Testing – Average & Peak EMI Detector Results
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) is the ability of a device to operate properly in its environment without disrupting the proper operation of other close-by devices.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) stands for the electromagnetic energy a device emits, and it can cause problems in other close-by devices if too high.
There are some EMI spikes, but they are all far below the corresponding limits.
MORE: Best Power Supplies
MORE: How We Test Power Supplies
MORE: All Power Supply Content
Current page: Transient Response Tests, Ripple Measurements and EMC Pre-Compliance Testing
Prev Page Protection Features, DC Power Sequencing, Cross-Load Tests and Infrared Images Next Page Performance, Noise and Efficiency
Aris Mpitziopoulos is a contributing editor at Tom's Hardware, covering PSUs.