Qnap TS-559 Pro: Do More Drives In Your NAS Mean More Speed?
We know that adding drives to a RAID array can help improve performance. But does adding storage to a NAS device really help push throughput higher? We put four-bay and five-bay units from Qnap up against each other and benchmark their transfer rates.
Do More Hard Drives Equal Faster RAID?
Firmware: One For All
Similar to other NAS device manufacturers, Qnap offers a single firmware for all devices in a given product line. This has the advantage of allowing the firmware to be easily adapted to the different models, since both the hardware and the features are almost identical anyway. The differences are mostly in the details, for example the missing eSATA management menu item on a device without eSATA ports.
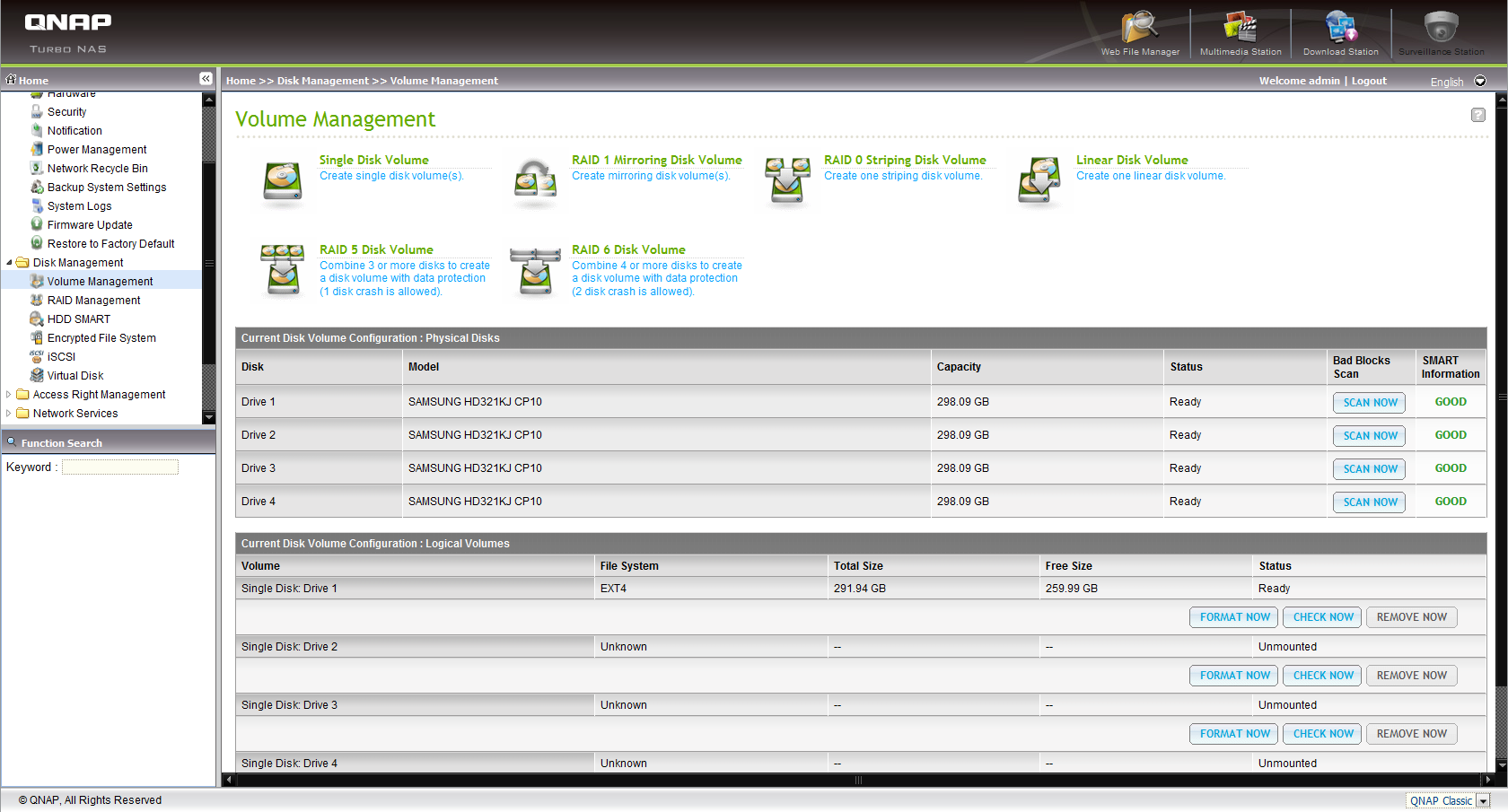
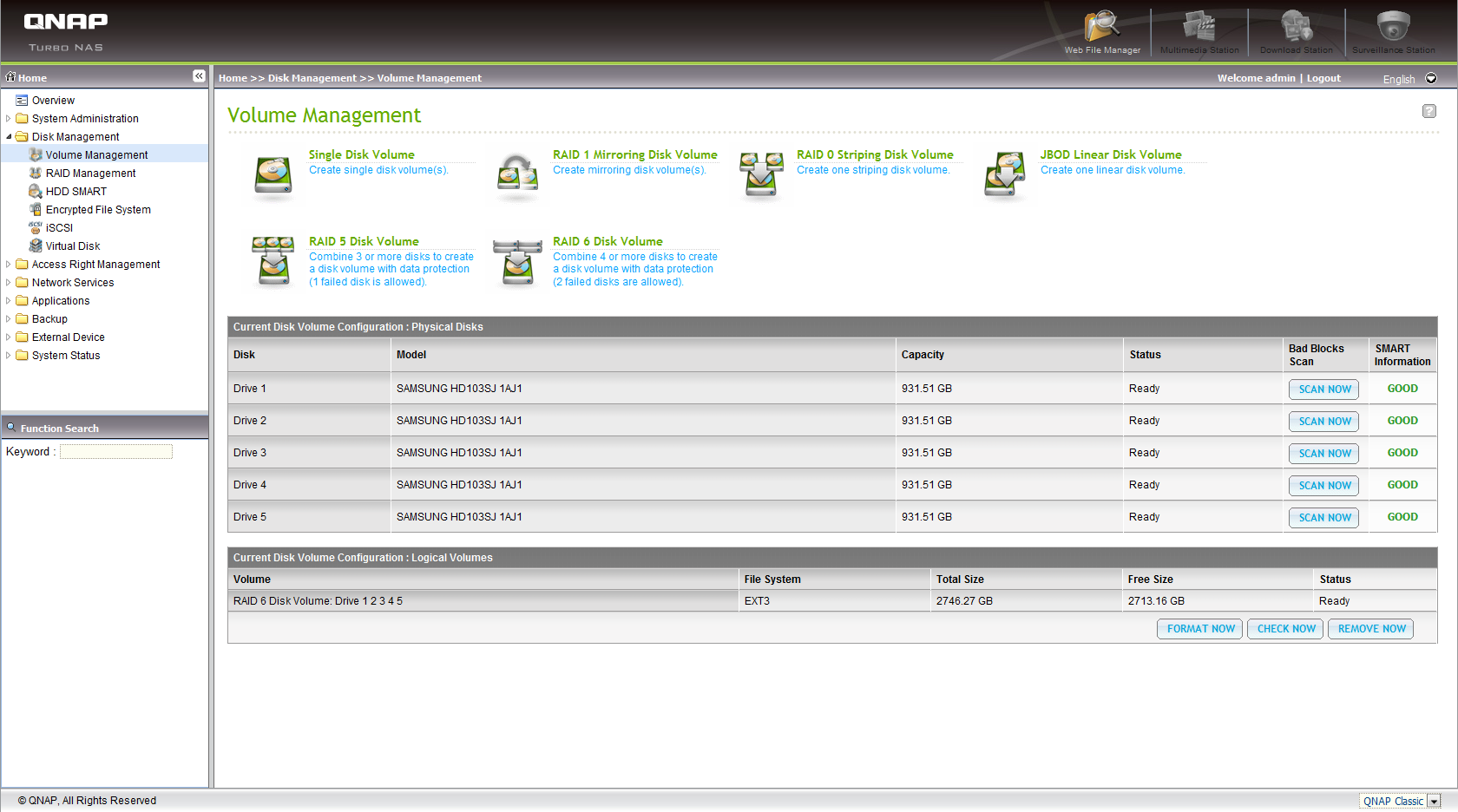
Because the TS-459 Pro and TS-559 Pro are based on identical hardware (except for the additional drive bay in the 559 Pro), the biggest differences in the Web-based administration interface are the hard drive identification and RAID mode management menus, with the TS-559 Pro simply allowing for the configuration of one more hard drive. Settings like the choice of file system or RAID mode are the same.
Pretty much all that remains when comparing mostly-identical NAS devices is the assumption that the fifth drive in the TS-559 Pro gives it some kind of performance advantage compared to the TS-459 Pro.
RAID In Theory
The choice of RAID mode and the question of whether the device is mostly going to be used for read or write operation are both relevant. Using a dedicated RAID controller and multiple drives produces a solid performance increase using RAID 5, if you're most concerned about read data rates. RAID 0, 1, and 6 modes also benefit from increasing the number of hard drives for read operations. However, the specific transfer rate increase depends on other factors as well: stripe size, the number of I/O requests, and whether they are sequential or random, not to mention the hard drives you are using. Pretty much the same factors play a role in affecting write performance, although things get a bit more complicated.
The vast majority of NAS devices for the consumer market lack a dedicated RAID controller for managing XOR operations, and that goes for the TS-459 Pro and TS-559 Pro as well. XOR is the basic mathematical operation to create (or restore) data redundancy for an array. These operations are handled by the dual-core Intel Atom D510 CPU instead (also known as host-based RAID), which can have a somewhat limiting effect on RAID array performance.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Take a look at the following pages to find out whether the additional disk in the TS-559 Pro has any effect on transfer rates, and if so, how much.
Current page: Do More Hard Drives Equal Faster RAID?
Prev Page A Closer Look At The Devices Next Page Test System, Details, Power Consumption-
thomaseron "We put four-bay and five-bad units..."Reply
Haha! ;-)
EDIT: They have corrected it now... :-) -
Zoidman I set a TS-459 up at my work, and that machine is a piece of beauty! It runs a copy of linux on it which is root accessible by SSH thus unlocking all the potentials you could ever want! It adds a huge amount of value to the devices in my opinion and would recommend it to a business looking for a basic backup system.Reply -
ProDigit10 Who would want to pay that for a nas server?Reply
Just purchase a micro atx board + case + Atom N550/D525 and 2GB of ram, and install 2 or 4 harddrives in RAID.
It'll cost you less than $400!
5 drives and up is indeed harder to get, but definitely NOT worth trice the price!
Besides, the Atom is a very small CPU which would bottleneck when 2 or 3 drives are copy/moving data. I don't think it's even wise from performance standpoint of view to buy any Atom NAS server with more than 3 or 4 drives!
comment made before reading article. -
Agges Supporting ProDigit10's sentiment..Reply
How about adding a 'building your own NAS/server' guide, including testing the sweet-spot for price/performance for various set-ups..? -
mjw It looks like the network may be a bottleneck in a number of your tests. It would be interesting to see if the performance increases when the dual gigabit NICs are run in teaming mode.Reply -
KentC I bought an Acer Home Server with 4 hot swap drive bays and one drive bay with a 1tb drive with the server OS for $350. It looks like these units provide less and cost almost three times as much. Why are they so expensive? What does 3x the cost buy me?Reply -
joex444 I'm with mjw here. If the highest number you ever achieved is 116MB/s you're limited by GbE rather than anything else. When a 2 drive RAID1 performs the same as a 5 drive RAID5 you have some other problem.Reply
I run an external 8 bay unit, all drives filled with 2x250GB drives for OS and 6x750GB drives for RAID5. The biggest problem I have in terms of getting an idea of the true transfer rates capable is the fact that the RAID5 can write faster than the other array reads. And copying from an array to itself always has issues. So in real-world apps, my write speeds are limited by the read speed of other devices. The only logical way to untangle the two is to run a separate 6 drive RAID5 array, but I'm out of PCIe 8x slots to do so (as well as money). -
mikem_90 Part of what you pay for is the software development for all the features they give out of the box. Sure you could build your own, but it might not be as compact while offering hot swap and have an well designed interface with the well integrated features.Reply
These systems offer some very nice features I don't mind paying for.
Keep in mind that this is the corporate version, it has a much beefier CPU than the cheaper ones that cost a few hundred dollars less. They don't offer the same performance, but not everyone needs to use volume based encryption and send the files back and forth over SSL encrypted links.