Vista Workshop: More RAM, More Speed
Does No Swap File Equal Better Performance?
Since swapping files to virtual memory on the hard drive has the single largest impact on system performance, we asked ourselves what would happen if we deactivated Windows' paging file completely. Note that Microsoft does not recommend this course of action, as demonstrated in the following popup message.
Warning message when deactivating the paging file.
We were not deterred by this warning, though. Interestingly, we were unable to delete the pagefile.sys file, even when Windows was no longer using it. Since it retains its last allocated size, you should set it to the smallest possible value (16 MB) before deactivating it.
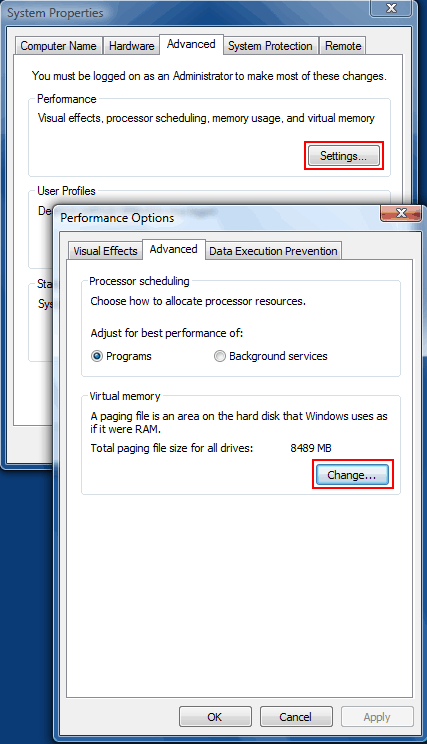
These are the settings....
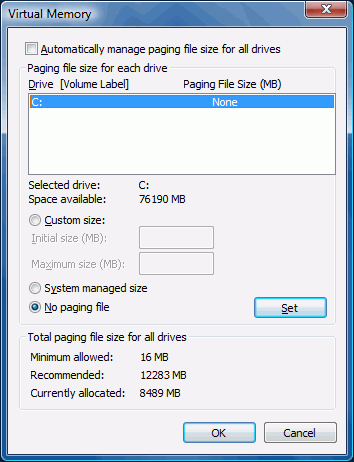
...for deactivating the paging file.
Again, we conducted this test with RAM sizes ranging from 8 GB to 512 MB. While working without a paging file was possible without any problems with 8 GB, the situation quickly became critical with less memory installed.
With 8 GB and no swap file, the system was fine. Even in some memory intensive scenarios such as opening files in Photoshop CS3 with a total file size of 3 GB, the system remained very responsive and even snappy, never writing to disk once.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
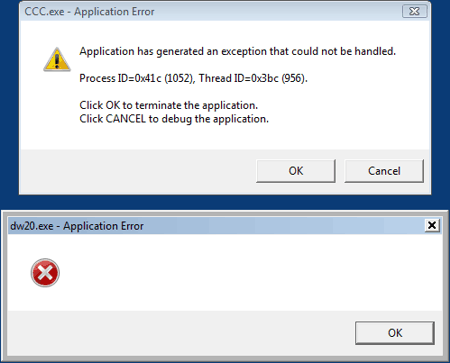
When the memory size is reduced to 2 GB , applications immediately crash as soon as the system runs out of RAM and Windows is unable to write the files to virtual memory on the hard drive. This situation is especially critical if the memory shortage hits one of the Windows system components - that may quickly result in the Windows Aero turning itself off as a result of the graphics driver crashing. The only remedy in such a situation is rebooting the system.
A crash with the swapping file off.
With only 512 MB of RAM installed, it is no longer possible to open even small Windows applications such as Notepad. After a short while, the system will crash all by itself, even when sitting idle.
Obviously, we would recommend never deactivating the swapping file with small memory sizes installed.
Current page: Does No Swap File Equal Better Performance?
Prev Page More RAM - Additional Memory Used By Windows Next Page The Trouble With 32 bit Applications-
trifler We need to see benchmarks comparing Vista with 2MB, 4MB, and 8MB. I can't tell my boss that the new high-end computers should have 8MB without some numbers.Reply -
I think meant GB not MB there Trifler... 8MB of ram is not very much... and a "high-end computer" should have at least 2GB of RAM for a 32-bit system, and is OS dependant for 64-bit systems... vista depends on the ver you use as to how much ram is max.Reply
I have 1 GB of RAM and am using 80% after a normal boot (plus a few non-essential apps... but they make doing things easier -
SkyPRZ There is a "test setup" but not followed by any test but directly by the conclusion.Reply
Did I miss something?
Nevertheless I've already built a system with Vista 64 & 8GB ram few weeks ago and wanted the test to comfort decisions I made. -
master9716 with 2 gigs of ram my 64bit runs ultra fast compared to 32bit , I have 3 hdds quad 6600. it should be the otherway around though . On my laptop with 1.5 gigs vista basic runs prety bad I will reinstall see what happens . We need to see some load time benchmarks !!! eventhough this is an old articleReply -
Darthb0b0 on page 7, how are you changing the amount of ram a particular app is using? is this only applicable to 64-bit windows, or could you also change this with 32-bit?Reply -
Darthb0b0 One other thing. on page 5 you say that w/4gb of ram it has no benefit to go to 64 bit due to the larger memory foot print required - essentially eating up the extra memory. The extra system memory used is 757 - 549 = 208. Yet the extra addressable memory gained is 4096 - 3581 = 515. The difference is still a net gain of 307mb of ram. Or am I missing something?Reply
Also, is the reason that only 3.5GB is available in the 32-bit environment due to the 512mb video card and MMIO? If so, what will happen in a 32 or 64 bit system if you have a video setup with 2gb of video ram? Will you only have 2GB of main memory available? -
Darthb0b0 One answer found:Reply
Significant chunks of address space below 4GB (the highest address accessible via 32-bit) get reserved for use by system hardware:
• BIOS – including ACPI and legacy video support
• PCI bus including bridges etc.
• PCI Express support will reserve at least 256MB, up to 768MB depending on graphics card installed memory