Can AMD'S 65 nm Core Fight Back?
Athlon 64 X2 Details
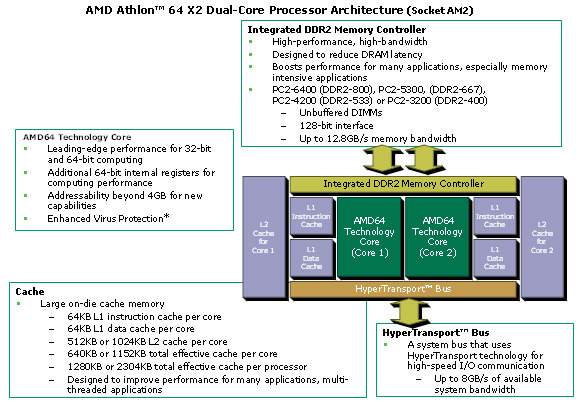
Source: AMD.
The AMD64 processor design has not changed much since its introduction in 2004. The first AMD64 processors came with a single or dual channel DDR400 memory controller: Socket 754 used single channel and Socket 939 dual channel. Processors were transitioned from 130 nm to 90 nm structures over time, and AMD was good at introducing modified steppings on a regular basis. These usually helped to improve processor efficiency, or were a result of production tweaks.
The introduction of Socket AM2 served the purpose of transitioning from DDR400 to DDR2-800 memory. This brought only a little performance benefit, but it helped AMD create a single platform for budget PCs, mainstream systems and enthusiast solutions. The company accomplished this by providing Sempron, Athlon 64 and 64 X2 CPUs, and the Athlon 64 FX for Socket AM2.
AMD's current Athlon 64 X2 dual core features two processing core with dedicated L1 and L2 caches for each core, on a single die. A cross-switch takes care of inter-core communication and access to the dual channel DDR2-800 memory controller, as well as the HyperTransport channel, which is used to interface with the rest of the system. HyperTransport is a serial, high-speed point-to-point protocol, as opposed to Intel's Front Side Bus. The other significant difference - aside from the integration of the memory controller - is the L2 cache memory: Intel has one shared cache that is used by both caches, while AMD still relies on exclusive caches.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Athlon 64 X2 Details
Prev Page AMD Positions Brisbane To Replace Windsor Next Page AMD Outputs 65 nm Silicon
Patrick Schmid was the editor-in-chief for Tom's Hardware from 2005 to 2006. He wrote numerous articles on a wide range of hardware topics, including storage, CPUs, and system builds.