OnePlus One Review
The OnePlus One has an off-contract price starting at only $299, but don’t call this smartphone cheap. Hiding behind the OnePlus One’s 5.5-inch HD screen is some high-end hardware.
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
OnePlus One Software Tour
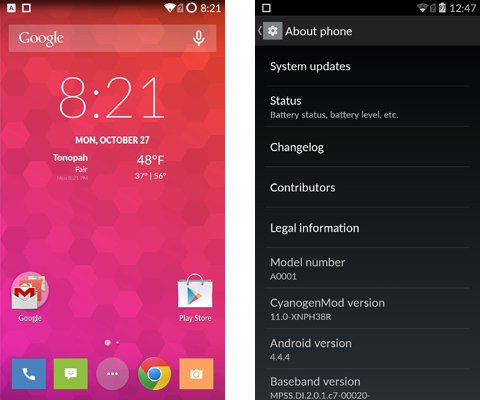
The OnePlus One is the first phone to use CyanogenMod (CM) exclusively (the Oppo N1 offered CyanogenMod as an option alongside ColorOS). Specifically, it uses CyanogenMod 11s, a slightly tweaked version of the standard CM 11 ROM.
Built on Android 4.4.4 KitKat, CyanogenMod 11s includes access to Google’s Play Store and comes preinstalled with the usual Google Apps, so the One provides the full Google experience out of the box. The big difference between CM and the different flavors of Android other OEMs offer is freedom.
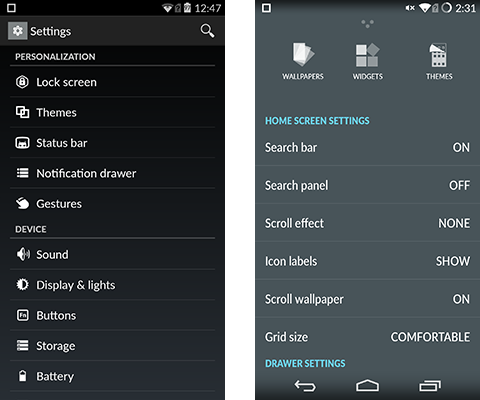
Customization
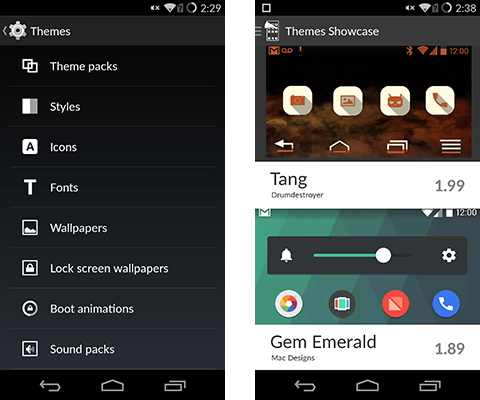
CM offers the flexibility to customize the interface’s appearance in several ways, including its comprehensive support for themes. There’s a wide variety of theme packs available, which include both static and dynamic wallpapers, custom icons, color choices, boot animations, and more. All of these visual tweaks are accessible either through the Settings menu or the Design Gallery app, which isn’t included in regular CM 11. The default “Hexo” theme is also exclusive to CM 11s.
Trebuchet, CM’s custom launcher, gives the user a great deal of control over the home screen, including the ability to change the number of home screens and the number of rows and columns available. There’s also an option for hiding icon labels, but icons in the App Drawer can’t be rearranged or grouped into folders.
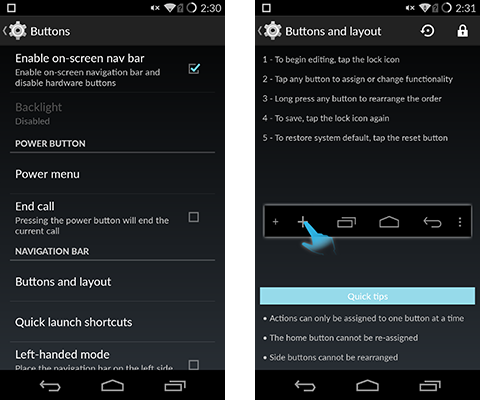
Beauty is only skin deep, but not CM’s customizability. The layout of items in the status bar and the quick settings ribbon or grid can be rearranged. Physical buttons can be remapped or provide additional functionality. For example, enabling keyboard cursor control allows the text cursor to be controlled by the volume buttons when the keyboard is onscreen. Even the onscreen navigation bar can be modified with new buttons or just reordered. With CM, if you can see it, you can probably change it.
Unique to the OnePlus One and CM 11s is the ability to choose between using either the capacitive physical buttons below the screen, or disabling them and using "soft buttons" on the screen itself.
Features
CM 11 provides several enhancements to the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) build, like an interactive status bar; tapping the date opens the Calendar app. Another cool feature, a carryover from the Oppo N1, is the ability to use gestures to control some aspects of the phone while the screen is off. For example, double-tapping the screen turns the phone on, while drawing a "V" activates the LED's on the back to act as a flashlight. The Camera app is quickly accessed by drawing a circle. Music playback can also be controlled with the screen off by swiping down with two fingers to play or pause the current song and drawing less-than or greater-than symbols to skips tracks.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
In actual use I found that while the gestures worked most of the time, it wasn't always consistent and often required the gesture to be repeated before it would work. Another drawback is that it’s not currently possible to create your own custom gestures.
The OnePlus One comes with AudioFX, which replaces the DSP Manager app that comes with CM 11. In addition to having a nicer interface, it adds a plethora of equalizer presets and other sound quality settings for getting the most out of your speakers or headphones.
CyanogenMod’s Profiles are context-aware groups of settings and preferences. For example, you can create a “Silent” profile that turns off the phone ringer and audio alerts, which is automatically triggered when your office’s Wi-Fi network is detected. Profiles can be created for any number of environments or situations, like home, car, school, or work. They can be activated manually by long pressing the power button, or triggered automatically when in range of a specified Wi-Fi or Bluetooth network, NFC tag, or by a time-sensitive alarm. Additional triggers can be added via third-party apps.
CyanogenMod also adds some useful security tools like a built-in OpenVPN client and Privacy Guard, which provides granular control over permissions on a per-application basis. It also includes system-wide integration of WhisperPush, an open source solution for encrypting SMS messages. For this to work however, both parties must be using the open source TextSecure app (available for iOS and Android). If both parties aren’t using TextSecure, the app defaults back to normal, unencrypted messaging.
It’s worth noting that CM 11s on the OnePlus One does not support the performance options—like CPU overclocking—that are included in regular CM 11. In fact, the One comes unrooted with a locked bootloader from OnePlus. However, there are instructions on the OnePlus website for unlocking the bootloader and rooting the phone for the experienced Android user. The Android developer options are still accessible by tapping on the software build number in the Settings menu seven times.
With its extensive customizability, useful feature set, and overall clean and uncluttered interface, CyanogenMod’s popularity within the Android community is understandable. It also makes a good OS choice for the OnePlus One. CM 11s gives OnePlus a fully functional and unique Android OS experience without the cost of developing their own customized ROM. CyanogenMod has also guaranteed supporting the OnePlus One and CM 11s for two years.
Current page: OnePlus One Software Tour
Prev Page OnePlus One Look And Feel Next Page Camera: Hardware-
MrEssesse You forgot to mention how the iphone 6 plus costs 299 $ with a 2 year contract, unlocked its around 700 $.Reply -
Mike Coberly So the device itself supports the CDMA bands, but is not compatible with one of the major CDMA carriers here in the US? What a shame. :( This could easily replace my now aging Galaxy Note 3.Reply -
Memory Ever Summary is all kind of noise voice out because it's a China phone.Reply
If this is a phone from Apple, people will only ask when they can buy it. They don't real care about of the specification.
This is the different. -
house70 Got one for my wife, she loves it, esp. that she doesn't have to keep an eye on the battery icon anymore. This thing will run forever... Getting another one for myself.Reply
For about USD 350 you can't really do any better. They could sell it for 550-600, but they won't.
CM12 (Lollipop- based) is around the corner.
Only thing they botched really big was the sales; this phone had a huge potential to when first launched, but making it almost impossible to buy doesn't help. -
uplink-svk As owner of three 1+1 phones I'm heavily dissapointed with this phone. I really loved the Crysis Music trailer, and there I decided to go for this phone.Reply
Things that really dissapointed me are:
- display is yellowish, at least was on all three pieces I owned
- it's made out of cheap plastics, I don't care it feels "great", I wanted metalic phone, like they said it's gonna be in the beginning
- one of the pieces was doing purplish photos
- it's way too big
- CM is fine, but still misses some of the basic features offered by 3rd party GUi from Samsung/HTC, which are in my eyes normal - RMAing the 1+1 is a hell, You need to send it back, wait and stuff, thank You, but no
In general I bought the first one for 290 euro, second one for 250 euro, and third one for 390 euro, which are pretty good prices in my country for these phones, and all were a disaster :\ -
rexter This is what Nexus 6 should have been - price-wise. Watch out Google here's OnePlus. Too bad, you'll need an invitation to get one, why not invite me instead if I give them my e-mail; this just show that the company don't have much stocks to share to every, I suppose? and that pink wall paper reminds me of Ubuntu. I like the black one if I can get my hands on one... or two.Reply -
Karksken Can you use this one as phone too or is it just a tablet(review). Smartguys please give us on smartPHONES also the real info as Phone quality, connection quality, e.a. info when you get the out of memory error when there is still a lot of mem available and you SIM is disconnected. How does the apps interact with the phone part.Reply -
D A The invites are easy to get with a little patience. I just bought three of them in the last tow weeks. All my invites I got where from google + where previous buyers are giving out the invites hourly. Jut go onto Google plus and do a search for "Oneplus Invite", then click "MOST RECENT". be patient and keep refreshing and be ready to respond to a post where someone is offering an invite... respond with your email address that you would like one. I did this for all three of my invites, there was only one person that did not send me the invite. I was able to get all the invites within an hour.Reply