Tom's Hardware Verdict
With interchangeable lenses and a 12-MP sensor, the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera provides a lot more flexibility and resolution than other modules.
Pros
- +
Interchangeable lenses offer great flexibility
- +
Tripod screw mount for great stability
- +
Ease of use no matter the model of Pi
Cons
- -
Software is a little underdeveloped
- -
No lenses included in the box
- -
Pricey when lenses are included
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
The Raspberry Pi Camera Module is one of those add ons that we love to play with. Creating images and videos using a $35 Raspberry Pi in real time is still mind blowing for most. You can even use your Raspberry Pi as a PC webcam. But the two previous first-party camera modules have suffered with a fixed focus, albeit good quality, lens and fragile construction.
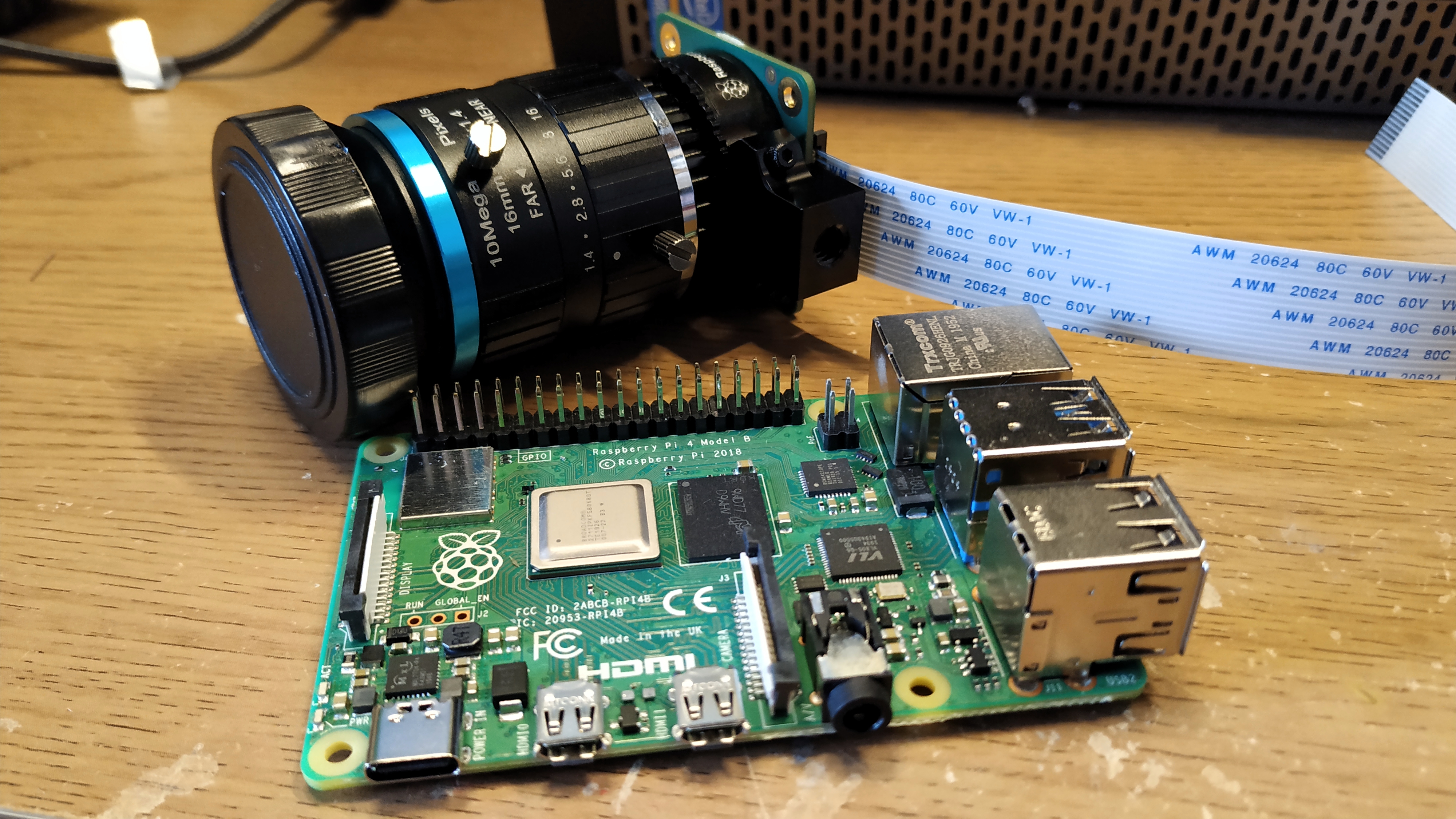
Enter the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera, a new module that ups the image quality with a new 12-MP sensor and supports interchangeable lenses and tripod-mounting. The module is larger and, at $50 without any of the required lenses, quite a bit more expensive than prior models, but the increased resolution and flexibility make it a great choice for photography-intensive projects.
Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera Design
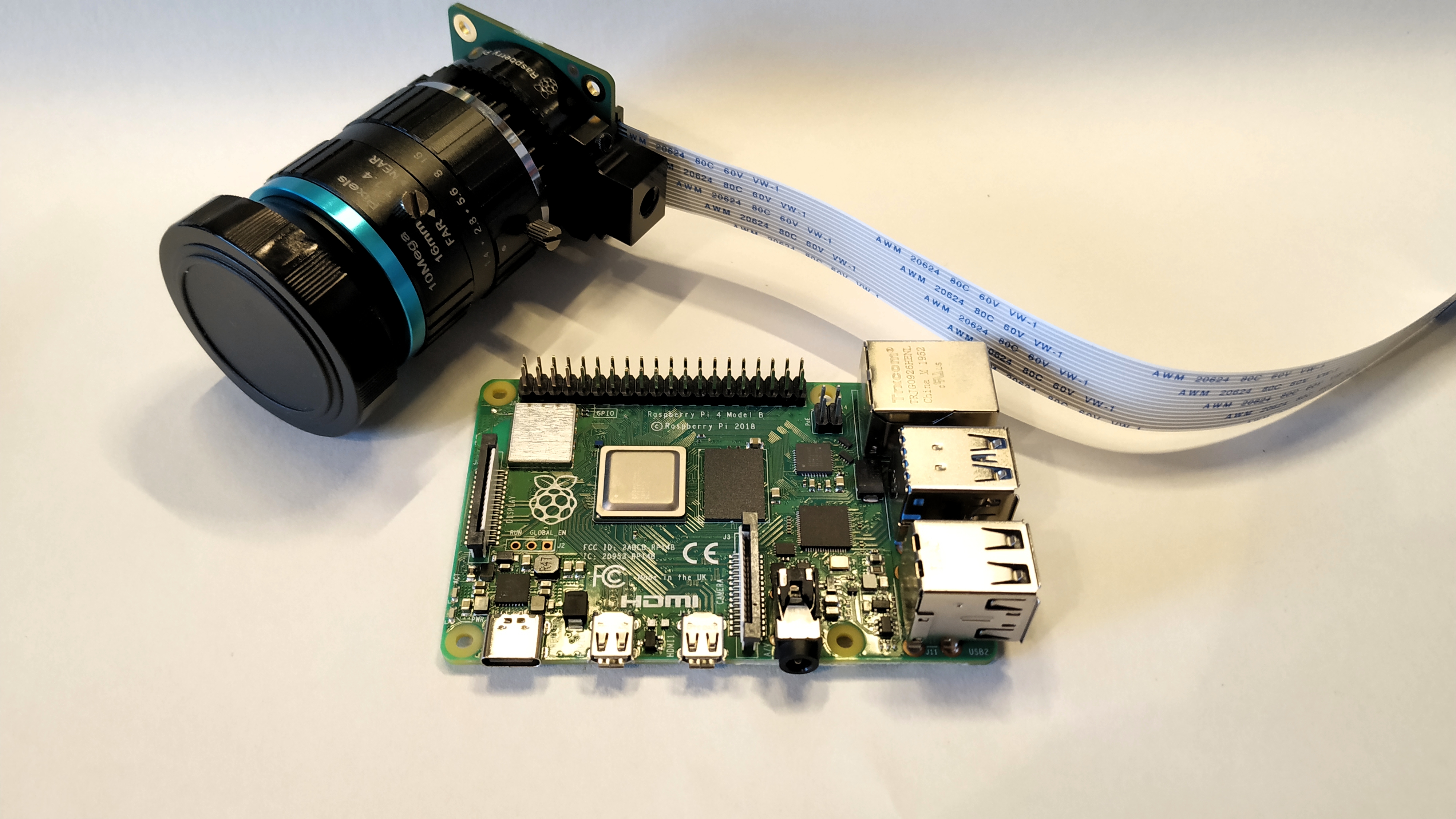
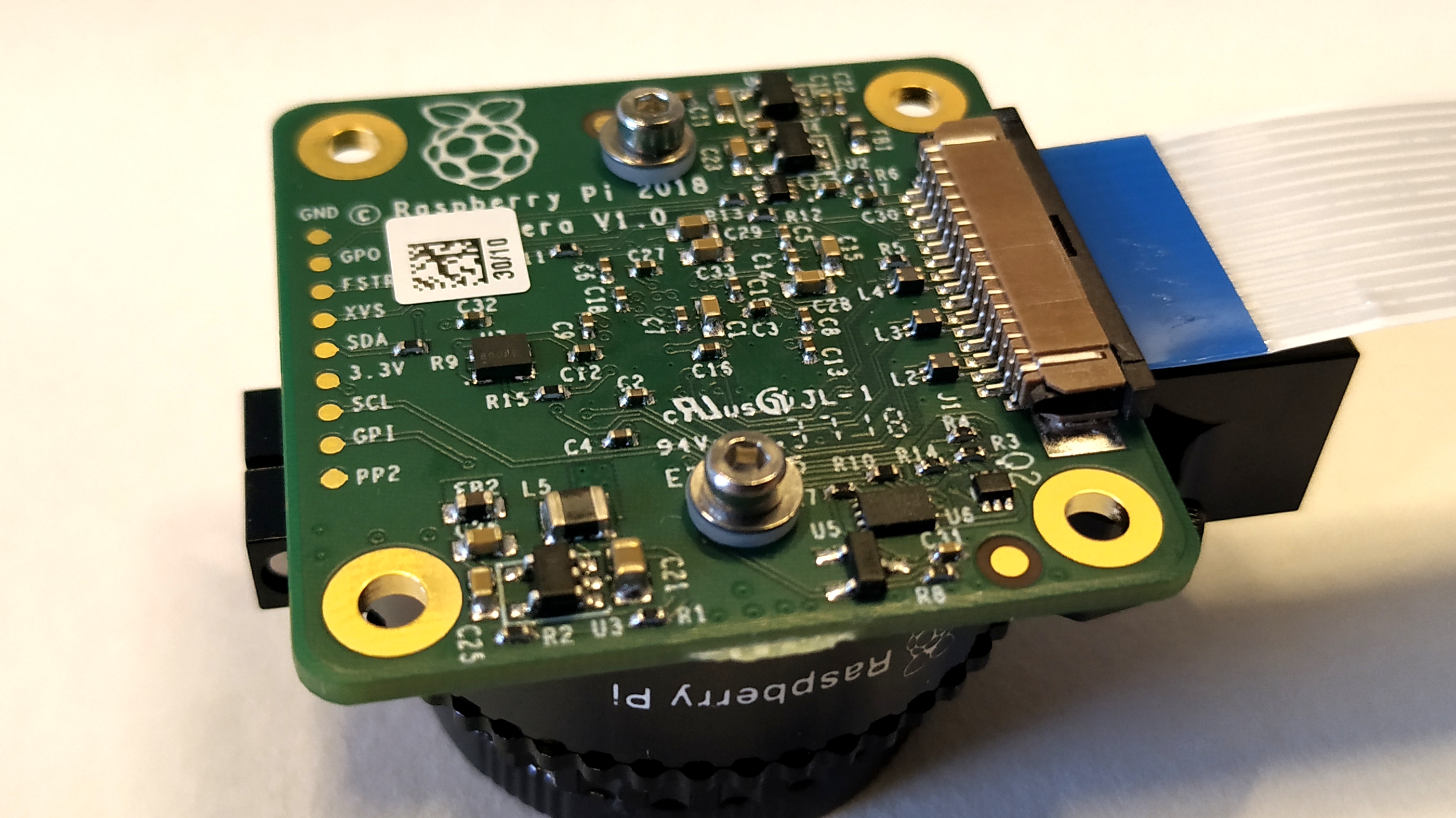


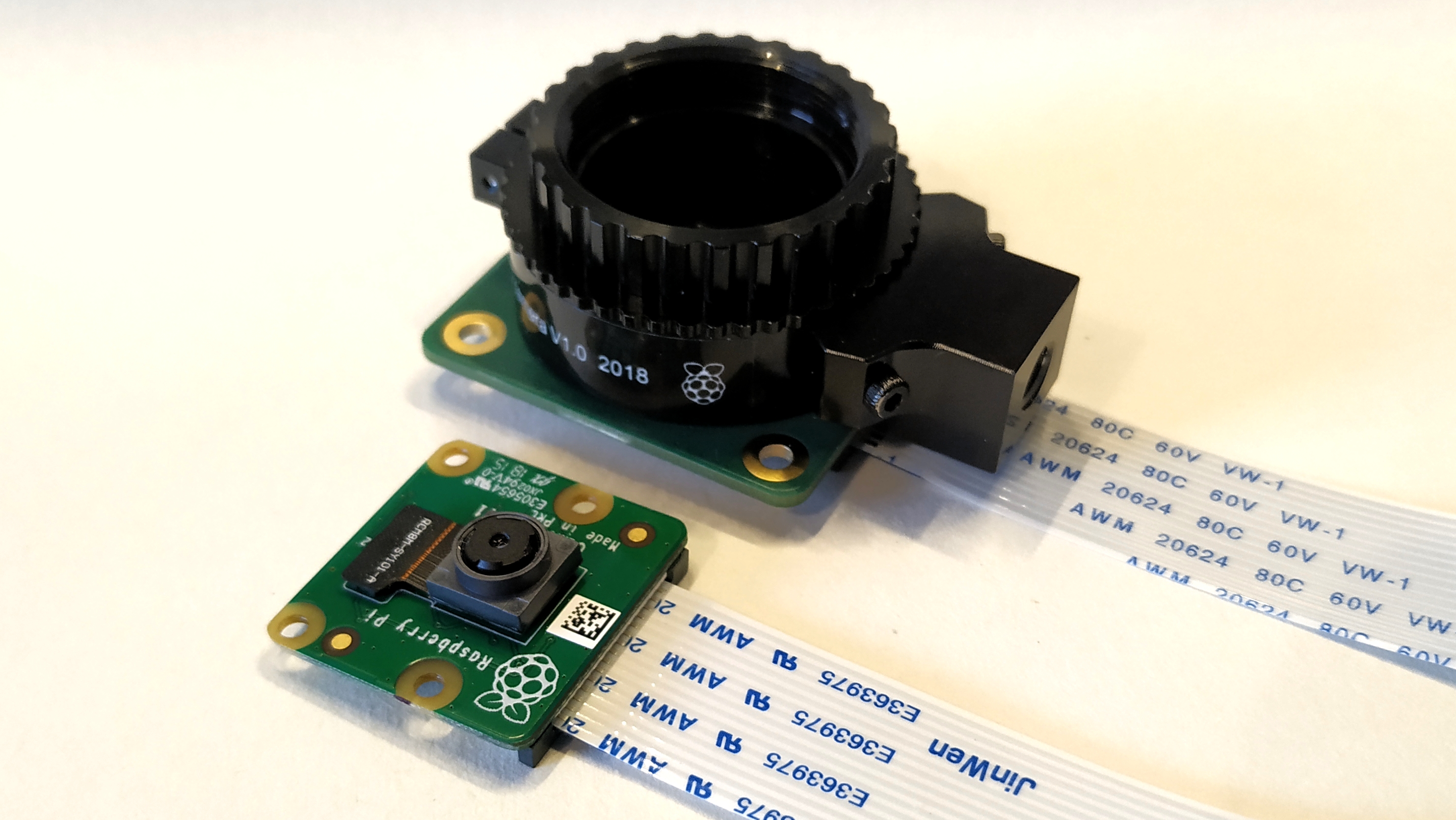
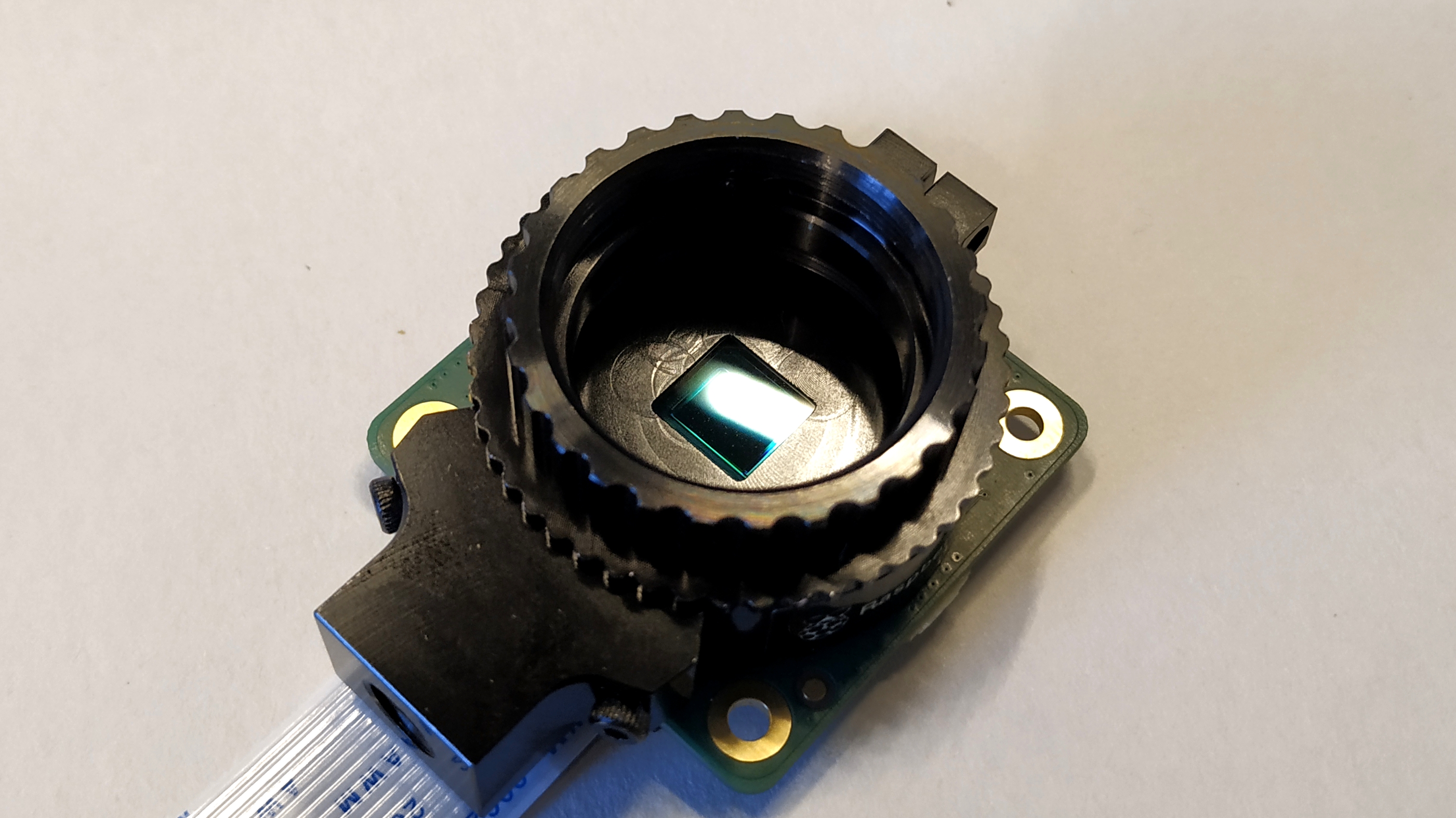
A 12.3 megapixel Sony IMX477R sensor on the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera offers significantly more pixels than the 8-MP Pi Camera V2, the previous first-party module which will remain on sale. The camera is also much larger than previous models, measuring 38mm square, versus 24mm by 23mm for the V2.
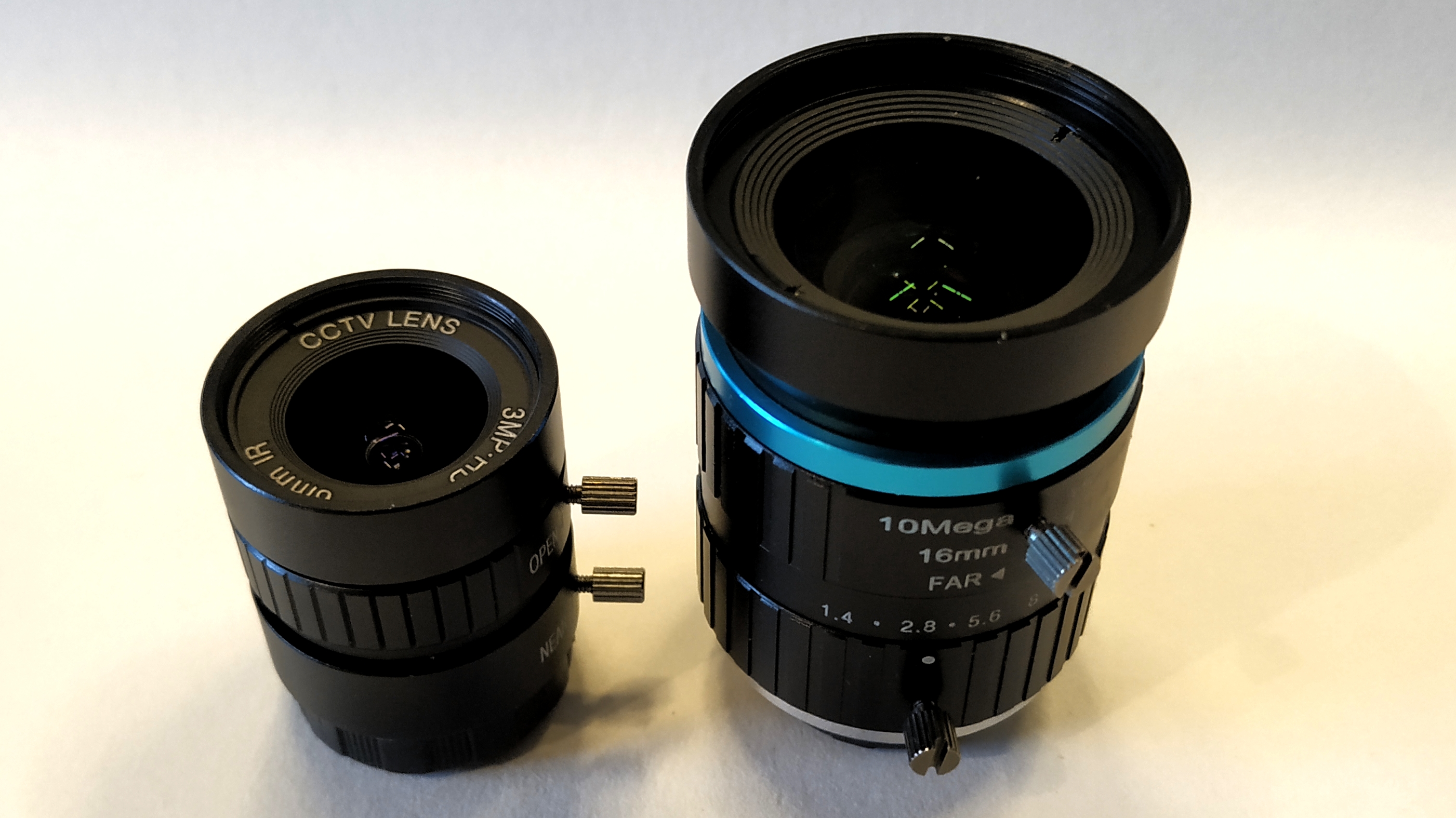
The reason for the size increase is due to an interchangeable C mount where compatible lenses (sold seperately) can be screwed into place. The included adapter will also enable CS lenses to be used with the camera.
At the four corners of the camera are M2.5 screw holes, which can be used to mechanically connect the camera to an object / frame. At the base of the camera is a 0.25-inch screw point for connecting the camera to a standard photography tripod.
The final hardware feature is the inclusion of a 200mm ribbon cable compatible with the CSI (camera) connector on all models of Pi, with the exception of the Pi Zero range which requires an adapter for the later boards. Take care when inserting the cable into your powered down Raspberry Pi as the connection is fragile.
When using the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera, you will need to have a reliable power source. In our tests with a Raspberry Pi 4 we found that the screen would blank when taking an image due to the amount of power being used. The solution is to use the official Raspberry Pi USB charger or another which provides at least 3 amps and 5 volts of reliable juice.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
The camera is nothing without a lens, and in our supplied review unit we tested a 6mm CCTV C mount lens and a 16mm CS mount lens. The lenses retail for $15 and $50 respectively and you’ll need to buy one right away because the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera module doesn’t include one in the box.
Software For the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera
To use any of the official cameras with a Raspberry Pi we first need to enable the camera interface in the Raspberry Pi Configuration tool (sudo raspi-config)l. Then, after a reboot, we can start taking pictures.
You may be thinking that we could use the Raspberry PI High Quality Camera with applications such as Cheese or guvcview, but sadly this is not easily done, and in our tests the images created with Cheese had a nasty purple tint, and guvcview would refuse to start with the camera connected. Hopefully, future software updates will resolve these issues.
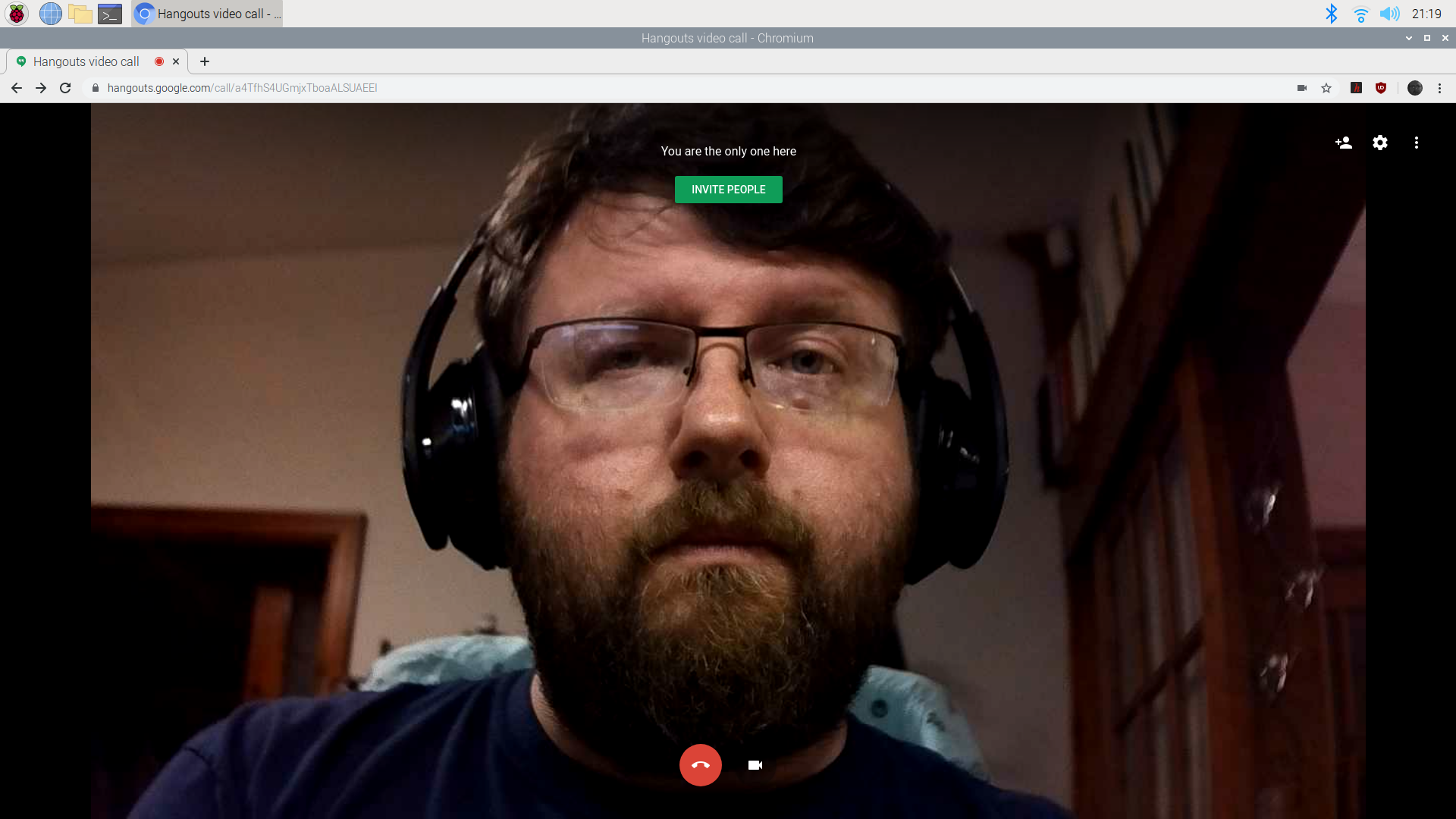
However, on the bright side, the Chromium browser did recognize the Raspberry Pi High Quality Cameras as a webcam and we were able to use it successfully in Google Meet. Presumably, any other web-based camera application would work just as well.
Capturing Test Images with Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera
The first time we take a picture with any official camera, we use raspistill, Raspbian’s built-in capture command, which can quickly show if the camera is connected and working as expected. To test the focus of the camera we ran raspistill with the -k switch, which enabled us to set the focus of the lens.
The Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera’s maximum resolution is 4056 x 3040 pixels (5K) and this produces an image of around 6MB in size. Images are typically saved as JPG, but we can also select RAW, GIF, BMP, PNG, YUV420, RG8888 file formats.
Another way to capture images and video is via the Picamera Python module which enables the camera to be used in projects powered by the popular programming language. With Picamera we can trigger the camera to take an image / video using sensors and inputs connected to the GPIO. At the time of writing the Picamera library has basic functionality and can record 1080p video and 5K images, and also manipulate the images on the fly. Enhanced functionality for the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera is still a little way off yet, developers are working to make this happen.
Image Quality of the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera
The previous camera modules provided a decent entry into photography with Raspberry Pi, but they images that were at best “good”. With a fixed focus lens, the subject had to be brought to the lens and composition was cramped. Version 2 of the Raspberry Pi Camera Module did feature a focus ring to alter the focus of the camera. But this required a special tool to rotate, otherwise you'd risk scratching the lens. Color reproduction was poor and image quality was grainy. But for less than $30 (sometimes less than $10) what did we expect?
With the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera, we see much sharper images with rich colors. A manually controlled focus means that we can compose our shots and focus in on specific areas and blur out the rest of the shot for that professional look.



We took the same shots using the older V2 camera and the new High Quality Camera and as you can see the images are vastly superior with the new camera.
Overall the image quality with the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera is much better. Indoors and out, we were able to take clear images and change the light levels manually and focus our shots according to the subject. Sadly the weather was not with us at the time of review; rain and electronics rarely mix so further testing will be conducted and added to the review.
Capturing Video with the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera

To record video on the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera, we can use the Python Picamera library or we can use <CODE>raspivid</CODE> in the terminal. The video output from the latter is in H264 format, which can be played using the VLC or omxplayer media players. At the time of writing the playback is not perfect, and can jump around erratically from time to time. But playing the same video on our Lenovo laptop provided a smooth experience.
So can the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera capture 4K video? Sorry, no. The best is still 1080p at 30 fps. We did push the camera a little further and managed to get 1080p at 60fps, but it was a little glitchy. To capture higher fps videos we need to drop the resolution. We captured decent footage at 800x600 120fps but it was a little glitchy. We found that converting the video to m4v via the excellent Handbrake video conversion tool provided much better playback.
Will this Camera Work With the Raspberry Pi Zero?
Yes it will, if you have a Pi Zero with the small CSI connector then you can connect up the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera Module and use it in a project. We tested 1080p video recording and still images at max resolution on a Pi Zero. All worked well, if a little slowly compared to a Pi 4. So if you are planning to use the Pi Zero with this camera, don’t expect high speed reactions for trail cameras or home security. But you will get great results.
The Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera is designed to work with the majority of Pi. The only exception being the first generation of Pi Zero which have no CSI port. But which model is best? Well for larger still images we need to use more GPU memory, around 256MB for a 5K image. So the absolute minimum Pi would be a Pi 2. But for the best results a Pi 3B+ or 4 would be the boards to aim for.
Bottom Line
If you’re really serious about using a Pi to capture really good images, the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera is your best choice. At $50 for the module plus at least $15 for a lens, the High Quality Camera doesn’t come cheap, particularly when you can buy the Module V2 for under $30 or third-party modules for less than $10. However, if you can spend the premium, the ability to mount the High Quality Camera to a tripod alone is worth the cost of admission and the higher-quality sensor and lens flexibility seal the deal.

Les Pounder is an associate editor at Tom's Hardware. He is a creative technologist and for seven years has created projects to educate and inspire minds both young and old. He has worked with the Raspberry Pi Foundation to write and deliver their teacher training program "Picademy".
-
Blayzeing I've noticed this post talks a lot about the ability to focus the lens on the High Quality Camera, and the inability to do so on the V2 Pi Camera, however you can change the focus on the V2 Pi Camera. Earlier models of the camera (and most third-party clones) have the focus fixed with a dot of glue (even these can be adjusted with enough effort, though I wouldn't want to suggest everyone do that - it's definitely worth just grabbing a V2 camera) but the V2 Pi Camera module is a lot easier to adjust the focus of; one that I purchased (and one that a friend purchased) even came with a small wrench to adjust it easily.Reply
The main difference in the comparison photos shown in the article seems to be the focus, and seem to give the impression that the only way to do close focal work is to use the new camera, but this is not the case. I would be very interested in seeing the same comparison photos but with the focus appropriately set on the V2 module, or even better, it would be good to see comparisons in low-light performance from the new module due to the increased bit depth (I think? I haven't fully read the specs) and sensor size. -
Simon Anderson ReplyBlayzeing said:...the V2 Pi Camera module is a lot easier to adjust the focus: came with a small wrench to adjust it easily
I'd love to see that on the features list on the box: "super easy focus wrench included!" ;)
But yeah I think the comparison photo examples were unfair: clearly the V2 was just out of focus. 8MP up to 12MP is not a big difference... Hell i used to take better photos on my original 1.2MP fujifilm camera back in the day...
Given lens quality and sensor size/quality are more important than megapixels anyway i'm sure it's a huge improvement either way. Was looking up some more figures:
The sensor is an IMX477: it has 7.9mm image diagonal, the V2 is 4.6mm... For camparison, a micro 4 thirds sensor (about the smallest sensor size you get with a decent camera) is about 22mm. So not a huge sensor but a big improvement for signal to noise ratio no doubt. -
Blayzeing ReplySimon Anderson said:The sensor is an IMX477: it has 7.9mm image diagonal, the V2 is 4.6mm... For camparison, a micro 4 thirds sensor (about the smallest sensor size you get with a decent camera) is about 22mm. So not a huge sensor but a big improvement for signal to noise ratio no doubt.
Yeah, I'd love to see some photos that'd allow for comparison on that front, I've wondered how one of these would perform, say, strapped to a telescope compared to the V2.
Simon Anderson said:I'd love to see that on the features list on the box: "super easy focus wrench included!" ;)
Also yeah, to be honest I was surprised when it came with one! I had managed to adjust the focus on my old 1.3 module some years back, so when it came to a robotics project earlier on this year I suggested to my friends that we just use one before one of them chimed in to say that his latest purchase of a V2 board came with a wrench that made it really easy to adjust - and low and behold, the next one we got also came with an adjustment tool (this one was more of a funnel though that sat on top of the lense during adjust men, which made it a little awkward to use)! I tried again to change the focus on a 1.3 module and I admit this time around I struggled to get it to move very much. -
rotoffset sir, i am new here. i wish to ask how to preview the shot outdoor ?? if the display LCD is not connected and what about power source??Reply -
edwardv ReplyAdmin said:With interchangeable lenses and a 12-MP sensor, the Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera provides a lot more flexibility and resolution than other modules.
Raspberry Pi High Quality Camera Review: Interchangeable Lenses, Powerful Sensor : Read more
I would like to see this using Sony's new AI enhanced image sensor. -
dr_ecksk Reply
It won't fit without an adapter, but Canon EOS to C-mount adapters are available. Try Amazon or B&H Photo.xxyyzz666 said:So I am not a camera person - will the lens from Cannon EOS 50D fit? -
k9gardner You give two examples of lenses that can be used with this camera module, but were any of them taken with the cheaper CCTV lens? I would like to see that compared to a properly focused V2 camera image.Reply