35 AMD CPUs Tested for Power Consumption
Energy Consumption: The Processor and Cool'n'Quiet Mode
Let’s start with the measurements that were taken with the processor in standby mode, with Cool’n’Quiet mode activated. In this case, the CPU switches down to the lowest possible clock rate, and depending on which CPU model is used, may also deactivate some core items and then tells the motherboard to lower the core voltage. In this case the core is lowered to 1.0 V.
In order for Cool’n’Quiet mode to work, it must be activated via the BIOS. In most cases, though, it is activated by default.
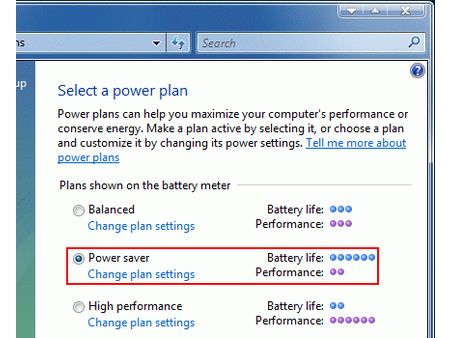
The operating system must also offer a way for the processor’s clock rate to be lowered. With Vista, in the “Control Panel”, an option called “Energy Options” is selected and changed to “Energy save mode”.
Choosing the energy saving mode lowers the CPU’s clock rate
The unburdened processor will, if the motherboard and operating system do not conflict, fall into Cool’n’Quiet mode and dynamically lower its clock rate. A Cool’n’Quiet driver is necessary for Windows XP users; it can be downloaded from AMD’s website . The latest version of the AMD driver is 1.3.2.0053.
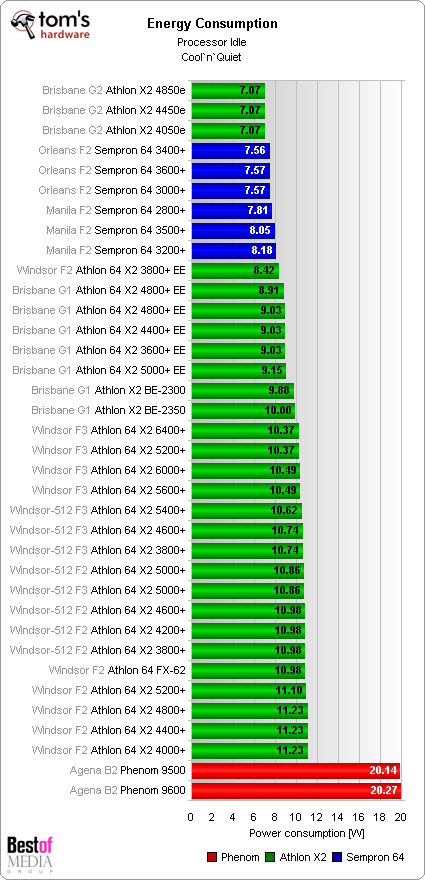
The Phenom uses twice as much energy and comes in last place, while the new “e” models live up to their names and achieve new bests. Because the Sempron 64 processors only have one core, they trail behind the classic Athlon 64 X2 models.The combined values give the logical succession that is seen on the chart.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Energy Consumption: The Processor and Cool'n'Quiet Mode
Prev Page Testing 35 AMD Processors Next Page Energy Consumption: Cool’n’Quiet and the Complete System-
Excellent article! It would be nice to see similar article for Intel processors because even if they are less power hungry, the Intel chipsets are not the "greenest". I am just considering a 24/7 home server and this information is very useful for me. Thank you!Reply
-
Good article! You have the wrong processor name listed for the 2.10 GHz G1 Brisbane as "Athlon 64 X2 4800+ EE". It should be 4000+. I was a bit confused when I read the performance charts and noticed two 4800+ listed until I realized the mistake.Reply
-
xoham Intel is not the greenest if it is less power hungry? Do they not meet RoHS standard or something?Reply -
zenmaster He said the "Intel Chipsets" are not the greenest.Reply
The are still built on the 90nm process.
The P45 will introduce the 65nm process on the chipsets.
The latest AMD Chipsets use the 55nm process.
In regards to CPUs, The Intel CPUs generally use less than the AMD CPUs.
He was simply pointing out that the CPUs lose some of the benefeit of their low power consumption due to the chipset.
For lower-end chips sitting idle, the difference in power usage of the chipsets can be significant. If you are looking at a higher-end chip under load, the power usage of the chipset becomes nominal. -
einheriar besides that intel still has the memory controller as a separate chip on the motherboard, where as amd has that included on the chip.. therefor a higher chip power use might be offset by the absence of the external memory controller, which would become visible when idling ..Reply -
so my x2 4000 ee (in tables interpreted as one of 4800's - due mistake) isn't so bad after all, I don't care about 2w/hour, when I have 24" lcd :-)Reply
-
Mathos The extra power consumption on the Phenom is due to the fact that the NB/IMC voltage stays at 1.250v even when the rest of the processor is running in standby. Kinda of annoying that they put it that high, since with a bios that still has the p-states section you can easily under volt the IMC without losing stability, especially at stock speeds. That will cut down on the idle and load power usages drastically.Reply -
royalcrown I like how review site all push efficiency now since AMD can't really compete on performance. Yawn.Reply -
jprevost Bravo for a great technical article. I can't tell you guys how nice it is to see some great charts. Charts are good, and you guys are good at charts, just don't stop adding to them!Reply