Kill SCSI II: NetCell's RAID 0 Performance + RAID 5 Security Equals SyncRAID
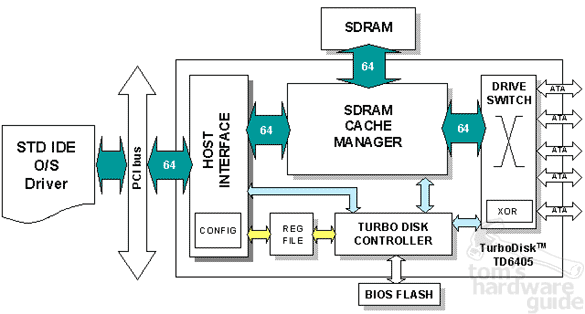
NetCell 6405: The SyncRAID Architecture In Detail
64 bit data buses as far as the eye can see. The catch, however, is the drive switch with integrated XOR engine, which stores 64 bit words instead of data blocks and thus comprises two or four drives.
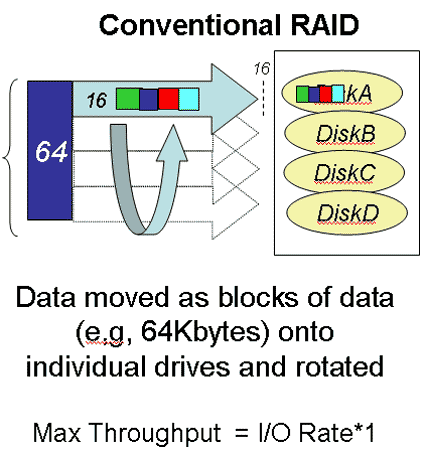
Normally a RAID is written with data blocks of a fixed size (64 kB). This means that parity information has to be generated for every block. The more hard drives are used, the more likely the XOR unit will be the bottleneck.
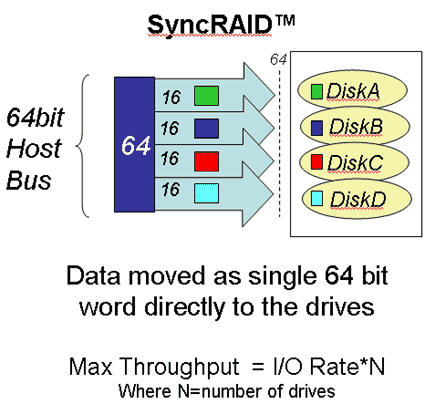
Unlike NetCell, since SyncRAID writes 32- or 64 bit words to data carriers (three- or five-channel operation). This means that parity has to be generated only once for all three or five hard drives.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: NetCell 6405: The SyncRAID Architecture In Detail
Prev Page NetCell TurboDisk NC5464 Next Page Comparison With Previous Technologies
Patrick Schmid was the editor-in-chief for Tom's Hardware from 2005 to 2006. He wrote numerous articles on a wide range of hardware topics, including storage, CPUs, and system builds.