Intel Tiger Lake-U CPUs Could Embrace LPDDR5 RAM
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful

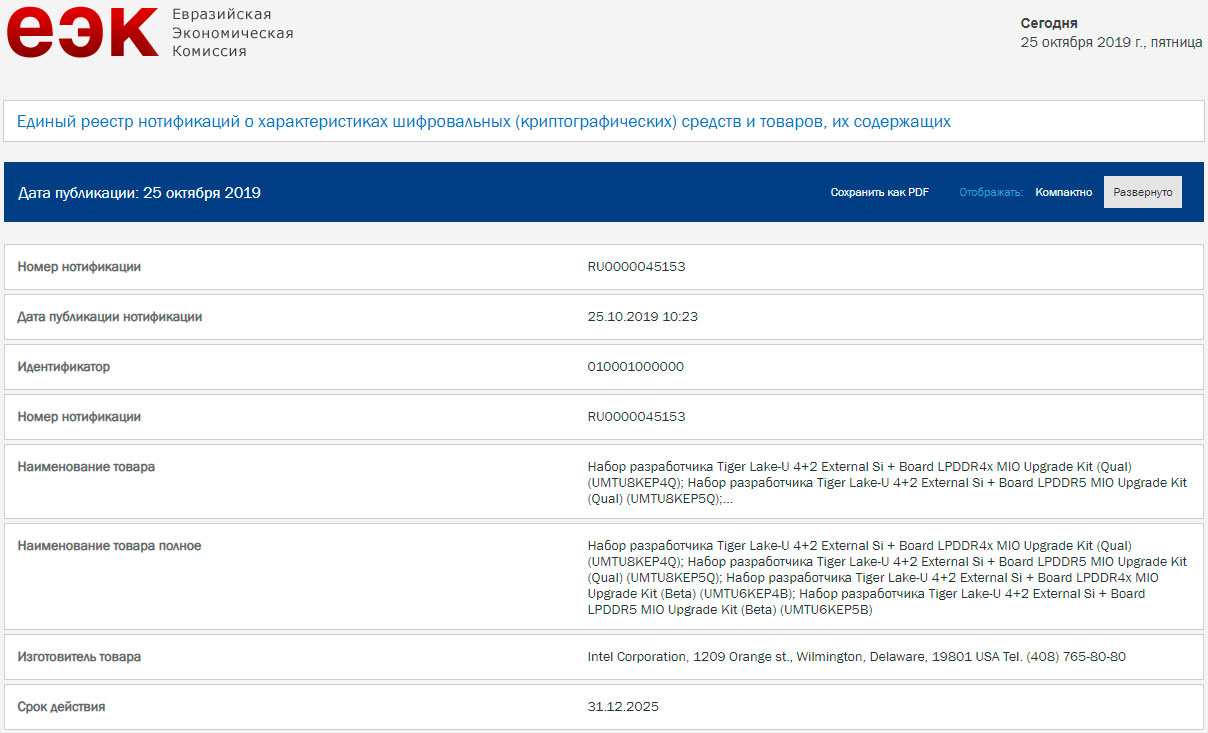
An unidentified quad-core Tiger Lake-Y (TGL-Y) processor popped up a few months ago using LPDDR4X memory. Today, the well-known hardware leaker known as @KOMACI_ENSAKA spotted an Eurasian Economic Commission (EEC) submission that suggests Intel's upcoming Tiger Lake-U (TGL-U) CPUs for thin-and-light laptops will be compatible with LPDDR5 memory,
While LPDDR4X is maxed out at 4,266 Mbps, LPDDR5 will pave the way for data rates up to 6,400 Mbps. More importantly, LPDDR5 is expected to consume up to 30% less power than LPDDR4X. This is critical, considering Intel's U-series (and Y-series) processors are aimed at mobile devices where longer battery life is highly appreciated.
Memory industry leaders SK Hynix and Samsung have shared goals of rolling out DDR5 RAM by the end of this year. So it's feasible for Tiger Lake-U, which is scheduled for release next year, to leverage new LPDDR5 memory.
Tiger Lake is pegged to be the successor to Ice Lake, which means it'll be the second family of chips to hail from Intel's 10nm process node. Tiger Lake should debut with many interesting improvements though.
For starters, the Tiger Lake has already been seen using a 50% larger L3 cache . The 10nm chip will likely incorporate Intel's latest Gen 12 graphics technology and pack up to 96 Execution Units (EUs). Tiger Lake might also support PCIe 4.0. A recent Phantom Canyon NUC leak listed a 28W Tiger Lake-U with four PCIe 4.0 lanes.
Odds are Intel is preparing Tiger Lake to compete with AMD Renoir APUs, which are also rumored to land next year. According to one Linux patch , it's possible that Renoir will arrive with support for LPDDR4X-4266 memory. If that's the case, Tiger lake should have the upperhand -- at least when it comes to higher memory support.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.

Zhiye Liu is a news editor, memory reviewer, and SSD tester at Tom’s Hardware. Although he loves everything that’s hardware, he has a soft spot for CPUs, GPUs, and RAM.