Early Verdict
It's the fastest client SSD every given to the public but you need the workload to take advantage of it. Under lighter workloads the SM951 offers nearly identical performance with more available user capacity (on the 400GB model). Professional users will find the 750 1.2TB model as the best choice for the appropriate workloads.
Pros
- +
Performance, Price (400GB Model), Software Package, Reliability
Cons
- -
Price (1.2 TB Model), Capacity Selection
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Introduction
Despite Samsung's enthusiastic claim of offering the first consumer-orientated NVMe SSD, Intel ends up with the checkered flag. PCIe-based SSDs represent the pinnacle of storage performance. But in the seven years since Fusion-io released its ioDrive, few native PCIe-based solid-state drives have surfaced. The enterprise segment, where the ioDrive resides, prioritizes performance over cost. The rest of us live in a world where $5000 PCs (much less single components) are rare.
The enterprise drives storage with large R&D budgets, and desktop derivatives often follow with less aggressive specifications. Intel and its competitors already have NVMe products in datacenters. They're so fast that we often find them in cache systems as tier 0.
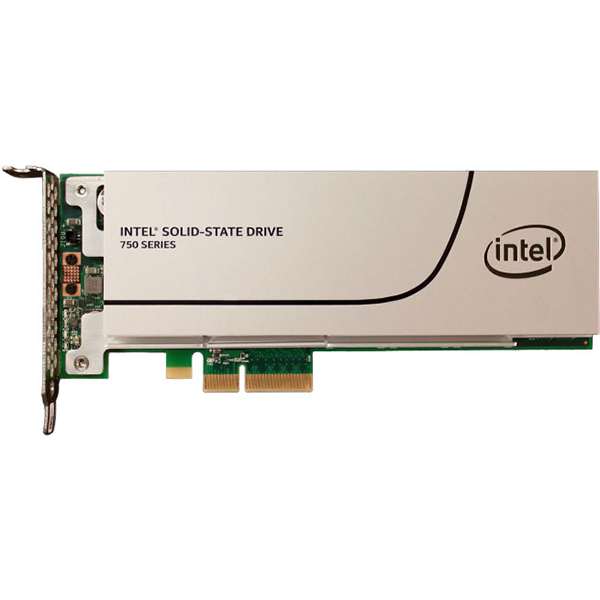
Intel's SSD 750 is a client-oriented high-performance SSD based on the same controller used in the DC 3700/3600/3500 families. This latest series was designed for use in workstation environments or enthusiasts who demand the best possible storage experience. The 750 Series utilizes Non-Volatile Memory Express technology to deliver exceptional performance with low system resource overhead. Given the pedigree and feature set, you don't even need to ask if the SSD 750 is fast. Do you need to ask a Lamborghini owner if his car is quick?
The half- and full-height cards offer more surface area than a 2.5" drive to mount components, which is good because Intel's third-generation controller with NVMe optimization uses more channels to the flash than typical eight-channel processors in this space. The performance comes from reading and writing to 18 flash packages at one time on the 1.2TB model we're testing today. Intel does manage to stuff these components into a 2.5" version with stacked PCBs as well, but the add-in card with its larger surface cooling area requires less airflow to keep the drive happy.
Technical Specifications
Intel released the SSD 750 Series in two form factors and two capacity sizes for a total of four product SKUs. Most will purchase this drive in its traditional half-height half-length (HHHL) PCIe card form factor. As mentioned, Intel also has a 2.5" 15mm model (SFF-8639 connector) for system integrators to use in small form factor designs. The two capacity sizes could be somewhat contentious: 400GB and 1.2TB. The 750 Series suffers a wide gap in pricing between the 400GB ($389) and 1.2TB ($1029) models. We would love to see an 800GB version fill this space at less than $800. The 750 Series ships with a half-height and full-height adapter bracket, as well as USB media with the drivers and Intel's SSD Toolbox utility software. Both capacities should be available by the end of April 2015.
Under the large heat sink is the same third-gen controller modified for NVMe. It employs 18 channels to read and write to the flash. The low-overheard command set paired with the large number of channels and Intel's 20nm MLC ONFi NAND flash delver sequential read performance at up to 2400 MB/s. It's difficult to say that with a straight face; I feel the corners of my lips pressing against my ears. The SSD 750 Series doesn't let up when it comes to sequential writes either, at least on the 1.2TB model. Intel claims 1200 MB/s sequential write performance. The 400GB model purportedly achieves 2200 MB/s sequential reads and 900 MB/s sequential writes. Those numbers remain aggressive, even though the 400GB model only uses half as many channels to the flash.
Intel claims 4KB random read performance just shy of a half a million IOPS (440,000 to be precise, though at this level, who's counting?). The 4KB random write IOPS peak at 290,000. The 400GB model is nearly as fast with random data: 430,000 read IOPS and 230,000 in writes.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Normally, when enterprise components make the transition to the desktop, issues arise due to heat and power consumption. The Intel SSD 750 Series didn't have any problems in these areas during our testing. We reached out to Intel to find out what process node the controller was built on, but the company wants to keep that information private. Still, we asked because the 750's controller is the coolest NVMe-capable processor we've tested to date. With moderate airflow in your system, the drive remains cool, even under heavy loads. The 2.5" model requires three times the cooling capacity due to its smaller form factor and more compact design.
At idle, the 750 Series products consume just 4W of power. That jumps to 25W under heavy load. The consumption is more than a typical SATA-based SSD, but the power to IOPS ratio is very good. Compared to SATA-based products, the SSD 750 is four times faster at peak performance.
The Intel 750 Series is covered by a five-year warranty and is rated at 70GB written per day.
MORE: Best SSDs For The Money
MORE: How We Test HDDs And SSDsMORE: Storage in the Forums
MORE: All Storage Articles

Chris Ramseyer was a senior contributing editor for Tom's Hardware. He tested and reviewed consumer storage.
-
mapesdhs Typo on the 1st page, it states, "Up To 22400 MB/s" for sequential read.Reply
Presumably that's supposed to be 2400. ;)
Ian.
PS. Would be handy to include just one good normal SATA SSD as
a comparison reference, eg. 850 Pro 512GB.
-
CRamseyer Thanks Ian, we'll get the typo fixed ASAP.Reply
Let me see what I can do about putting a 2.5" performance drive in the charts. I'm building new charts now for PCIe-based devices.
Looks for the other SM951 capacity sizes and Predator soon. -
tridon ReplyPS. Would be handy to include just one good normal SATA SSD as
a comparison reference, eg. 850 Pro 512GB.
For those of us that don't have these number in our heads, I get no real sense of how fast this really is compared to my ssd. -
unityole from what I see, intel with lower performance number is likely due to lower performance controller or flash or firmware, whichever it maybe we all know samsung like to clock controller/flash higher for better looking performance. reason that random write at QD1 is so fast probably because of NVMe. can't wait to see this go up against SM951 NVMe.Reply -
unityole ReplyFor those of us that don't have these number in our heads, I get no real sense of how fast this really is compared to my ssd.
from HDD to SSD you see the huge latency drop by about 50x, where as fastest SSD compare to ram is maybe 30-50x dependent on ram/ssd. with NVMe can look forward to at least another 3x loss in latency.
basically it'll be so much more snappier than your ssd for sure. -
AndrewJacksonZA Does this quote from page 5 apply to this card: "In time, we hope to see a RAID 0 NVMe boot environment that would give this test a little more meaning."Reply
Is this card bootable in Windows 10 or not? -
CRamseyer I haven't tested it in Win 10 yet but I don't see MS going backwards with NVMe and not allowing it to boot.Reply
-
ralanahm Hi thank you for the article. If you ever reviewed a Mushkin scorpion deluxe could it be added to the chart? it has 2000 MB/s. the top one is a four 480-ssd raid on a card.Reply
http://poweredbymushkin.com/catalog/36-scorpion-deluxe-pcie-ssd
-
Arabian Knight NVMe Samsung SM951 is coming soon . and I think it will outperform this card ;) ..Reply
-
atheus Maybe it's just me (I doubt it) — when I see an article on something like this the biggest question on my mind is what exactly am I going to get from going with something like this for a system build rather than 2.5" SATA SSD at less than half the price. In order to understand that, I've got to go dig out another article with 2.5" SSD stats and compare them there. Please consider putting the most prevalent main drive option of today into the charts next time you pop out a NVMe article.Reply