Plextor M6V SSD Review
Value-oriented shoppers in the market for an SSD don't have to settle for TLC-based drives. Plextor found another way to reduce prices with two-bit-per-cell MLC: just use flash with smaller cells.
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Mixed Workloads & Steady State
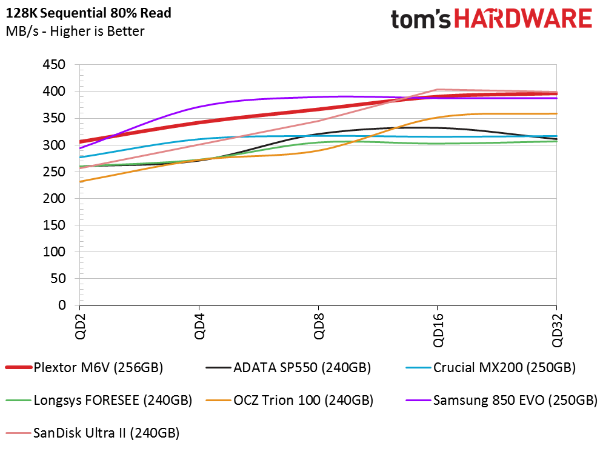
80 Percent Sequential Mixed Workload
Our mixed workload testing is described in detail here, and our steady state tests are described here.
Mixing sequential reads and writes separates the drives more than the 100 percent read or write workloads we just saw. At a queue depth of two, the M6V outperforms the other products in our chart. By a queue depth of four, Samsung's 850 EVO moves to the top, though the M6V remains close.
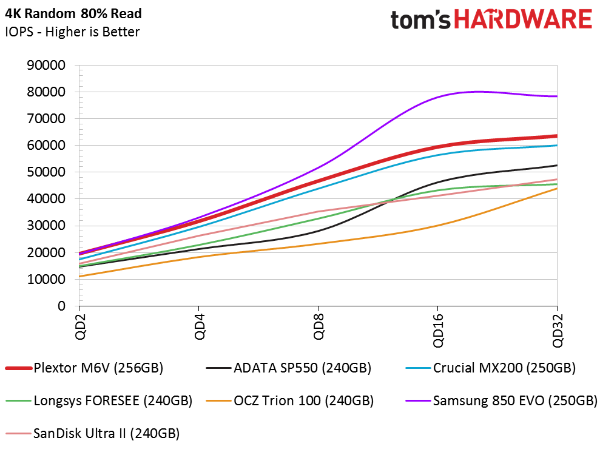
80 Percent Random Mixed Workload
Mixing in random data spreads the field of low-cost SSDs even more. We've known for a long time that the 850 EVO is better than the competition when it comes to performance metrics that matter. Plextor's 256GB M6V closes the gap, but fails to achieve the same level of mixed random throughput that Samsung's 850 EVO delivers.
Sequential Steady State
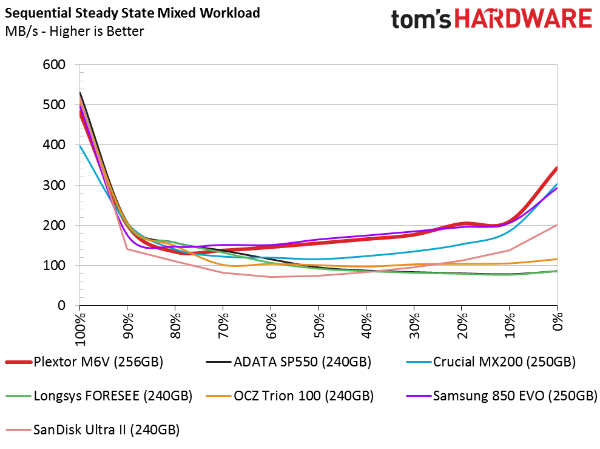
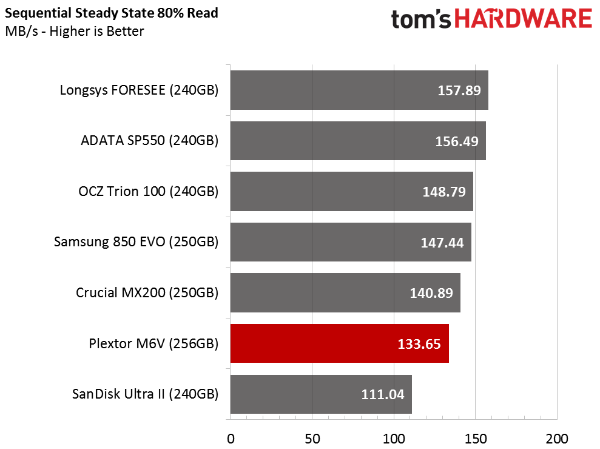
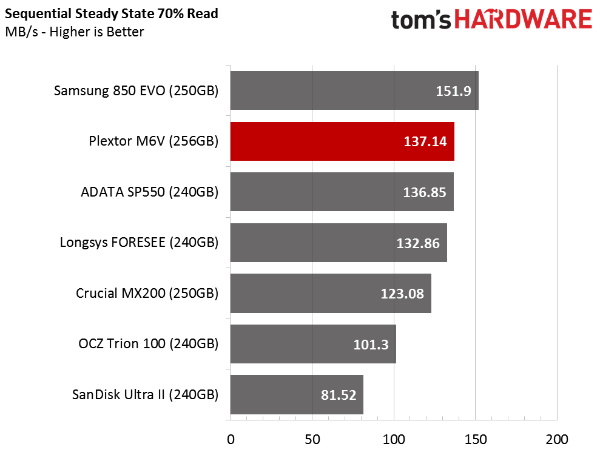
The next two sections employ difficult workloads that follow long conditioning periods. Most of the folks interested in entry-level SSDs will not get their drives down to these conditions; it takes a professional application to push performance this low. With the SSDs nearly full, however, it's easier to get them into a steady state condition, and that may be a concern for some users.
The M6V performs well in this test, but only compared to other low-cost models. Drives like the SanDisk Extreme Pro and the Samsung 850 Pro fare much better than the models we're charting.
Random Write Steady State
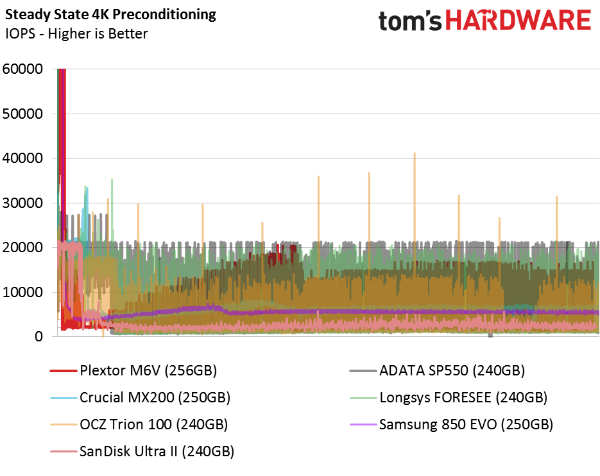
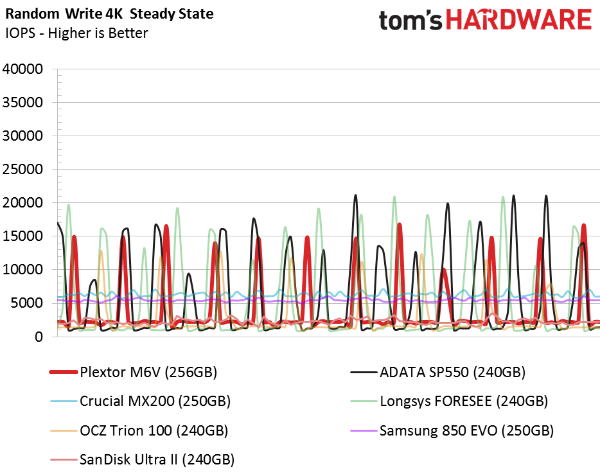
The random write steady state test has two purposes. First, it determines how far IOPS can drop. Second, it allows us to measure performance consistency. Again, most PC users will never see performance fall to this level. But we know that a consistent showing here is indicative of better RAID performance in a striped array. Ever since Intel released drivers that enable TRIM in RAID 0, low-cost solid-state arrays have become more popular.
Plextor's M6V exhibits a low ceiling and a fairly high (for this price range) peak. These drives would not make good candidates for RAID arrays because most of the random write IOPS happen at the lower tier. However, this drive does generate higher steady state random write numbers compared to most of the TLC-based drives. Samsung's 850 EVO is the exception.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Mixed Workloads & Steady State
Prev Page Four-Corner Performance Testing Next Page Real-World Software Performance
Chris Ramseyer was a senior contributing editor for Tom's Hardware. He tested and reviewed consumer storage.
-
jimmysmitty Man I remember when Plextor was the name when it came to CD burners. You wanted a great burner? You got a Plextor.Reply
How times have changed.... -
g-unit1111 Reply17039348 said:Man I remember when Plextor was the name when it came to CD burners. You wanted a great burner? You got a Plextor.
How times have changed....
Yeah I still have my B940 that I use for backups and as long as that still works I will continue to use it. -
Quixit ReplyMan I remember when Plextor was the name when it came to CD burners. You wanted a great burner? You got a Plextor.
How times have changed....
They have to sell something, not much money in burners these days.
-
CRamseyer When Plextor handed over burner manufacturing to LiteOn things went down hill. You could buy the same model with LiteOn branding and flash it to the Plextor firmware and same a few dollars. I still have all of my Plextor hardware going back to the old SCSI 50-pin units.Reply
Remember bit to bit copying that would write the copy protection to the new media? -
jimmysmitty Quixit, I get that. It is just me reminiscing about the good ol days.Reply
17039993 said:When Plextor handed over burner manufacturing to LiteOn things went down hill. You could buy the same model with LiteOn branding and flash it to the Plextor firmware and same a few dollars. I still have all of my Plextor hardware going back to the old SCSI 50-pin units.
Remember bit to bit copying that would write the copy protection to the new media?
I do. Was one of the things that made Plextor great, as well as their very fast burning speeds. They were able to burn more reliably at higher speeds than the competition which is what made them truly great.
It is too bad that their new field is not the same, I would buy a Samsung Evo or Intel SSD over this any day. -
qlum We use quite a decent amount of them at work as the 120gb ones are quite cheap and at their price you otherwise only get old low end models you generally don't want.Reply -
kalmquist I agree that the M6V is too expensive. (As I write this, the 256GB model is $97 on Amazon.). The 240GB Sandisk Extreme Pro, which outperforms most other SATA SSD's at high queue depths and has a 10 year warranty, is now $95 on several sites (including Amazon). The 256GB Mushkin Reactor, which uses the same controller as the M6V, is selling for $80 on Newegg, and that's high because the 250GB Samsung 850 EVO is selling for $78.Reply
-
Nintendork For consumer grade use, high queu depths means nothing, most the use as an OS-gaming drive revolves around QD 1-4.Reply
The 850EVOs offer twice the total written capacity (and it can be more than that). -
mapesdhs Yet another pointlessly expensive lesser grade SSD. The 256GB M6V is 81 UKP here, whereas the 850 EVO 250GB is less than 60. Why on earth would anyone buy an M6V?Reply
Ian.