Four SAS 6 Gb/s RAID Controllers, Benchmarked And Reviewed
We got our hands on four SAS 6 Gb/s RAID controllers from Adaptec, Areca, HighPoint, and LSI and ran them through RAID 0, 5, 6, and 10 workloads to test their mettle. Does your system need eight more ports of connectivity? We can answer that!
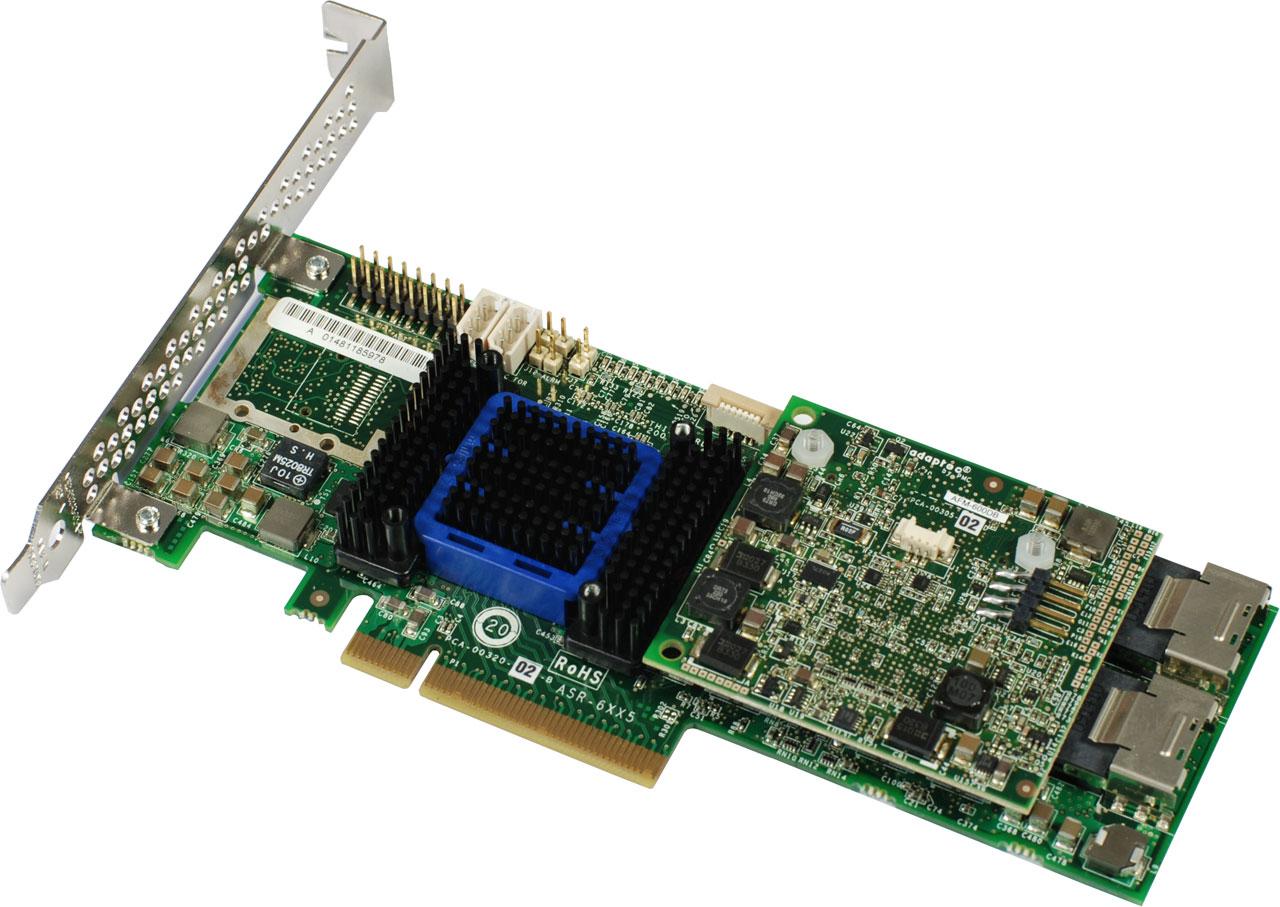
Adaptec RAID 6805
Chip manufacturer PMC-Sierra introduced its "Adaptec by PMC" Series 6 RAID controller family in late 2010. The Series 6 controller cards are based on the dual-core ROC (RAID On Chip) SRC 8x6G controller, which supports 512 MB cache and up to 6 Gb/s per SAS port. There are three low-profile models available: Adaptec RAID 6405 (four internal ports, about $320), Adaptec RAID 6445 (four internal and four external ports, about $475), and our test subject, the $460 Adaptec RAID 6805, which features eight internal ports.
All models support JBOD as well as RAID levels 0, 1, 1E, 5, 5EE, 6, 10, 50, and 60.
Connected to the host system with its x8 PCI Express 2.0 interface, the Adaptec RAID 6805 supports up to 256 devices via SAS expanders. According to manufacturer specs, the sustained data transfer rate to the host computer can reach up to 2 GB/s, while the peak performance can reach 4.8 GB/s on the aggregated SAS ports and 4.0 GB/s on the PCI Express interface – the latter is the maximum theoretical transfer rate of a PCI Express 2.0 x8 bus.
Maintenance-Free ZMCP
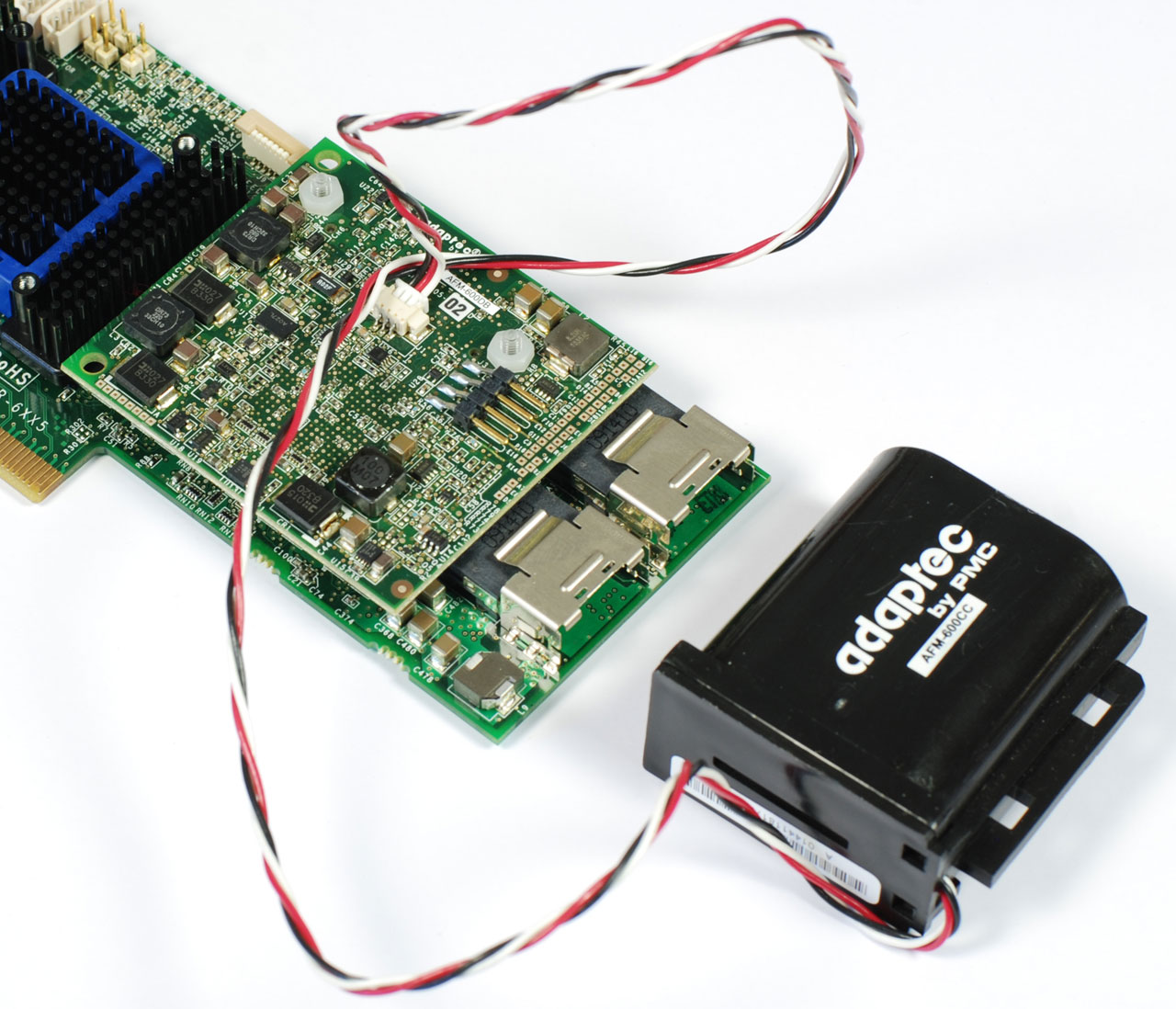
Our test sample came with Adaptec's Flash Module 600, which implements Zero Maintenance Cache Protection (ZMCP) and renders obsolete the traditional Battery Backup Unit (BBU). The ZMCP module is a circuit board with a 4 GB NAND flash chip, used to back up the contents of the controller's cache in the event of a power failure.
Because the copy operation from cache to flash is very fast, Adaptec's able to use a capacitor to keep power flowing, rather than a battery. The capacitor's advantage is that it should last as long as the card, whereas battery backup has to be replaced every couple of years. Additionally, once cached in flash memory, saved data lasts for years if need be. In comparison, you generally get about three days of data retention from a battery backup unit before the cached information is lost, forcing you to move fast on recovery. As the ZMCP's name suggests, it's a zero-maintenance solution, able to withstand extended power loss.


Performance
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
The Adaptec RAID 6805 in RAID 0 mode falls short of its competitors in our streaming read/write tests. Then again, RAID 0 probably isn't a typical use case for a business looking at data protection (though it could be for a workstation user rendering video). Sequential reads clock in at 640 MB/s and sequential writes are almost identical at 680 MB/s. In those two metrics, LSI's MegaRAID 9265-8i tops the charts. Adaptec's RAID 6805 performs better in the RAID 5, 6, and 10 tests, but isn't really a first-place finisher. In an SSD-only setup, the Adaptec controller reaches up to 530 MB/s, but is outperformed by the Areca and LSI controllers.
Adaptec's card automatically recognizes what it calls a Hybrid RAID configuration, which consists of mixed hard drives and SSDs, offering RAID levels 1 and 10 in that configuration, and claiming to outperform the competition through special read/write algorithms. This consists of directing the read operations exclusively to the SSDs, while write operations obviously have to be passed on to both the disk drives and SSDs. Thus, read performance should come close to an SSD-only setup, while write performance should be no worse than an all-disk-based setup.
Our tests results don't quite reflect such a theoretical situation, though. With the notable exception of the Web server benchmark, where data rates of the hybrid setup do, in fact, approach what we'd expect from the pure SSD configuration, the mixing SSDs and hard drives isn't able to get anywhere close to an SSD-only arrangement.
The Adaptec controller fares much better in the hard disk I/O performance tests. Regardless of benchmark type (database, file server, Web server, or workstation), the RAID 6805 controller goes head-to-head with Areca's ARC-1880i and LSI's MegaRAID 9265-8i and consistently achieves first or second place. Only the HighPoint RocketRAID 2720SGL trails in the I/O performance benchmark. Replacing the hard disks with SSDs, LSI's MegaRAID 9265-8i shines and leaves the three other controllers in its dust.
Current page: Adaptec RAID 6805
Prev Page SAS: When SATA Is Not Enough Next Page Adaptec RAID 6805: RAID Software And Array Setup-
americanherosandwich Great review! Though I would have like to see some RAID 1 and RAID 10 benchmarks. Don't usually see RAID 0 for expensive SAS RAID Controllers, and more RAID 10 configurations than RAID 5.Reply -
purrcatian I just sold my HighPoint RocketRAID 2720 because of the terrible drivers. Not only do the drivers add about 60 seconds to the Windows boot, they also cause random BSODs. The support was a joke, and the driver that came on the disc caused the Windows 7 x64 setup to instantly BSOD even though the box had a Windows 7 compatible logo on it. I even RMAed the card and the new one was exactly the same.Reply -
dealcorn Very cool, fast and expensive means not home server stuff. For that, try the IBM BR10I, 8port PCI-e SAS/SATA RAID controller, which is generally available on eBay for $40 with no bracket (I live for danger). You are stuck with 3 GB/sec per port, but if you add $34 for a pair of forward breakout cables you have 8 sata ports at a cost of under $10 per port. The card requires a PCIe X8 slot but if you only give it 4 lanes (the number of lanes offered by our Atom's NM10) if will give each port 1.5 Gb/sec. Cheap SAS makes software RAID 6 prudent in a home storage server.Reply -
slicedtoad I have pretty much no use for anything other than raid 0 but it was still an interesting read. I think i prefer this type of article over the longer type with actual benchmarks thrown in (not for gpu or cpu reviews though).Reply -
pxl9190 Only wish this review had came earlier !Reply
I had a hard time deciding between 9265-8i, 1880 and 6805 a month ago. I bought the 6805 and always wondered why RAID-10 was not as fast as I thought it should be. This reviewed proved my worries.
I eventually went to RAID 6 with 6 Constellation ES 1TB disks. Here's where the adaptec really shines. This is for a photo/video storage/editing disk array.
Admittedly if I have a choice again I would have picked the Areca after seeing the numbers. Adaptec was the cheapest among all of them so it's not too much of a regret. -
Great review! As I am in the process of building a new home file server and always have a habit of going overboard in such situations, I will be referring back to this article many more times before purchasing.Reply
That said can you please talk more to the differences performance wise between SATA and SAS? I understand the reliability argument, however I wonder if for my purposes I would not be better served by using cheaper SATA disks over SAS disks?
I would also love some direction with regard to a good enclosures/power supplies for a hard drive only enclosure. I realize I am quickly priced out of an enterprise solution in this arena, but have seen at least a couple cheaper options online such as the Sans Digital TR8M+B. (This enclosure is normally bundeled with some RocketRaid controller which I would probably discard in favor of either the Adaptec or LSI solution.) -
You are missing a huge competitor in this space. Atto RAID Adapters are on par and I think the only other one out there, why are they not compared in this review?Reply
-
Marco925 I bought the Highpoint, for it's money, it was incredible value at a little under $120Reply -
stuckintexas I evaluated all but the Highpoint for work. What isn't shown, and would be unrealistic for a home user, is that the LSI destroys the competition when you throw on a SAS expander. With 24 15k SAS drives, the LSI card tops out at 3500MB/s, RAID0 sequential write, while the Areca isReply