SLI Is Coming: Time To Analyze PCI Express
Taping Connectors, Updating The BIOS
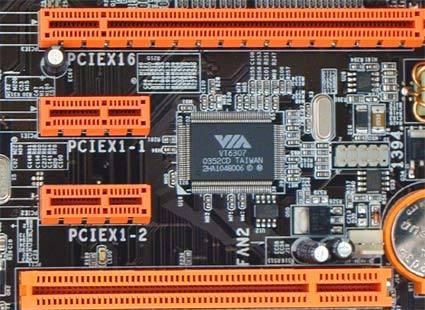
The upper slot holds a x16 PCI Express graphic card. The "x16" here simply represents a combination of 16 logical PCI Express lanes. By blocking some contacts with tape it is possible to get the card to run at slower modes.
Retail motherboards generally cannot be operated at slower PCIe modes, because Intel did not provide for this option (though they are common in AGP-based systems.) Yet, this can be achieved by nicely asking a motherboard manufacturer to provide a suitable BIOS version, and then blocking all unnecessary pins with tape as mentioned above. This is a pretty simple way to test slower transfer rates.
| PCI Express Lanes | Bandwidth per Stream | Bandwidth, duplex |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 256 MB/s | 512 MB/s |
| 2 | 512 MB/s | 1 GB/s |
| 4 | 1 GB/s | 2 GB/s |
| 8 | 2 GB/s | 4 GB/s |
| 16 | 4 GB/s | 8 GB/s |
Shown above is a x16 PCI Express slot as well as the contacts that have been taped to achieve a specific transfer mode. Click to enlarge.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Taping Connectors, Updating The BIOS
Prev Page PCI Express Mode Examination With SLI Pending Next Page Motherboard: DFI LANParty 925X-T2
Patrick Schmid was the editor-in-chief for Tom's Hardware from 2005 to 2006. He wrote numerous articles on a wide range of hardware topics, including storage, CPUs, and system builds.