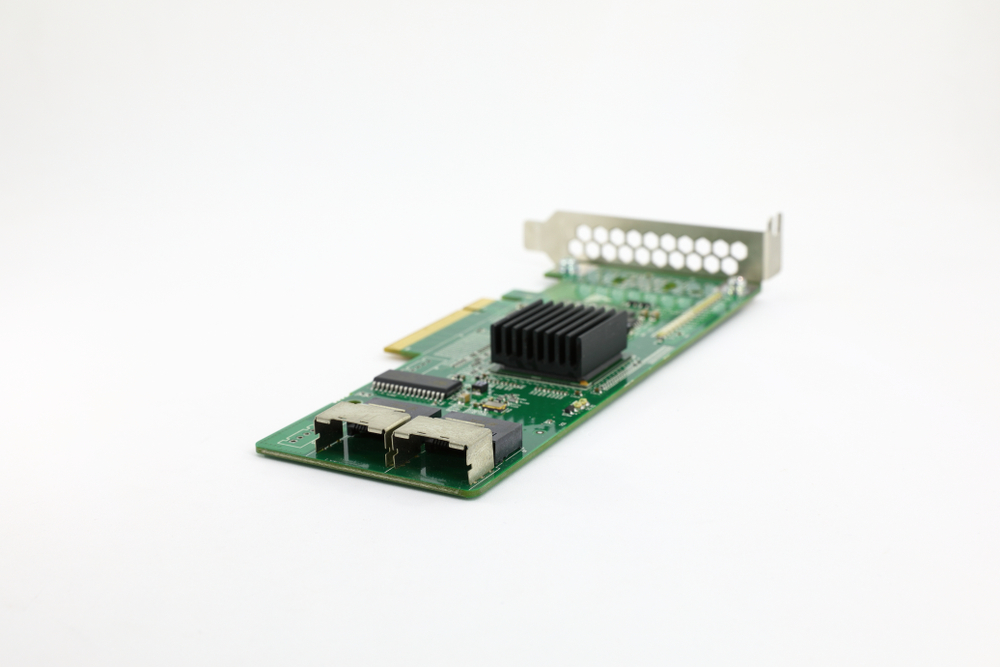
What Is a RAID Controller? A Basic Definition
RAID stands for redundant array of independent disks. This is a type of data storage virtualization technology that lumps physical disk drive components together to drive data redundancy and/or improvement.
A RAID card manages a PC’s hard disk drives or solid-state drives (SSDs) so that they work together and drive redundancy and/or performance. It can be hardware (a RAID card) or software.
There are different types of RAID, as dictated by the Storage Networking Industry Association.
Common RAID Levels
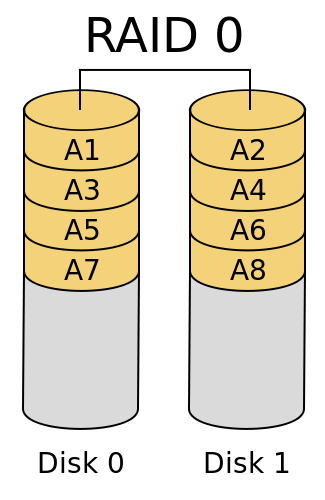
- RAID 0 - evenly distributes data across at least two disks without parity bit information, redundancy and fault tolerance
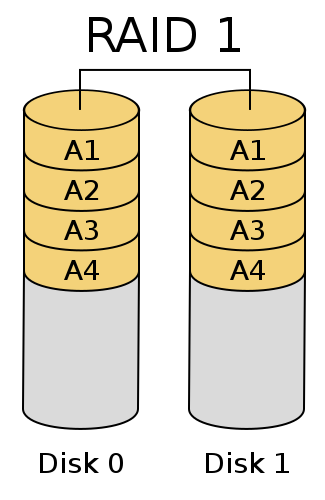
- RAID 1 - makes a copy of data on at least two disks without parity information, striping or spanning disk space across multiple disks
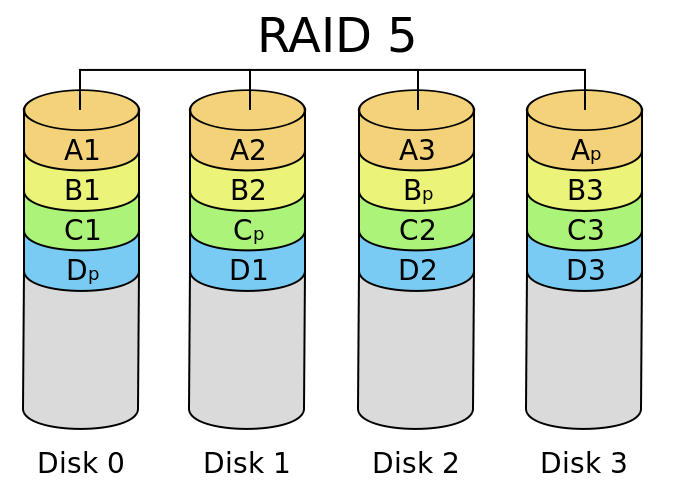
- RAID 5 - distributes data across two or more disks with distributed parity
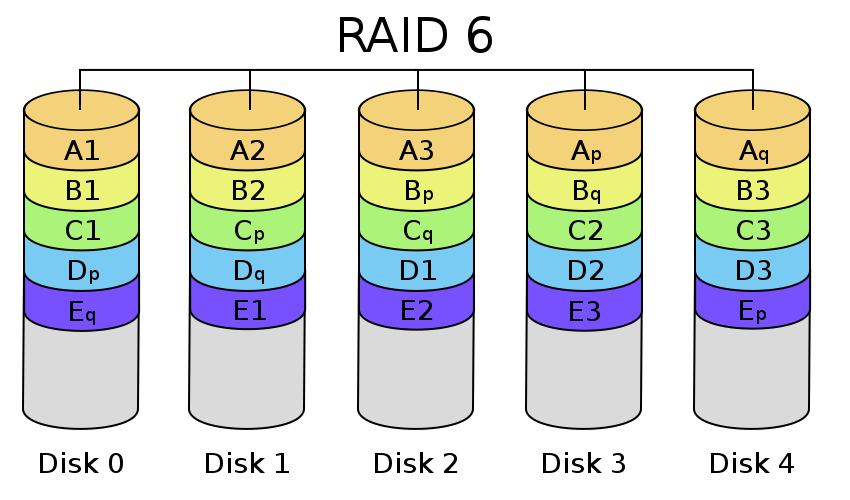
- RAID 6 - same as RAID 5 but with one more parity block (a form of data storage)
Less Common RAID Levels:
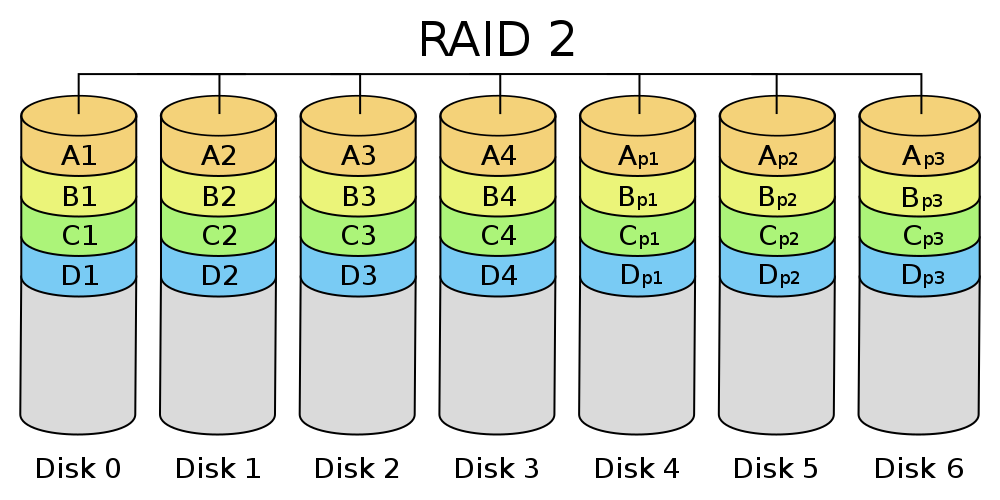
- RAID 2 - distributes data evenly in bits, rather than blocks
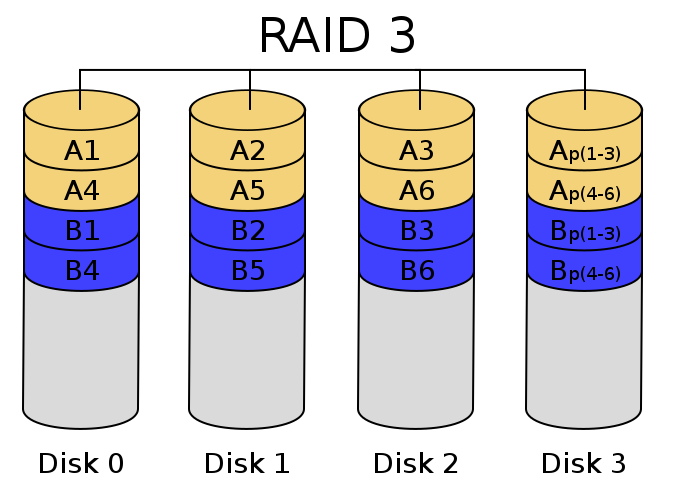
- RAID 3 - byte-level striping with a parity disk
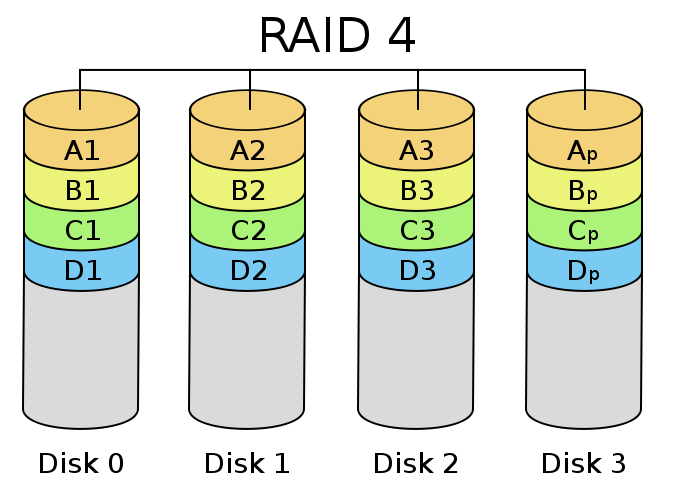
- RAID 4 - block-level striping with a parity disk
Nested RAID Levels
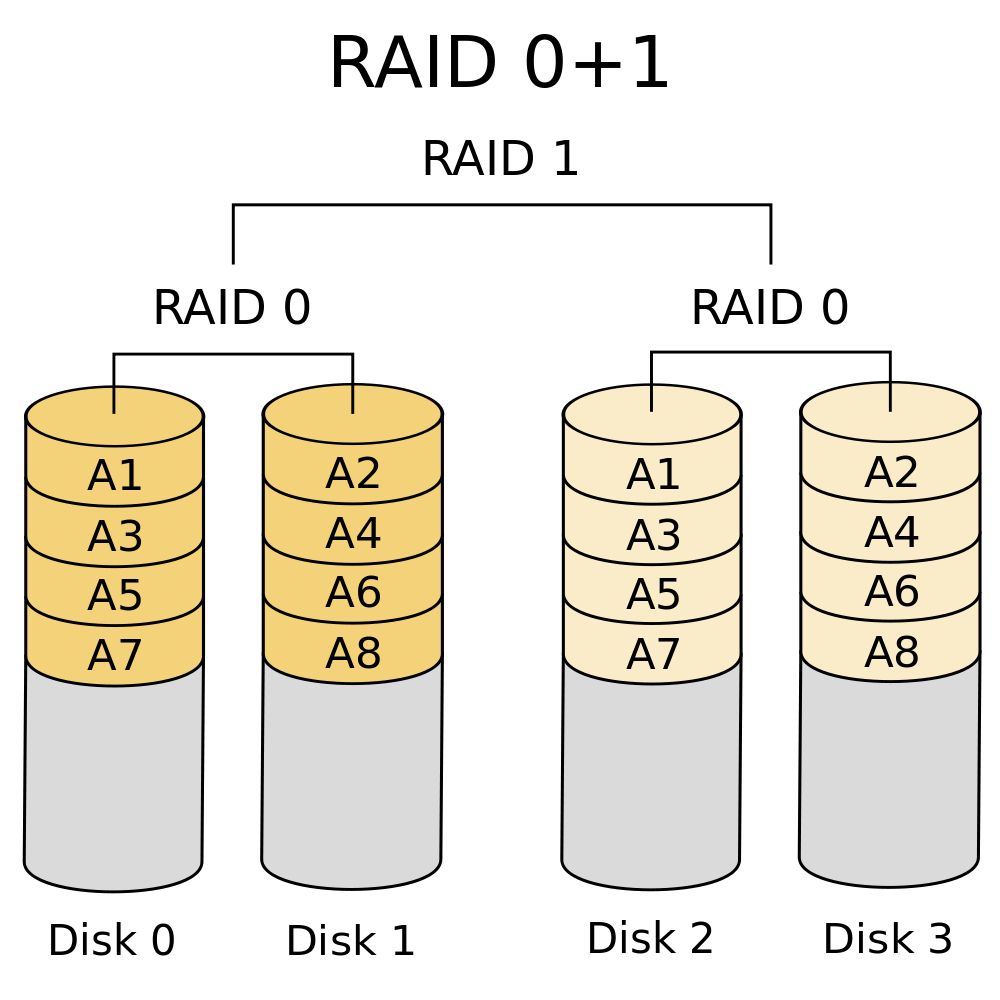
There are also RAID levels combining two or more of the above RAID levels. For example, RAID 0+1 (aka RAID 01) and RAID 0+3 (aka RAID 03).
This article is part of the Tom's Hardware Glossary.
Further Reading:
- Why I Will Never Buy a Hard Drive Again
- Best Memory 2018: Fast, Cheap & RGB
- How To Set Up RAID In Windows 10
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.

Scharon Harding has over a decade of experience reporting on technology with a special affinity for gaming peripherals (especially monitors), laptops, and virtual reality. Previously, she covered business technology, including hardware, software, cyber security, cloud, and other IT happenings, at Channelnomics, with bylines at CRN UK.