AMD EPYC Rome Specs Leak: From 8 Cores Up to 64 Cores
A recent Eurasian Economic Commission (EEC) listing has seemingly revealed AMD's entire next-generation EPYC, codenamed Rome, processor lineup with core counts and TDP (thermal design power). Belgian retailer 2Compute has listed the boost clocks and cache size for the enterprise-level chips, which are slated to hit the market before the end of 2019.
The EPYC Rome parts feature AMD's latest Zen 2 processor microarchitecture. Taiwanese foundry TSMC produces the multi-core monsters for AMD under the 7nm manufacturing process. The new chips will be marketed under the EPYC 7000-series. Unlike the first EPYC models that carry the EPYC 7001 branding, the second-generation processors will take the EPYC 7002 moniker. Once again, AMD will be using the "P" suffix to denote the models that are designed specifically for single-socket server configurations.
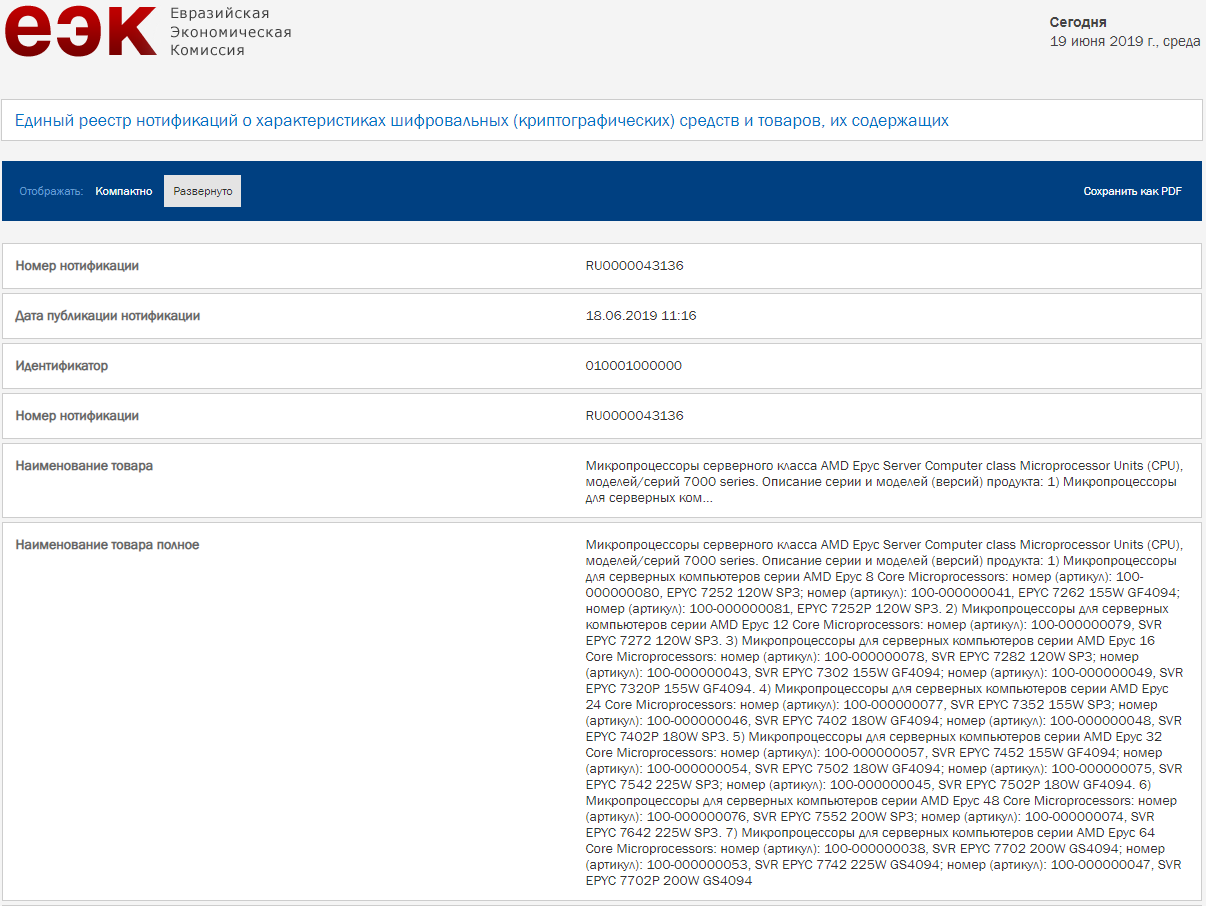
According to the EEC entry, AMD plans to offer a very diverse EYPC Rome product stack that includes entry-level octa-core models up to the flagship 64-core chips. The current listing has the EPYC Rome family at 19 members, but AMD could add more as necessary. The boost clocks for the chips are between 3.2 GHz and 3.4 GHz. Cache configurations start from 32MB and scale up to 256MB.
AMD EPYC Rome Specifications
| Model | Cores | Threads | Boost Clock | Cache | TDP |
| EPYC 7742 | 64 | 128 | 3.4 GHz | 256MB | 225W |
| EPYC 7702P | 64 | 128 | 3.35 GHz | 256MB | 200W |
| EPYC 7702 | 64 | 128 | 3.35 GHz | 256MB | 200W |
| EPYC 7642 | 48 | 96 | 3.4 GHz | 256MB | 225W |
| EPYC 7552 | 48 | 96 | 3.35 GHz | 192MB | 200W |
| EPYC 7542 | 48 | 96 | 3.4 GHz | 128MB | 225W |
| EPYC 7502P | 32 | 64 | 3.35 GHz | 128MB | 180W |
| EPYC 7502 | 32 | 64 | 3.35 GHz | 128MB | 180W |
| EPYC 7452 | 32 | 64 | 3.35 GHz | 128MB | 155W |
| EPYC 7402P | 24 | 48 | 3.35 GHz | 128MB | 180W |
| EPYC 7402 | 24 | 48 | 3.35 GHz | 128MB | 180W |
| EPYC 7352 | 24 | 48 | 3.2 GHz | 128MB | 155W |
| EPYC 7302P | 16 | 32 | 3.3 GHz | 128MB | 155W |
| EPYC 7302 | 16 | 32 | 3.3 GHz | 128MB | 155W |
| EPYC 7282 | 16 | 32 | 3.2 GHz | 64MB | 120W |
| EPYC 7272 | 12 | 24 | 3.2 GHz | 64MB | 120W |
| EPYC 7262 | 8 | 16 | 3.4 GHz | 64MB | 155W |
| EPYC 7252P | 8 | 16 | 3.2 GHz | 32MB | 120W |
| EPYC 7252 | 8 | 16 | 3.2 GHz | 64MB | 120W |
*Specifications in the table are unconfirmed
The EPYC 7252, 7252P and 7262 are at the bottom of the spectrum with eight cores, 16 threads and a TDP that ranges from 120W to 150W. The EPYC 7272 is the only 12-core, 24-thread model listed.
The EPYC 7282, 7203 and 7302P models are said to have 16 cores, 32 threads and a TDP that starts from 120W to 155W. On the other hand, the EPYC 7353, 7402 and 7402P feature 24 cores and 48 threads, while the EPYC 7353, 7402 and 7402P are listed with 32 cores and 48 threads. Both the 24-core and 32-core models have TDPs that span from 155W to 180W.
As we approach the top of the pyramid, we find the EPYC 7542, 7552 and 7642 with 48 cores and 96 threads. The added cores also bring higher TDP ratings, between 200W and 225W.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
For this generation, the EPYC 7702, 7702P and 7742 will carry the flagship title. The trio is reportedly equipped with 64 cores and 128 threads of processing power.
From a specs standpoint, AMD's upcoming EYPC Rome processors already look very convincing. If the performance is there and the chips are priced competitively, AMD should have no problems taking on Intel's Cascade Lake Xeon CPUs.

Zhiye Liu is a news editor, memory reviewer, and SSD tester at Tom’s Hardware. Although he loves everything that’s hardware, he has a soft spot for CPUs, GPUs, and RAM.
-
InvalidError EPYC maxing out at 64 cores is much of a 'leak' when the first pictures of Lisa showing an eight chiplets EPYC package are several months old and we've known chiplets had eight cores each for quite a while too. Practically confirmed except for lack of model number attached to it for over six months.Reply -
BulkZerker ReplyInvalidError said:EPYC maxing out at 64 cores is much of a 'leak' when the first pictures of Lisa showing an eight chiplets EPYC package are several months old and we've known chiplets had eight cores each for quite a while too. Practically confirmed except for lack of model number attached to it for over six months.
True, however this gives us an idea of the product stack -
Rob1C Uncertain about the accuracy of the information but the TDP is the same as the last one: AMD Epyc - so that suggests a clock bump.Reply