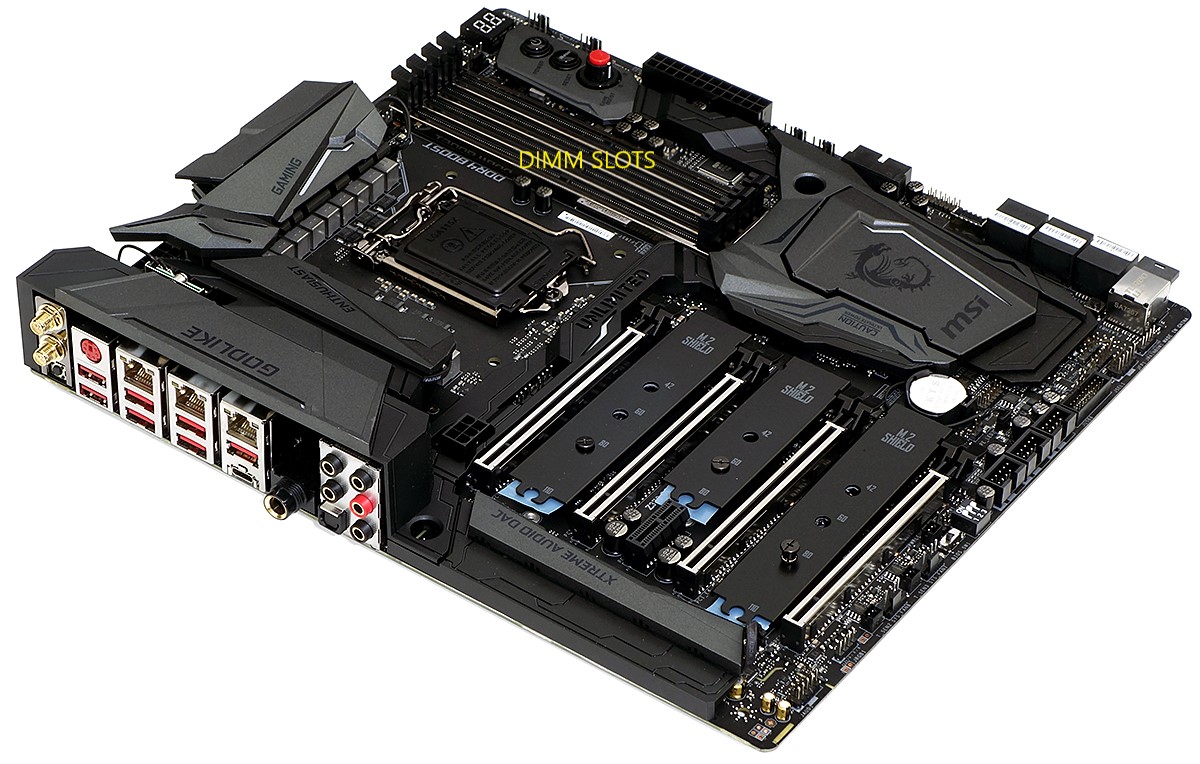
What Are DIMM Slots? A Basic Definition
DIMM (dual in-line memory module) slots are the place on your motherboard where the RAM goes. As such, you may also see DIMM slots referred to as “RAM slots.”
The more DIMM slots your motherboard has, the more RAM you can install. Your motherboard may have anywhere from one to eight DIMM slots, but most mainstream motherboards have four.
Motherboards come in three sizes. They are, from smallest to biggest, Mini-ITX, Micro-ATX and ATX. Mini-ITX motherboards usually have a maximum of two DIMM slots in order to save space. Motherboards running low-end chipsets also tend to have just two DIMM slots. Contrastingly, motherboards based on high-end chipsets, like AMD’s X399 chipset for its Threadripper CPUs or Intel’s X299 chipset for its Core X CPUs, have eight DIMM slots.
So how many DIMM slots do you actually need? It depends on how much RAM you want and how many DIMMs you'll use to get there. 16GB of RAM should do the trick if you’re mostly focused on mainstream tasks and games, while 32GB is more than enough. You can achieve 32GB RAM with two DIMM slots (using two 16GB RAM sticks). However, it’d be cheaper to reach 32GB of RAM via four DIMM slots (using four 8GB RAM sticks).
This article is part of the Tom's Hardware Glossary.
Further Reading:
- Dissecting the Modern Motherboard: Connectors, Ports & Chipsets Explained
- How to Choose a Motherboard
- Best Motherboards
- Best Memory 2018: Cheap, Fast, Cheap & RGB
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.

Scharon Harding has over a decade of experience reporting on technology with a special affinity for gaming peripherals (especially monitors), laptops, and virtual reality. Previously, she covered business technology, including hardware, software, cyber security, cloud, and other IT happenings, at Channelnomics, with bylines at CRN UK.