Gigabyte M.2 PCIe Riser Cards Take Storage Performance to New Level
Gigabyte has introduced the CMT4034 and CMT4032 M.2 PCI-Express (PCIe) riser cards for consumers who need the utmost storage performance.
M.2 solid-state drives (SSDs) are getting bigger and faster by the day. There is no denying that the M.2 form factor is the future for data storage. Unfortunately, the majority of modern motherboards only come with a single M.2 slot unless you start shopping in the really high-end section. And most budget-conscious consumers won't pay a heavy premium for an extra M.2 slot. That's where Gigabyte's CMT403x series M.2 PCIe riser cards come into play. The add-in cards allow users to use multiple M.2 SSDs with the PCIe protocol in their systems as long as there is a PCIe 3.0 x8 or x16 lane available on the motherboard. Since the both the CMT4034 and the CMT4032 lack the PCIe switching feature, the motherboard needs to support the PCIe bifurcation functionality.
The CMT403x series M.2 PCIe riser cards, with dimensions of 150 millimeters x 68.9 millimeters, respect the low-profile form factor. Nevertheless, they come with both a low-profile and full-height I/O brackets to virtually fit into any system. The riser cards possess a blue PCB complemented by a metallic black heatsink with the Gigabyte branding to provide cooling for the M.2 SSDs.
Gigabyte CMT4032
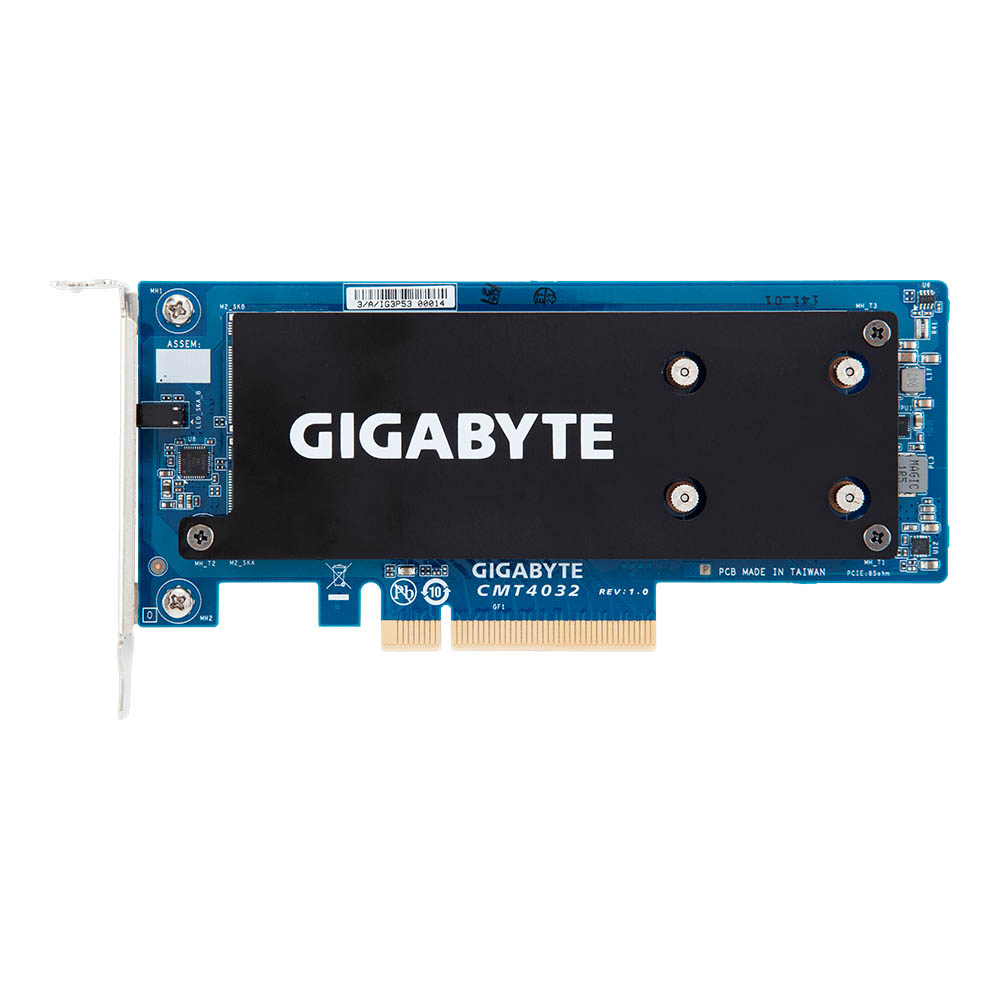
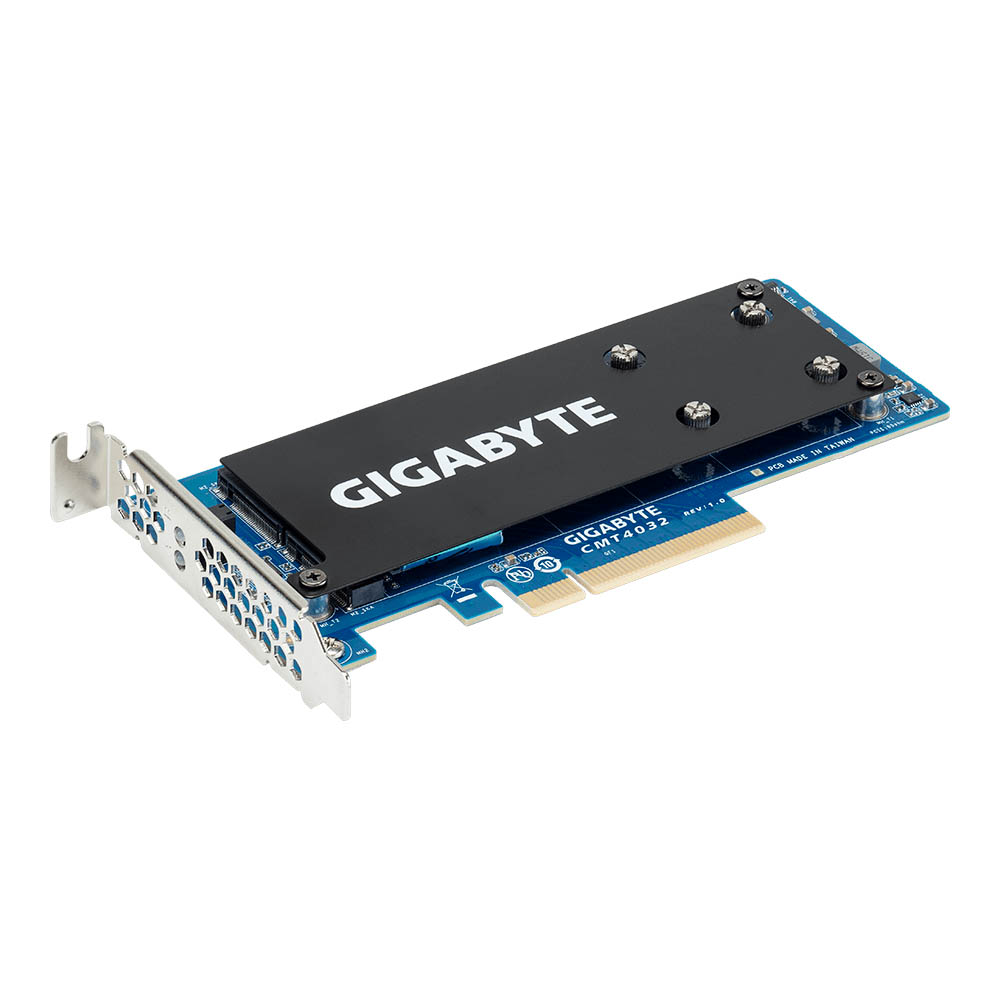


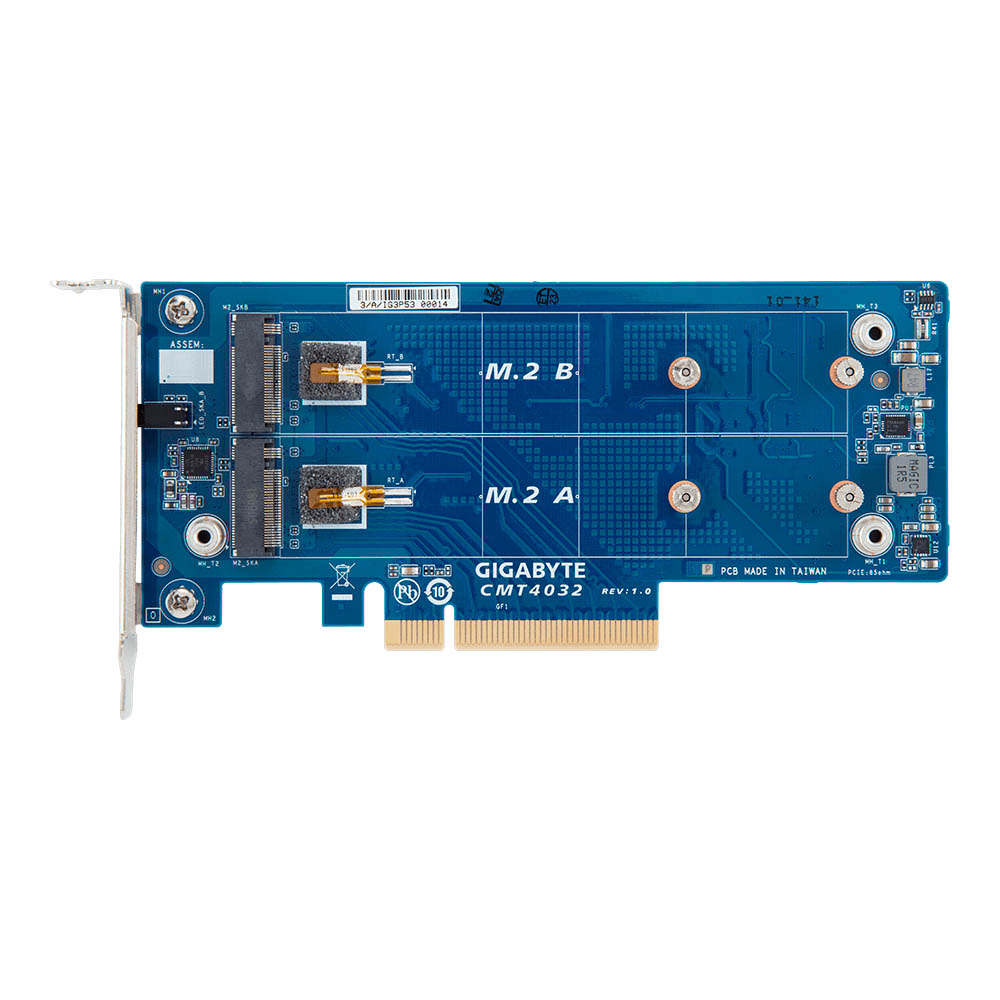
The CMT4032 accomodates up to two PCIe 3.0 x4 SSDs with the 2280 or 22110 form factors. This riser card is made up of a single PCB with two M.2 M-Key slots. The CMT4032 requires a free PCIe 3.0 x8 lane to work properly.
Gigabyte CMT4034
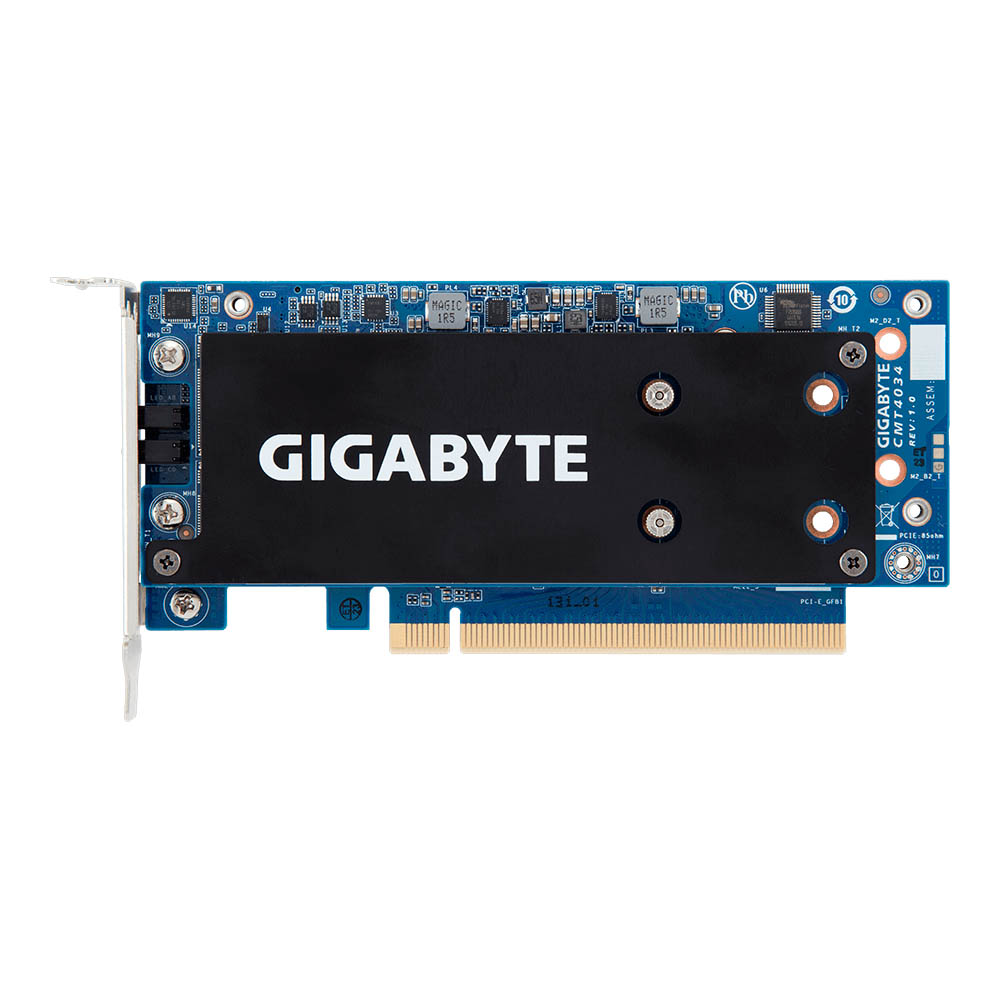
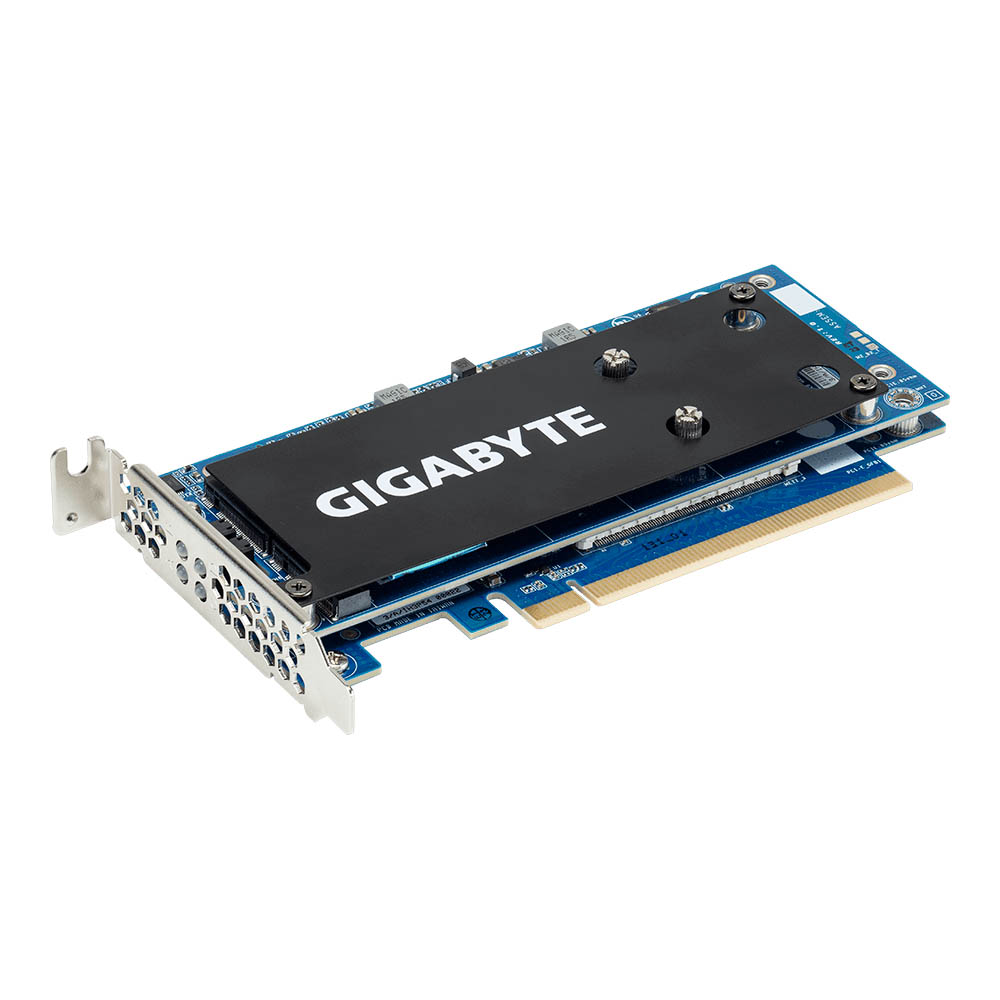


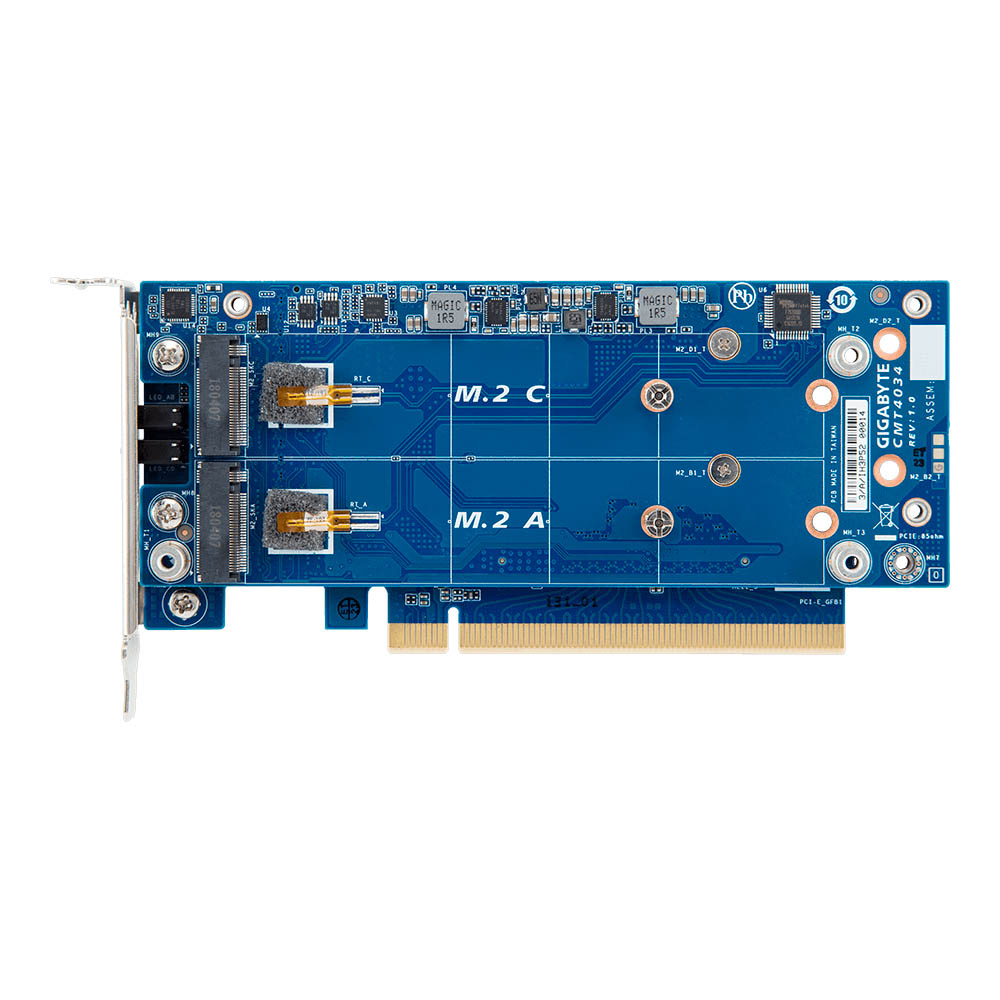
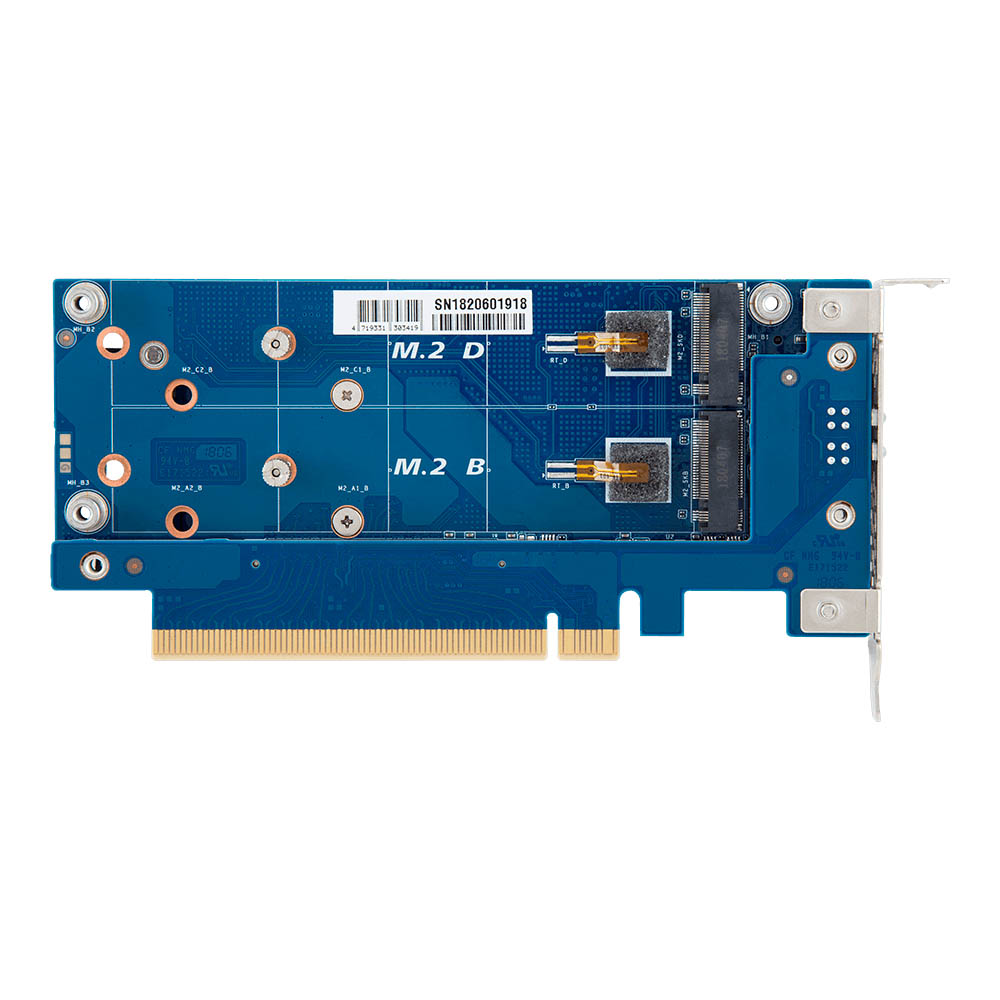
Gigabyte also offers the CMT4034 for hardcore enthusiasts and prosumers who want to max out their systems' storage performance. The CMT4034 houses up to four PCIe 3.0 x4 SSDs, thanks to its dual-PCB design. Two M.2 M-Key slots are placed on each side of the primary PCB, while the secondary PCB is responsible for communicating with the PCIe 3.0 x16 lane on the motherboard.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
At the time of this article, Gigabyte hasn't revealed the pricing and availability for the CMT4032 and CMT4034 M.2 PCIe riser cards.

Zhiye Liu is a news editor, memory reviewer, and SSD tester at Tom’s Hardware. Although he loves everything that’s hardware, he has a soft spot for CPUs, GPUs, and RAM.
-
hotaru251 hmmm I have an older desktop that has no m.2 slots on motherboard but i dont use any of the pci slots...how would I be able to tell if they were 3.0 or not? (its about 5 yrs old or so now)Reply -
takeshi7 Do these require PCIe bifurcation support on the motherboard, or does the card handle it on its own?Reply -
Brian_R170 Does this mean we'll soon be seeing another Optane-RAID review with four of the 905p M.2 SSDs in RAID 0?Reply -
bit_user Reply
If the CPU is a desktop Sandybridge (or older), then it's only PCIe 2.0. If it's Ivy Bridge or newer, then they might be PCIe 3.0.21116325 said:hmmm I have an older desktop that has no m.2 slots on motherboard but i dont use any of the pci slots...how would I be able to tell if they were 3.0 or not? (its about 5 yrs old or so now)
As @Non-Euclidean said, just look around at the motherboard until you see what looks like the model number. Do a search (or visit the manufacturer's website) and you'll probably find the owners' manual, which will spell out the different slots' specs and configuration options. -
SkOrPn No mention of the need for Bifurcation requirement? Without PCIe port bifurcation enabled in the BIOS, either hidden or via switch, the Motherboard and OS will have no clue what to do with an adapter such as that. PCIe was designed for one device per slot regardless how many lanes it has. PCIe port bifurcation was developed by Intel to get around this limitation. Cmon Liu, you should know this stuff. How does this adapter work on a x8 or x16 slot without bifurcation support? Not very many consumer boards will have that, if any at all.Reply
EDIT: OK, Gigabyte clearly states these riser cards are only meant for their Purley Server systems, which obviously have Bifurcation built in. -
compprob237 Reply
Well, only the Threadrippers really have enough PCI-E lanes to do that. You could squeak by on the i9 Skylake-X chips but the GPU would be limited to x8 and that assumes all but 4 lanes are used exclusively by these. Meanwhile, the Threadripper would only use up half of its lanes so you could have dual x16 (theoretical, but not realistic) GPUs in SLI on top of the 8-way raid.21116991 said:@Brian, why stop at 4 when 2 of these cards can net you an 8-way raid 0. LoL -
Diji1 What happens if you do not have PCI-E lanes available? Does it not work at all or work but with degraded performance if something else is sharing or what?Reply -
emeraldsmines1990 Reply21118053 said:What happens if you do not have PCI-E lanes available? Does it not work at all or work but with degraded performance if something else is sharing or what?
If you dont have lanes available then the empty slot you have will be disabled. and cant be used.
Some motherboards have PLX Switches to share lanes ... but are very expensive ones.