Intel experimenting with direct liquid cooling for up to 1000W CPUs - package-level approach maximizes performance, reduces size and complexity
Intel has reportedly been working on this for years
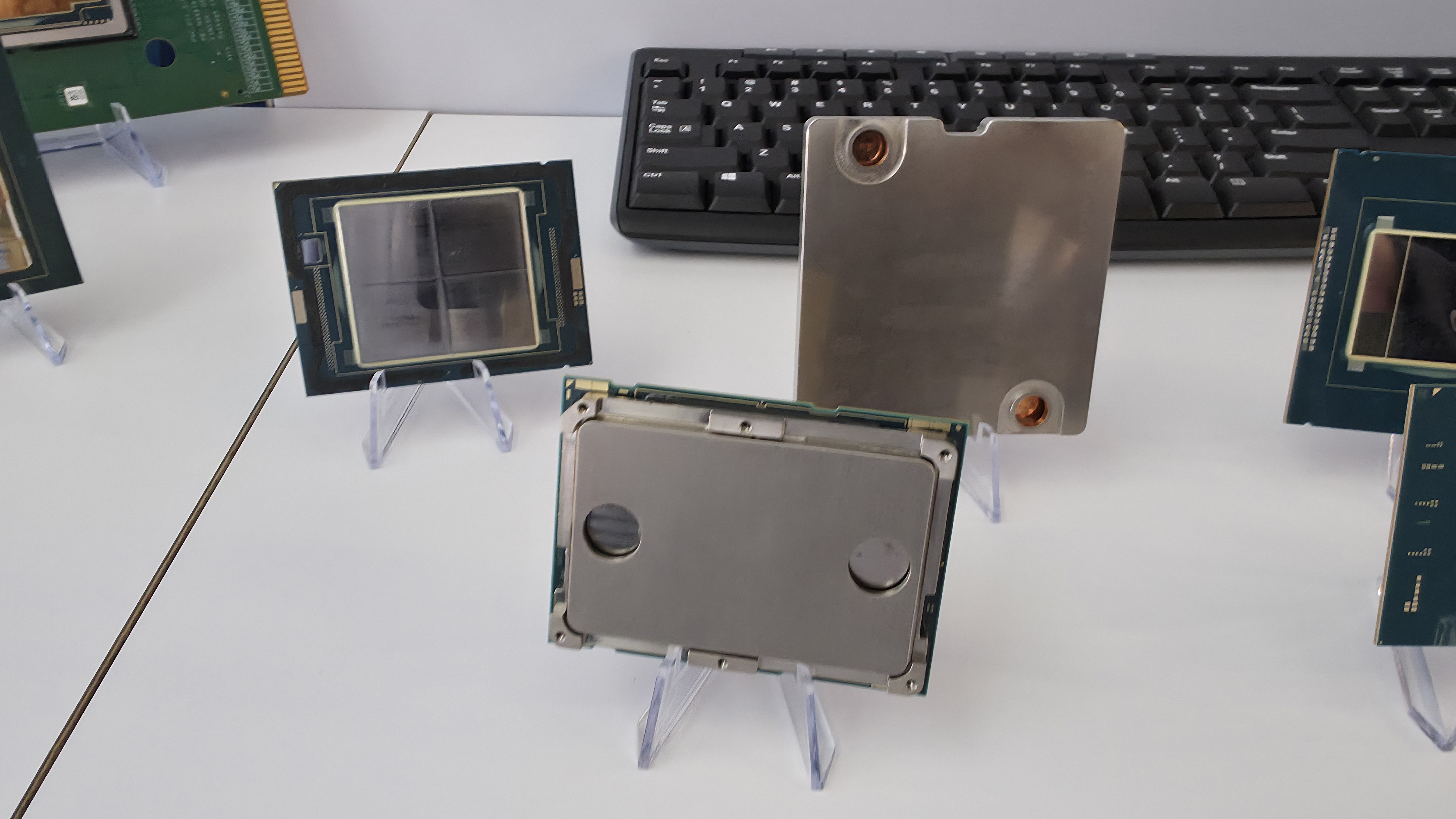

Intel is testing a new way to tackle the growing heat output of its power hungry chips. At its recent Foundry Direct Connect event, the company showcased an experimental package-level water cooling solution designed to more efficiently cool CPUs . Intel has working prototypes for both LGA (Land Grid Array) and BGA (Ball Grid Array) CPUs, with demos using Intel’s Core Ultra as well as Xeon server processors.
The cooling solution doesn’t apply coolant directly to the silicon die. Instead, a specially designed compact cooling block sits atop the package, featuring microchannels made of copper that precisely guide the coolant flow. These channels can be optimized to target specific hotspots on the die, potentially improving heat removal where it matters the most.
Intel claims the system can dissipate up to 1,000 watts of heat using standard liquid cooling fluid. That kind of thermal load isn’t typical for consumer CPUs, but it could be relevant for high-end AI (Artificial Intelligence) workloads, HPC (High Performance Computing), and workstation applications.
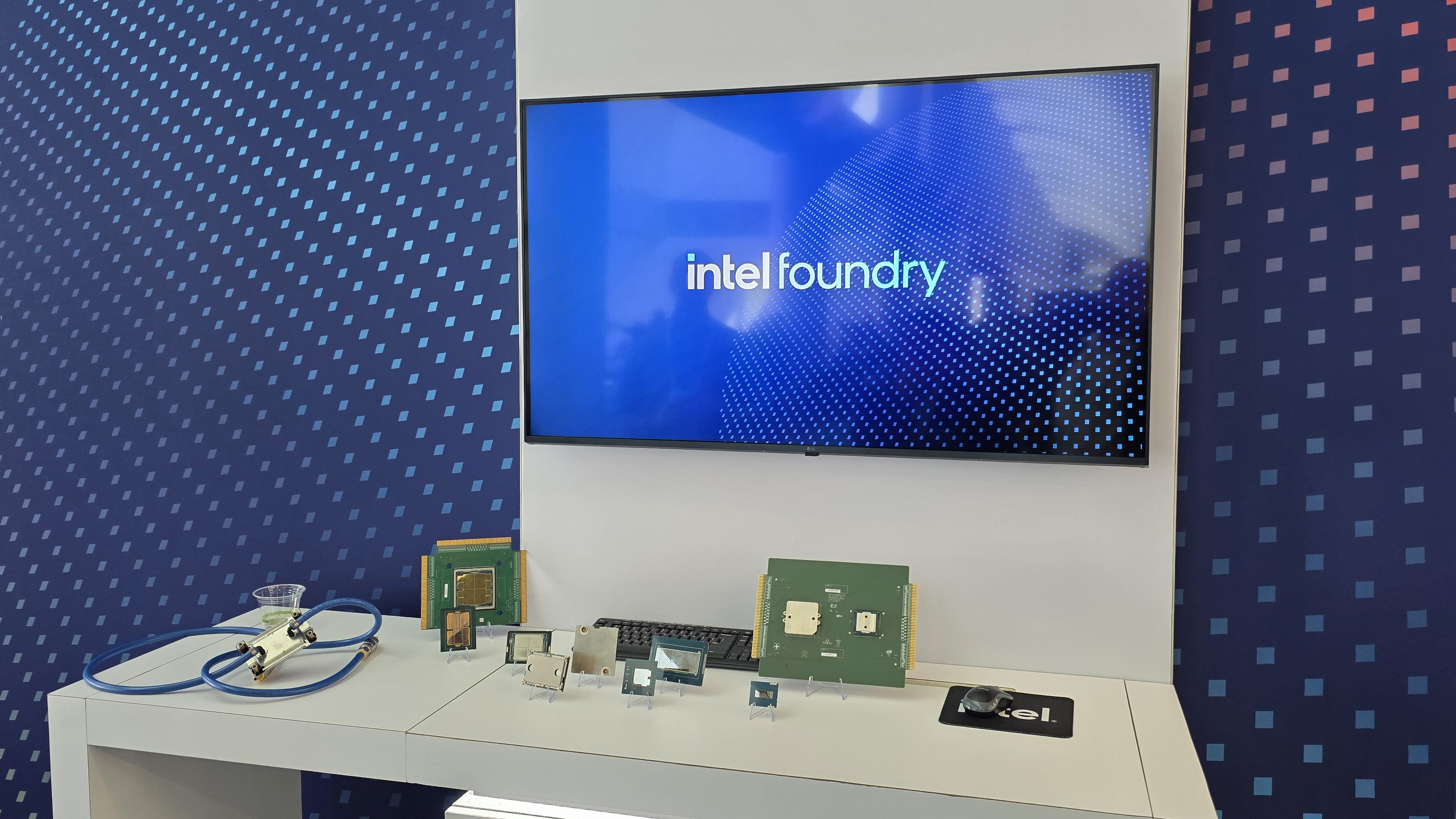
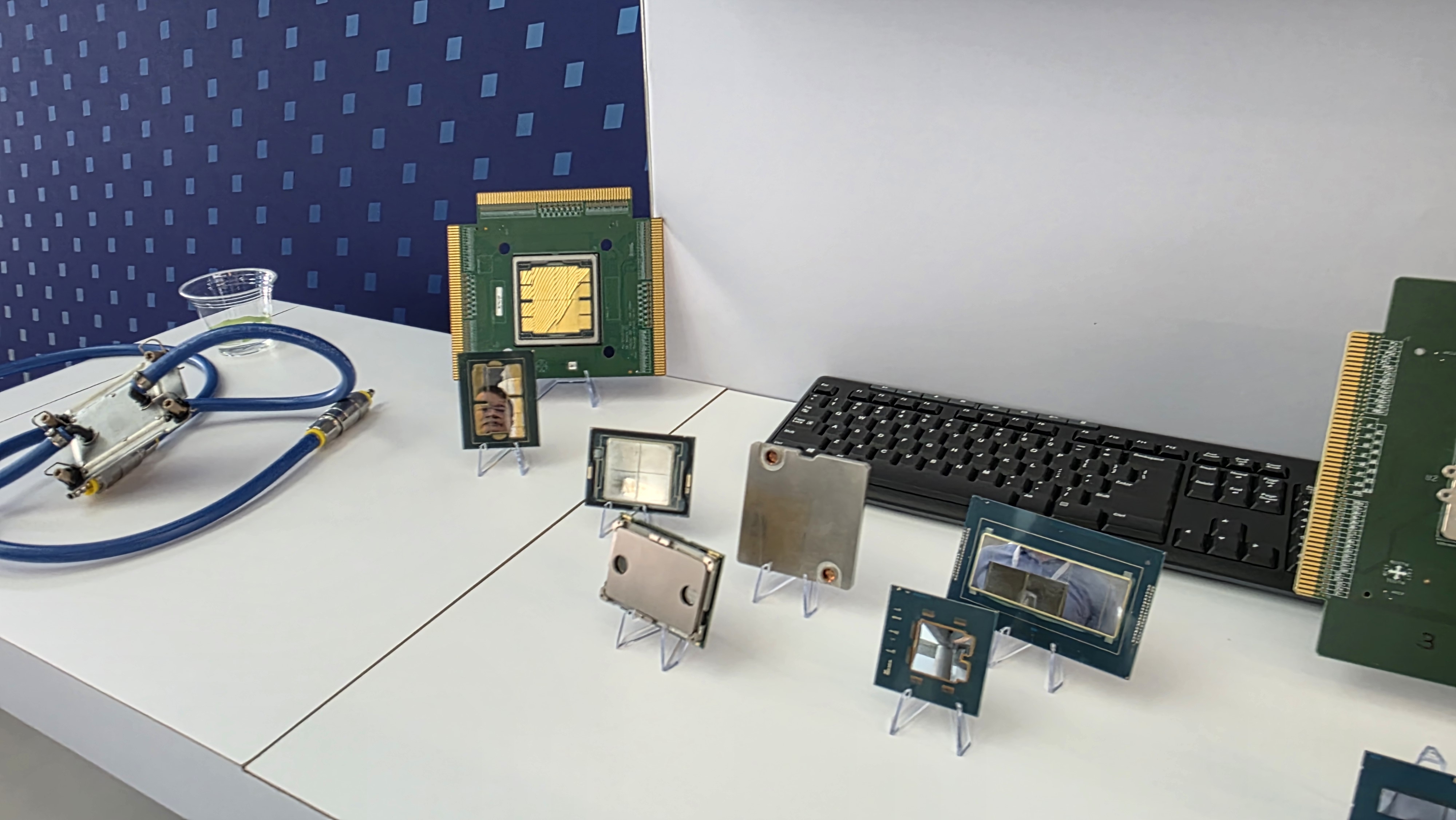
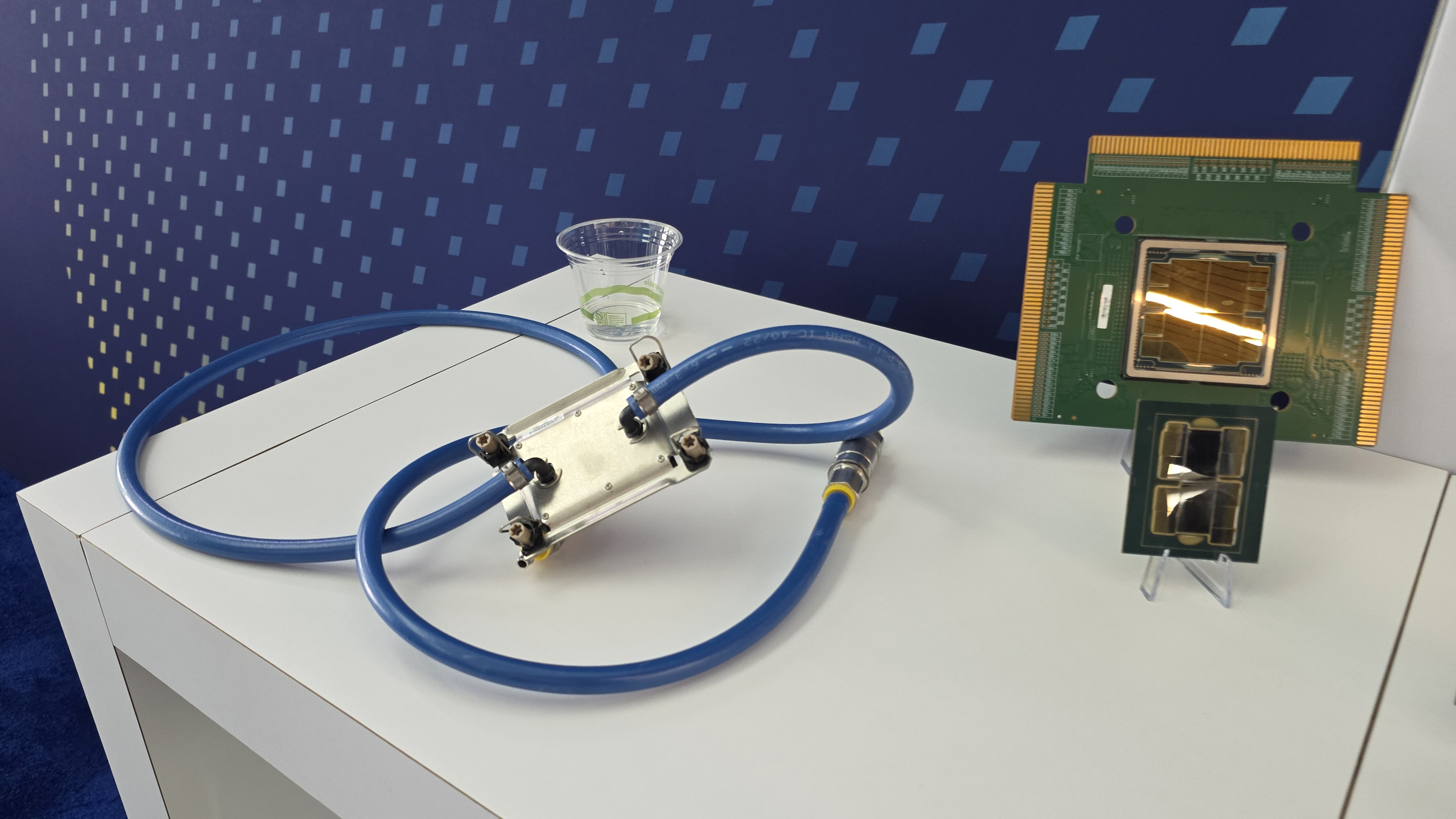

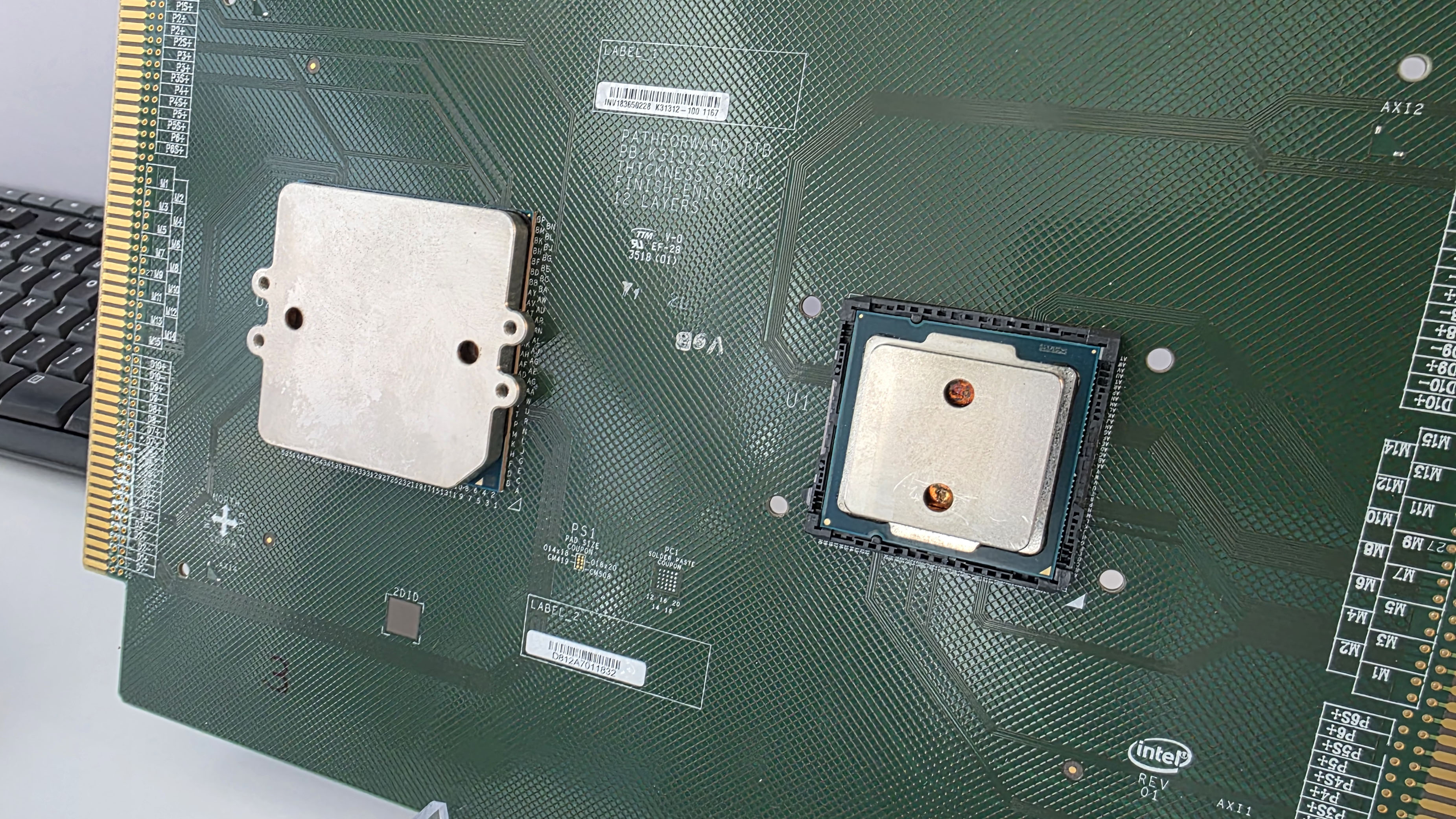




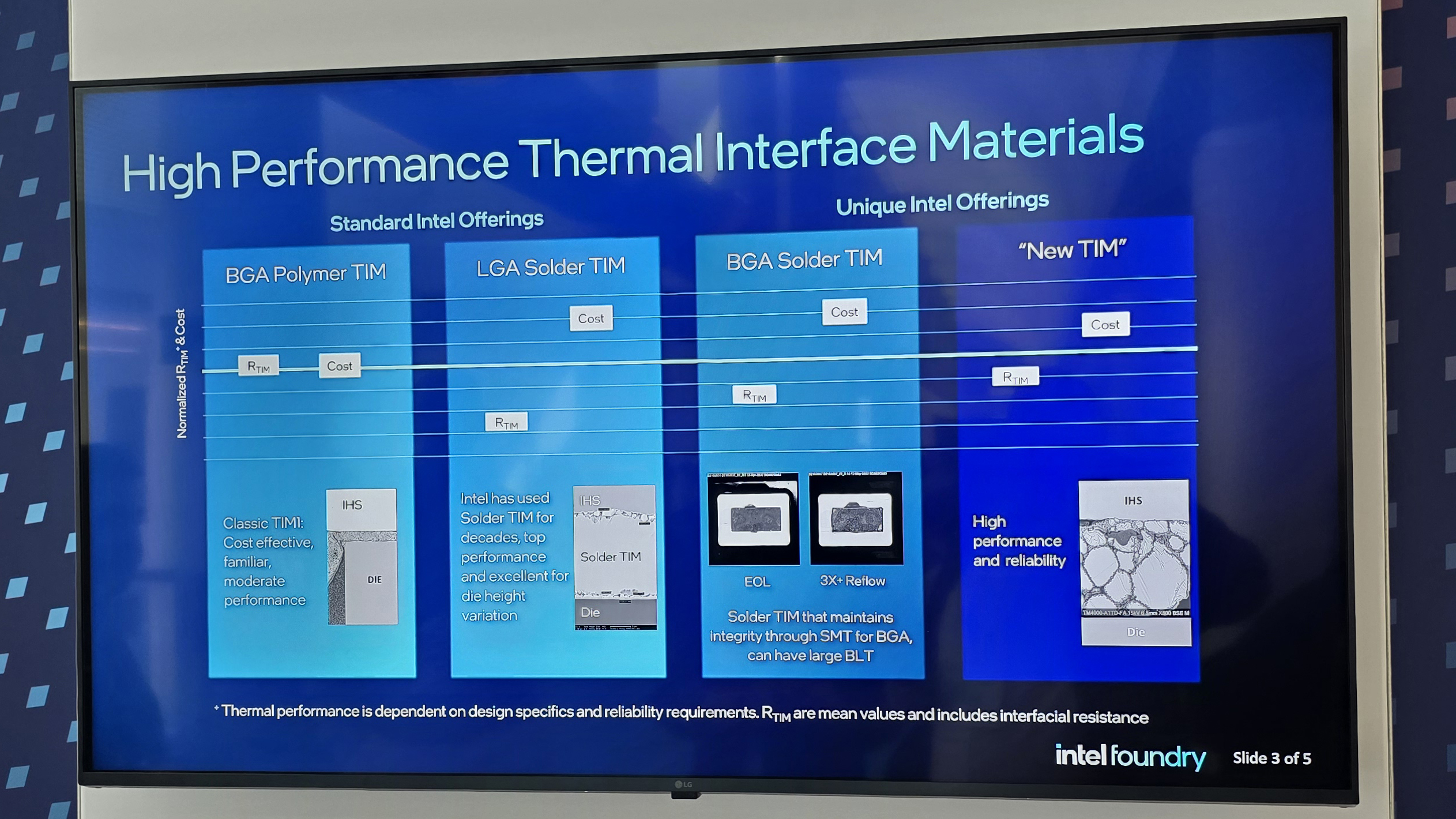
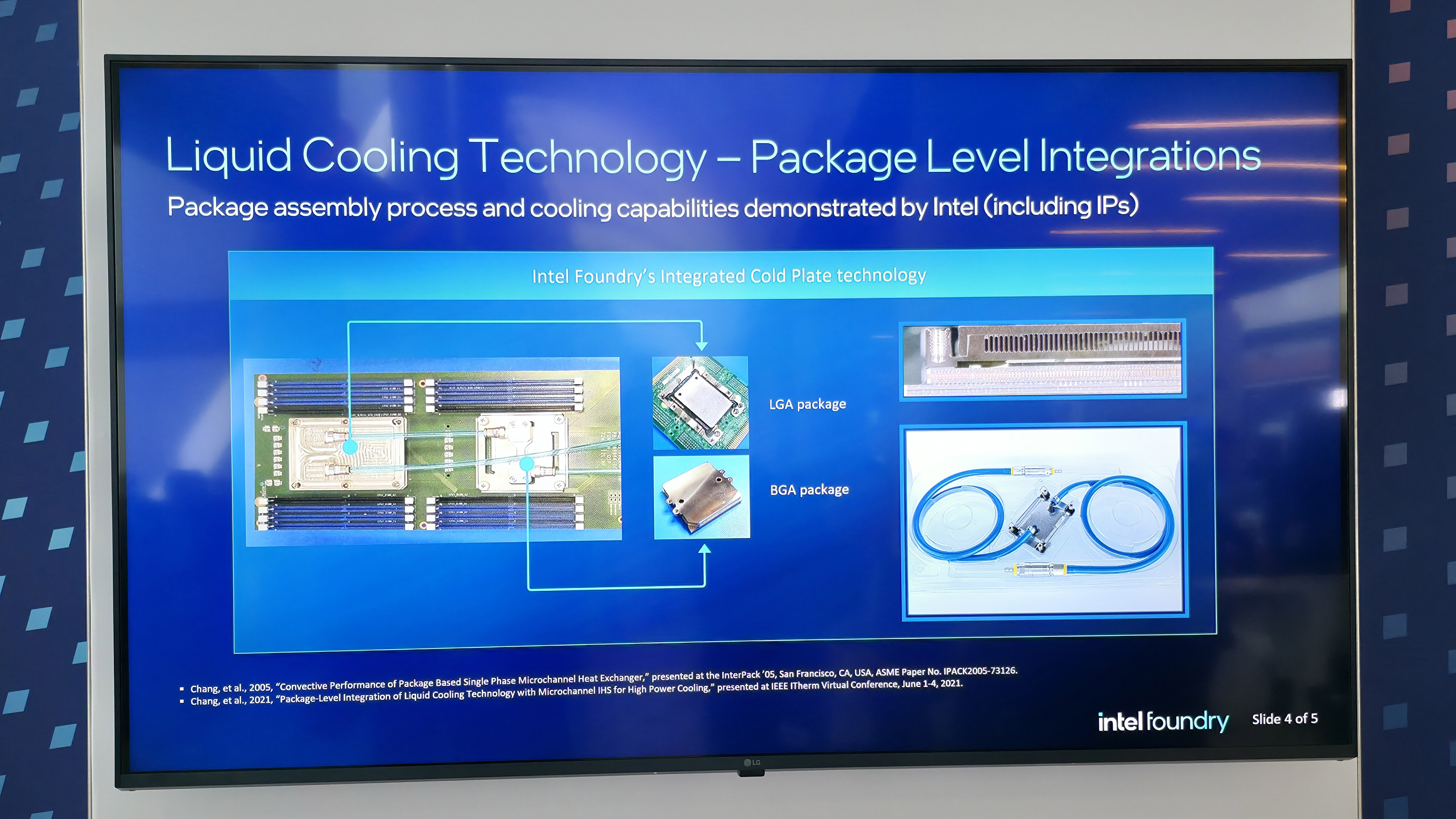

The cooling assembly is also said to make use of solder or liquid metal TIM (Thermal Interface Material), which is said to offer better contact than polymer based TIM. Compared to a traditional liquid cooler mounted to a delidded bare die, Intel says this solution can deliver 15–20% better thermal performance.
Notably, Intel’s approach isn’t just a lab experiment. The company has reportedly been working on this technology for years. With rising thermal demands from modern chip designs, Intel is now exploring how to produce this system for real-world deployment.
While Intel refines its prototype, the enthusiast community is already experimenting with similar concepts. YouTuber octppus recently modified the heatspreader of an Intel Core i9-14900KS, machining it into a functioning miniature water block. With internal channels carved into the IHS (Integrated Heat Spreader) and sealed under acrylic, the mod somewhat mirrors Intel’s concept in DIY fashion.
Intel hasn’t confirmed when or if this cooling approach will hit mainstream products, but the demonstration is critical for CPU thermal design. As power consumption and package density increase, direct cooling may become a necessity for both professional and enthusiast hardware in the coming future.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Follow Tom's Hardware on Google News to get our up-to-date news, analysis, and reviews in your feeds. Make sure to click the Follow button.

Kunal Khullar is a contributing writer at Tom’s Hardware. He is a long time technology journalist and reviewer specializing in PC components and peripherals, and welcomes any and every question around building a PC.
- Paul AlcornEditor-in-Chief
-
Reverend_Clint I worked on a complete watercooled sappire rapids server that needed more power than we had in the lab. 2 cpus, 4 GPUs, Ram, and PSUs were liquid cooled.Reply -
thestryker While I doubt the economic realities would never make sense this would be an interesting option for something like a KS part.Reply
I imagine as chips shrink and cooling becomes more problematic the answer at the consumer level will probably be something along the lines of a vapor chamber IHS and/or thinner TIM. -
truerock My understanding is that when Intel (and AMD) went to liquid metal solder and stopped using thermal paste - that knocked off about 90% of the inefficiency of removing heat externally from a CPU. Perhaps some type of super-conductive-carbon-based-paste and carbon-based-lid might squeeze out another 5% to 9%.Reply
To address heat in the future, I think they will need to work at the diode level inside of the CPU. -
thestryker Reply
What they both use is actually rather thick, but it has very good heat conducting properties. The thickness however is why consumer available liquid metal is more effective than what they use. It's entirely possible they could engineer a different type of TIM which is more effective.truerock said:My understanding is that when Intel (and AMD) went to liquid metal solder and stopped using thermal paste - that knocked off about 90% of the inefficiency of removing heat externally from a CPU.
Roman actually talked about this specifically in a recent video about TIM and conductivity:
1BfSx5IG42cView: https://youtu.be/1BfSx5IG42c?si=9hG4KtLEfCdziPPg -
Vanderlindemedia Replytruerock said:My understanding is that when Intel (and AMD) went to liquid metal solder and stopped using thermal paste - that knocked off about 90% of the inefficiency of removing heat externally from a CPU. Perhaps some type of super-conductive-carbon-based-paste and carbon-based-lid might squeeze out another 5% to 9%.
To address heat in the future, I think they will need to work at the diode level inside of the CPU.
We need solder, plus copper. That's pretty much the closest you can get. Anything "more" requires hefty tech such as direct die cooling and such. Not for consumers, not for enterprise. -
TerryLaze Reply
Yeah yeah, funny.Alex/AT said:1000W CPU? Wow. Now you'll actually be able to bake an egg.
But the point of cooling is to keep the CPU below 100° ,for servers probably even lower?! You'll have the same issues backing an egg as on a 200-300W CPU because any part of the CPU and the cooling system has to be below 100° to keep the CPU at below 100°. -
Alex/AT Reply
What I'm pointing at, with 1000W heat spreader really should be equipped with some frying pan or room heater forms to combine the function.TerryLaze said:Yeah yeah, funny.
But the point of cooling is to keep the CPU below 100° ,for servers probably even lower?! You'll have the same issues backing an egg as on a 200-300W CPU because any part of the CPU and the cooling system has to be below 100° to keep the CPU at below 100°.
And if to become serious, yeah, maybe direct cooling approach is living its last days and vapor cameras / heatpumps should actually be used to make that difference between CPU heatsink and spreader temps indeed.
-
TerryLaze Reply
NO PART OF A COOLING SYSTEM CAN GO ABOVE THE TEMP OF THE CPU.Alex/AT said:What I'm pointing at, with 1000W heat spreader really should be equipped with some frying pan or room heater forms to combine the function.
...
If it goes above that temp then it can't cool anymore.
Any and all cooling is a room heater because where else is the heat supposed to go to.
To bake anything (better) you need a CPU that can go above 100 and use it without any cooling at all so that all of the heat goes into the thing you are baking.