500 MHz FSB? Core 2 Duo Overtakes Core 2 Extreme
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Overclocking Basics Are Basic Math
A processor's clock speed is derived from the system base clock, which is 266 MHz in the case of the Intel FSB1066 bus, multiplied by a so-called clock multiplier. The Core 2 Duo E6300 runs at 1,866 MHz (1.86 GHz), which it reaches by multiplying 266 MHz by 7. It would be just perfect to select a higher core clock speed by increasing the multiplier, but unfortunately the CPU manufacturers lock the multiplier at the default value.
This means that the only way to run a processor beyond its rated clock speed is to increase the system clock speed. Current platforms such as the P965 chipset offer great overclocking margins, but be sure that you know of the dependencies related to the system clock: the main memory clock speed is derived from the base clock as well. If you increase the 266 MHz base clock to 333 MHz, the memory will be running at the same 25% clock speed increase. In turn, this means that you either have to purchase high-performance memory for overclocking, or you have to set the memory to a slower speed, so it still works at your preferred overclocking settings.
Here is a simple example that should work on many P965 enthusiast motherboards:
| Overclocking Example | Core 2 Duo E6300 | ... overclocked |
|---|---|---|
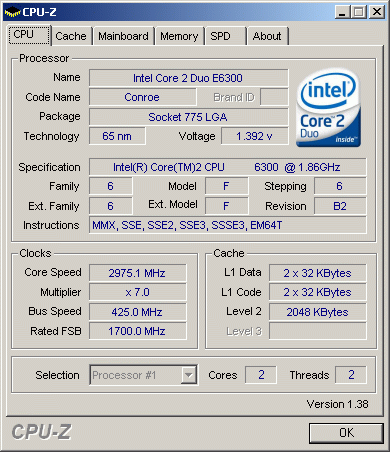
| Front Side Bus | 266 MHz (FSB1066) | 425 MHz (FSB1700) |
| Multiplier | X7 | X7 |
| Core Clock Speed | 1,866 MHz | 2,975 MHz2 |
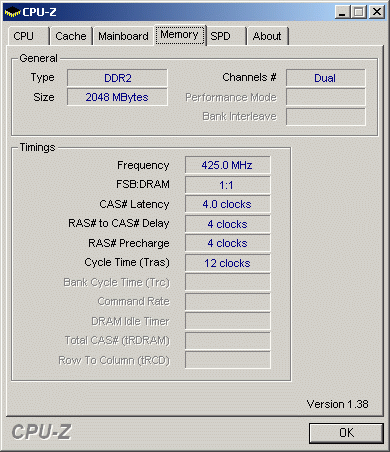
| Memory Ratio | 2:3(400 MHz FSB to 400 MHz RAM) | 1:11(425 MHz FSB to 425 MHz RAM) |
| Memory Speed | DDR2-800 | DDR2-850 |
- We had to reduce the memory ratio, because the DDR2 speed would have reached 637.5 MHz or DDR2-1275, which is too much for most memory available today.
- You might have to increase CPU core voltage to reach 2.5+ GHz.
In this example we overclocked the Core 2 Duo E6300 from 1.86 GHz to 2.975 GHz. We increased the core voltage from 1.15 V to 1.40 V.
Watch out: even at the 1:1 memory ratio, the DDR2 RAM clocks at 425 MHz (DDR2-850).
For more information on overclocking please check out our article series on overclocking:
- Overclocking Guide Part 1: Risks, Choices and Benefits
- Overclocking Guide Part 2: Suggested Components and Settings
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Overclocking Basics Are Basic Math
Prev Page The Core 2 Duo Processor Family Next Page The Candidate: Core 2 Duo E6300
Patrick Schmid was the editor-in-chief for Tom's Hardware from 2005 to 2006. He wrote numerous articles on a wide range of hardware topics, including storage, CPUs, and system builds.