DDR DRAM FAQs And Troubleshooting Guide
Add us as a preferred source on Google
Why Does XMP Have Two Profiles?
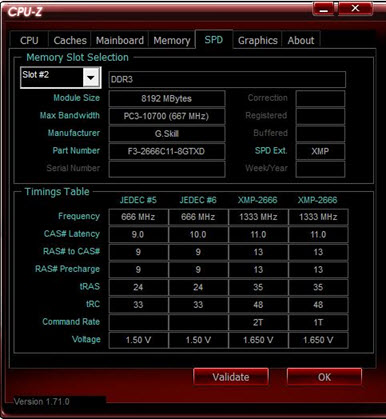
Most manufacturers provide two profiles for DRAM. The first, or specification profile, adheres to the base timings as sold. The second profile is generally aimed at enthusiasts and is a little more performance-oriented, but these tighter timings might not be stable in certain configurations. Often, this is a tighter command rate, as pictured below. The command rate often needs to be increased as additional DIMMs are added.
Some DRAM with aggressive XMP profiles provide a slower secondary profile to increase compatibility, as an intermediate step between default and rated values.
Stay On the Cutting Edge: Get the Tom's Hardware Newsletter
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Why Does XMP Have Two Profiles?
Prev Page What Are XMP, AMP, DOCP And EOCP? Next Page What Is Flex Mode?TOPICS
47 Comments
Comment from the forums
-
das_stig With AMD motherboards, you should set the memory to unganged mode for a tiny performance improvement unless you're running a webserver.Reply -
Mahruay Nice read although could you explain what real world improvements can be seen in faster RAM.Reply -
boju Nice article, answers a lot for people and definitely will link for future references. I need to ask though, is there any reason to discriminate DDR3 as per title?Reply -
clonazepam I hope the next part covers performance when using say 3 sticks, where 2 are dual channel, 1 is single channel. Some real world results would be stellar (maybe as a follow-up?)Reply
I'd also like to see RAM drives covered. Suppose you allocate 4GB out of 16 for a RAM drive. How does the software create the 4GB? Is it using a single chunk of memory, is it taking 1GB from each of the 4 sticks? Is it from the beginning, middle or end of the 16GB of memory?
Covering how to identify true "memory leaks" versus a more common scenario where RAM usage grows intentionally from the caching of more and more assets. -
damric Great article, Tradesman! I give it Two thumbs up and two big toes up too!Reply
Only 1 issue:
Ganged vs Unganged: that actually doesn't have to do with single or dual channel.
Quote AMD:
Ganged mode means that there is a single 128bit wide dual-channel DRAM Controller (DCT)
enabled. Unganged mode enables two 64bit wide DRAM Controllers (DCT0 and DCT1).
The recommended setting in most cases is the Unganged memory mode. Ganged mode may allow slightly
higher Memory performance tuning and performs well in single-threaded benchmarks.
Depending on the motherboard and BIOS, it may be required manually setting the timing parameters for each
DCT (in Unganged mode) when performance tuning the memory or fine tuning the timings. Some BIOS
versions apply the same timings automatically for both DCTs in an Unganged mode.
Unganged is like a normal divided highway with two directions. Ganged let's traffic use all of the lanes in one direction at a time. Unganged is said to be more efficient but no one really ever tested this thoroughly to see if any applications would be better served in ganged instead. You could still have unganged single channel or dual channel, and ganged single channel or dual channel. If that's confusing I'll try to explain with more complicated interstate highway anecdote.
Lastly, I see you have a new AMD rig. Did your head explode when you saw how much more difficult it is to tune memory on that platform than on your past intel rigs?
-
Shankovich Awesome article! These kinds of articles is what brought me to Tom's in the first place years ago!Reply