Goodbye to Hulking PCs: Athlon Mini-PCs Set The Trend
How The Heat Pipe Works
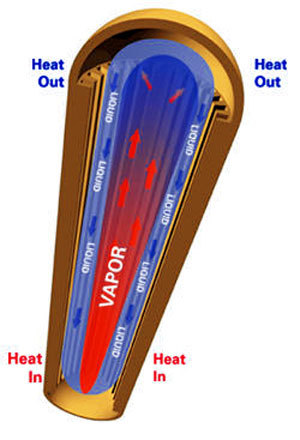
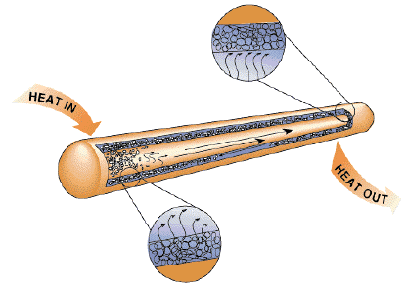
A schematic illustration of the structure and function of a heat pipe.
A heat pipe transports heat from one point to another via a vacuum-sealed metal pipe. The pipe holds a liquid that usually contains 90% water, with the rest consisting of other special ingredients that optimize heat transfer. Here's how it works: the liquid is held under low pressure so that the evaporation temperature is about 30 degrees Celsius. Under cold temperatures, there's very little water in the pipe. The water evaporates only when the other end of the pipe comes into direct contact with the CPU, whereupon the heat is transported into the cold end of the pipe. The temperature difference between the two ends of the pipe is about eight degrees Celsius on average, depending on the liquid that is used, as well as the length of the pipe. An important factor for the effectiveness of the pipe is its installation position: the end meant for heat dissipation must be positioned higher than the end meant for heat absorption. So, when the heat pipe is positioned vertically (90 degrees between the points of heat absorption and heat dissipation), it attains a maximum effectiveness of 95%.
The concept behind the heat pipe.
Mini Power Supply With 200 Watts
The power supply that comes installed in the mini-PC might be very compact, but it is enough to power the mini-PC, even when all the components are running and both PCI slots are equipped with additional peripheral devices.
The power supply provides 200 Watts of power.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: How The Heat Pipe Works
Prev Page Quiet Operation With The Heat Pipe System, Continued Next Page The mini-PC improves the ergonomics at the workplace.