Hercules 16/12 FW: Affordable, Professional-Quality Multichannel Audio
Behavior At 24 Bits/96 KHz
As usual, moving to 96 kHz resulted in only a fairly modest improvement in performance. This is all the more true since Hercules uses a filtering system that keeps the bandwidth from widening when you move to that sampling frequency.
- Frequency response (20 Hz - 20 kHz) : +0.02, -0.30 dB
- Weighted SNR : 105.1 dB(A)
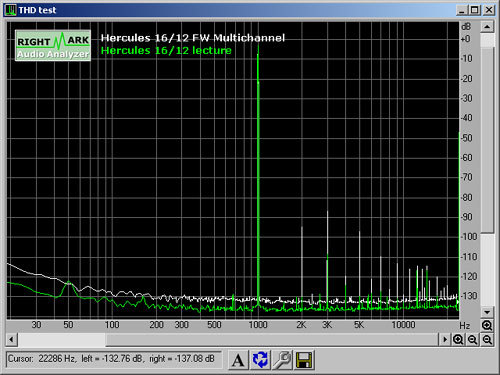
- Distortion : 0.010%
- Stereo separation : 106.6 dB
Frequency response : No problem in the audio spectrum, but response didn't widen towards the top, since the filtering Hercules uses seems to be the same as at 48 kHz.
Noise level : The noise level was a little lower than at 48 kHz. We aren't complaining...
Dynamic range : Fine dynamic performance at 105 dB
Distortion : Distortion was identical to the result at 48 kHz, but could be lower if the level were reduced a little.
Intermodulation : Extremely low intermodulation distortion; you're not likely to perceive it.
Stereo separation : Again the results are excellent, around 105 dB in the middle part of the spectrum and 100 dB at both ends.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Overall, the Hercules 16/12's performance was very good, even excellent, compared to a consumer-level product. However, we had hoped for a slightly better SNR and slightly lower distortion. But that shouldn't make you hesitate to choose this model if it meets your needs! A test we ran using an E-MU sound card for recording and the 16/12 only for playback resulted in lower noise and distortion levels.
With the 16/12 used only for playback, you can see that the noise level was significantly lower, as was distortion, which dropped from 0.0074% to 0.0006%.
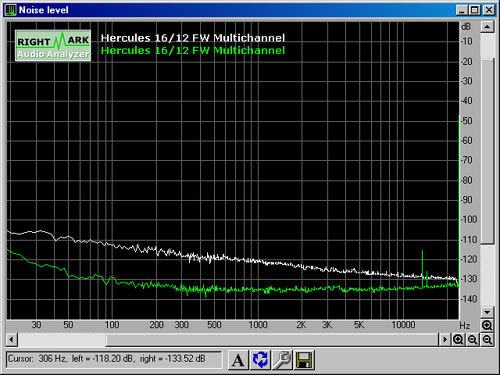
The device's weakest point, however, was operation with unbalanced inputs. In that configuration, performance dropped significantly, mainly for noise and those areas of performance that can be affected by it. Operating in 24 bits / 48 kHz, the SNR went from 102 dB to a little more than 92. When switching to unbalanced, a drop in performance is to be expected, but here it was more than what we'd hoped for. The difference isn't catastrophic, but for highly demanding work you'll need to take care to use only balanced connections.
The comparison of noise levels in balanced (green) and unbalanced mode (white) showed a marked increase in unbalanced mode.
-
dr3tri Article does not tell whether this can do MIDI merge between it's two MIDI IN or not. Could you tell it in here, at comments section? Anyone?Reply