Intel Core i5-8600K Review: Coffee Lake's Jolting Value
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Scientific & Engineering Computations, HPC Performance
For these tests, we’re using the SPECwpc benchmark suite for workstations with its wide variety of tasks. It measures a number of very different mathematical computations optimized for parallelization. They typically make heavy use of available memory bandwidth and cache, plus expose issues with latency.
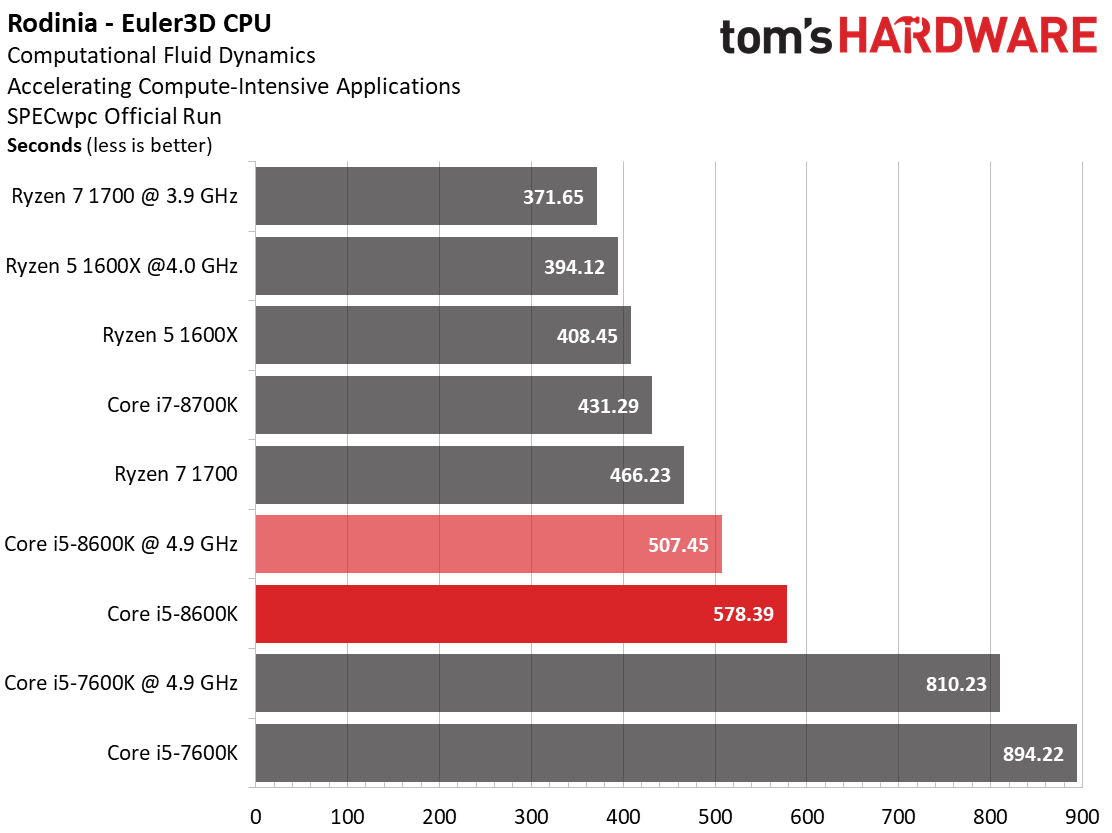
Rodinia
The pre-Euler3D CFD test (Computational Fluid Dynamics benchmark) runs very well on AMD's CPUs, suggesting scaling based predominantly on core count. It is interesting, however, that the overclocked Intel CPUs don't seem to benefit as much from higher operating frequencies.
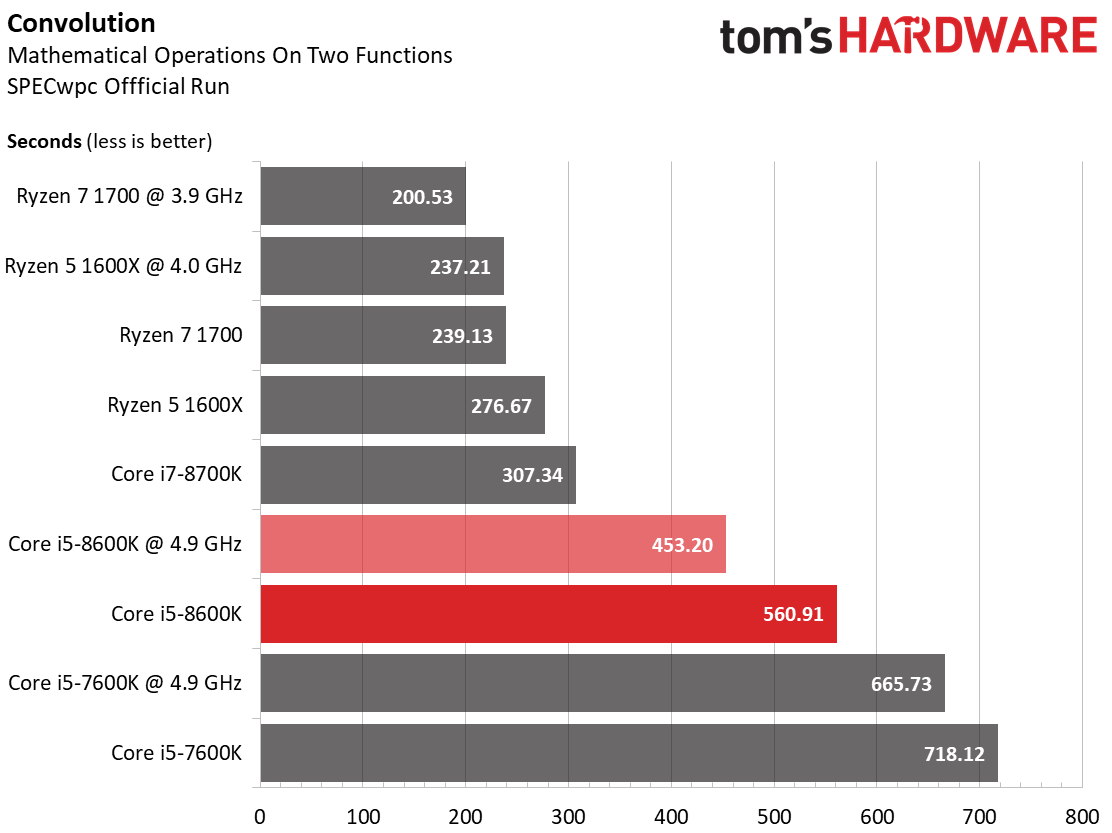
Convolution
In this benchmark, a mathematical operation is performed on two functions (convolution), which results in a third function. Performance scales according to core count. Clock rate has far less impact, which gives AMD the advantage.
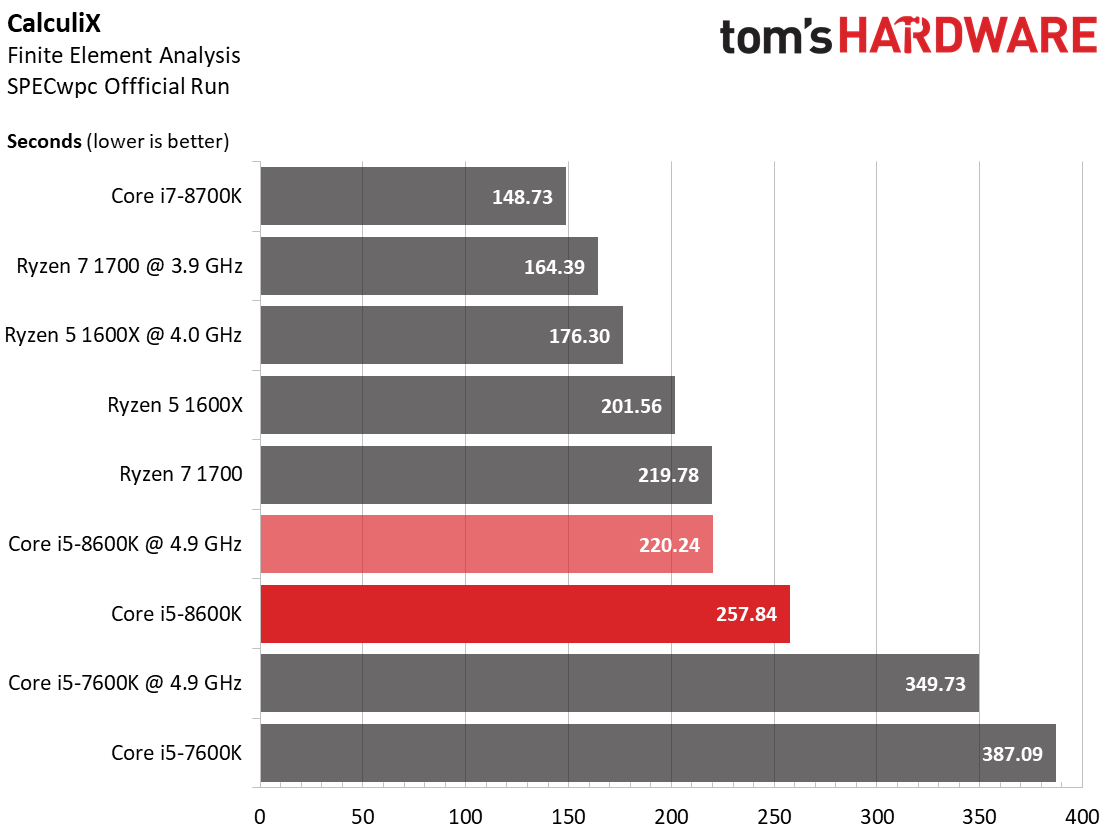
CalculiX
This test is based on the finite element method for three-dimensional structural computations. Intel’s higher frequencies help Core i7-8700K secure the win. Meanwhile, a lack of Hyper-Threading punishes Core i5.
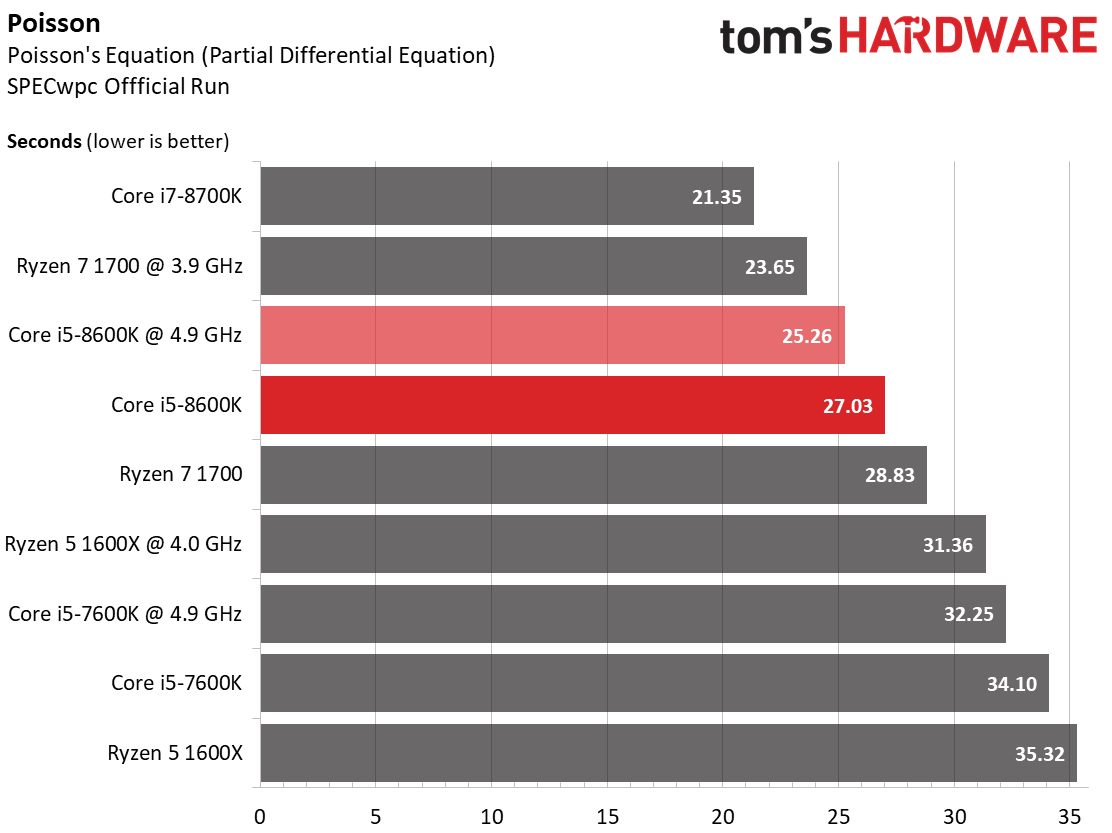
Poisson's Equation
Poisson's Equation is a second-order partial differential equation widely used in physics for boundary value problems.
Both of Intel's new six-core models serve up compelling performance, though overclocking doesn't yield explosive gains. What's more, the -8600K cannot catch Ryzen 7 1700. On paper, AMD's chip is more expensive. But when you factor in a cheaper motherboard and bundled cooler, it'd actually save you money.
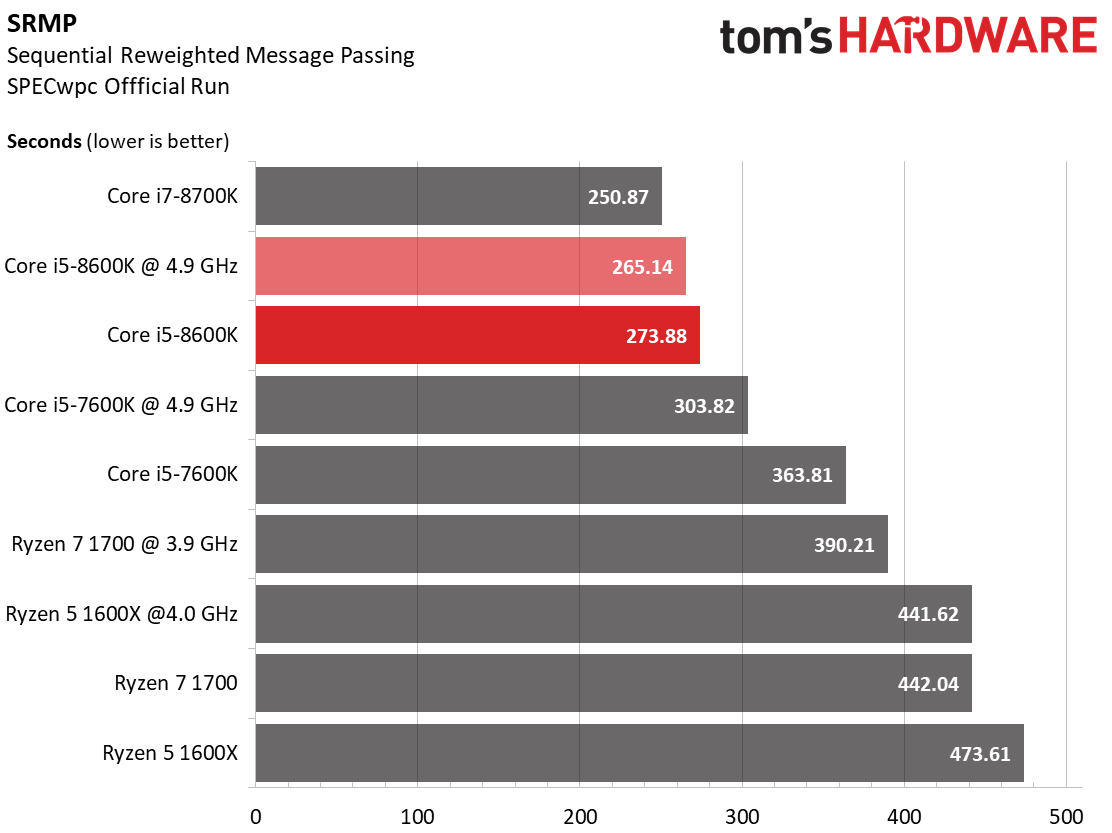
Sequential Reweighted Message Passing (SRMP)
These are algorithms for discrete energy minimization. The workload benefits from core count, clock rate, and architectural improvements, it appears. For some reason, though, AMD's Ryzen 7 and 5 just don't show well, even though our logs show them to be fully utilized.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
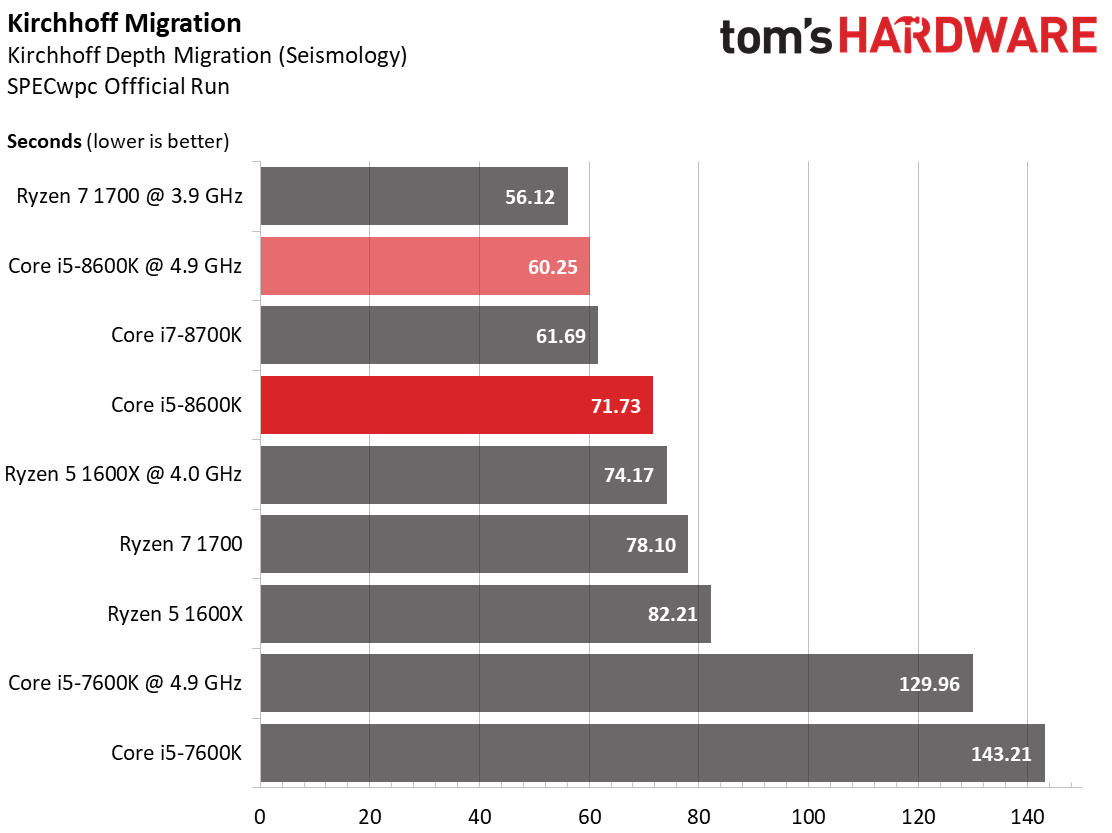
Kirchhoff Migration
The earth’s subsurface structure can be determined via seismic processing. One of the four basic steps in this process is the Kirchhoff Migration, which is used to generate an image based on the available data using mathematical operations.
This benchmark and its underlying computations turn out to be a great fit for AMD, particularly when the Ryzen 7 1700 is overclocked.
The Core i5-8600K struggles in many of these tests due to its lack of Hyper-Threading. If it had simultaneous multi-threading, however, it'd basically be as fast as Core i7-8700K. If you run a lot of professional software, take the step up and go for Core i7 or one of the higher-end Ryzen chips. Core i5-8600K is serviceable in workstation apps, but it's really meant for gaming and desktop productivity.
MORE: Best CPUs
MORE: Intel & AMD Processor Hierarchy
MORE: All CPUs Content
Current page: Scientific & Engineering Computations, HPC Performance
Prev Page CPU Computing & Rendering Performance Next Page Overclocking, Power Consumption & Temperatures
Paul Alcorn is the Editor-in-Chief for Tom's Hardware US. He also writes news and reviews on CPUs, storage, and enterprise hardware.
-
logainofhades Great CPU, but the overall platform cost is a bit of a turn off, for me. I'd rather get a 1600, and a B350 board, to allow for a better GPU, if buying new. As stated in the review, even a 1700, with a less expensive board, is a very compelling option.Reply
-
AS118 Seems like a good product, but I'd like to see what the 8600 and 8500 non-k offers, and perhaps next year with the B360 boards that give them a more budget "locked cpu" option.Reply
I also feel that the availability will be low for Coffee Lake until the end of this year, particularly throughout the holiday season. Due to that concern (as well as the total cost of platform ownership) I think that Ryzen with its 1600 and 1700 CPU's along with the 1600x will be the value kings this year, with Coffee Lake not hitting it's stride until early next year.
The fact that AMD's stuff doesn't have the same availability issues makes it a strong contender, imho, although Black Friday and Christmas sales will also like make Kaby Lake (and even Sky Lake) stuff at clearance prices appealing too, despite the lack of cores you'll find in Ryzen and now Coffee Lake. -
almostdecent Since the chart shows the i5-8600k and the i5-8600K@4.9GHz at the same $260, I presume that means you achieved the overclock with the stock cooler.Reply -
ammaross It's kind of disappointing to see so many benchmarks where an i5 does as well or better than it's i7 counterpart. It just shows how poorly threaded some of these applications really are and almost necessitates running two benchmarks simultaneously to really judge the merit of these multi-core CPUs. Maybe run the photoshop test while rendering with After Effects or run a game benchmark while doing CPU h.265 handbrake.Reply -
almostdecent It is worth mentioning that this is essentially a paper launch at the moment, since none of the Coffee Lake processors are available anywhere.Reply
http://www.nowinstock.net/computers/processors/intel/
and the rare place that has any, such as Microcenter, have gouging prices. Such as selling the plain i7-8700 (not the K version) with an MSRP of $300 for sale for $429.
http://www.microcenter.com/product/486087/Core_i7-8700_Coffee_Lake_32_GHz_LGA_1151_Boxed_Processor -
InvalidError Reply
On September 20, Intel responded to a story about yet another 10nm schedule slip by saying that Cannon Lake will begin shipping in limited quantities to some laptop manufacturers with production ramping up in 1H2018. Limited Coffee Lake volume could be due to Intel deciding to upgrade production lines to 10nm for Cannon Lake instead of 14++.20281291 said:I also feel that the availability will be low for Coffee Lake until the end of this year, particularly throughout the holiday season. -
TJ Hooker Reply
Not sure if you were being sarcastic, but the 8600K doesn't have a stock cooler.20281420 said:Since the chart shows the i5-8600k and the i5-8600K@4.9GHz at the same $260, I presume that means you achieved the overclock with the stock cooler.
There are two different sets of graphs, one that looks at CPU only costs and the other that considers CPU, mobo, and cooler costs. In the latter, the 8600K at 4.9GHz is clearly shown to cost more.
-
InvalidError Reply
Intel hasn't included a stock HSF with their unlocked CPUs since Skylake so on top of paying more for the unlock, you also get shafted by the price of a stock cooler which you no longer get on top of it. You need an aftermarket cooler for both stock and OC.20281420 said:Since the chart shows the i5-8600k and the i5-8600K@4.9GHz at the same $260, I presume that means you achieved the overclock with the stock cooler.
Same thing with AMD's Ryzen nnnnX CPUs. -
YoAndy Reply20281216 said:Great CPU, but the overall platform cost is a bit of a turn off, for me. I'd rather get a 1600, and a B350 board, to allow for a better GPU, if buying new. As stated in the review, even a 1700, with a less expensive board, is a very compelling option.
A better GPU?//Why would you do that. at 1080p Ryzen will (bottleneck) hold back powerful GPU's, It won't give you equal performance. I bought a Ryzen for pure gaming and i ended up selling it.. -
acosta.87 Reply20281216 said:Great CPU, but the overall platform cost is a bit of a turn off, for me. I'd rather get a 1600, and a B350 board, to allow for a better GPU, if buying new. As stated in the review, even a 1700, with a less expensive board, is a very compelling option.
B350 VRM's are pretty low quality for any sort of OC unless it's a mild one so for me that's a no go. If you're primarily into gaming then the 1600 has nothing on the i5, it simply trails it whether at stock settings or OC'd and even at productivity it beats a 1600 Ryzen processors in most task even with a 6 thread deficit so it's a pretty good investment overall.