SilverStone Strider Gold S V2 750W Review
SilverStone is the only company with so many compact PSUs in its portfolio. A while ago, it released the second version of the Strider Gold S with 750W of capacity.
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Load Regulation, Hold-Up Time And Inrush Current
To learn more about our PSU tests and methodology, please check out How We Test Power Supply Units.
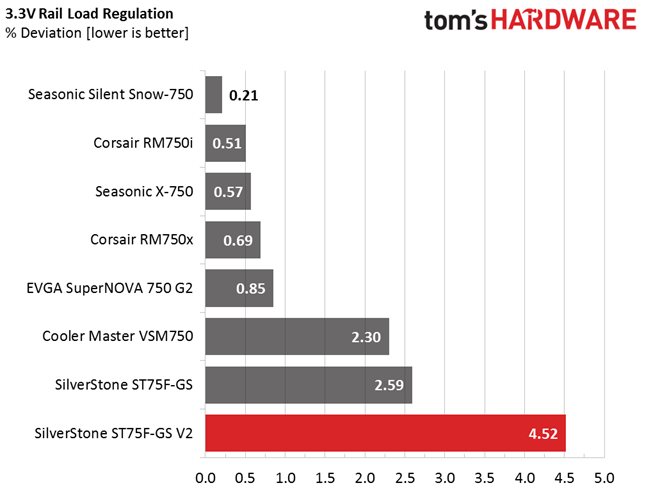
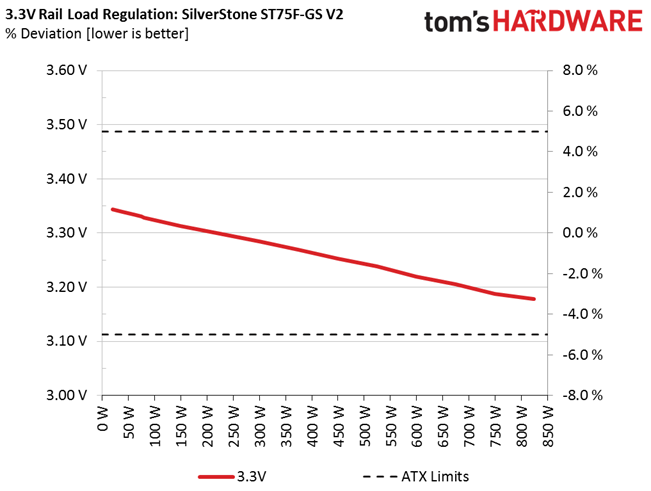
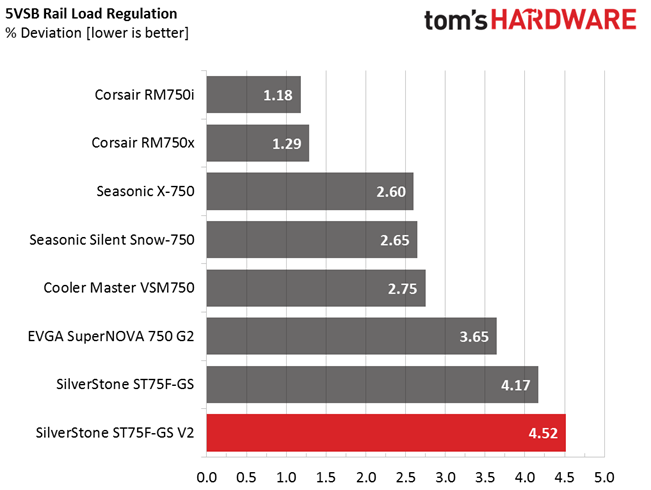
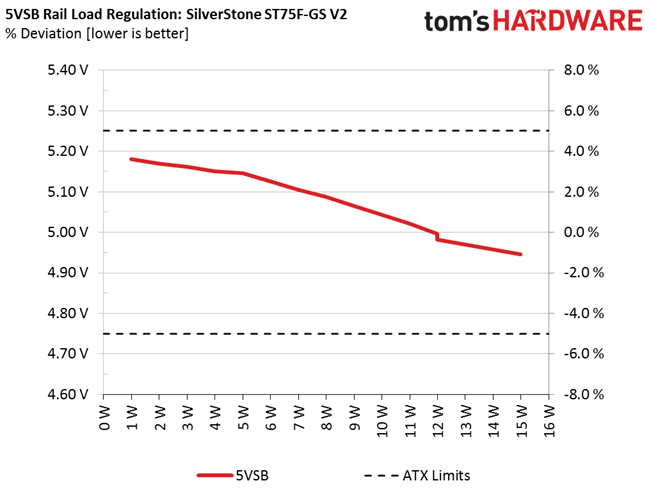
Primary Rails And 5VSB Load Regulation
Load Regulation testing is detailed here.
Hold-Up Time
Our hold-up time tests are described in detail here.
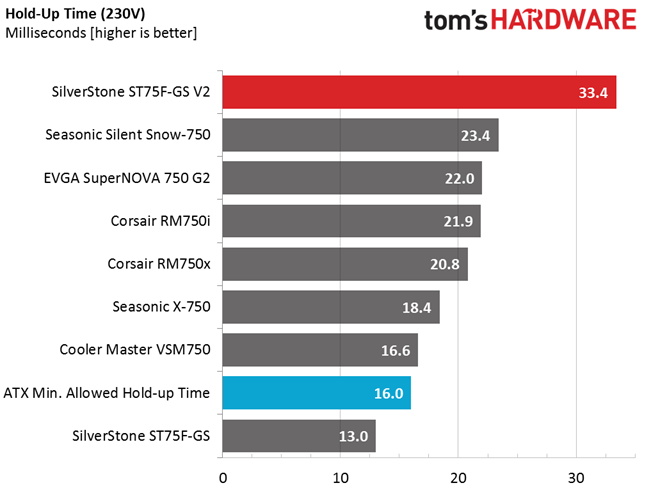
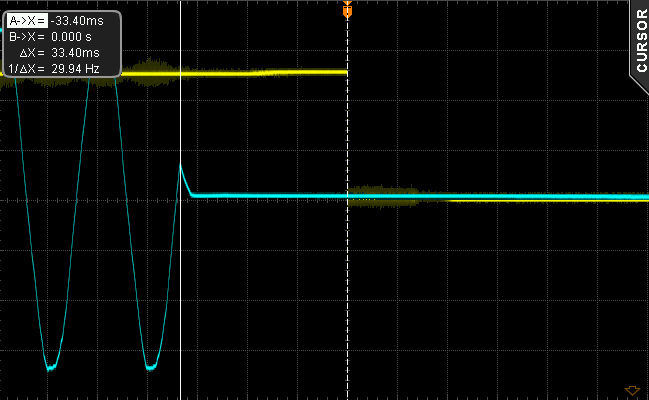
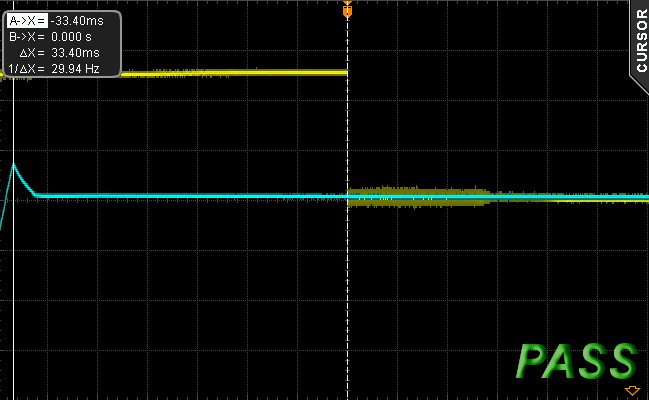
This is the first time we've measured a hold-up time that exceeds 30ms.
12/10/2015 update: We had some suspicions about how with only a 560 uF bulk cap this unit managed to achieve so high hold-up time, so we decided to check when the PWR_OK signal drops to 0 V (since we measure the AC loss to PWR_OK hold-up time). Normally this signal should drop to 0V when one of the rails falls below the ATX limit. To our surprise we noticed that the PWR_OK signal drops to zero when the +12V rail is at 10.2V and not at 11.4V. This trick prolongs the AC loss to PWR_OK time but the PSU can be dangerous for the system since instead of shutting down it continues to feed the parts with very low voltages. The actual hold-up time of this PSU is 11 ms, meaning that the PSU fails into this test.
Inrush Current
For details on our inrush current testing, please click here.
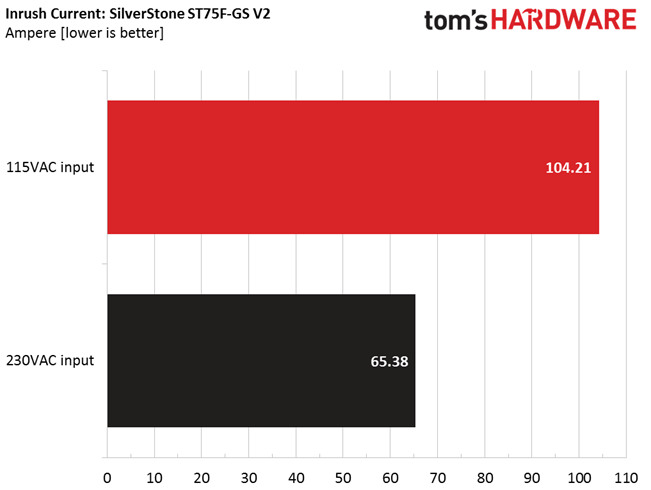
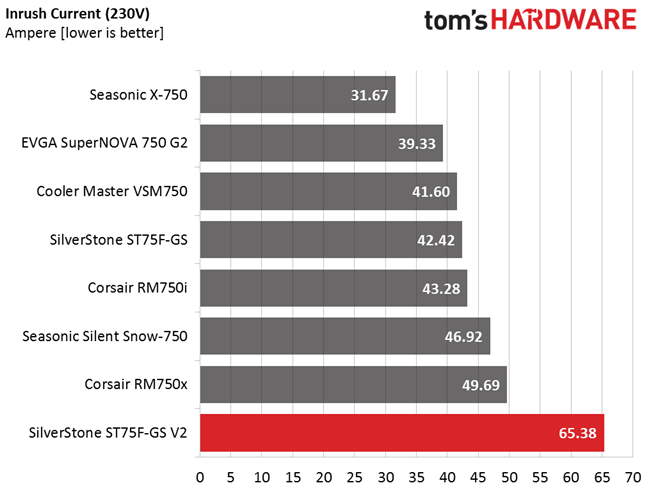
The large bulk cap and probably poor design choices lead to high inrush currents, which will stress your home's electrical circuit. A reading over 100A with 115V input is too high for a modern PSU like this one. The inrush current with 230V input is quite high as well.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Load Regulation And Efficiency Measurements
The first set of tests reveals the stability of the voltage rails and the PSU's efficiency. The applied load equals (approximately) 10 to 110 percent of the maximum load the supply can handle, in increments of 10 percentage points.
We conducted two additional tests. During the first, we stressed the two minor rails (5V and 3.3V) with a high load, while the load at +12V was only 0.10A. This test reveals whether a PSU is Haswell-ready or not. In the second test, we determined the maximum load the +12V rail could handle with minimal load on the minor rails.
| Test | 12 V | 5 V | 3.3 V | 5VSB | Power(DC/AC) | Efficiency | Fan Speed | Fan Noise | Temp(In/Out) | PF/AC Volts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% Load | 4.358A | 1.953A | 1.980A | 0.969A | 74.75W | 82.85% | 1330 RPM | 39.0 dB(A) | 38.83 °C | 0.983 |
| 12.202V | 5.118V | 3.330V | 5.146V | 90.22W | 42.94 °C | 115.1V | ||||
| 20% Load | 9.762A | 2.938A | 2.985A | 1.171A | 149.72W | 87.95% | 1450 RPM | 40.9 dB(A) | 39.21 °C | 0.994 |
| 12.176V | 5.095V | 3.313V | 5.125V | 170.24W | 43.50 °C | 115.1V | ||||
| 30% Load | 15.534A | 3.445A | 3.514A | 1.370A | 224.83W | 89.45% | 1460 RPM | 41.0 dB(A) | 39.93 °C | 0.997 |
| 12.151V | 5.076V | 3.299V | 5.105V | 251.36W | 45.26 °C | 115.1V | ||||
| 40% Load | 21.323A | 3.952A | 4.015A | 1.570A | 299.76W | 89.87% | 1470 RPM | 41.1 dB(A) | 40.76 °C | 0.998 |
| 12.127V | 5.060V | 3.285V | 5.087V | 333.55W | 47.23 °C | 115.1V | ||||
| 50% Load | 26.790A | 4.967A | 5.043A | 1.774A | 374.75W | 89.69% | 1470 RPM | 41.1 dB(A) | 41.64 °C | 0.998 |
| 12.104V | 5.036V | 3.269V | 5.065V | 417.84W | 49.17 °C | 115.1V | ||||
| 60% Load | 32.279A | 5.983A | 6.085A | 1.980A | 449.66W | 89.25% | 1470 RPM | 41.1 dB(A) | 42.28 °C | 0.998 |
| 12.079V | 5.012V | 3.253V | 5.043V | 503.83W | 50.71 °C | 115.1V | ||||
| 70% Load | 37.791A | 7.014A | 7.134A | 2.189A | 524.61W | 88.61% | 1470 RPM | 41.1 dB(A) | 43.96 °C | 0.999 |
| 12.054V | 4.988V | 3.238V | 5.021V | 592.03W | 54.36 °C | 115.1V | ||||
| 80% Load | 43.336A | 8.061A | 8.199A | 2.401A | 599.59W | 87.81% | 1470 RPM | 41.1 dB(A) | 44.40 °C | 0.999 |
| 12.027V | 4.962V | 3.219V | 4.996V | 682.84W | 56.53 °C | 115.1V | ||||
| 90% Load | 49.323A | 8.597A | 8.767A | 2.406A | 674.56W | 87.03% | 1470 RPM | 41.1 dB(A) | 44.69 °C | 0.999 |
| 12.002V | 4.944V | 3.205V | 4.982V | 775.10W | 59.15 °C | 115.1V | ||||
| 100% Load | 55.086A | 9.140A | 9.311A | 3.029A | 749.43W | 86.03% | 1470 RPM | 41.1 dB(A) | 46.17 °C | 0.999 |
| 11.977V | 4.923V | 3.188V | 4.946V | 871.18W | 63.42 °C | 115.1V | ||||
| 110% Load | 61.472A | 9.163A | 9.345A | 3.037A | 824.35W | 85.27% | 1470 RPM | 41.1 dB(A) | 46.28 °C | 0.999 |
| 11.951V | 4.912V | 3.178V | 4.936V | 966.71W | 63.76 °C | 115.1V | ||||
| Cross-Load 1 | 0.099A | 14.020A | 14.005A | 0.003A | 116.89W | 81.86% | 1470 RPM | 41.1 dB(A) | 41.87 °C | 0.992 |
| 12.165V | 4.978V | 3.276V | 5.130V | 142.80W | 50.94 °C | 115.1V | ||||
| Cross-Load 2 | 62.450A | 1.002A | 1.003A | 1.002A | 761.45W | 86.79% | 1470 RPM | 41.1 dB(A) | 43.79 °C | 0.999 |
| 11.980V | 5.015V | 3.226V | 5.032V | 877.35W | 60.22 °C | 115.1V |
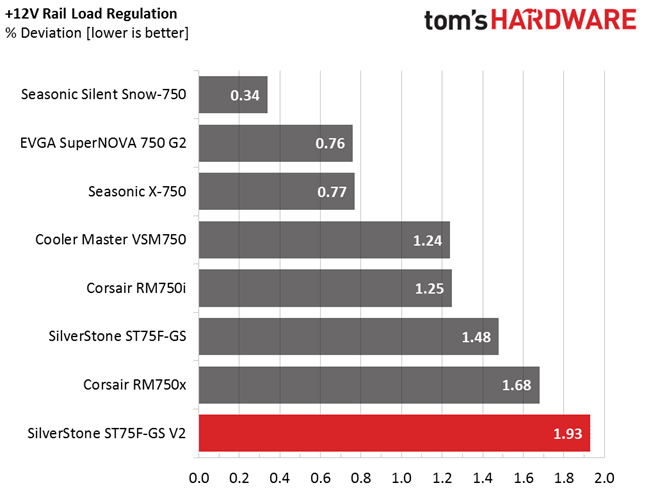
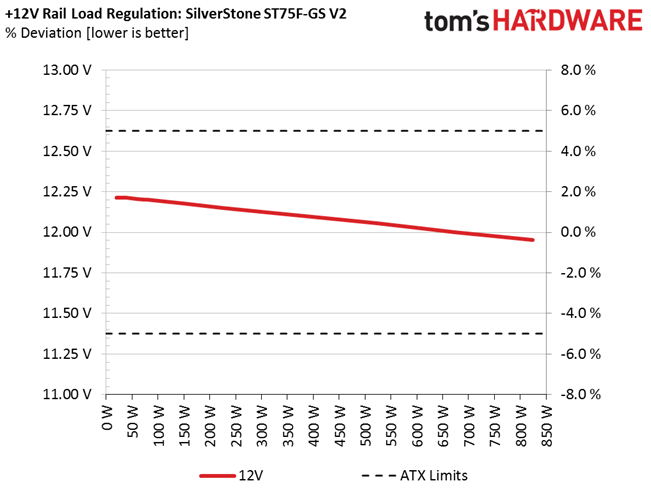
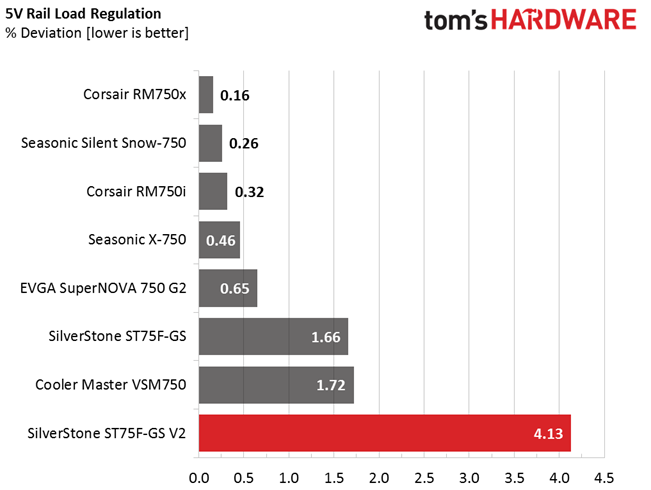
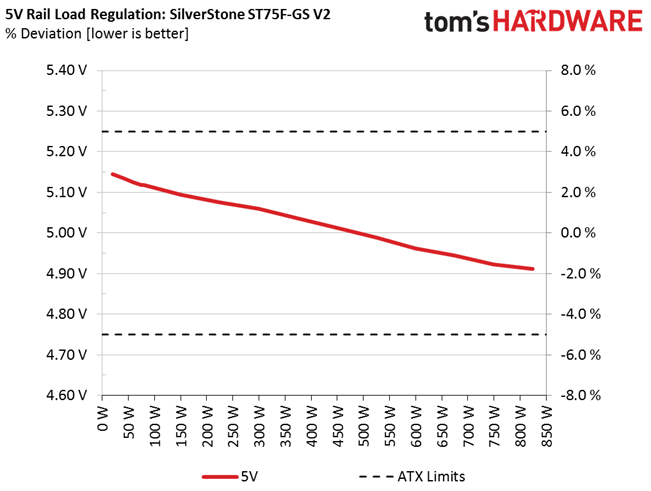
Load regulation is mediocre (+12V) to bad (minor rails). Under full load, the 3.3V rail drops below 3.2V. That's something we find to be unacceptable. In addition, the fan profile sets the cooler to almost full speed at high operating temperatures. The only redeeming quality is that, even at its top speed, noise output is low enough compared to other fans going all-out. Again, although this fan is rated for 2000 RPM, we only measured 1470 RPM at 100% duty cycle.
In our efficiency tests, the PSU easily cleared the low load (20% of maximum rated capacity) requirement. However, it was a little bit off with 50% load, and its efficiency was significantly lower than the minimum allowed level with 100% load. We'll reiterate that the 80 PLUS organization conducts its efficiency tests at much lower temperatures, so it's normal to see such significant differences between their results and ours. Nevertheless, this platform just isn't as efficient as other Gold-rated ones.
Current page: Load Regulation, Hold-Up Time And Inrush Current
Prev Page A Look Inside And Component Analysis Next Page Efficiency, Temperature And Noise
Aris Mpitziopoulos is a contributing editor at Tom's Hardware, covering PSUs.
-
Eggz At first glance, I thought this was a 750 w in an SFS form factor. Womp! . . . Still seems like a decent PSU, though.Reply


