Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Advanced Transient Response Tests
For details about our transient response testing, please click here.
In the real world, power supplies are always working with loads that change. It's of immense importance, then, for the PSU to keep its rails within the ATX specification's defined ranges. The smaller the deviations, the more stable your PC will be with less stress applied to its components.
We should note that the ATX spec requires capacitive loading during the transient rests, but in our methodology, we also choose to apply a worst case scenario with no additional capacitance on the rails.
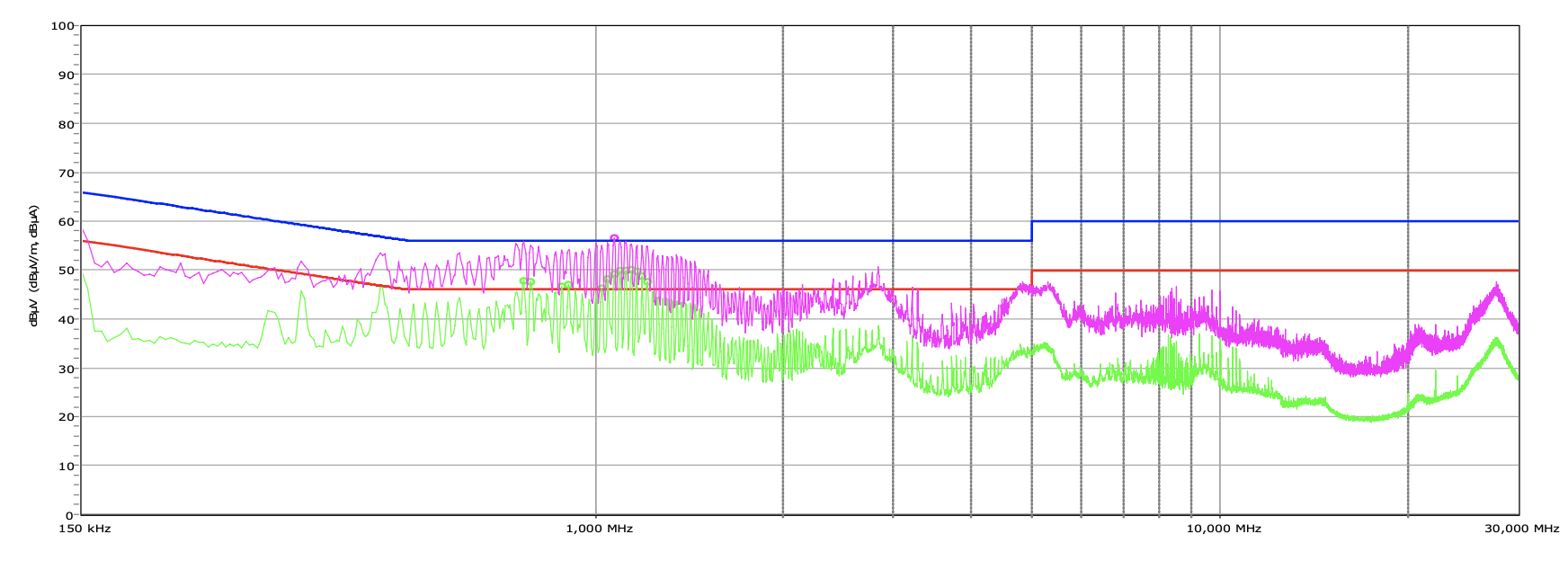
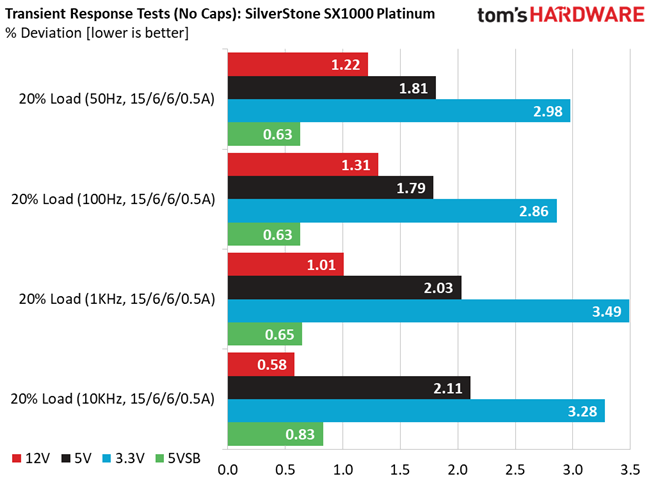
Advanced Transient Response at 20% – 20ms
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 12.071V | 11.924V | 1.22% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.029V | 4.938V | 1.81% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.325V | 3.226V | 2.98% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.055V | 5.023V | 0.63% | Pass |
Advanced Transient Response at 20% – 10ms
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 12.070V | 11.912V | 1.31% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.030V | 4.940V | 1.79% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.325V | 3.230V | 2.86% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.055V | 5.023V | 0.63% | Pass |
Advanced Transient Response at 20% – 1ms
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 12.069V | 11.947V | 1.01% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.030V | 4.928V | 2.03% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.325V | 3.209V | 3.49% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.055V | 5.022V | 0.65% | Pass |
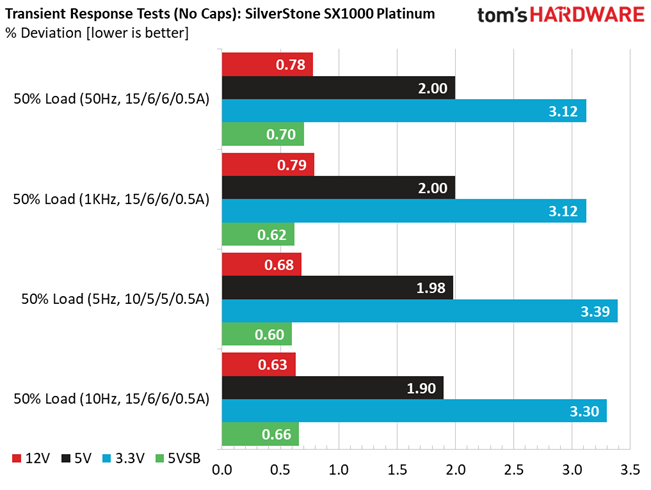
Advanced Transient Response at 50% – 20ms
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 12.039V | 11.945V | 0.78% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.006V | 4.906V | 2.00% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.301V | 3.198V | 3.12% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.020V | 4.985V | 0.70% | Pass |
Advanced Transient Response at 50% – 10ms
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 12.038V | 11.943V | 0.79% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.006V | 4.906V | 2.00% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.301V | 3.198V | 3.12% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.020V | 4.989V | 0.62% | Pass |
Advanced Transient Response at 50% – 1ms
| Voltage | Before | After | Change | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | 12.039V | 11.957V | 0.68% | Pass |
| 5V | 5.006V | 4.907V | 1.98% | Pass |
| 3.3V | 3.301V | 3.189V | 3.39% | Pass |
| 5VSB | 5.020V | 4.990V | 0.60% | Pass |
Results 25-29: Transient Response
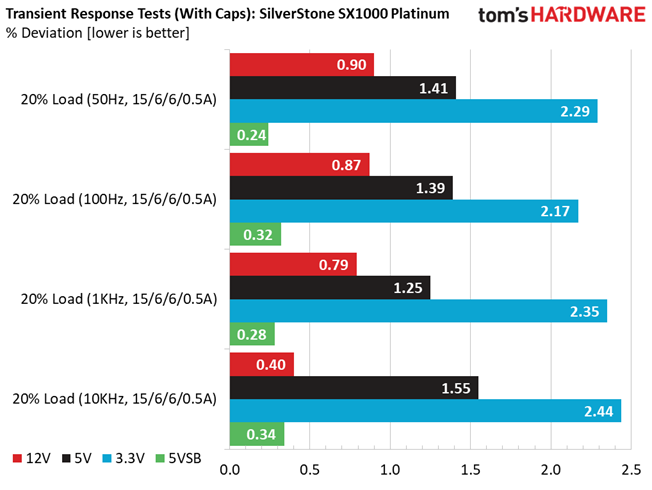
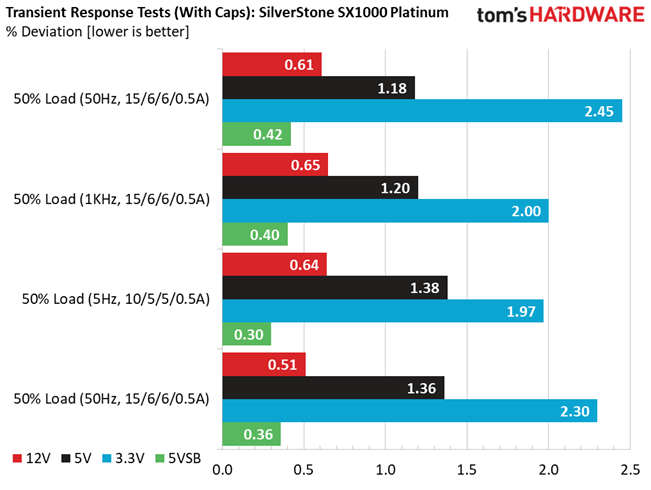
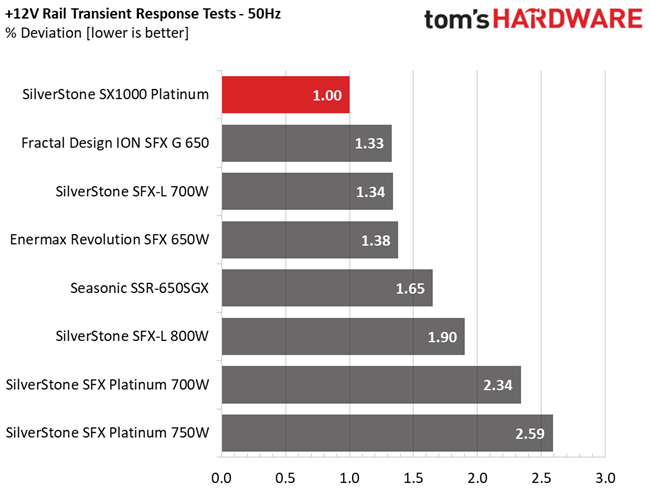
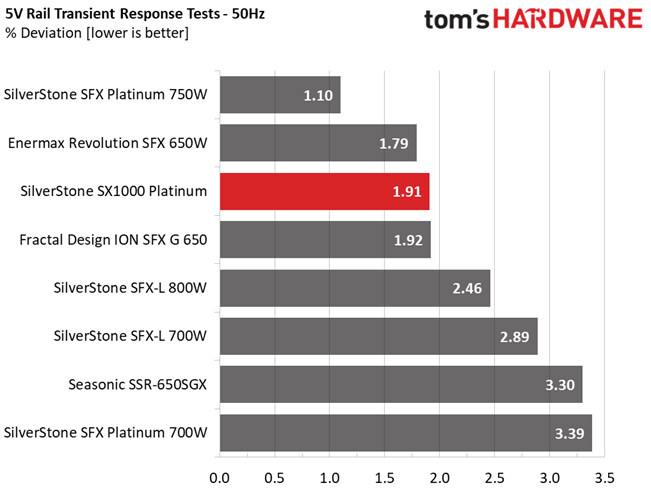
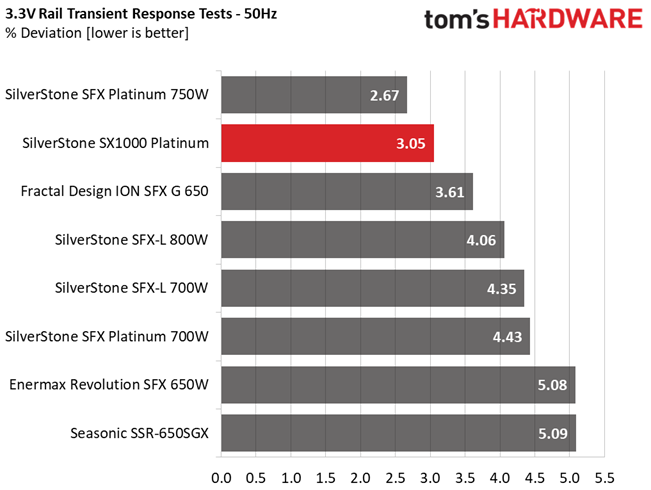
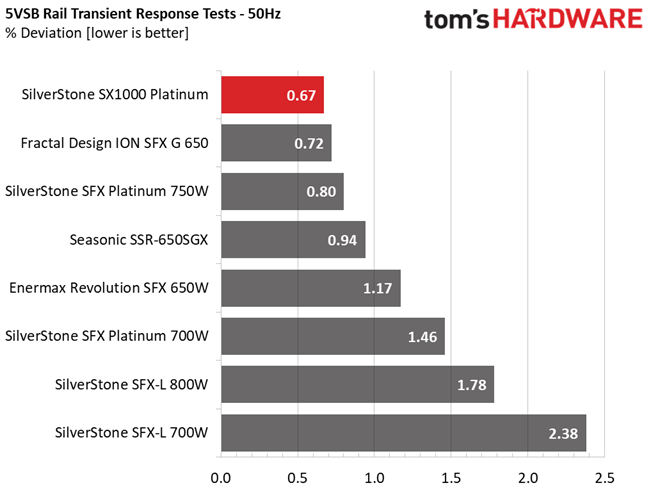
The transient response at 12V is among the best we have ever seen in this form factor category, meeting eye-to-eye many normal dimensions PSUs with similar capacity. Transient response is also good on the other rails.
Turn-On Transient Tests
In the next set of tests, we measure the PSU's response in simpler transient load scenarios—during its power-on phase. Ideally, we don't want to see any voltage overshoots or spikes since those put a lot of stress on the DC-DC converters of installed components.
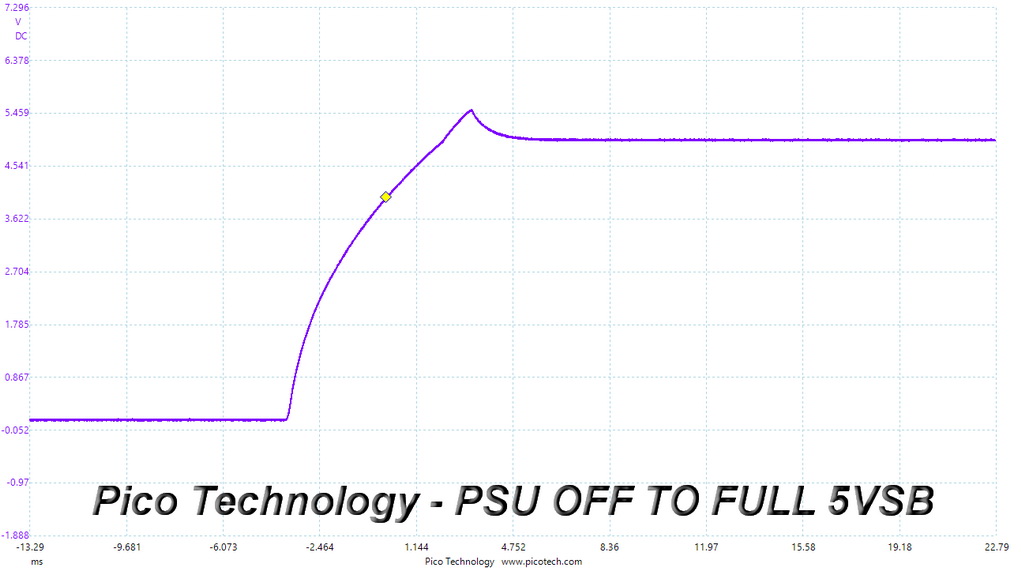
Turn-On Transient Response Scope Shots
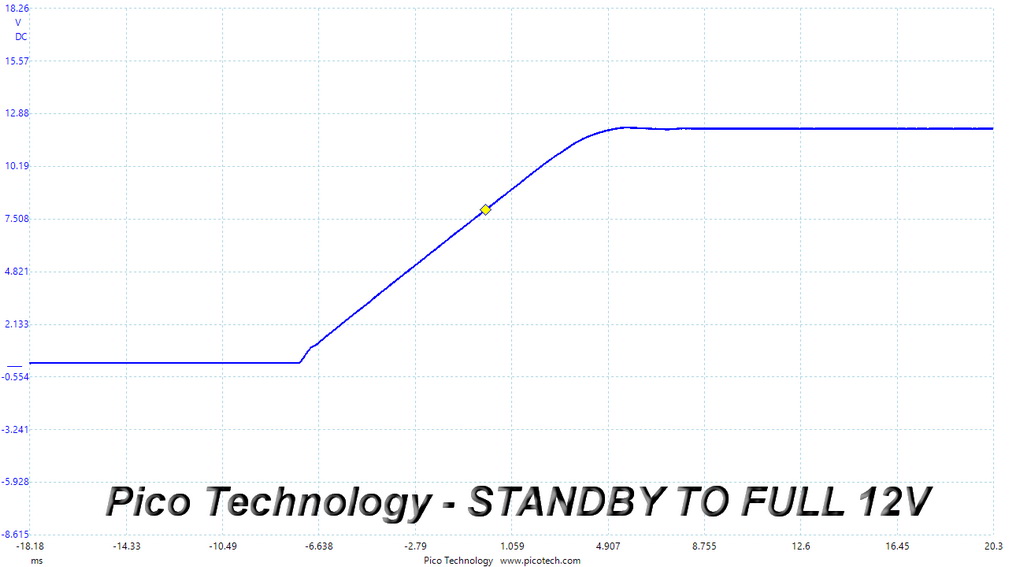
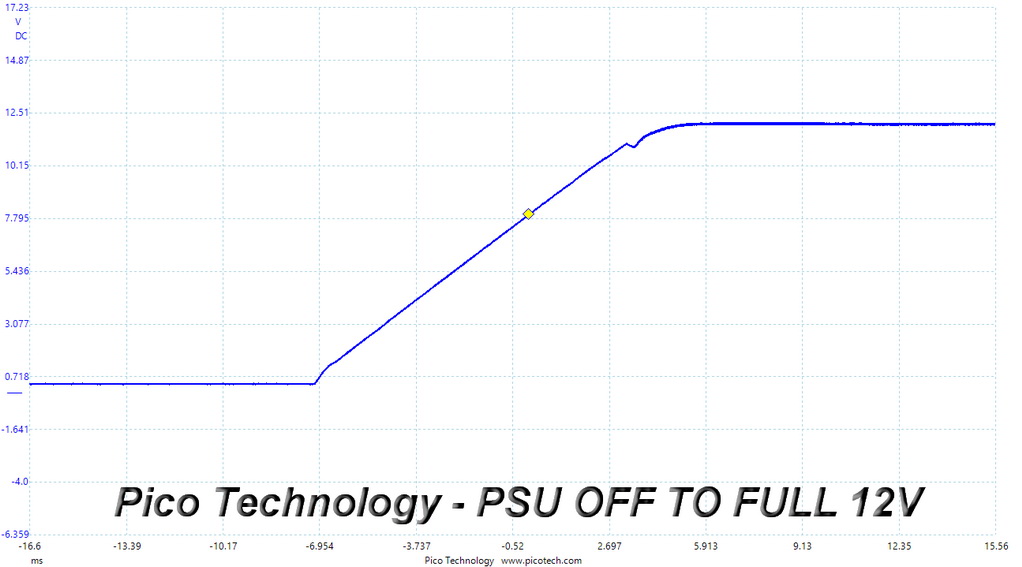
The voltage overshoot at 5VSB is quite high, at 5.53V, exceeding the limit. On the other hand, both 12V waveforms are close to perfect.
Power Supply Timing Tests
There are several signals generated by the power supply, which need to be within specified, by the ATX spec, ranges. If they are not, there can be compatibility issues with other system parts, especially mainboards. From year 2020, the PSU's Power-on time (T1) has to be lower than 150ms and the PWR_OK delay (T3) from 100 to 150ms, to be compatible with the Alternative Sleep Mode.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
| T1 (Power-on time) & T3 (PWR_OK delay) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Load | T1 | T3 |
| 20% | 156ms | 130ms |
| 100% | 155ms | 131ms |
The PWR_OK delay is within the 100-150ms region, but the Power-On time is higher than 150ms, so the PSU does not support the alternative sleep mode.
Ripple Measurements
Ripple represents the AC fluctuations (periodic) and noise (random) found in the PSU's DC rails. This phenomenon significantly decreases the capacitors' lifespan because it causes them to run hotter. A 10-degree Celsius increase can cut into a cap's useful life by 50%. Ripple also plays an important role in overall system stability, especially when overclocking is involved.
The ripple limits, according to the ATX specification, are 120mV (+12V) and 50mV (5V, 3.3V, and 5VSB).
| Test | 12V | 5V | 3.3V | 5VSB | Pass/Fail |
| 10% Load | 14.2 mV | 6.9 mV | 10.8 mV | 9.3 mV | Pass |
| 20% Load | 19.9 mV | 8.6 mV | 12.2 mV | 10.8 mV | Pass |
| 30% Load | 26.4 mV | 9.6 mV | 13.5 mV | 12.5 mV | Pass |
| 40% Load | 31.3 mV | 10.2 mV | 14.6 mV | 14.1 mV | Pass |
| 50% Load | 36.4 mV | 11.0 mV | 15.9 mV | 14.9 mV | Pass |
| 60% Load | 40.2 mV | 11.3 mV | 16.7 mV | 16.7 mV | Pass |
| 70% Load | 46.7 mV | 12.4 mV | 17.7 mV | 17.9 mV | Pass |
| 80% Load | 53.7 mV | 12.6 mV | 19.9 mV | 19.5 mV | Pass |
| 90% Load | 60.2 mV | 13.4 mV | 20.7 mV | 20.0 mV | Pass |
| 100% Load | 71.7 mV | 14.5 mV | 22.4 mV | 22.7 mV | Pass |
| 110% Load | 81.8 mV | 15.2 mV | 23.2 mV | 24.5 mV | Pass |
| Crossload 1 | 21.6 mV | 9.7 mV | 16.9 mV | 11.7 mV | Pass |
| Crossload 2 | 72.4 mV | 14.0 mV | 20.4 mV | 22.6 mV | Pass |
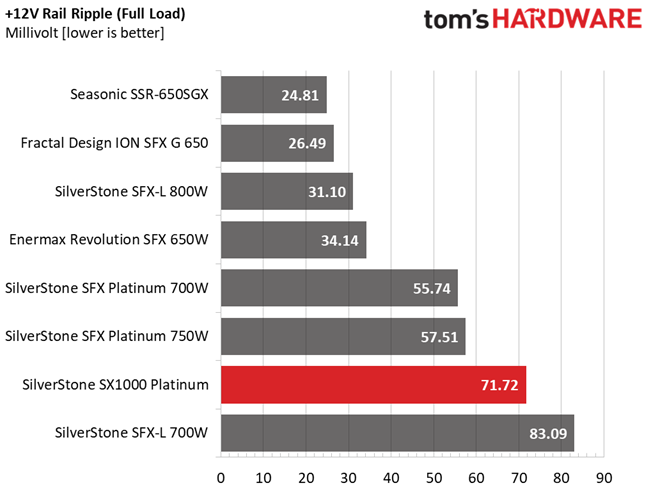
Results 30-33: Ripple Suppression
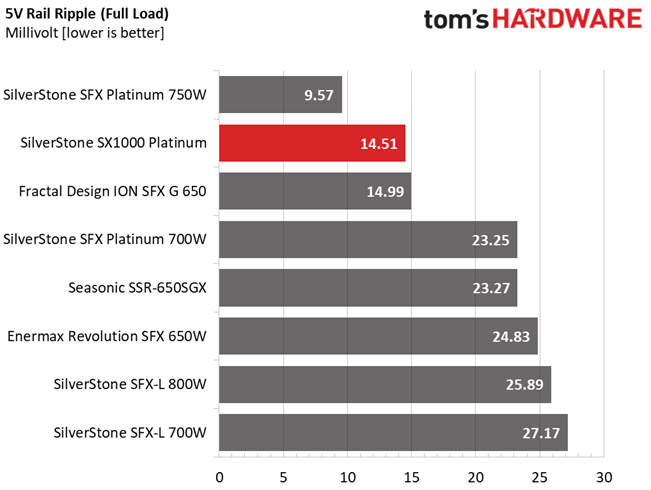
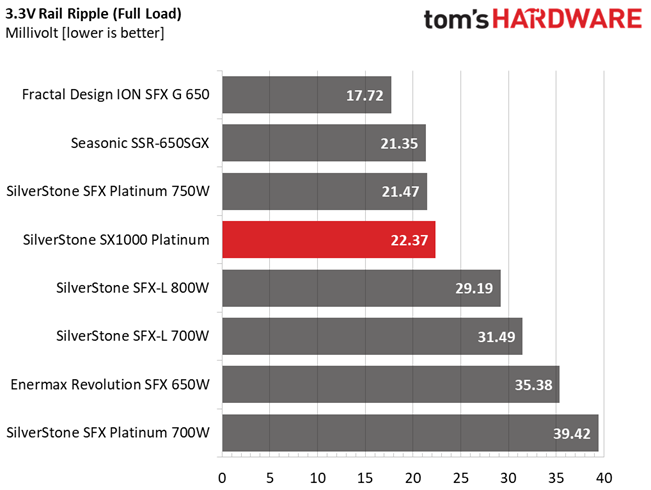
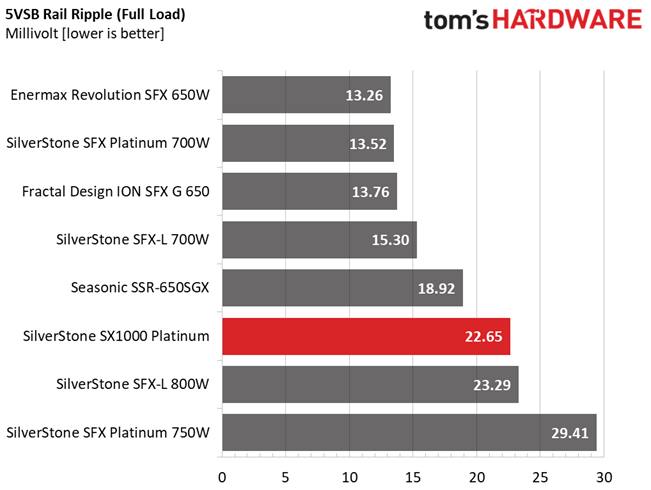
Ripple suppression is not so good at 12V. More filtering caps should be used, but the relatively small PCB sets the limits there. Cables with inline caps could be the solution for lower ripple at 12V, but most users don't like bulky cables, and we are on the same track.
Ripple At Full Load
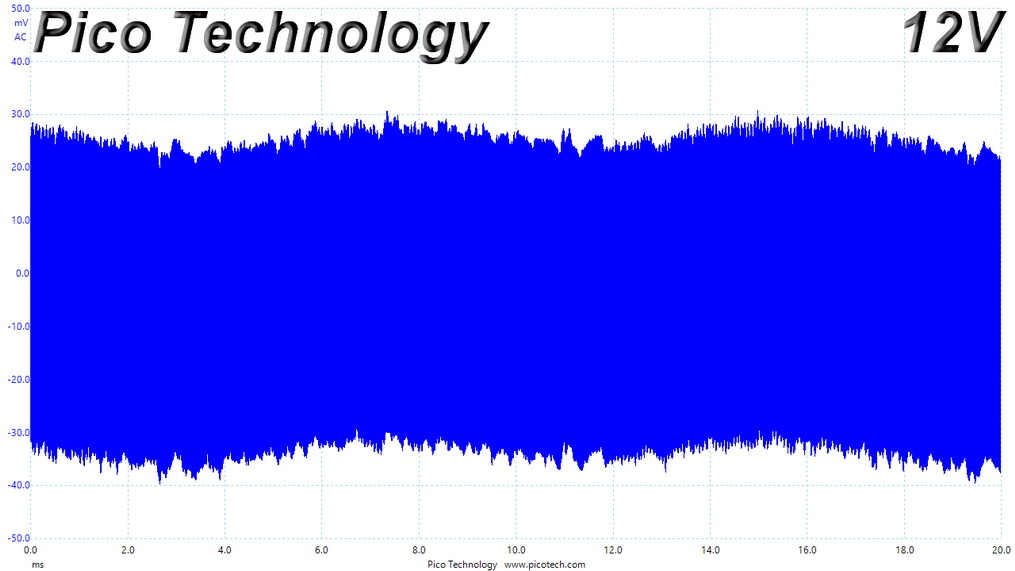
Ripple Full Load Scope Shots
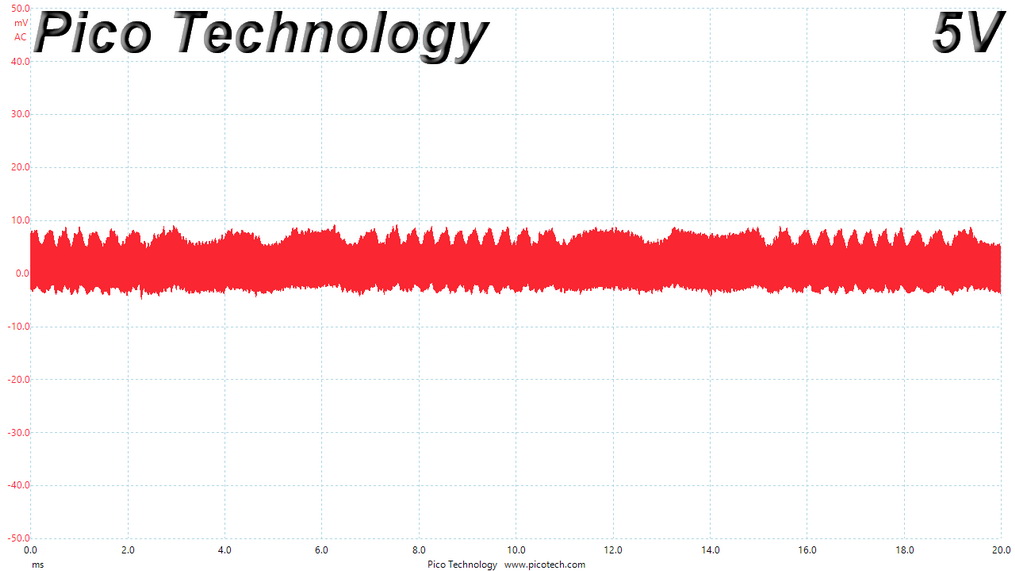
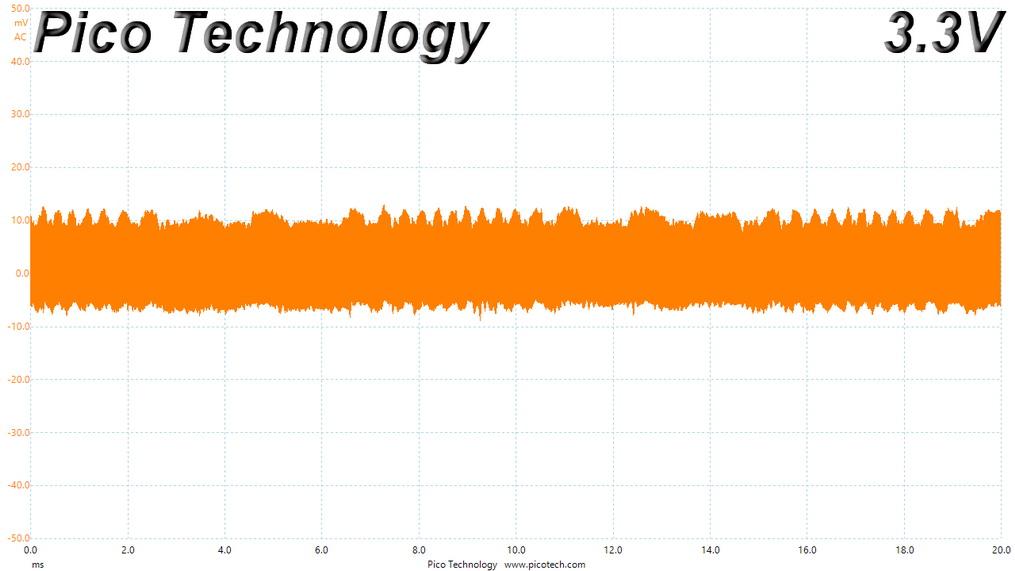
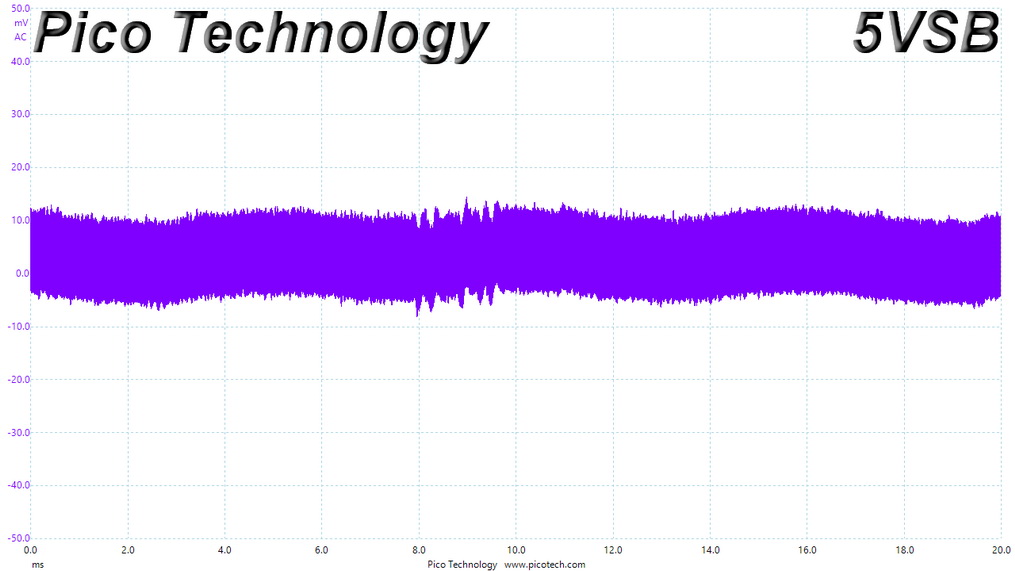
Ripple At 110% Load
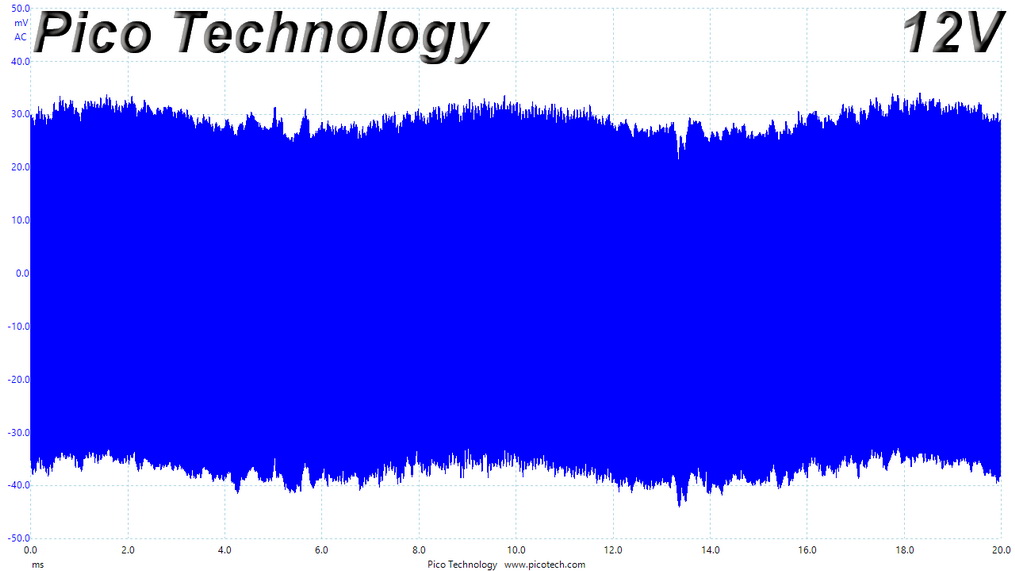
Ripple 110% Load Scope Shots
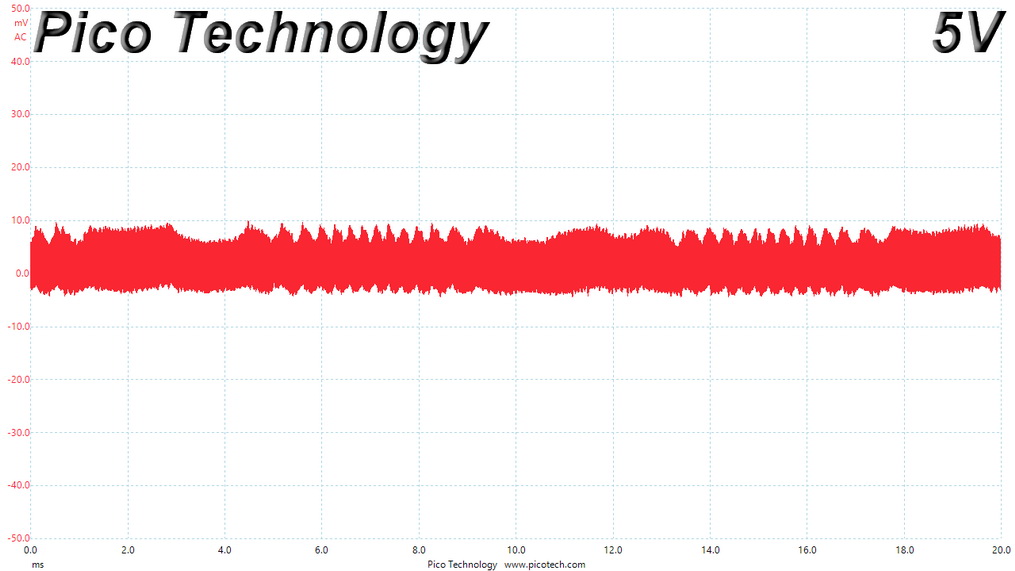
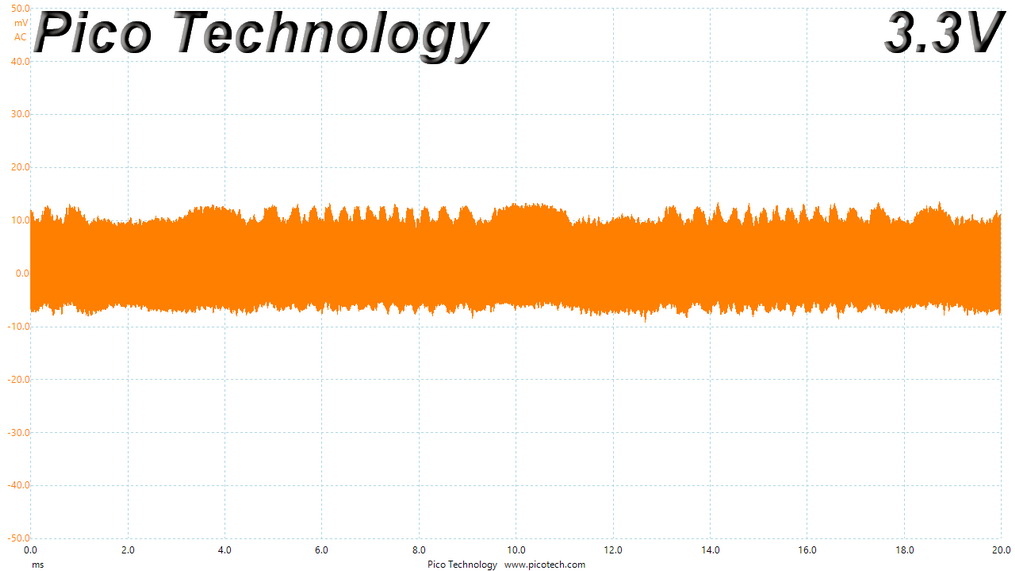
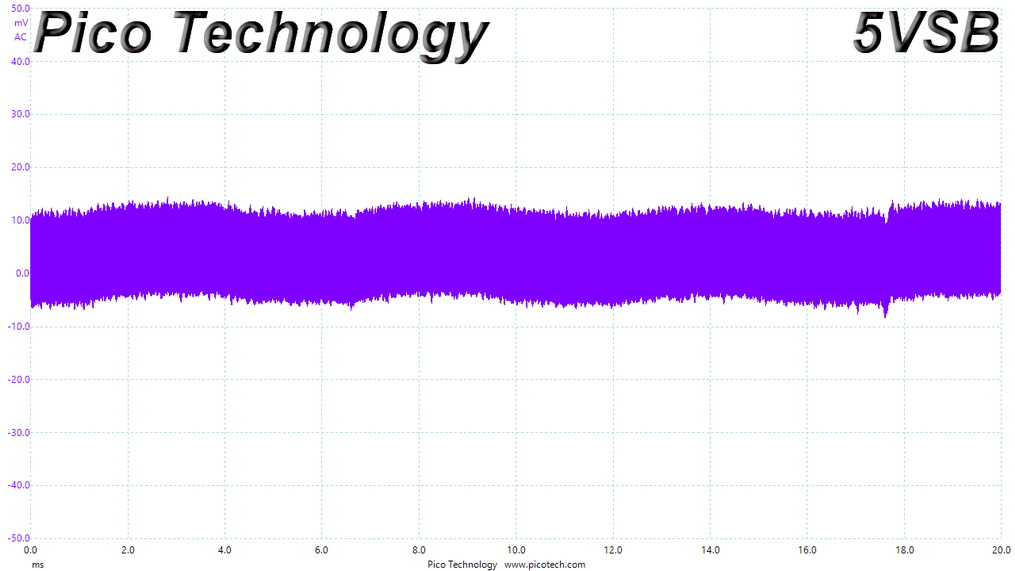
Ripple At Cross-Load 1
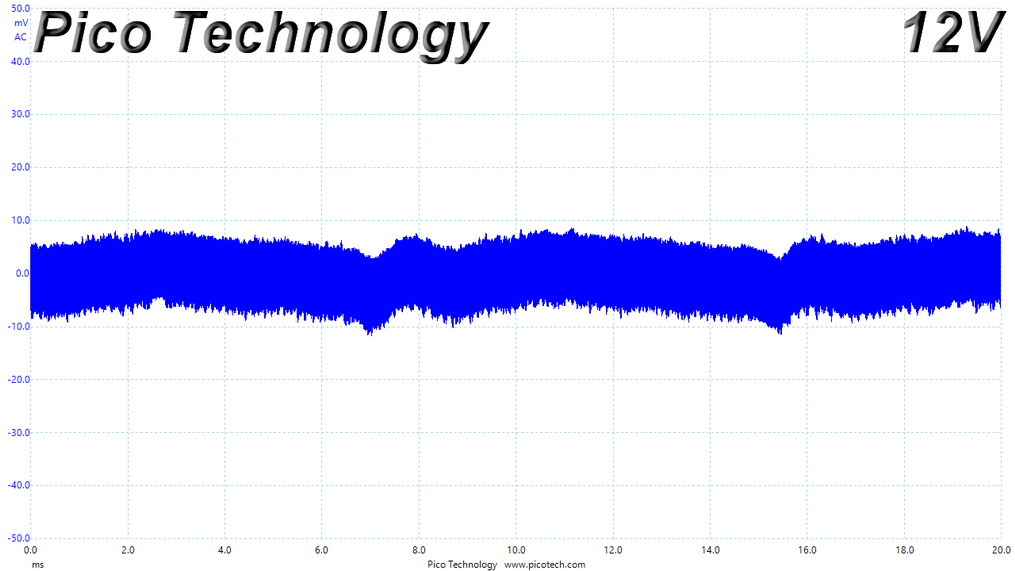
Ripple CL1 Load Scope Shots
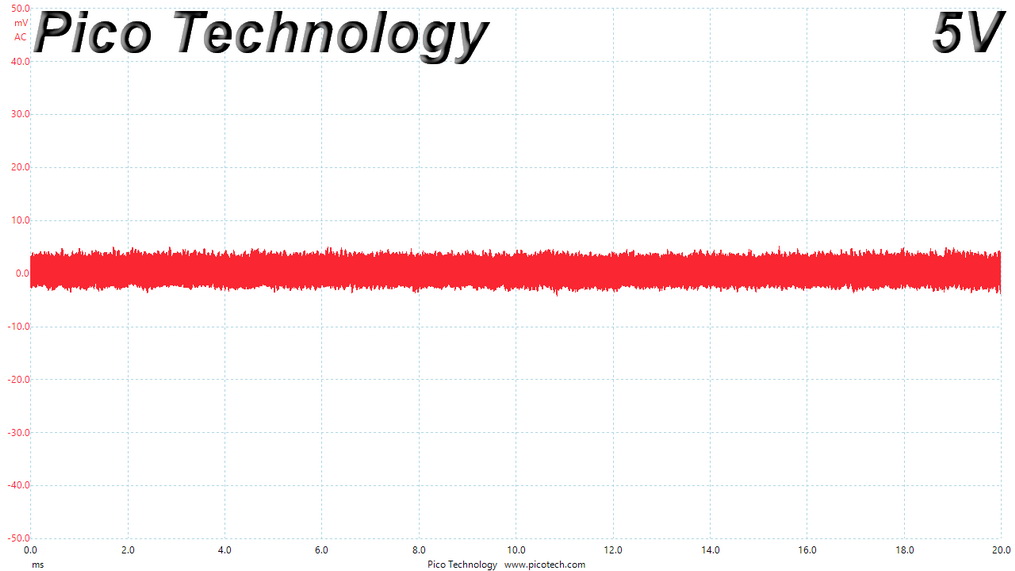
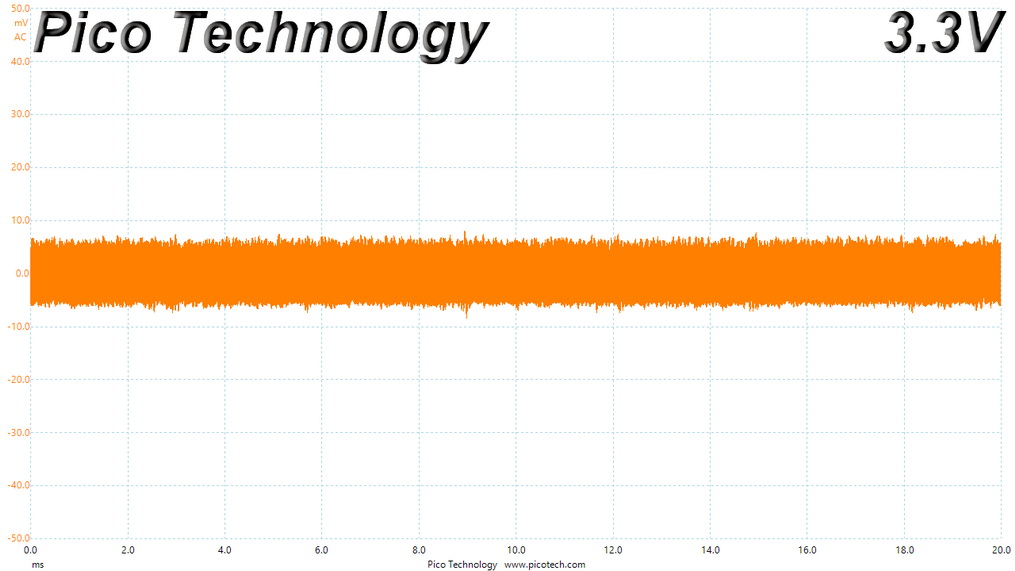
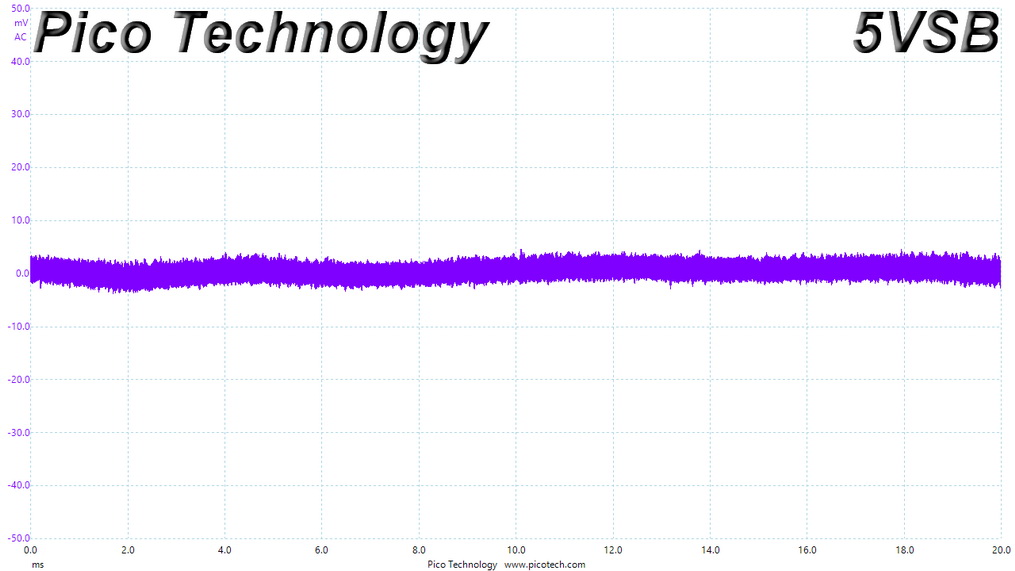
Ripple At Cross-Load 2
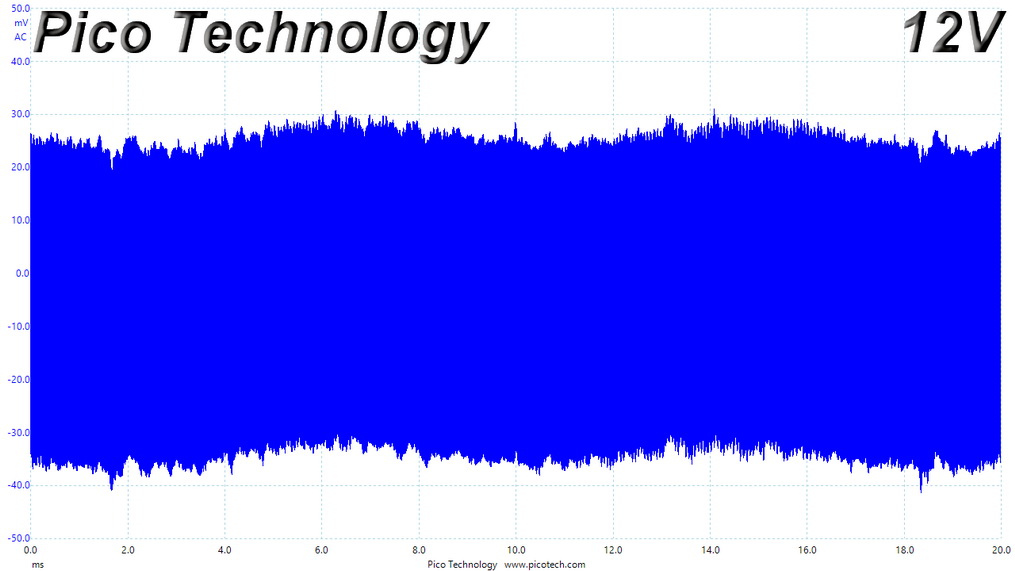
Ripple CL2 Load Scope Shots
EMC Pre-Compliance Testing – Average & Peak EMI Detector Results
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) is the ability of a device to operate properly in its environment without disrupting the proper operation of other nearby devices.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) stands for the electromagnetic energy a device emits, and it can cause problems in other nearby devices if too high. For example, it can be the cause of increased static noise in your headphones or/and speakers.
There are some high spurs, exceeding the limits, with the average detector, but things are way better with the peak EMI detector.
MORE: Best Power Supplies
MORE: How We Test Power Supplies
MORE: All Power Supply Content
Current page: Transient Response Tests, Timing Tests, Ripple Measurements and EMC Pre-Compliance Testing
Prev Page Protection Features, DC Power Sequencing, Cross-Load Tests and Infrared Images Next Page Performance, Noise, Efficiency and Power Factor
Aris Mpitziopoulos is a contributing editor at Tom's Hardware, covering PSUs.
-
littlechipsbigchips Why would anyone need 1000 watts in small itx case ? it will only take one GPU anyways and no one needs 1000 watts for that.Reply -
anonymousdude Replylittlechipsbigchips said:Why would anyone need 1000 watts in small itx case ? it will only take one GPU anyways and no one needs 1000 watts for that.
If you want to stay around 50% load for max efficiency then this needed. Especially when people cram like a 3090 and a 5950x/ into an ITX with custom water cooling and stuff just because they can. Alternatively they might be a modder where they need the smaller PSU for some reason. Definitely a niche product though. -
COLGeek I have the 700w version of this in a Fractal Design ITX case. It does not ship with the bracket necessary to mount to an ATX PSU location. Just sharing for others to be aware of.Reply
Nearly silent PSU, by the way. -
junglist724 Reply
My 3090FE trips OCP on my SF750 platinum in several games at 4K. Asus even said they measured up to 940W peak power draw from a 3090 in a recent video showcasing their new Thor PSUs. oy65PZCTIlc:2270View: https://youtu.be/oy65PZCTIlc?t=37m50slittlechipsbigchips said:Why would anyone need 1000 watts in small itx case ? it will only take one GPU anyways and no one needs 1000 watts for that.