NASA demonstrates space network speeds of up to 267 Mbps — Deep Space Optical Communications stretch beyond 140 million miles
Speeds across two tests span from 25 to 267 Mbps, and past Mars' orbit.
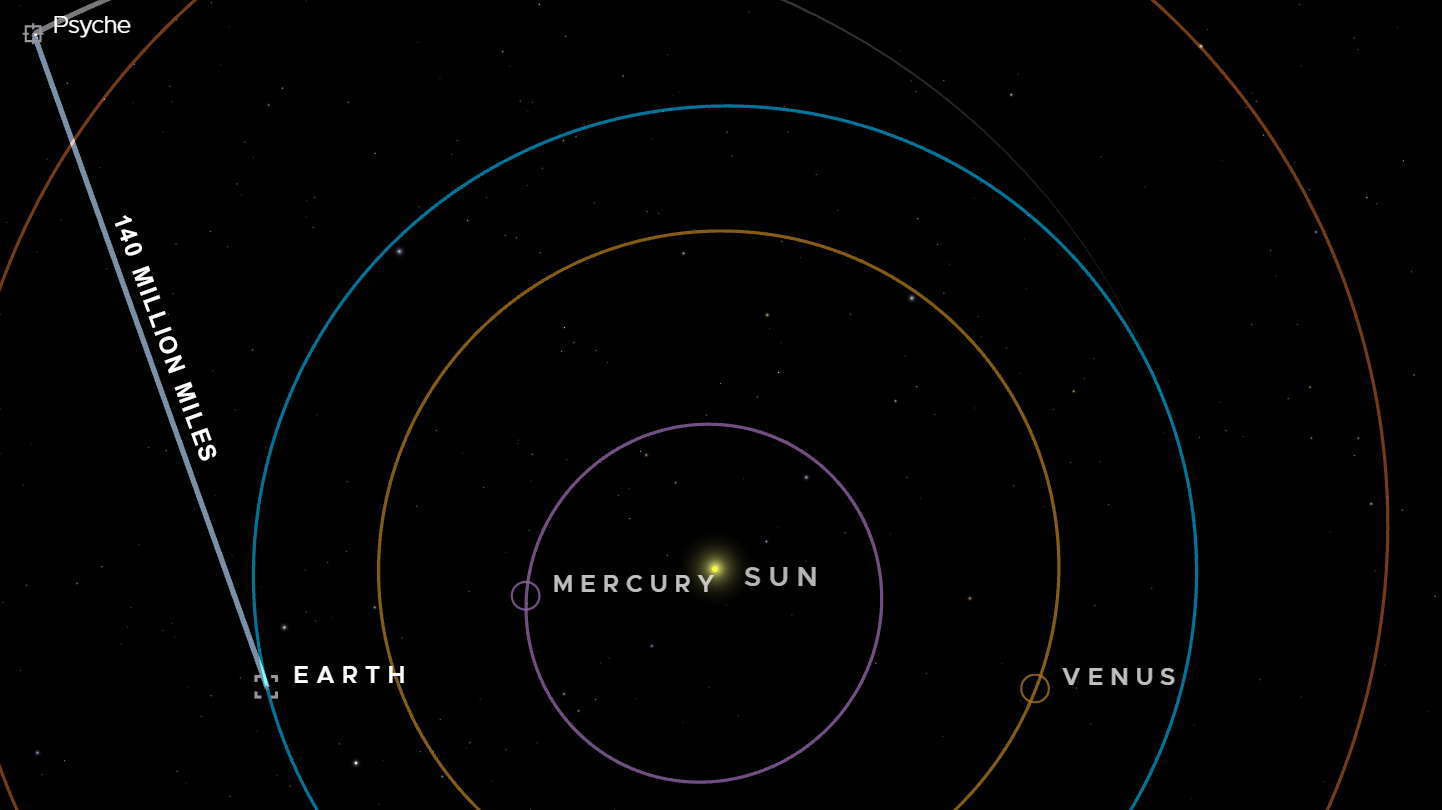
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory at NASA has achieved network speeds of 267 Mbps past the distance between Earth and the sun with its new Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) system, which was launched on October 5, 2023. This DSOC testing was done with NASA's Psyche spacecraft on December 11, 2023, while on its way to the asteroid of the same name in order to mine it for metal. Currently, the craft is "healthy and stable" on its way to an asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, NASA says.
NASA's Deep Space Optical Communications were first tested with Psyche on while transmitting 15 seconds of 4K video (below) from Earth to Psyche over a distance of 19 million miles — which is also 80 times the distance between the Earth and the moon, and 1.5 times the distance between Earth and the sun. At last, high-bandwidth Internet can operate on a truly galactic scale.
Compared to existing high-end radio frequency systems used by other spacecraft, DSOC is 10 to 100 times faster at its tested speeds of 267 Mbps at closer range and 25 Mbps from deep space. By NASA's numbers, this places the old systems at a peak speed of around 25 Mbps, with possibly greater gains over larger distances. A properly galactic (well, solar) speed boost, one could say.
More recently, NASA used the later communications transmitting tech to send demo data over 140 million miles away, 1.5 times the distance between the Earth and the sun. A slower "round trip" testing conducted on April 8 included high volumes of engineering data on the test itself sent back to Earth. The round trip test also used "digital pet photographs", which is almost certainly NASA code for "cat memes", considering the content of the original video sent to Psyche. That was 280 million miles in total, to Psyche and back.
However, a few downsides for DSOC still exist. For example, clear skies are required to transmit high-bandwidth data, and storms can disrupt the connection entirely. This makes it seem that the current communications systems may need to be kept in place for certain flight or safety-critical concerns with future spacecraft— though it's noted that an array of multiple ground stations could be set up to receive signals when one goes offline.
As noted by Ken Andrews, project flight operations lead at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), "The fact we're doing this now has surpassed all of our expectations."
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.

Christopher Harper has been a successful freelance tech writer specializing in PC hardware and gaming since 2015, and ghostwrote for various B2B clients in High School before that. Outside of work, Christopher is best known to friends and rivals as an active competitive player in various eSports (particularly fighting games and arena shooters) and a purveyor of music ranging from Jimi Hendrix to Killer Mike to the Sonic Adventure 2 soundtrack.
-
Xenophage Because of the inverse square law, I suspect your math about NASA's estimates of bandwidth is wrong. They said 10 to 100 times faster, and it *should* be the case that the farther out you go, the greater the advantages of laser communications over radio. It should not be a linear relationship.Reply -
usertests Reply
I'm not sure. Don't lasers behave similarly to other forms of communication in that they become diffuse over a distance?Xenophage said:Because of the inverse square law, I suspect your math about NASA's estimates of bandwidth is wrong. They said 10 to 100 times faster, and it *should* be the case that the farther out you go, the greater the advantages of laser communications over radio. It should not be a linear relationship. -
domih <<...At last, high-bandwidth Internet can operate on a truly galactic scale...>>Reply
Mmm... with a beefy latency of 4.2465 x 365 x 24 x 60 x 60 x 1000 = 133,917,624,000 milliseconds with the nearest star. Double it, for a response. -
artk2219 Reply
The speed of light, so fast, yet so slow, we haven't even touched a fraction of that speed with a physical object yet.domih said:<<...At last, high-bandwidth Internet can operate on a truly galactic scale...>>
Mmm... with a beefy latency of 4.2465 x 365 x 24 x 60 x 60 x 1000 = 133,917,624,000 milliseconds with the nearest star. Double it, for a response. -
Alvar "Miles" Udell And yet how many people in first world nations (primarily the USA) can't even get a cell signal or high speed internet access...Reply -
Amdlova Reply
If you think it's hard for the ones think on the third ones...Alvar Miles Udell said:And yet how many people in first world nations (primarily the USA) can't even get a cell signal or high speed internet access... -
Blastomonas May want to double check the distances quoted. I'm fairly sure that the sun is considerably further than 18 million miles away..Reply -
das_stig Well done NASA and yet Vermin Media can't even supply 50Mbps stable during peak hours.Reply -
HaninTH I wonder how random space "dust" will affect the signal and if the magnetic fields generated by some planets will do anything to it (Saturn & Jupiter). Also, how will stray light from stars and other interstellar objects come into play?Reply
Oh, to be able to live long enough to see some of these technologies being used and extended. What will we be doing in 100 years, assuming we don't get wiped out by some unforeseen event or we do it to it ourselves before then.