TSMC Second-Gen 3nm Arrives as N3E Chips Get Taped Out
Alphawave's ZeusCore100 is one of the first in line
Alphawave says it has taped out one of the industry's first chips made using TSMC's N3E fabrication technology, the second generation of a 3nm-class process node. The chip has been produced by TSMC (Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co.) and has successfully passed all the necessary tests. It will be demonstrated at TSMC's OIP forum later this week.
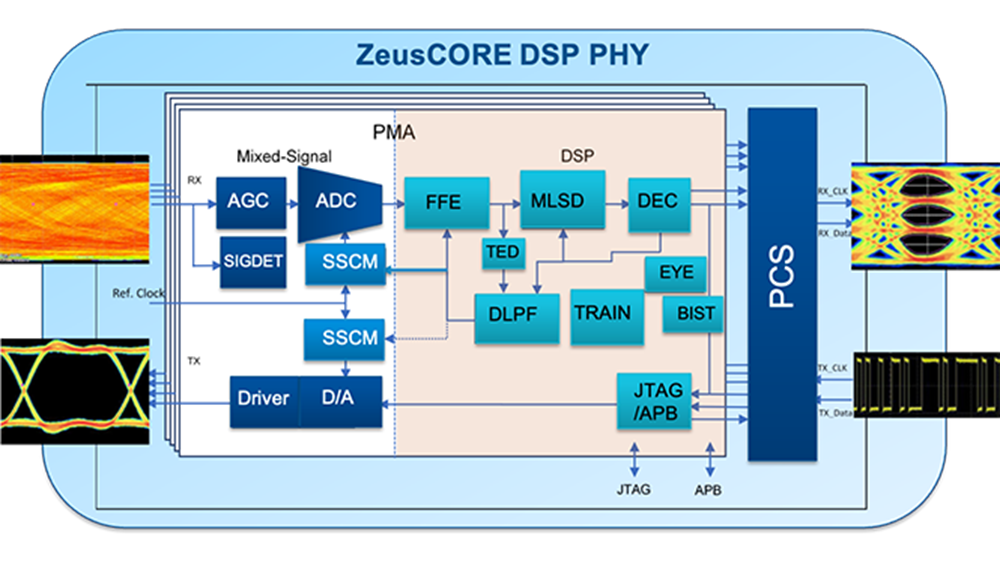
The chip in question is the Alphawave IP ZeusCORE100 1-112Gbps NRZ/PAM4 Serialiser-Deserialiser (SerDes) that supports numerous standards set to be popular in the coming years. That includes 800G Ethernet, OIF 112G-CEI, PCIe 6.0, and CXL3.0. The SerDes is said to support extra-long channels to enable flexible connectivity solutions for next-generation servers.
"Alphawave is proud to be among the first to utilize TSMC's most advanced 3nm technology," said Tony Pialis, president and CEO of Alphawave. "Our partnership continues to bring innovative, high-speed connectivity technology that will power the most advanced data centers, and we are excited to showcase these solutions at the TSMC OIP Forum event."
| Row 0 - Cell 0 | N3E vs N5 | N3 vs N5 |
| Speed Improvement @ Same Power | +18% | +10% ~ 15% |
| Power Reduction @ Same Speed | -34% | -25% ~ -30% |
| Logic Density | 1.7x | 1.6x |
| HVM Start | Q2/Q3 2023 | H2 2022 |
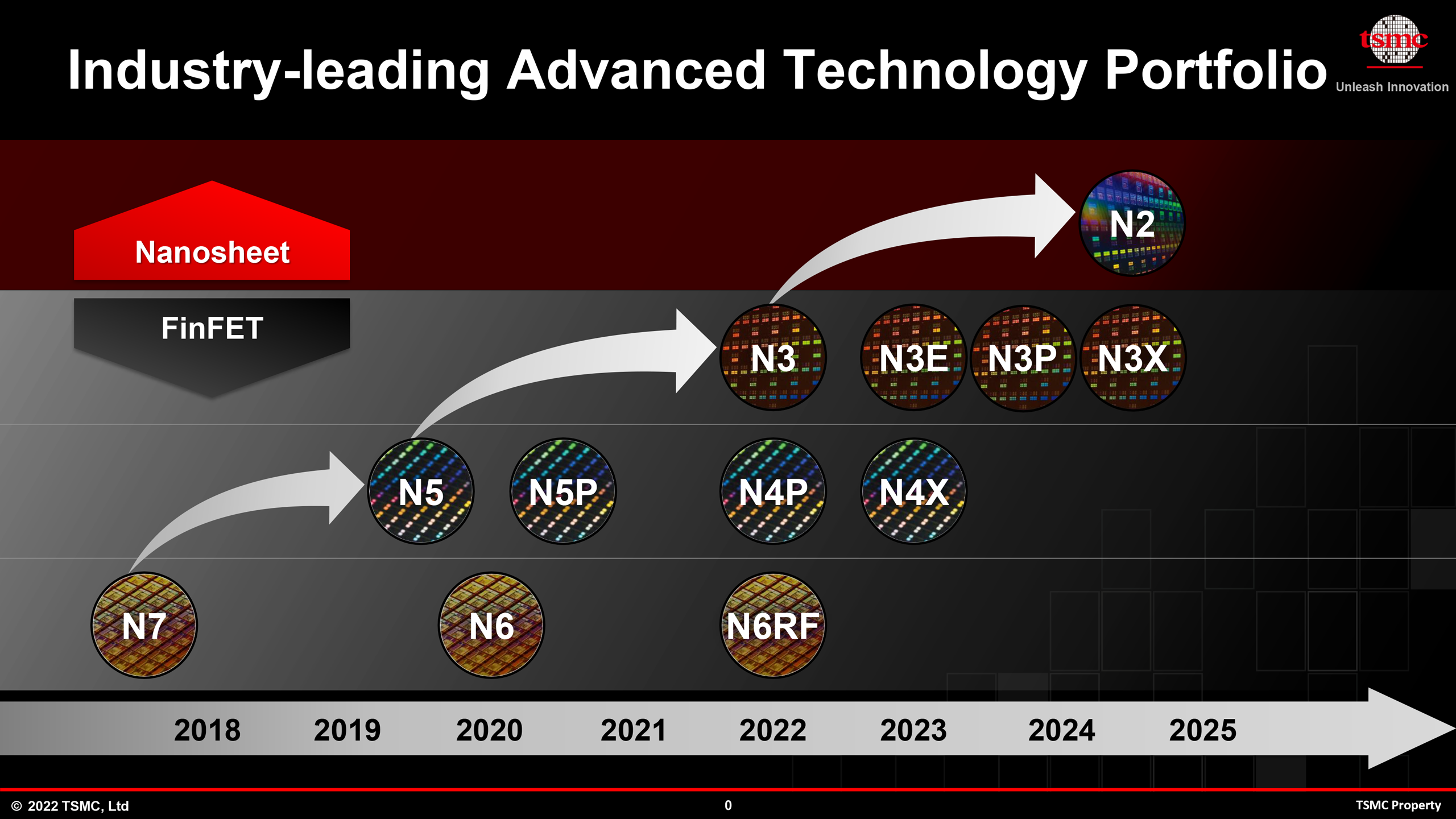
TSMC intends to introduce five 3nm class process technologies in the next two or three years. The first generation vanilla N3 node is expected to be used for a few designs by TSMC's alpha customers (read: Apple), whereas the second generation N3E will feature an improved process window, which means faster time to yield, increased yields, higher performance, and lower power.
N3E is expected to be adopted considerably more widely than vanilla N3, but its mass production is scheduled to start in mid-2023 or Q3 2023, about a year after TSMC initiates high volume manufacturing (HVM) using its N3 production node.
Like all Serialiser-Deserialiser chips, Alphawave IP's SerDes is a relatively small piece of silicon that can take advantage of a leading-edge process technology. Such designs can be used as a "pipe cleaner" to learn the peculiarities of the manufacturing node. To that end, it makes perfect sense for Alphawave to make its ZeusCORE100 on TSMC's N3E process.
After TSMC begins N3E HVM next year, it plans to offer three more 3nm class nodes, including performance-oriented N3P, N3S fabrication technology for chips that need high transistor density, and N3X manufacturing process for performance-demanding applications, such as microprocessors.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.

Anton Shilov is a contributing writer at Tom’s Hardware. Over the past couple of decades, he has covered everything from CPUs and GPUs to supercomputers and from modern process technologies and latest fab tools to high-tech industry trends.
-
thisisaname Would be good if you defined what Serialiser-Deserialiser chips where.Reply
A Serializer/Deserializer (SerDes) is a pair of functional blocks commonly used in high speed communications to compensate for limited input/output. These blocks convert data between serial data and parallel interfaces in each direction.