Intel Preps Two 13th Gen Raptor Lake Black Edition CPUs (Updated)
Intel's 13th Generation Raptor Lake family, with several members among the best CPUS, will soon welcome two new members. Sadly, the Core i5-13490F and Core i7-13790F may not be available in the U.S. market. Both chips have already emerged in Intel documents; however, they haven't found their way into Intel's ARK database, so their launch date is still up in the air.
With Alder Lake, Intel released the Core i5-12490F, a "Black Edition" gaming processor exclusive to the Chinese market. The Core i5-13490F is the direct successor to the Core i5-12490F, whereas the Core i7-13790F is a new addition since a Core i7-12790F has never existed. However, like the Core i5-12490F, the Core i5-13490F and Core i7-13790F are likely "Black Edition" chips because they come in black boxes as opposed to the typical blue Intel box, and Intel doesn't include a stock cooler. Furthermore, being F-series chips, the Core i5-13490F and Core i7-13790F lack integrated graphics, so pairing them with a discrete graphics card is a must.
The Core i5-12490F was just a means for Intel to maximize profits from its silicon production. To make a long story short, the chipmaker produced two dies for Alder Lake: C0 (8P+8E) and H0 (6P+0E). Intel utilizes the first for the high-tier chips, including the Core i9 and Core i7 SKUs, and the latter for low-tier chips, like the Core i5 and Core i3 SKUs. However, the lower tier SKUs have the benefit of using either silicon, allowing the chipmaker to repurpose C0 dies that don't meet the standards for the higher tier into the lower tier.
With Raptor Lake, there's a third die: the B0 die (8P-16E). According to the leaked CPU-Z screenshots, the Core i5-13490F employs the C0 die, and the Core i7-13790F has the B0 die. Therefore, the Core i5-13490F and Core i7-13790F are products of Intel's recycling efforts.
Core i5-13490F, Core i7-13790F Specifications
| Processor | Cores / Threads | P-cores / E-cores | P-Core Base / Boost (GHz) | E-Core Base / Boost (GHz) | L3 Cache (MB) | PBP / MTP (W) | Stepping | Ordering Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core i7-13790F* | 16 / 24 | 8 / 8 | ? / 5.1 | ? / ? | 33 | 65 / ? | B0 | BXC8071513740F |
| Core i7-13700F | 16 / 24 | 8 / 8 | 2.1 / 5.2 | 1.4 / 4.1 | 30 | 65 / 219 | B0 | BXC8071513700F |
| Core i5-13490F* | 10 / 16 | 6 / 4 | ? / 4.8 | ? / ? | 24 | 65 / ? | C0 | BXC8071513790F |
| Core i5-13400F | 10 / 16 | 6 / 4 | 2.5 / 4.6 | 1.8 / 3.3 | 20 | 65 / 148 | B0 / C0 | BXC8071513400F |
| Core i5-12490F | 6 / 12 | 6 / 0 | 3.0 / 4.6 | N/A | 20 | 65 / 117 | C0 | BXC8071512490F |
| Core i5-12400F | 6 / 12 | 6 / 0 | 2.5 / 4.4 | N/A | 18 | 65 / 117 | C0 / H0 | BXC8071512400F |
*Specifications are unconfirmed.
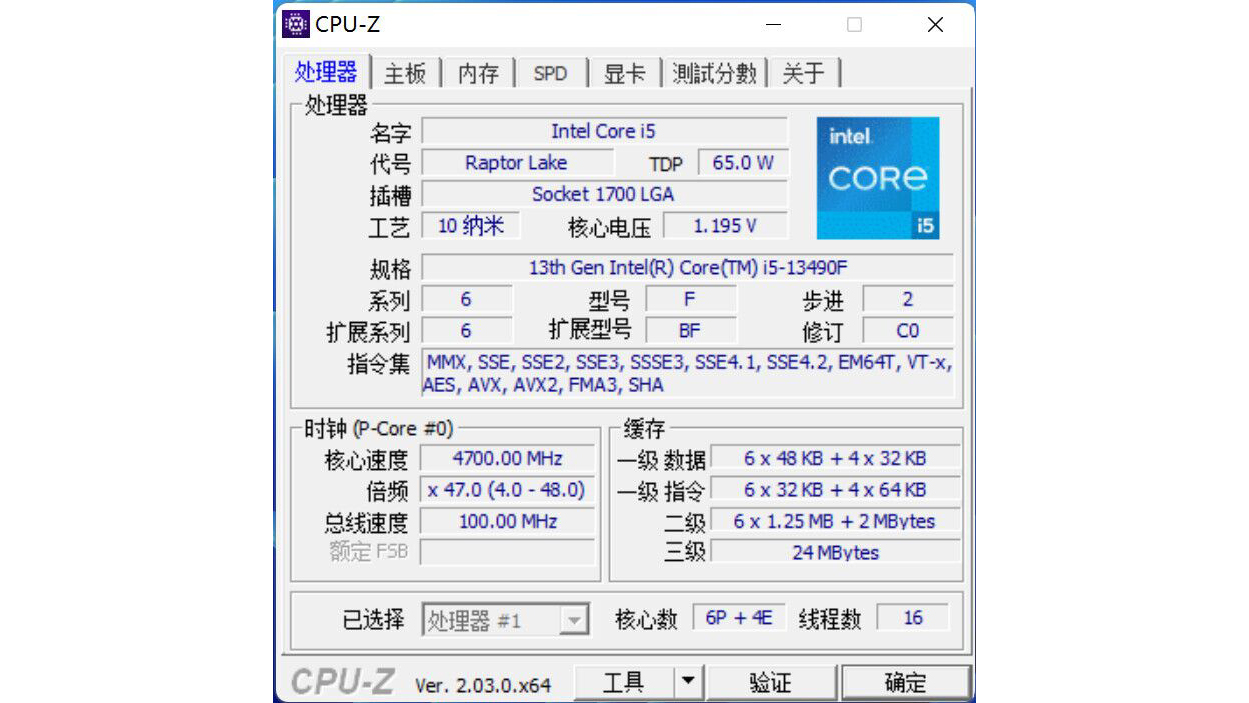
Twitter user wxnod has shared the alleged specifications for the Core i5-13490F, which appears to arrive with a significant upgrade. The Core i5-13490F seemingly has a 10-core, 16-thread configuration. However, it's the same configuration as the regular Core i5-13400F, which has proven to offer similar performance to the last generation's Core i5-12600K.
The Core i5-13490F wields six P-cores and four E-cores, so the most significant difference between it and its predecessor is the four additional E-cores. In addition, the CPU-Z screenshot showed the chip with a 4.8 GHz boost clock, which corresponds to the P-cores. It's a 200 MHz improvement over the Core i5-12490F and Core i5-13400F.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
The Core i5-12490F had more L3 cache than the Core i5-12400F. It's the same trend with the Core i5-13490F and Core i5-13400F, although the upgrade is slightly higher. The Core i5-12490F sports 2MB more than the Core i5-12400F. However, the Core i5-13490F's L3 cache is 4MB bigger than the Core i5-12490F and Core i5-13400F, putting it on the equivalent ground as the Core i7-13700F.
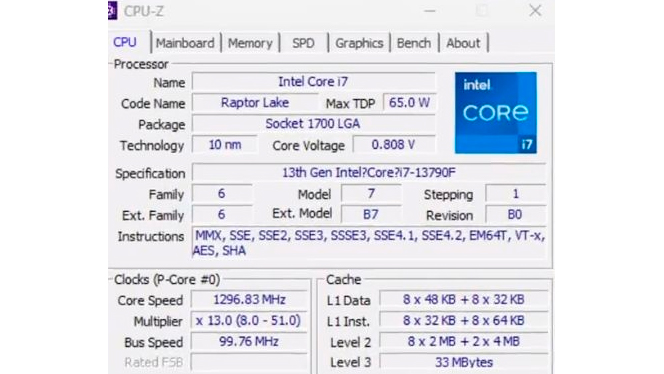
Meanwhile, the Core i7-13790F purportedly shares the same 16-core, 24-thread configuration as the Core i7-13700F. The setup is equivalent to eight P-cores and eight E-cores. In addition, the Core i7-13790F appears to have a 5.1 GHz boost clock, 100 MHz lower than the Core i7-13700F.
The Core i7-13790F's L3 cache is very peculiar. If the CPU-Z report is accurate, the chip has 33MB of L3 cache, placing it between the Core i7 (30MB) and Core i9 (36MB) parts.
Since they don't belong to the K-series tier, the Core i5-13490F and Core i7-13790F have a 65W PBP. The MTP is unknown, though. However, the previous Core i5-12490F and Core i5-12400F have the same 117W MTP, so it's not unreasonable to think that the Core i5-13490F could share the same 148W MTP as the Core i5-13400F.
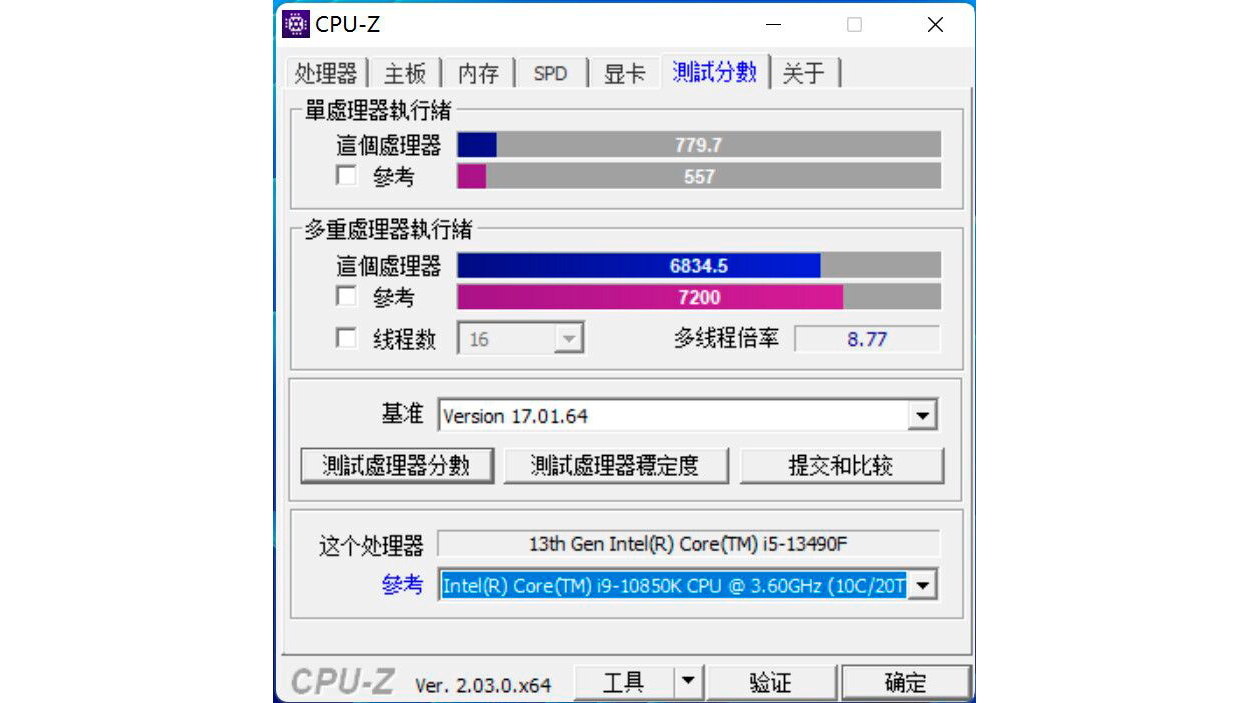
The Core i5-13490F scored 779.7 points on the single-core test and 6,834.5 points on the multi-core test. For comparison, the Core i5-13400F (via NotebookCheck) put 729.1 points and 6540 points on the single-and multi-core tests, respectively. That means the Core i5-13490F delivered 6.9% higher single-core performance and 4.5% multi-core performance than the Core i5-13400F.
On the other hand, the Core i5-12490F has a single-core score of 700 points and a multi-core score of 4,653 points. As a result, the Core i5-13490F outperformed the Core i5-12490F by 11.4% in single-core performance. In addition, the Core i5-13490F was up to 46.9% faster in terms of multi-core performance.
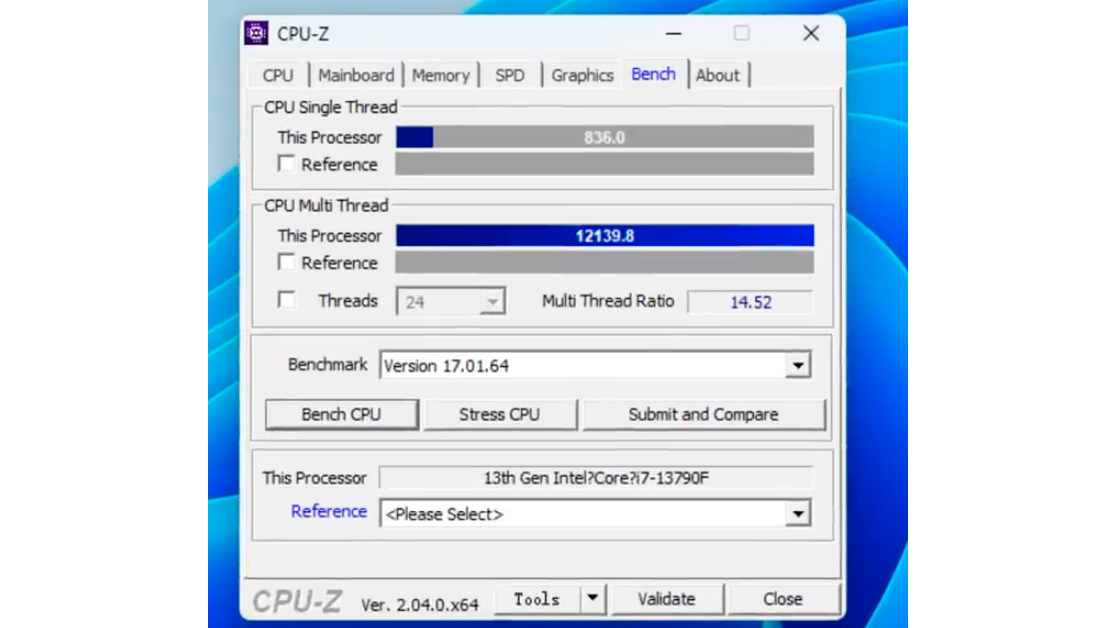
The Core i7-13790F had a single-core score of 836 points and a multi-core score of 12,139.8 points. One CPU-Z entry shows the Core i7-13700F with a 778-point single-core score and a 10,132-point multi-core score. Therefore, the Core i7-13790F had 7.5% higher single-core performance and 19.8% higher multi-core performance.
The Core i5-13490F currently retails for 1,599 yuan or $235.96, and the Core i7-13790F goes for 2,999 yuan, equivalent to $441.62. Of course, these are China-exclusive processors; nonetheless, they always find their way to the U.S. market through retailers allowing third-party sellers. For example, the Core i5-12490F is available at Newegg for $199.80, so it shouldn't be long before a Chinese merchant offers the Core i5-13490F or Core i7-13790F.

Zhiye Liu is a news editor, memory reviewer, and SSD tester at Tom’s Hardware. Although he loves everything that’s hardware, he has a soft spot for CPUs, GPUs, and RAM.
-
cyrusfox at the right price, the 13790F could be a beast, wonder if it will keep all 8E cores (I imagine it will as even the 13600k has 8E cores). I am running a 13700k right now, I fail to see a reason/need to get a 13900, but maybe I will change my tune when price and supply come back to a place to tempt me. 16e cores sounds fun.Reply -
usertests Typo:Reply
"However, the Core i5-13490F's L3 cache is 4MB bigger than the Core i5-12490F"
12490F -> 13400F -
bit_user Unrelated, but I think Intel missed a real opportunity with the small die (6P + 0E) Alder Lake. They could've sold a version of those as Xeon E-series and enabled the AVX-512 support on them.Reply
Since the Rocket Lake Xeon E-series launched, every Xeon-branded CPU has featured AVX-512. So, it would be a way for them to continue that segmentation, while providing an entry-level option for people who want AVX-512 at a lower price point than the Xeon W 2400-series. -
Amdlova Replybit_user said:Unrelated, but I think Intel missed a real opportunity with the small die (6P + 0E) Alder Lake. They could've sold a version of those as Xeon E-series and enabled the AVX-512 support on them. Since the Rocket Lake Xeon E-series launched, every Xeon-branded CPU has featured AVX-512. So, it would be a way for them to continue that segmentation, while providing an entry-level option for people who want AVX-512 at a lower price point than the Xeon W 2400-series.
I have dropped the need for new cpus when intel removes the avx512, why spend in new system if the intel removes the avx... for now avx2 -
MBOO7 If we are honest in terms of FHD or WQHD cpu gaming performance we already reached a point where it barely matters what cpu u are buying nowadays... this will be hard for Intel+AMD since people will nowadays even longer stay on their latest cpus. The potential jump in gaming performance would be neglectible.....Reply
Even gpus already reached performance in FHD/WQHD where you wont need anything new for who knows how long (in case you dont care about RT).
Retention times will be nowadays even longer (the same already applies to smartphones according to Gardner) -
bit_user Reply
Then it was a good move for AMD to buy Xilinx, since that gives them more traction in the embedded market, including things like the growing robotics market. More important is probably the datacenter market, where AMD is continuing to make inroads.MBOO7 said:this will be hard for Intel+AMD since people will nowadays even longer stay on their latest cpus.
If AMD can get its act together with its GPUs and streamline its support of popular machine learning frameworks, that's another huge market that's virtually untapped by them. However, that's a big "if". -
DMW888 Not sure if anyone knows this but the i5-13500 still isn't available in China.Reply
Intel is probably trying to maximize profit by pushing the i5-13490, however a large percentage of Chinese consumers are avoiding it due to it being only available in their market and have been choosing the 13400F instead. Hence the 13490 is now sold at or close to the same price as the 13400F.