Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
AMD Ryzen 9 7900X3D Productivity Benchmarks — The TLDR:
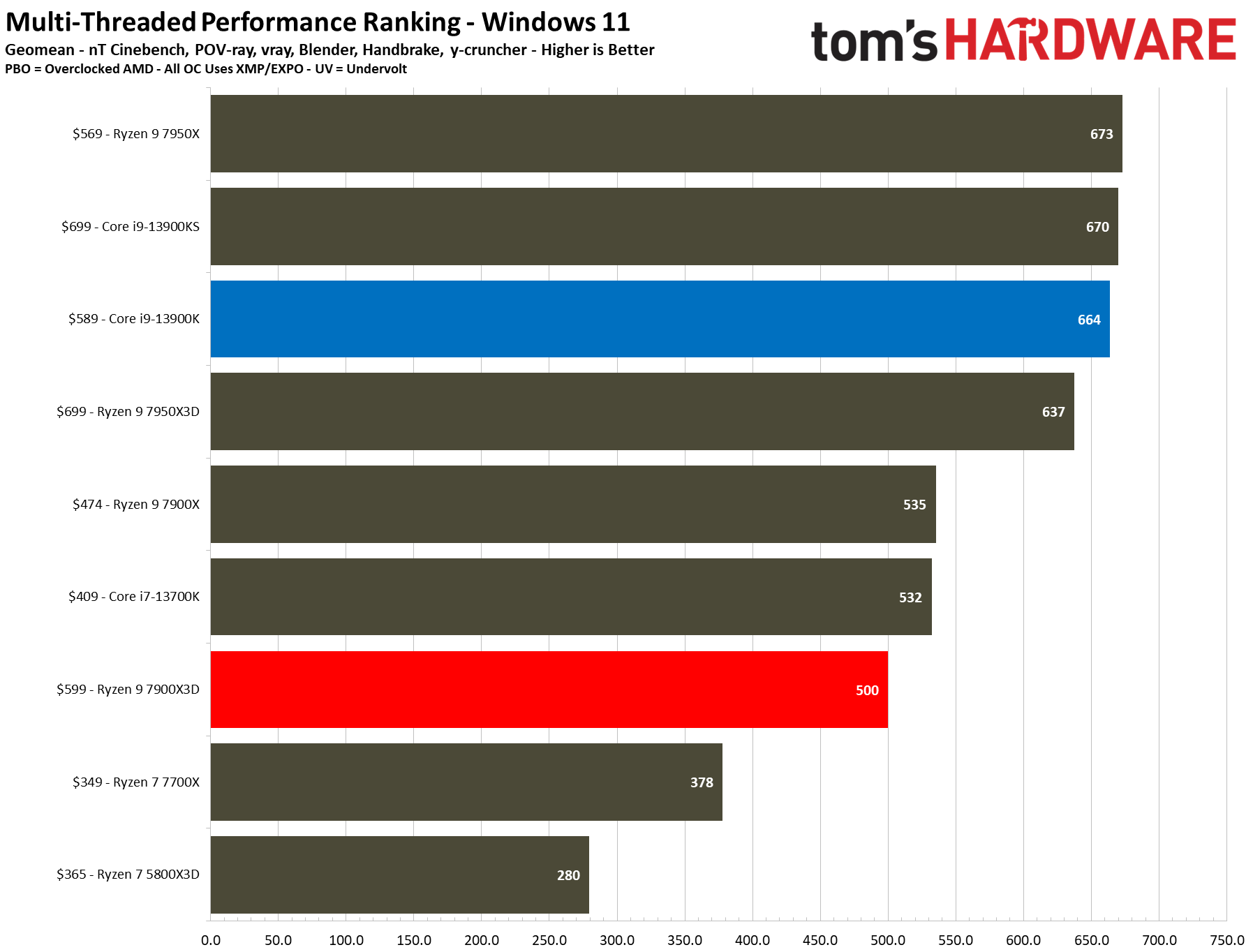
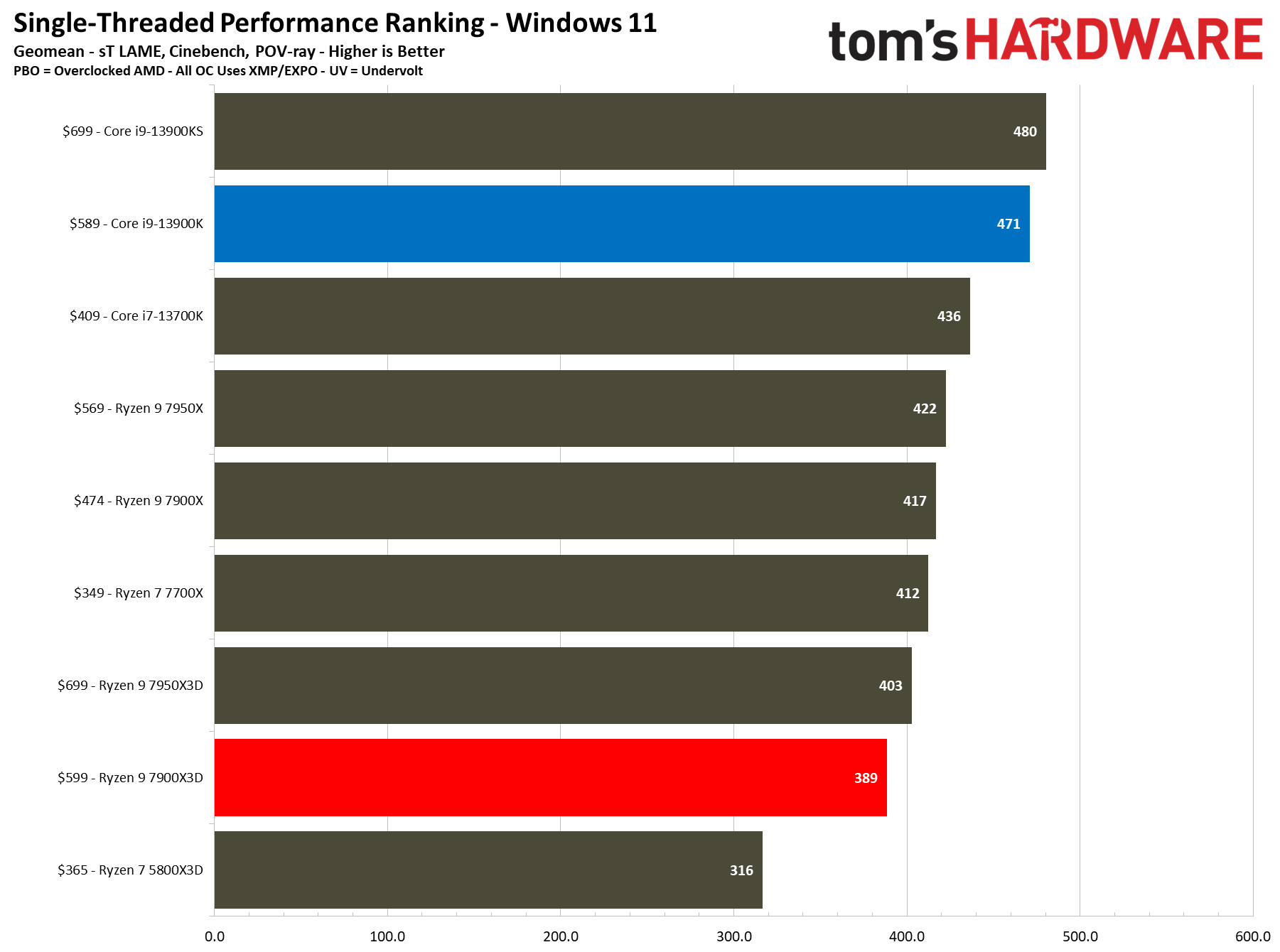
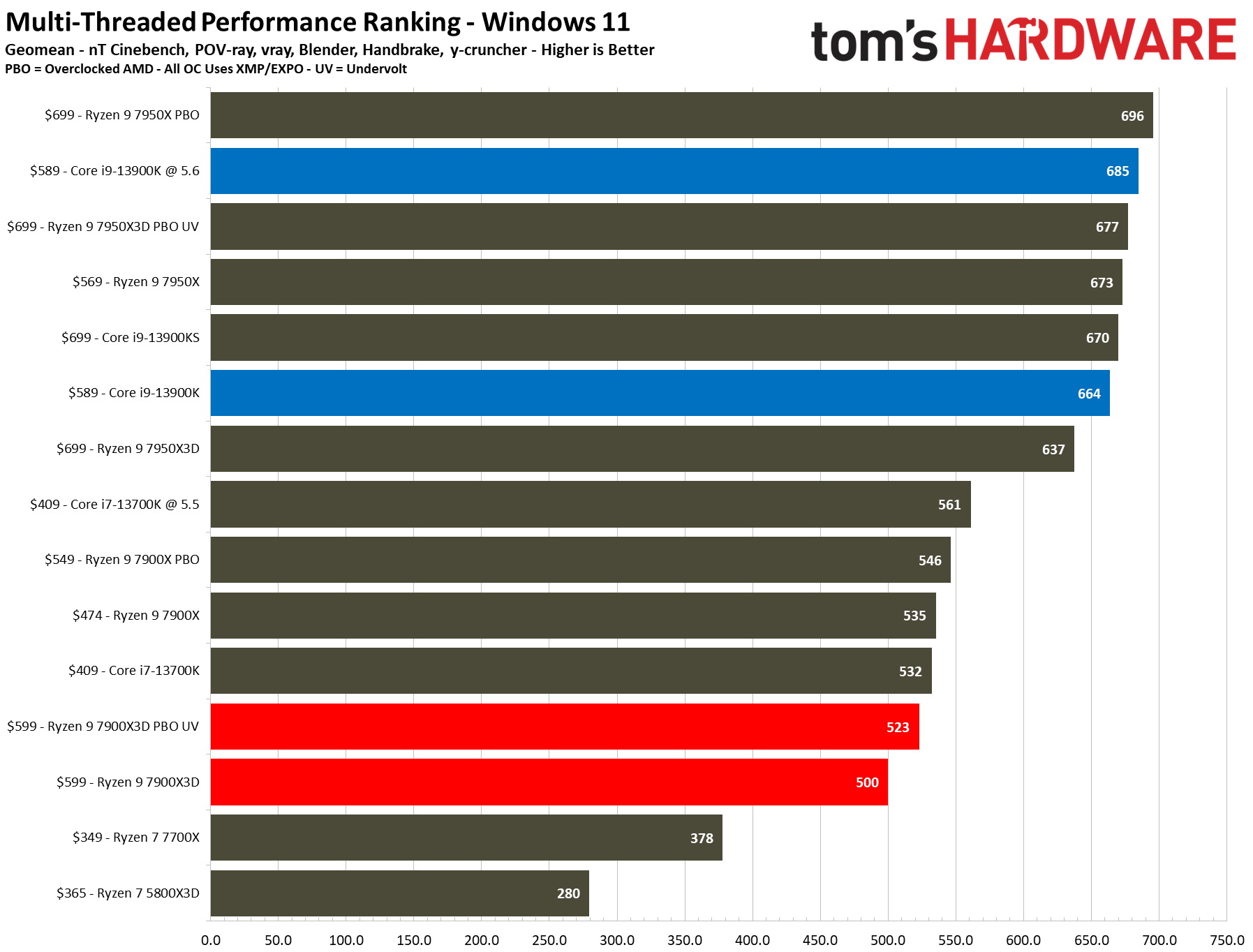
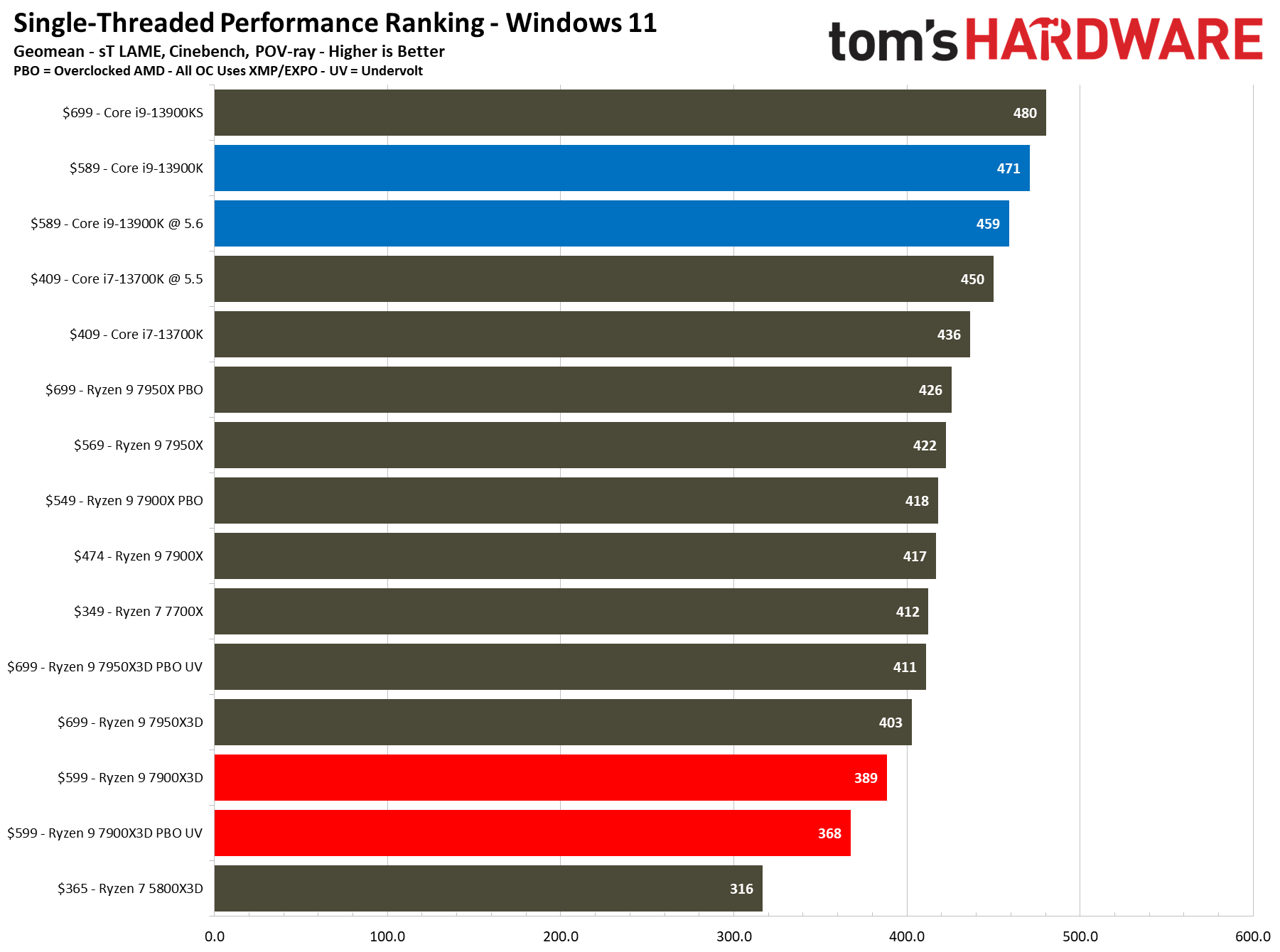
The first slides are simplified without the overclocking configs, while the remainder contains the full roster of tested configurations. We boil down productivity application performance into two broad categories: single- and multi-threaded. These slides show the geometric mean of performance in several of our most important tests in each category, but be sure to look at the individual benchmark results below.
The 3D V-Cache tech delivers explosive performance gains in gaming, but it also results in slightly lower performance in productivity applications due to power and thermal constraints — on paper, we’re looking at a 68W peak power reduction (42% less) for the 7900X3D compared to its vanilla 7900X counterpart, so we know the Ryzen 9 7900X3D will be somewhat slower.
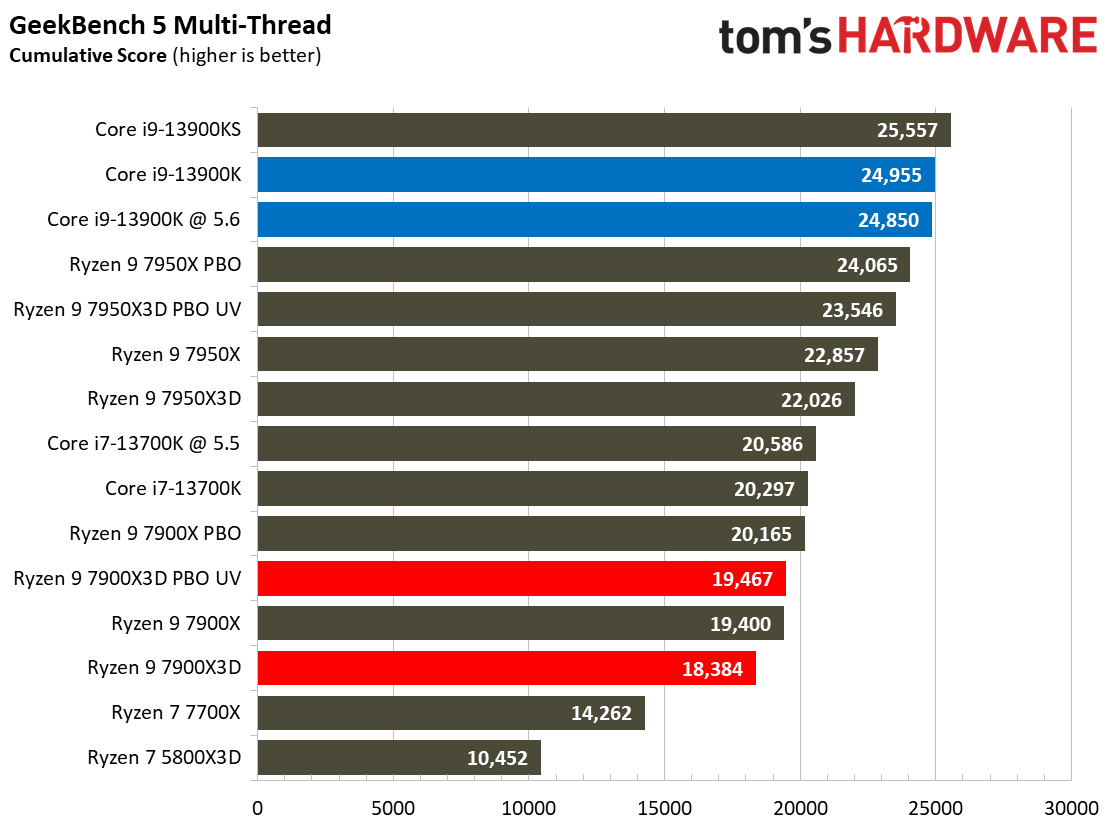
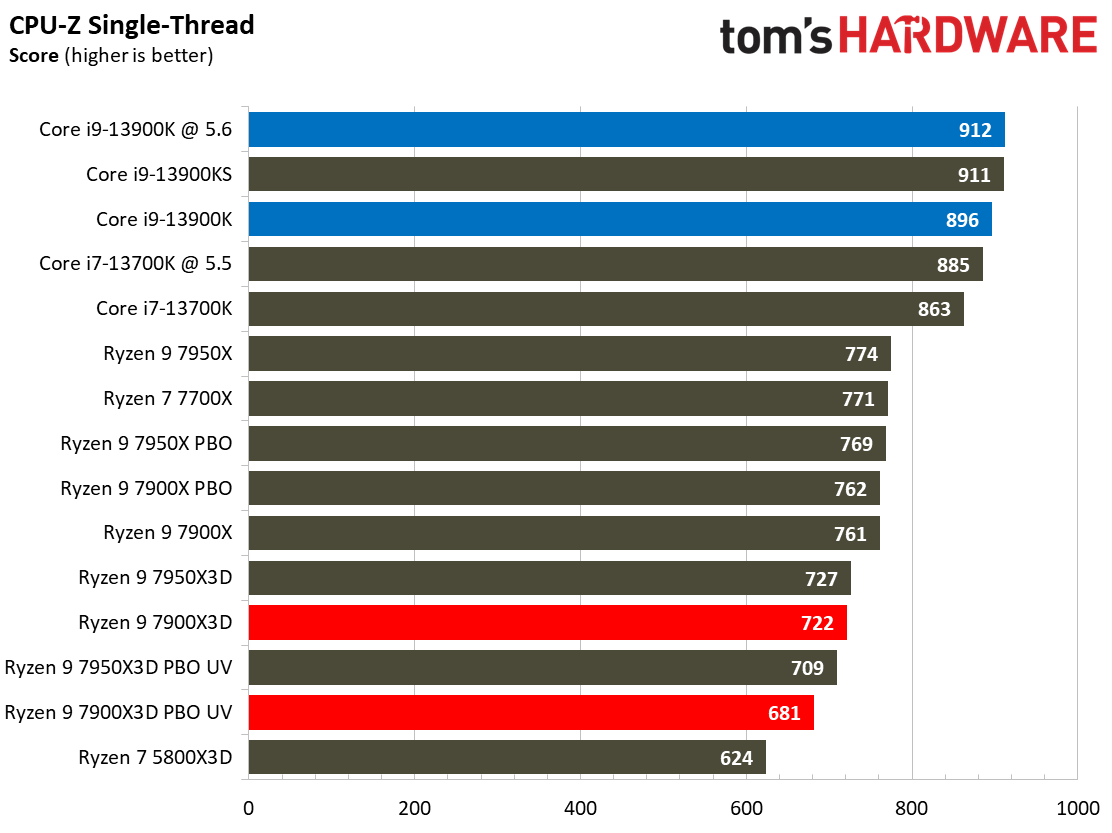
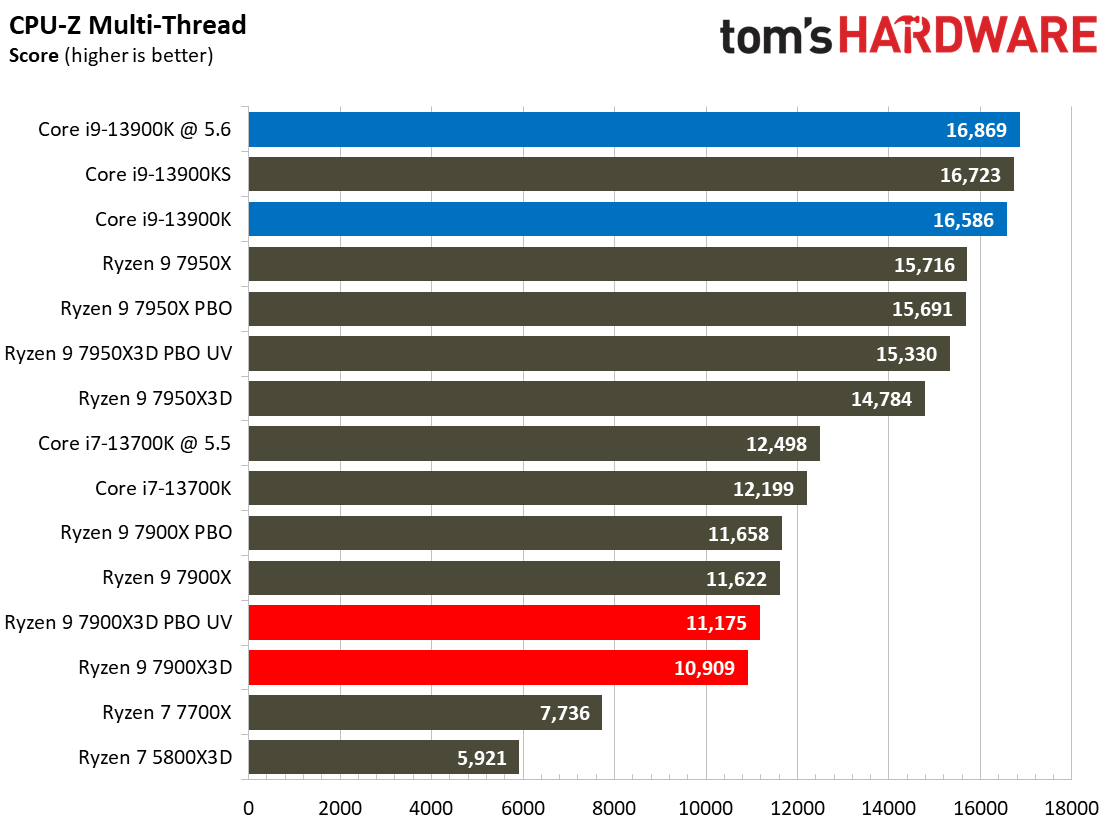
As such, it's no surprise that the Ryzen 9 7900X is 7% faster than the 7900X3D in this cumulative measure of threaded applications and 7% faster in single-threaded work.
Once again, the Ryzen 9 7950X3D outshines the 7900X3D. The 7950X3D is 27% faster in threaded work and 4% faster in single-threaded applications. That makes it hard to justify not plunking down 15% more cash for the 7950X3D to get the big payoff in threaded applications and multitasking.
The Core i9-13900K also shines in comparison. The 13900K is 21% faster than the standard Ryzen 9 7900X3D configuration in single-threaded work and 32% faster in threaded applications. Overclocking the 13900K and the 7900X3D brings those deltas to 18% and 30% in single- and multi-threaded work, respectively. Do keep in mind that the 7900X3D consumes far less power and will generate much less heat than the 13900K, but that comes at the expense of performance.
The Core i7-13700K is also a viable alternative in applications — it is 6% faster in multi-threaded and 12% faster in single-threaded work than the 7900X3D at stock settings.
The 8-core 5800X3D isn’t the best comparison to the 12-core 7900X3D, but it highlights just how much AMD has improved the performance of its X3D chips by bringing the tech to higher core count chips with a newer core architecture — the 7900X3D is 23% faster in single-threaded and 78% faster in multi-threaded work than the Ryzen 7 5800X3D.
We didn't find as much success undervolting with the 7900X3D as with the 7950X3D. While undervolting the 7950X3D actually delivered faster performance than its stock settings in single-threaded work, it resulted in lower performance in single-threaded work with the 7900X3D. We retested and re-optimized the configuration several times, but to no avail. Notably, PBO and undervolting capabilities vary by chip, so your mileage may vary, and we have seen this tendency with previous-gen Ryzen processors in the past. Meanwhile, we did see the expected improvements in many multi-threaded workloads.
| Tom's Hardware | Multi-Thread | Single-Thread |
| $569 — Ryzen 9 7950X | 100% | 87.9% |
| $699 — Core i9-13900KS | 99.5% | 100% |
| $589 — Core i9-13900K | 98.6% | 98.0% |
| $699 — Ryzen 9 7950X3D | 94.7% | 83.8% |
| $409 — Core i7-13700K | 79.1% | 90.8% |
| $599 - Ryzen 9 7900X3D | 74.2% | 80.9% |
| $358 — Ryzen 7 5800X3D | 41.5% | 65.9% |
Rendering Benchmarks on AMD Ryzen 9 7900X3D
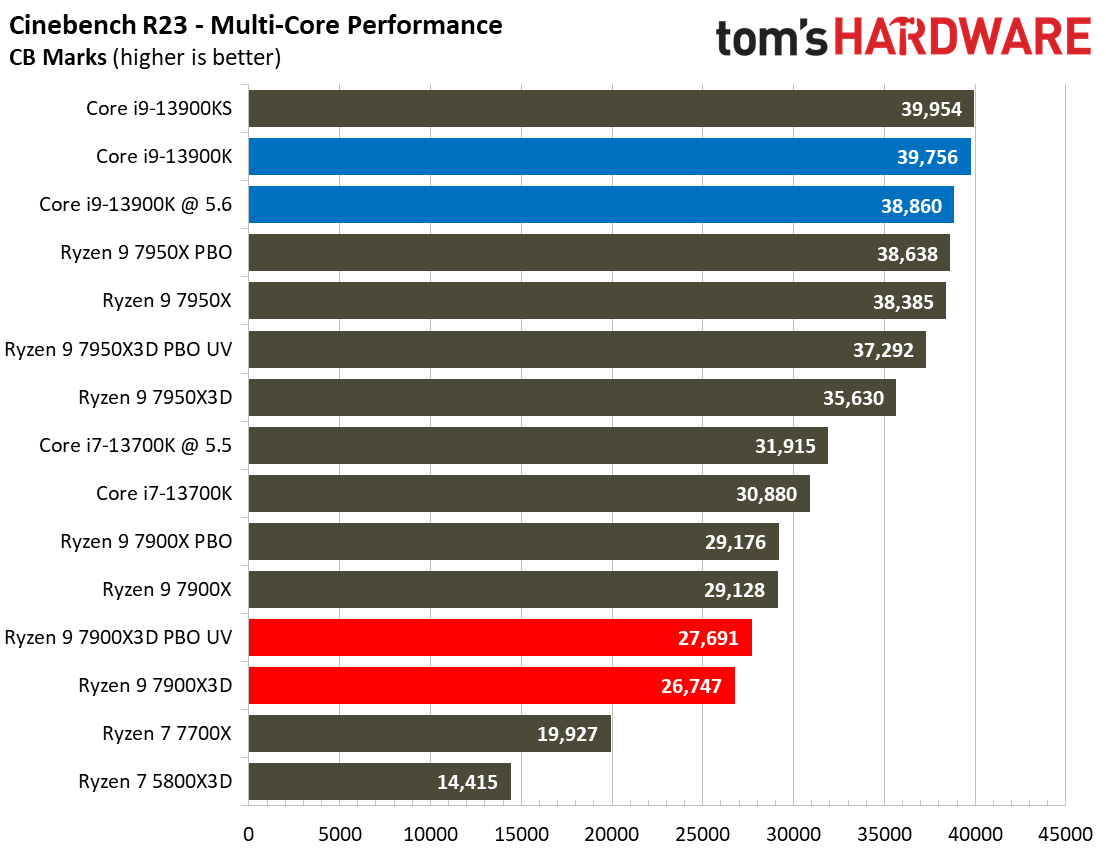
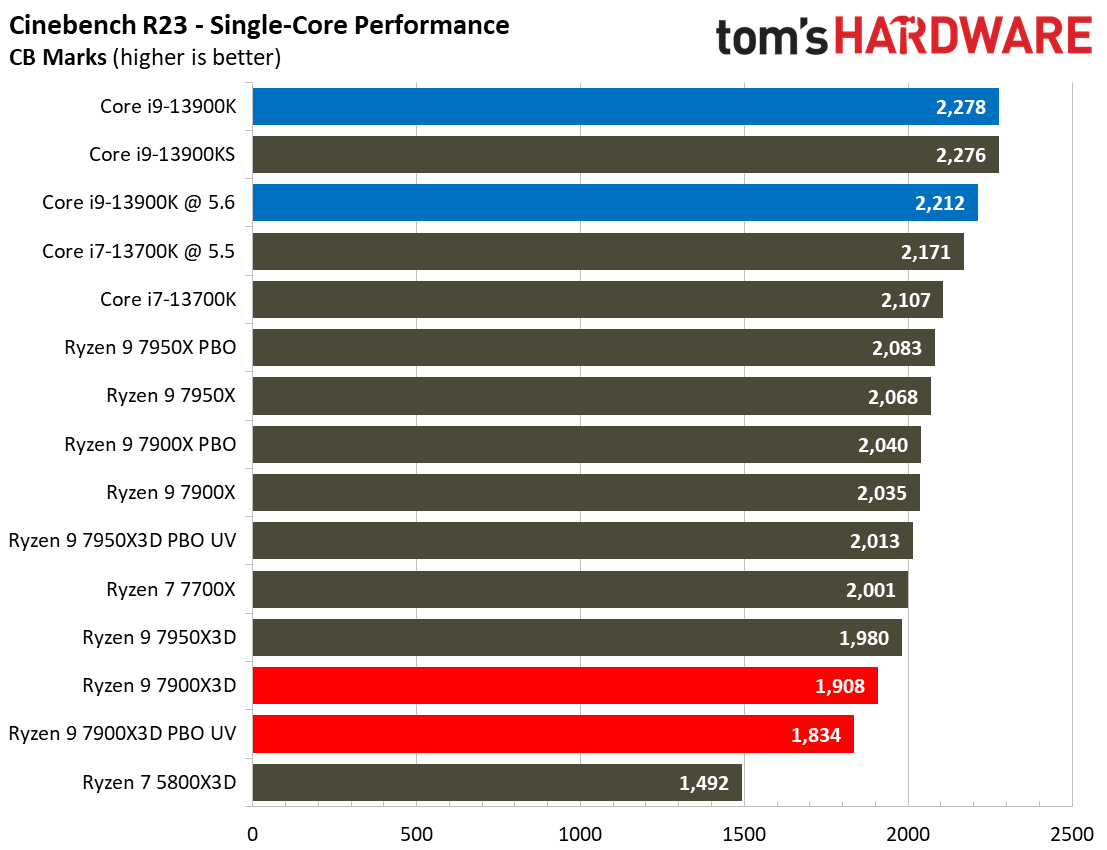
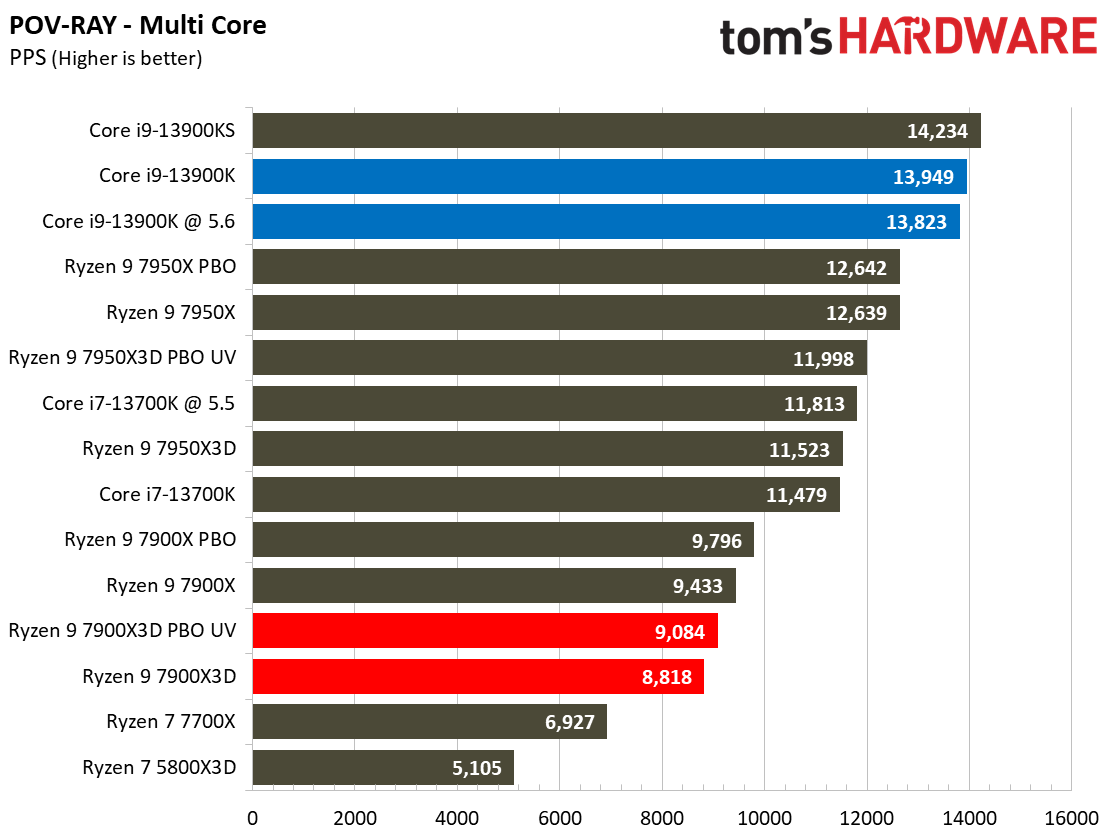
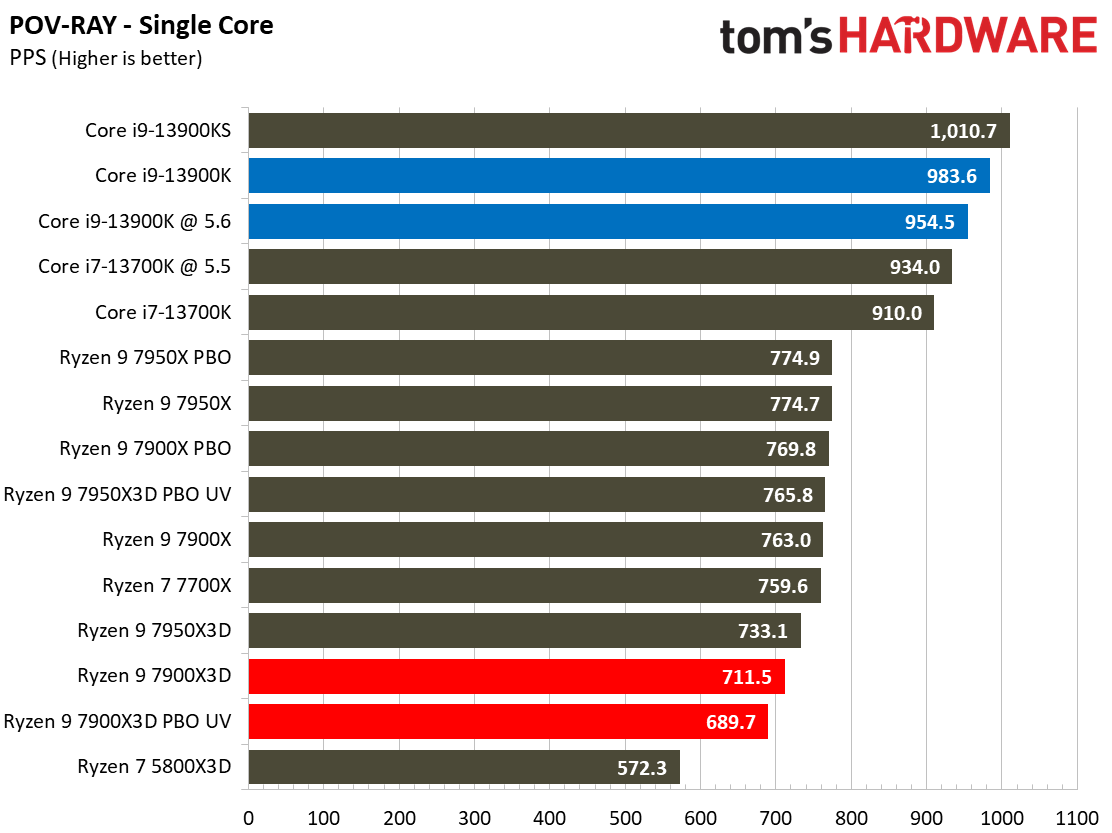
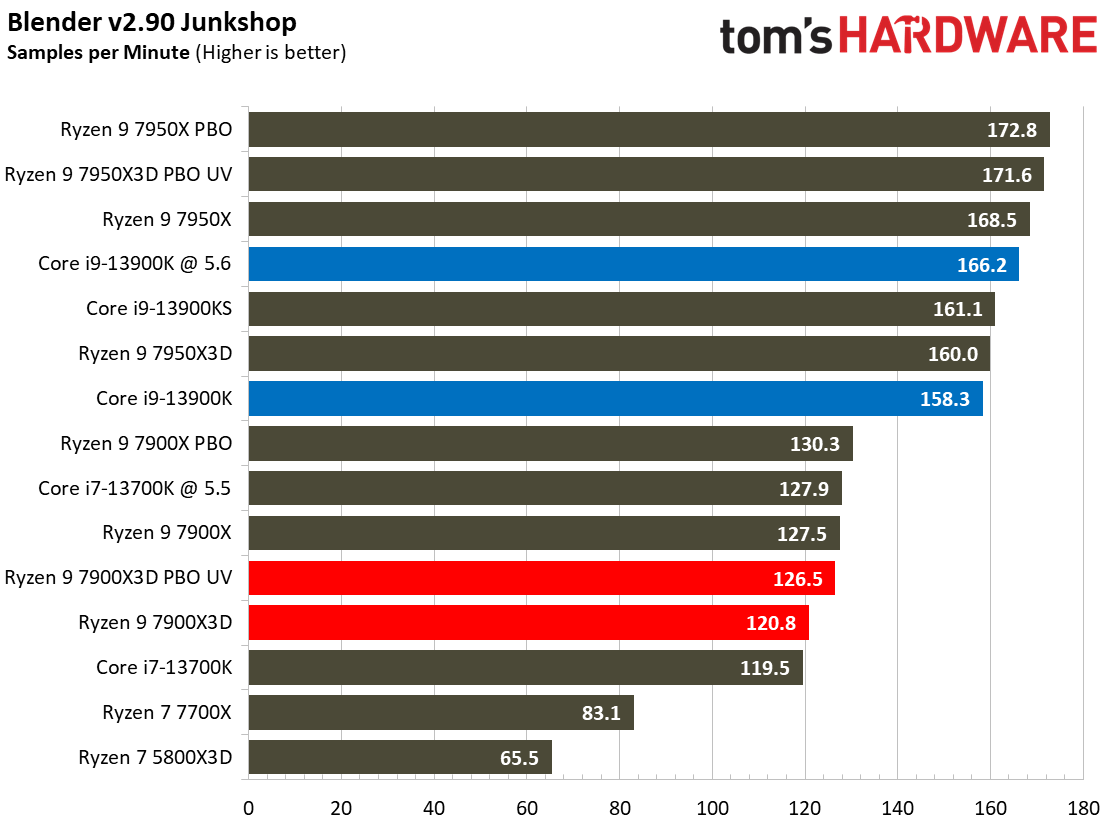
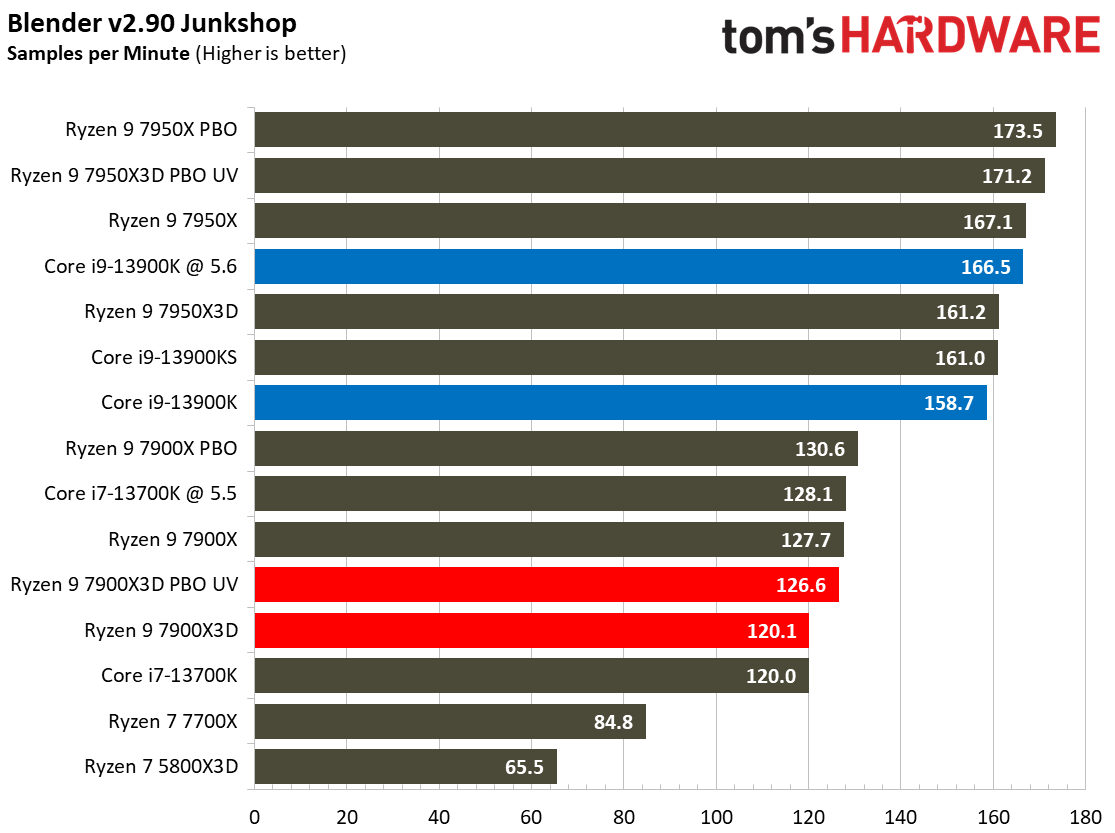
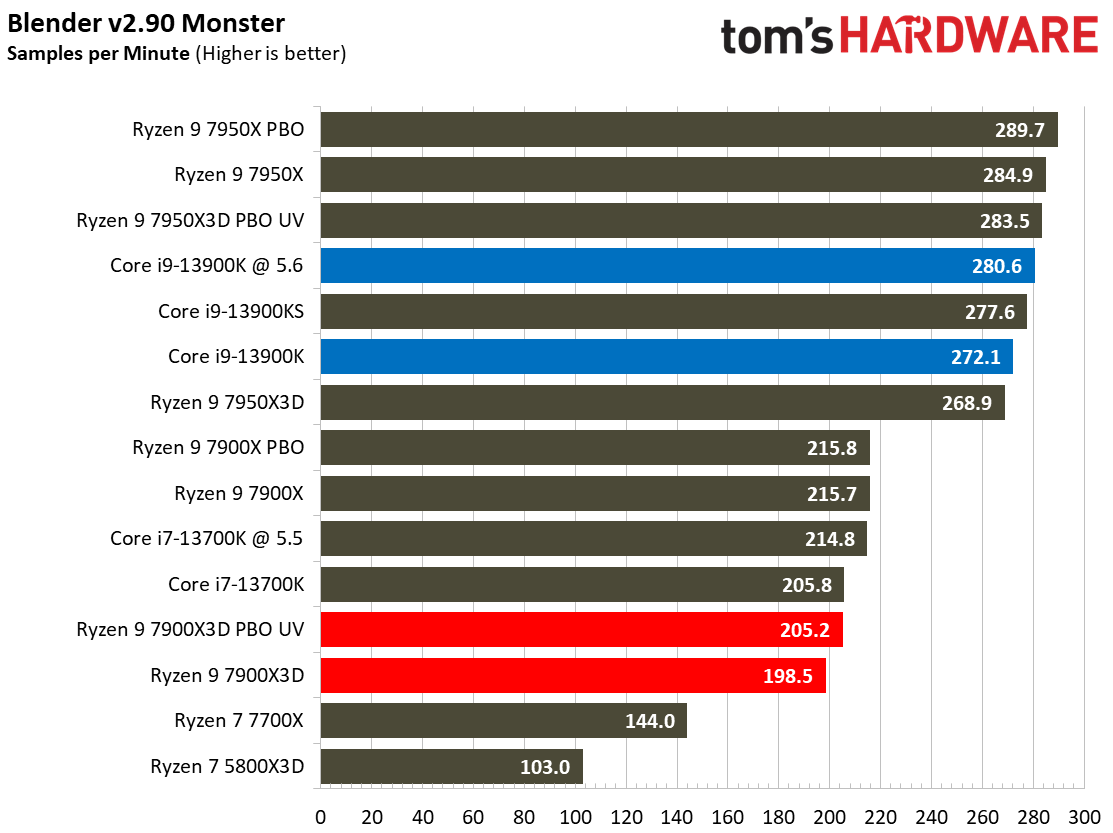
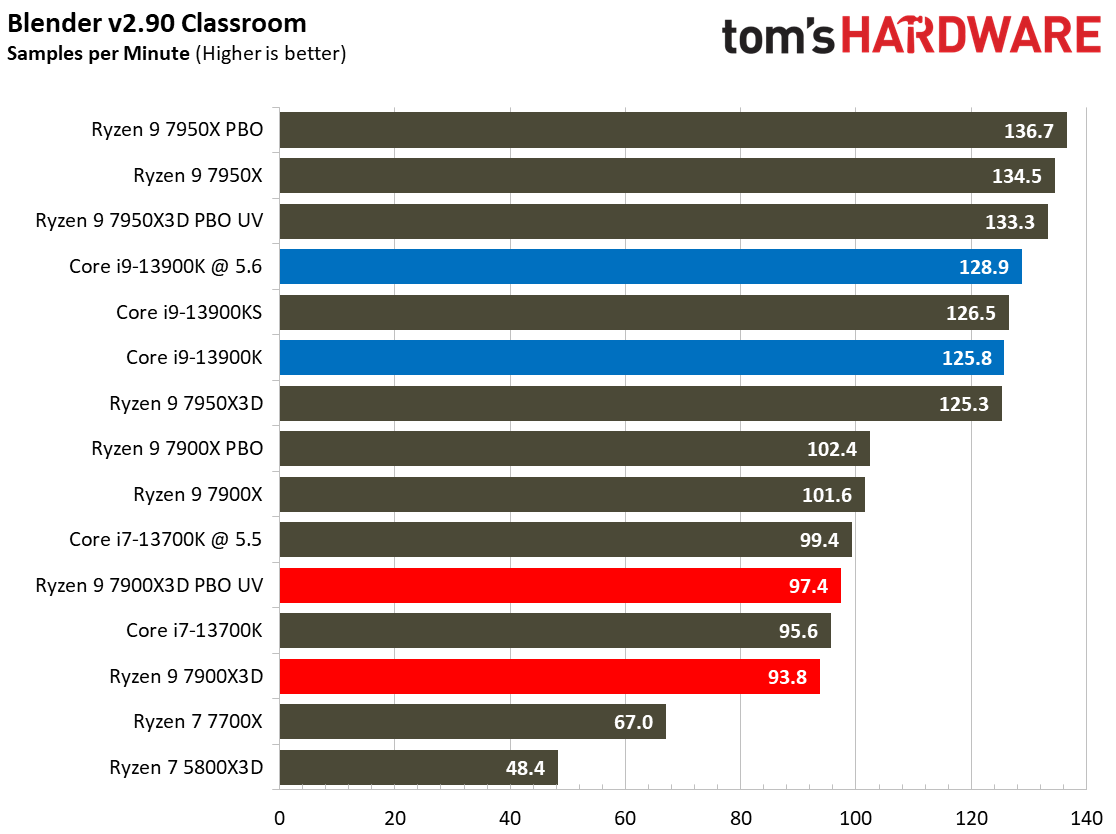
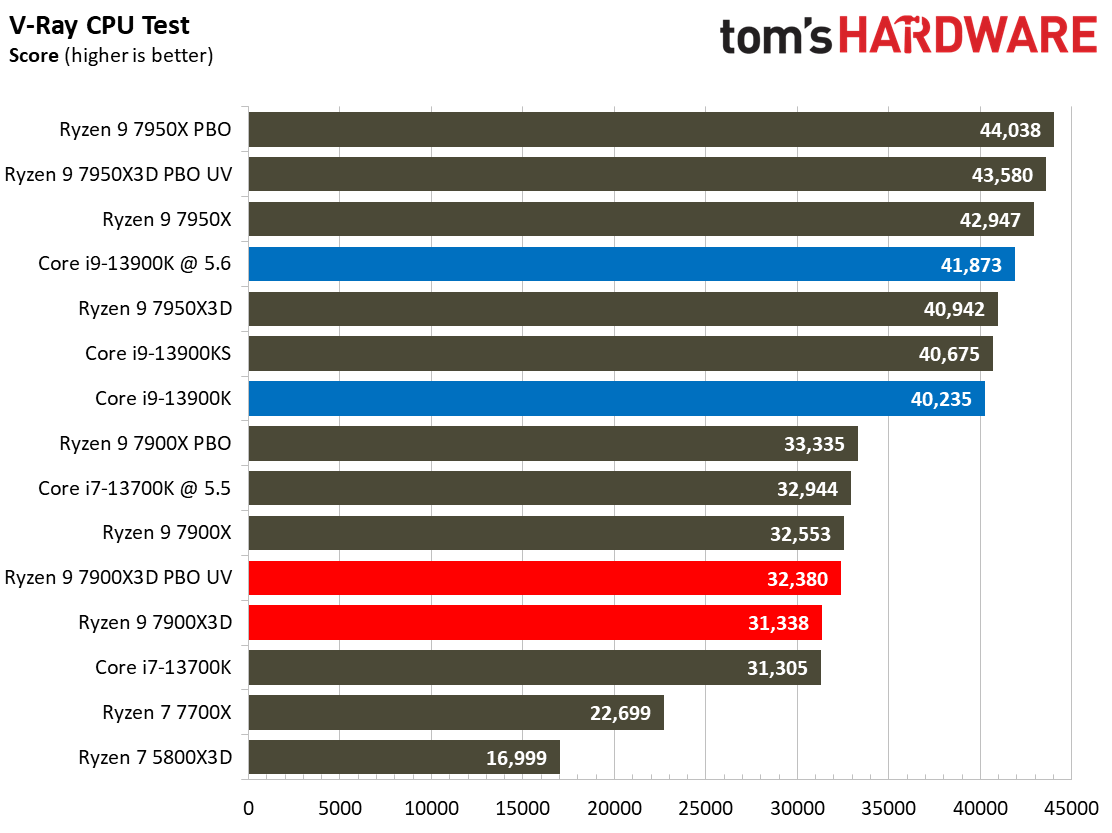
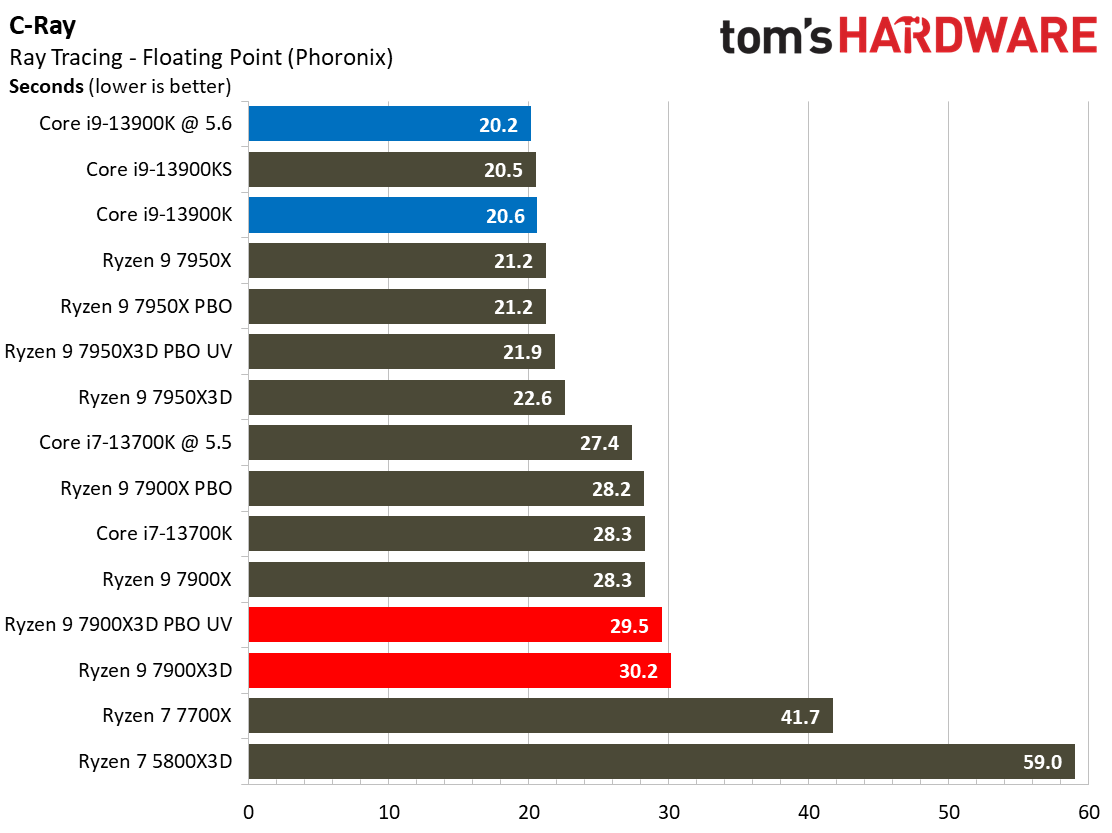
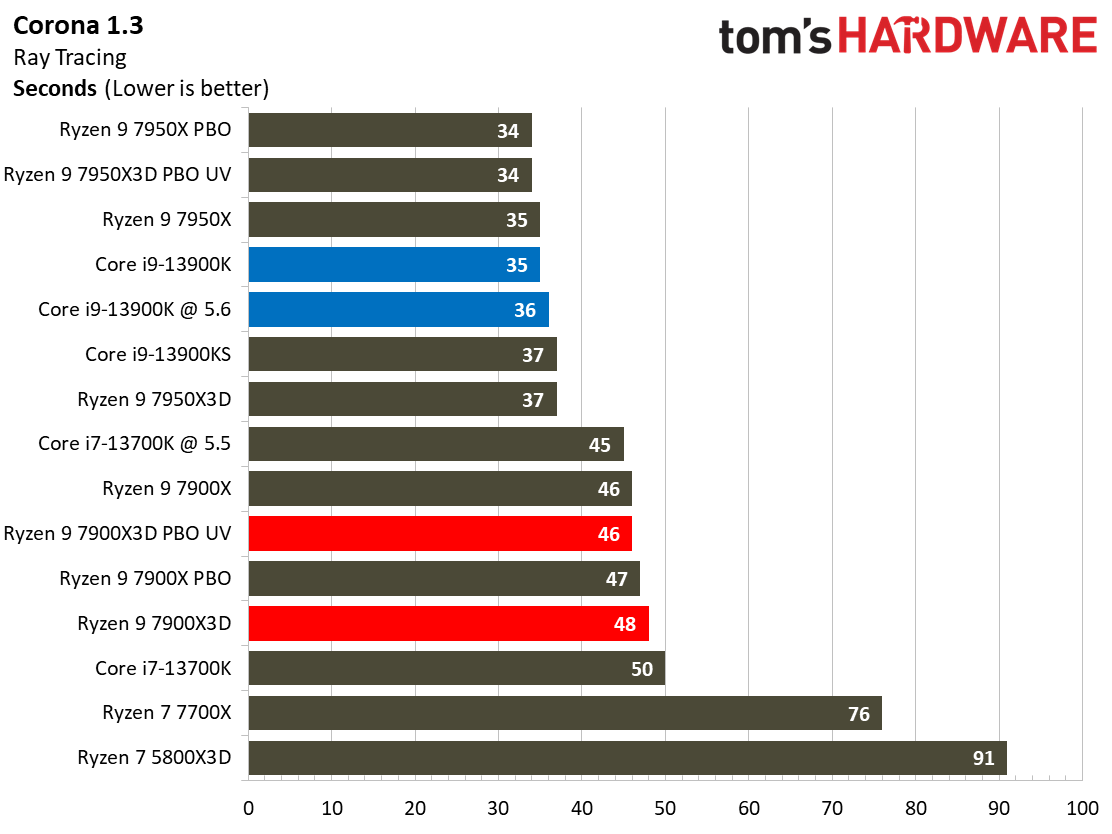
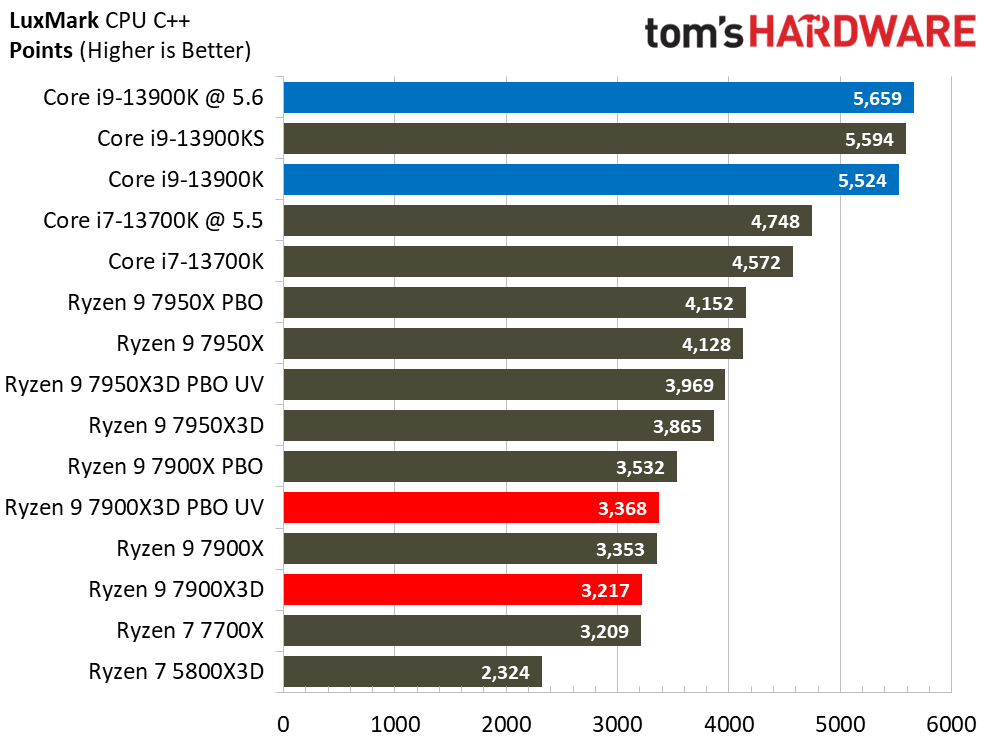
The Ryzen 9 7900X3D is significantly slower in heavily-threaded workloads than the vanilla 7900X, an unavoidable byproduct of its lower power thresholds. The 7900X3D lags its similarly-priced competitor, the $589 Core i9-13900K, by large margins, and often struggles to even tie the $409 Core i7-13700K, showing that it can't keep pace in productivity applications with significantly less expensive chips.
Engaging PBO and undervolting the 78900X3D helps in the threaded benchmarks but results in lower performance in single-threaded work. However, it doesn't improve the 7900X3D's footing against the other chips, which often extend their lead even further when overclocked.
Encoding Benchmarks on AMD Ryzen 9 7900X3D
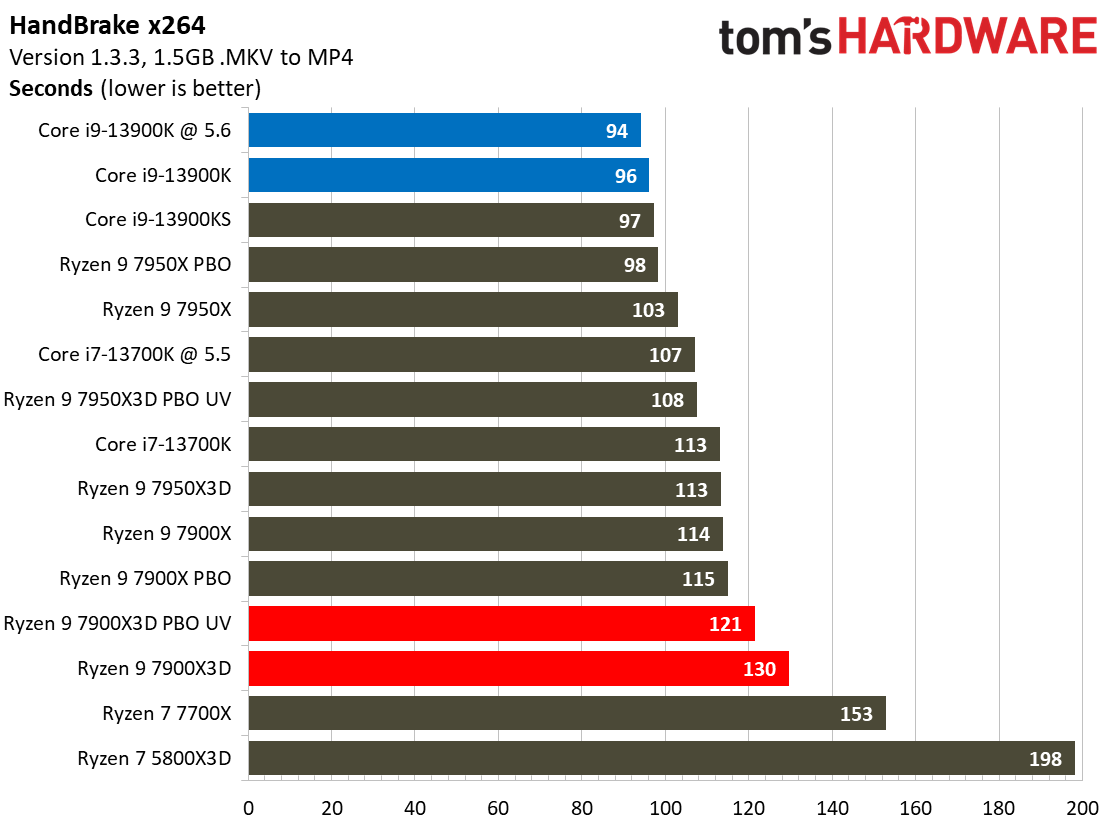
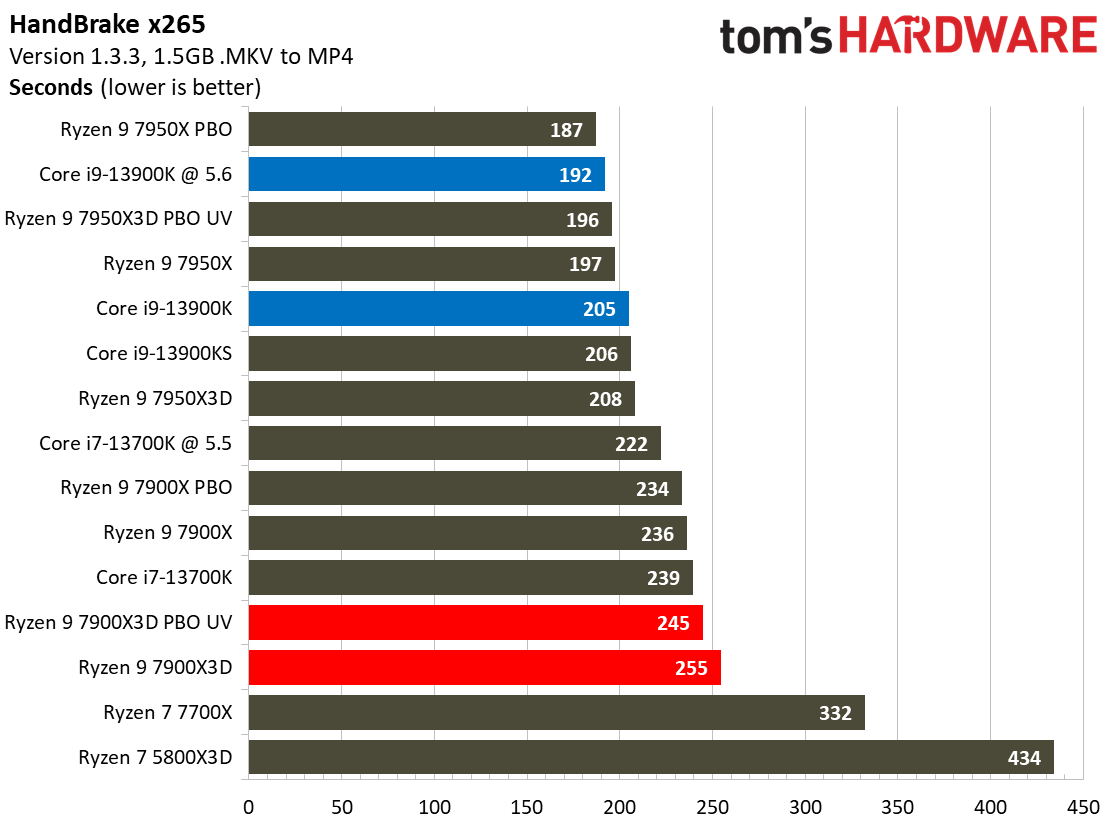
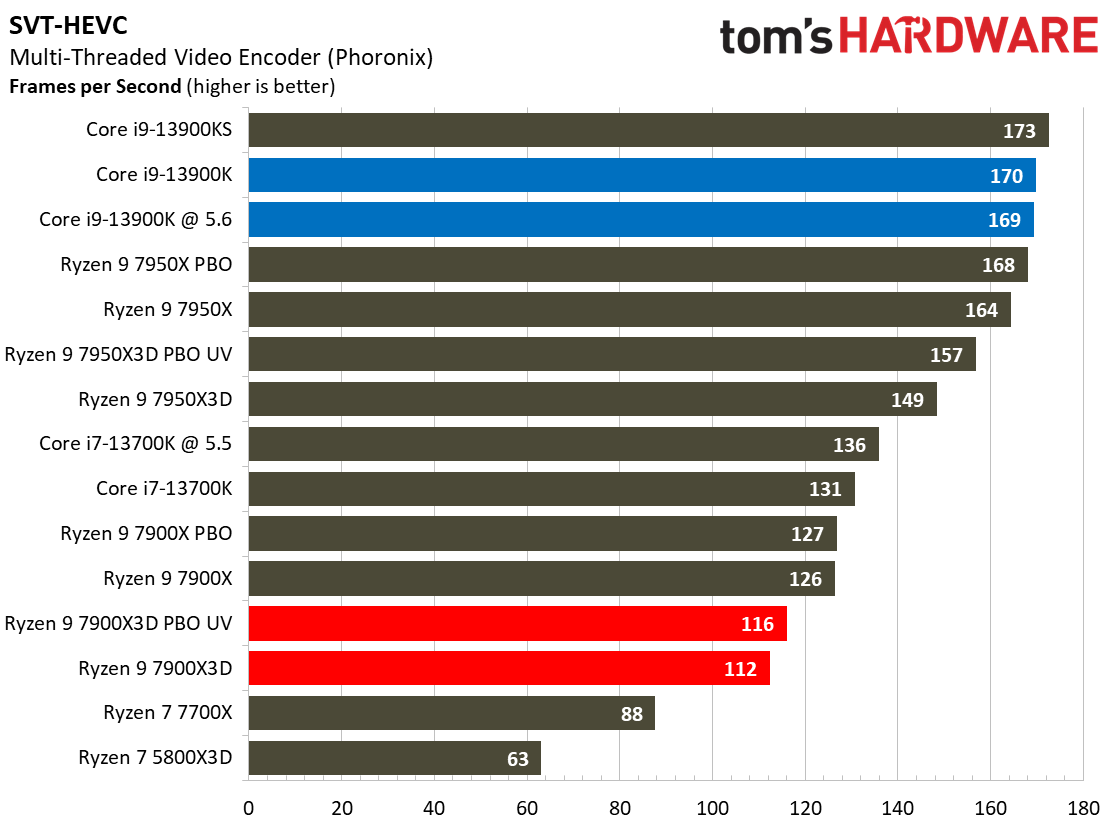
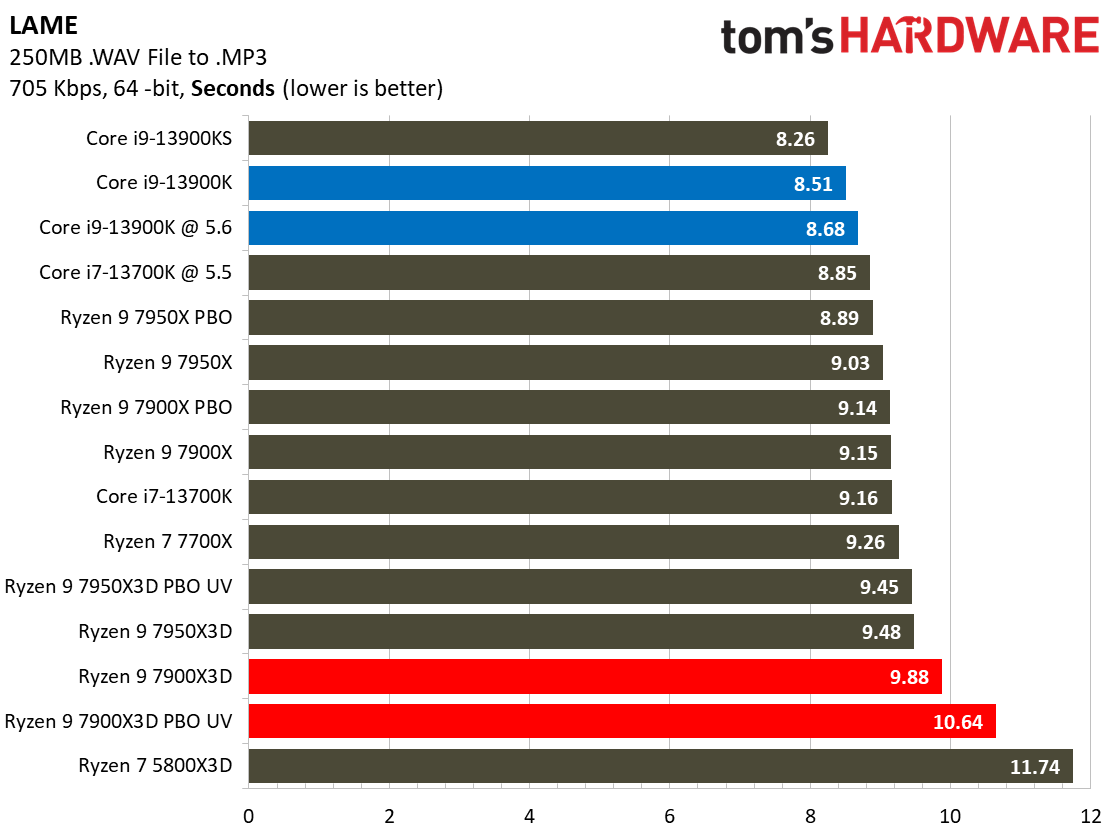
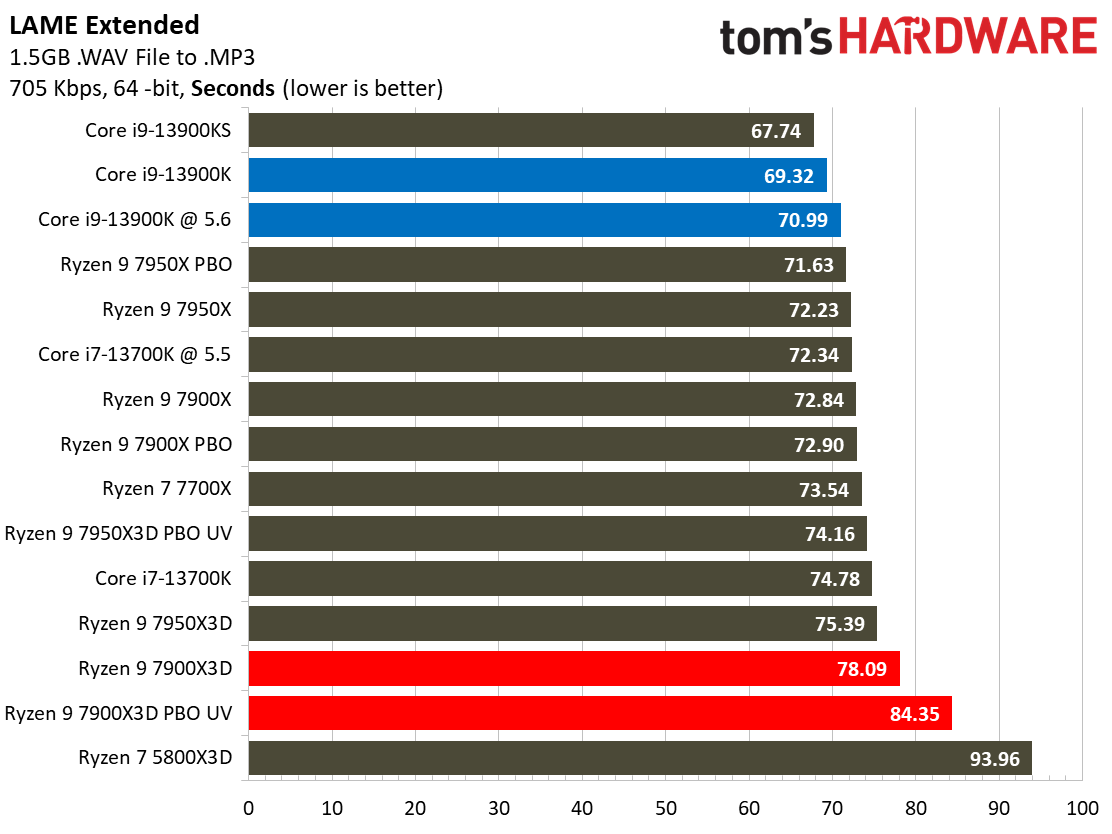
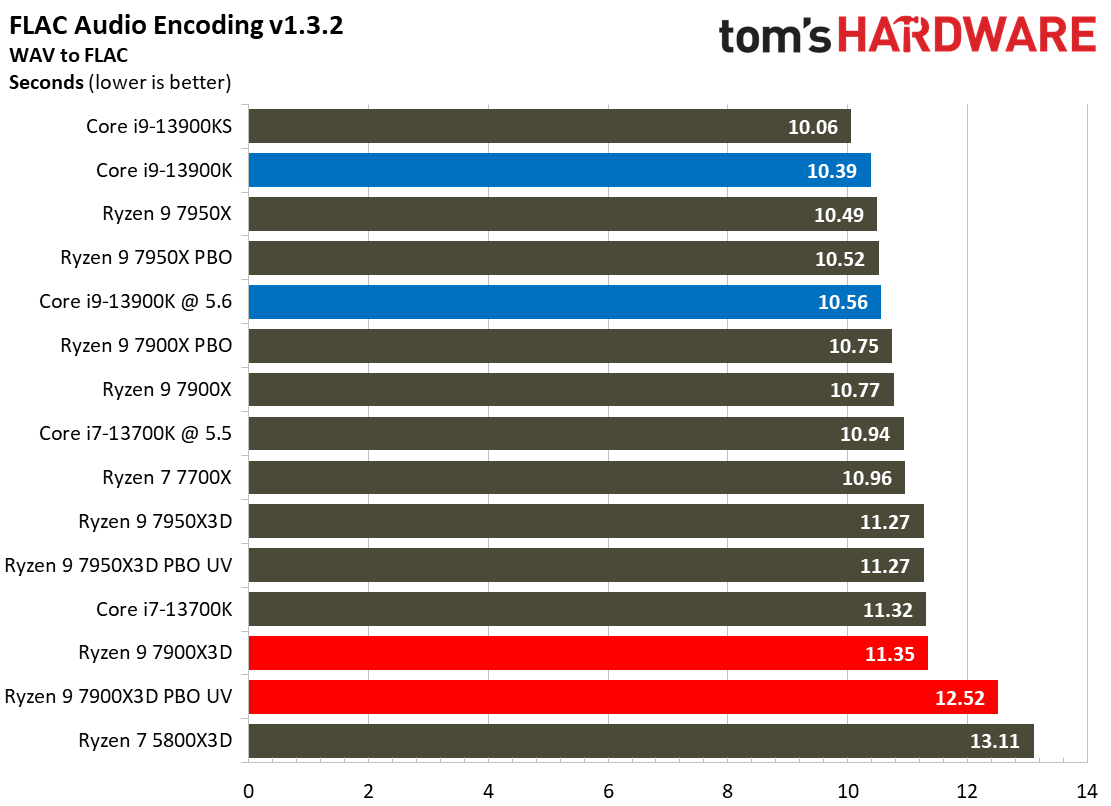
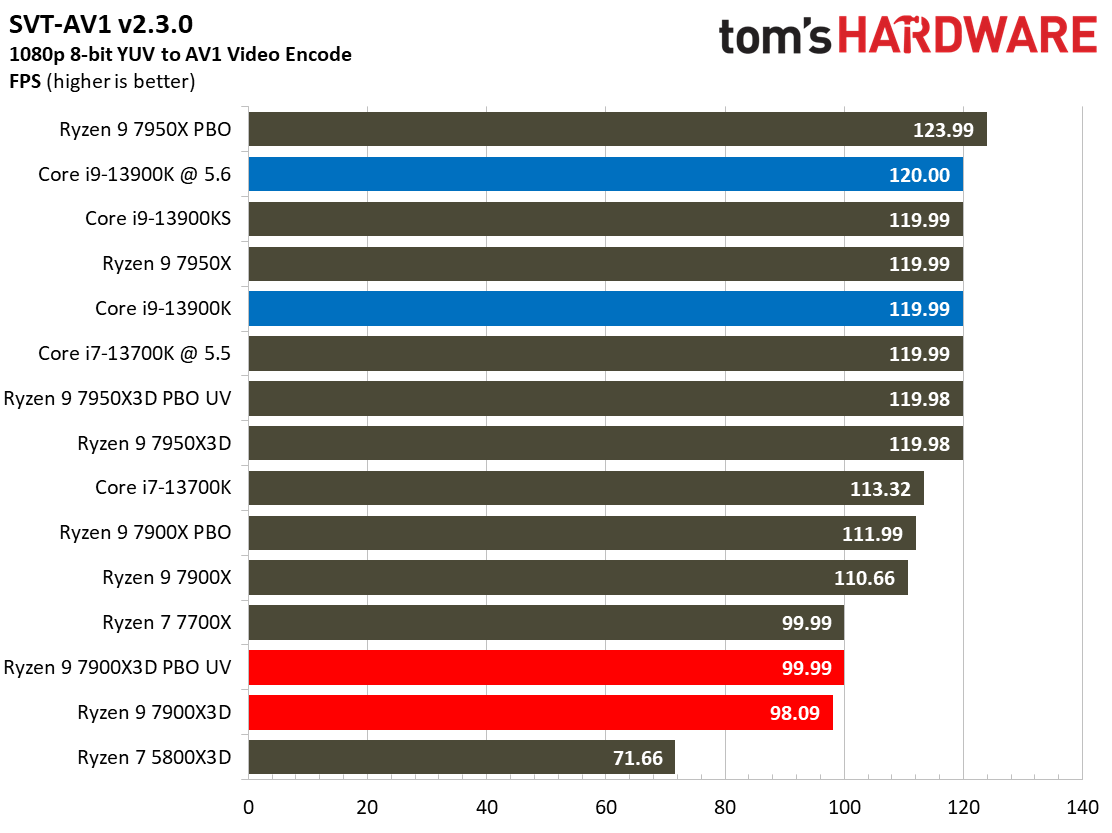
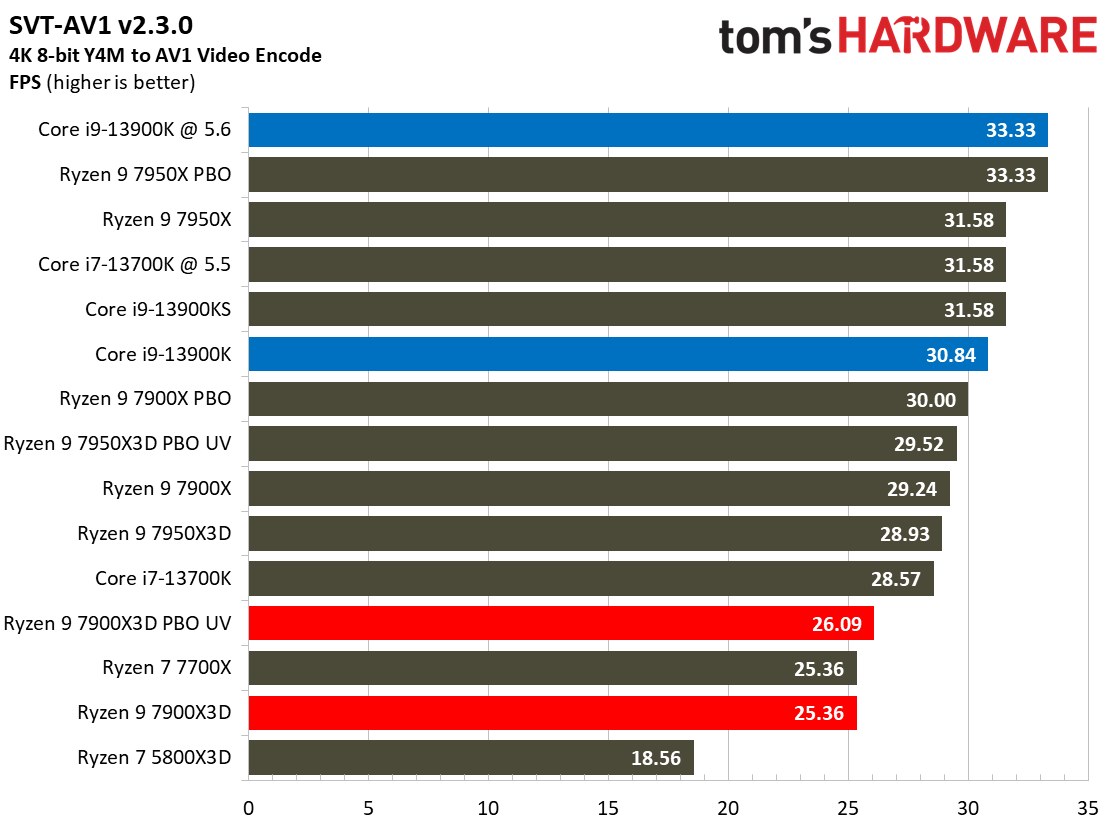
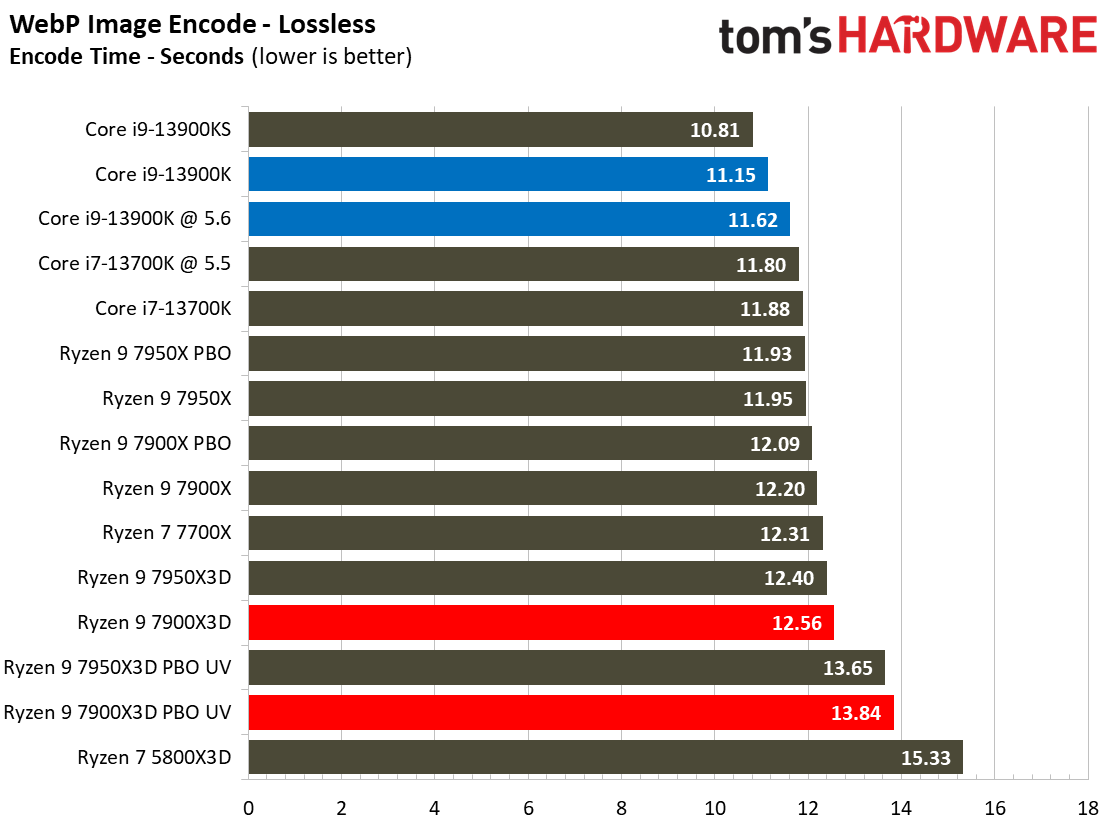
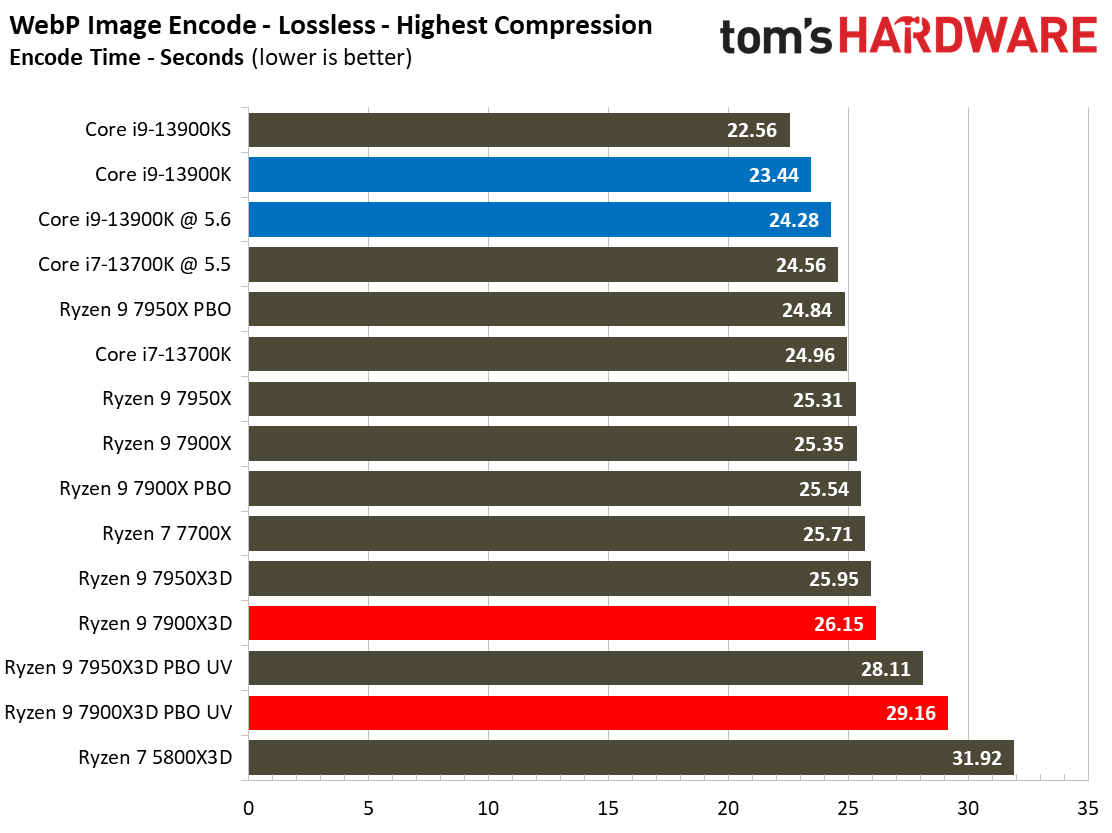
Most encoders tend to be either heavily threaded or almost exclusively single-threaded — it takes an agile chip to master both disciplines. Handbrake, SVT-HEVC, and SVT-AV1 serve as our threaded encoders, while LAME, FLAC, and WebP are indicative of how the chips handle lightly-threaded engines.
The Ryzen 9 7900X3D trails in the lightly-threaded applications — the other modern chips have much higher peak boost clock rates. The 7900X3D also isn't as fast as competing chips in the threaded benchmarks, either.
Adobe, Web Browsing, Office, and Productivity on AMD Ryzen 9 7900X3D
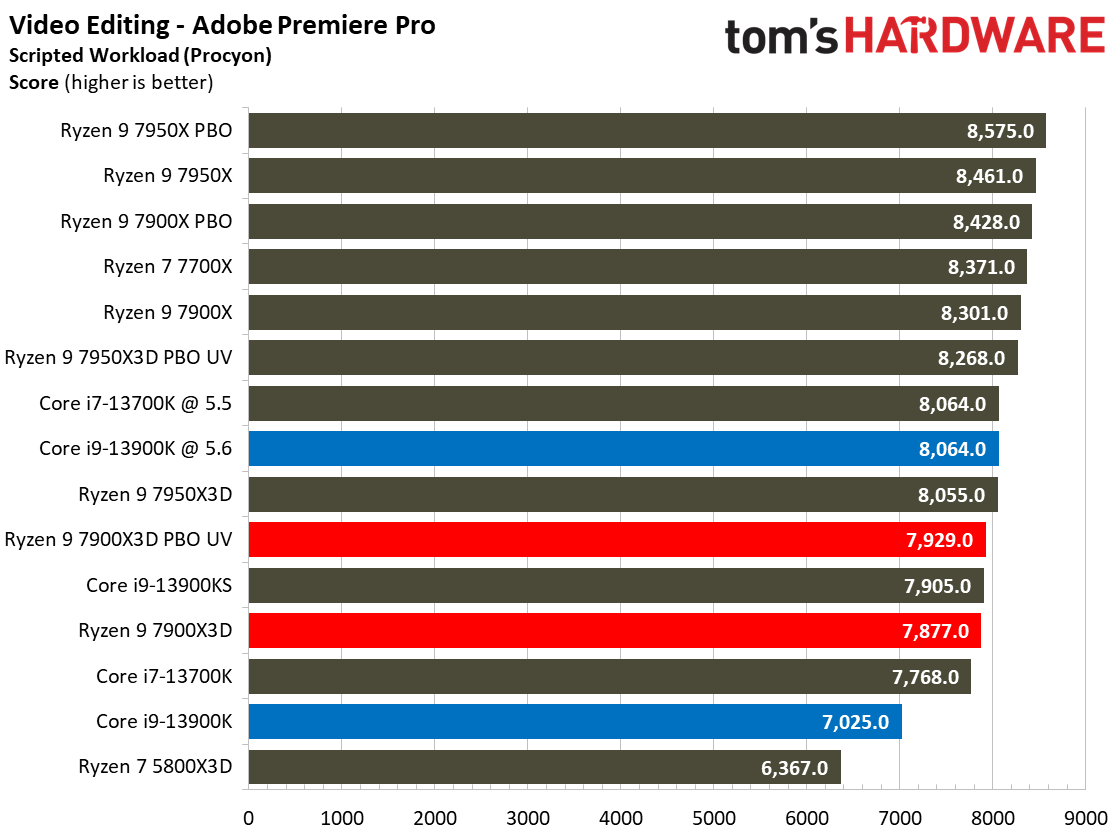
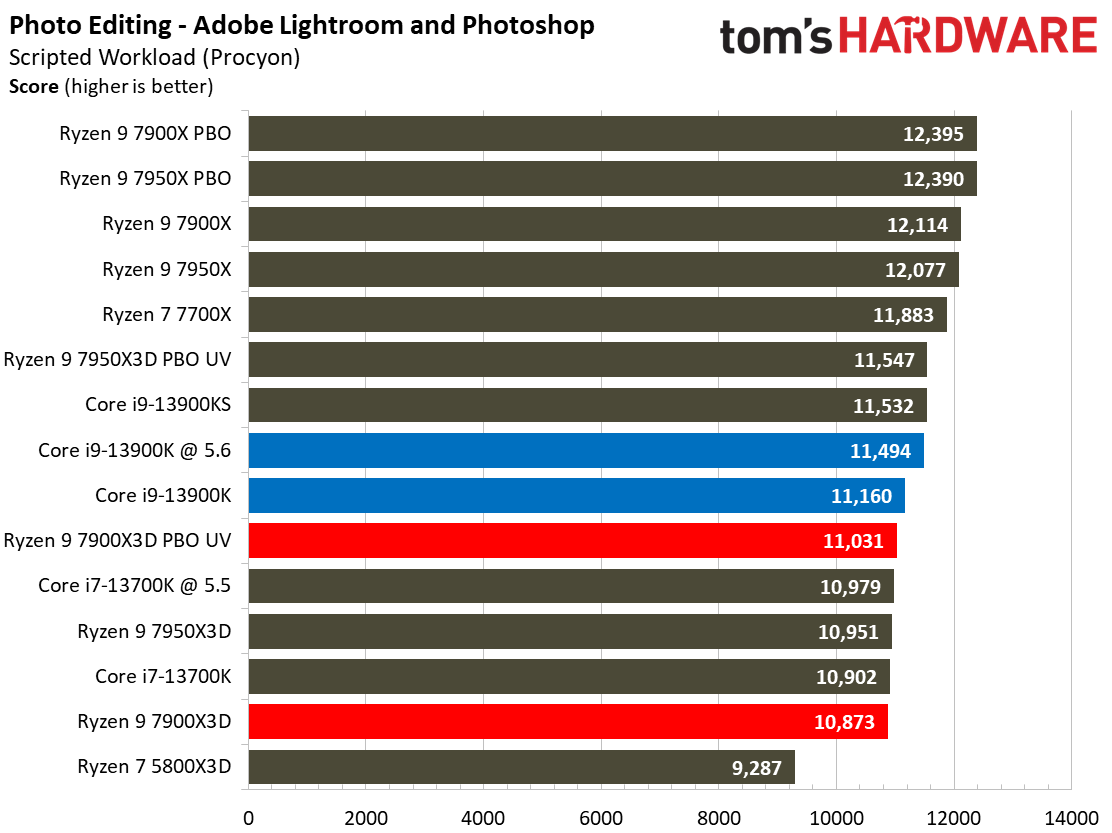
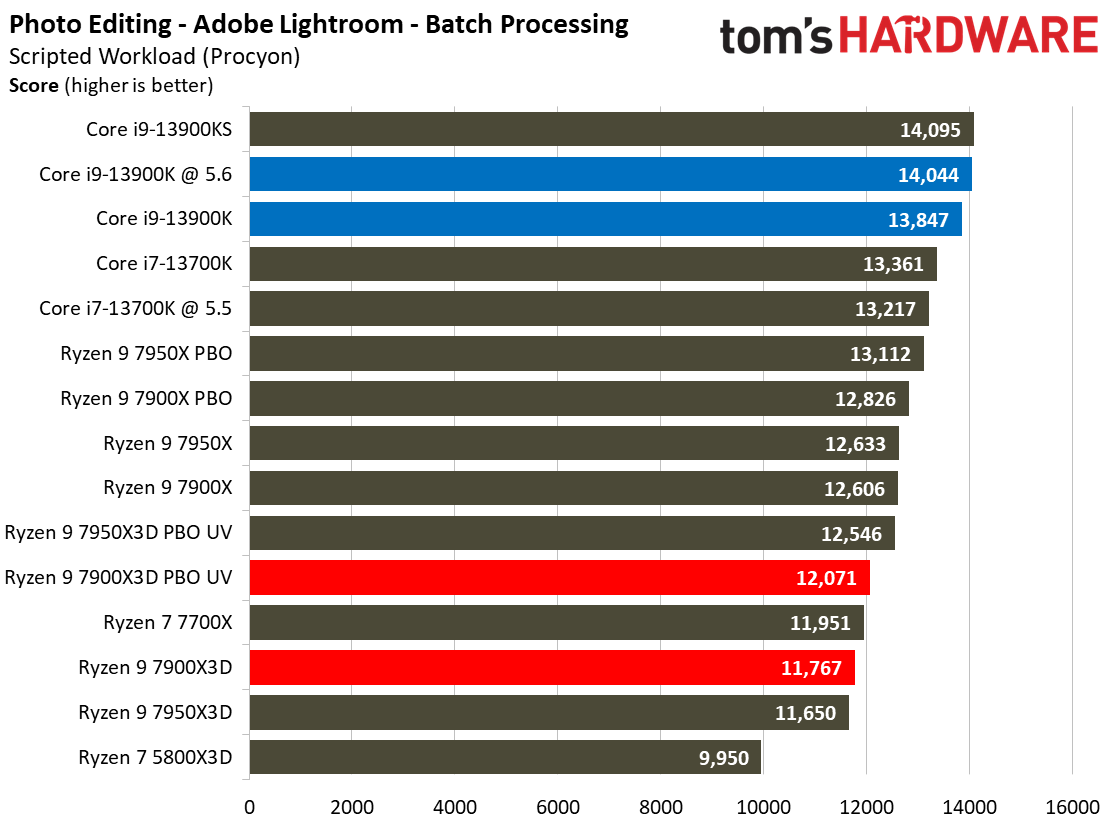
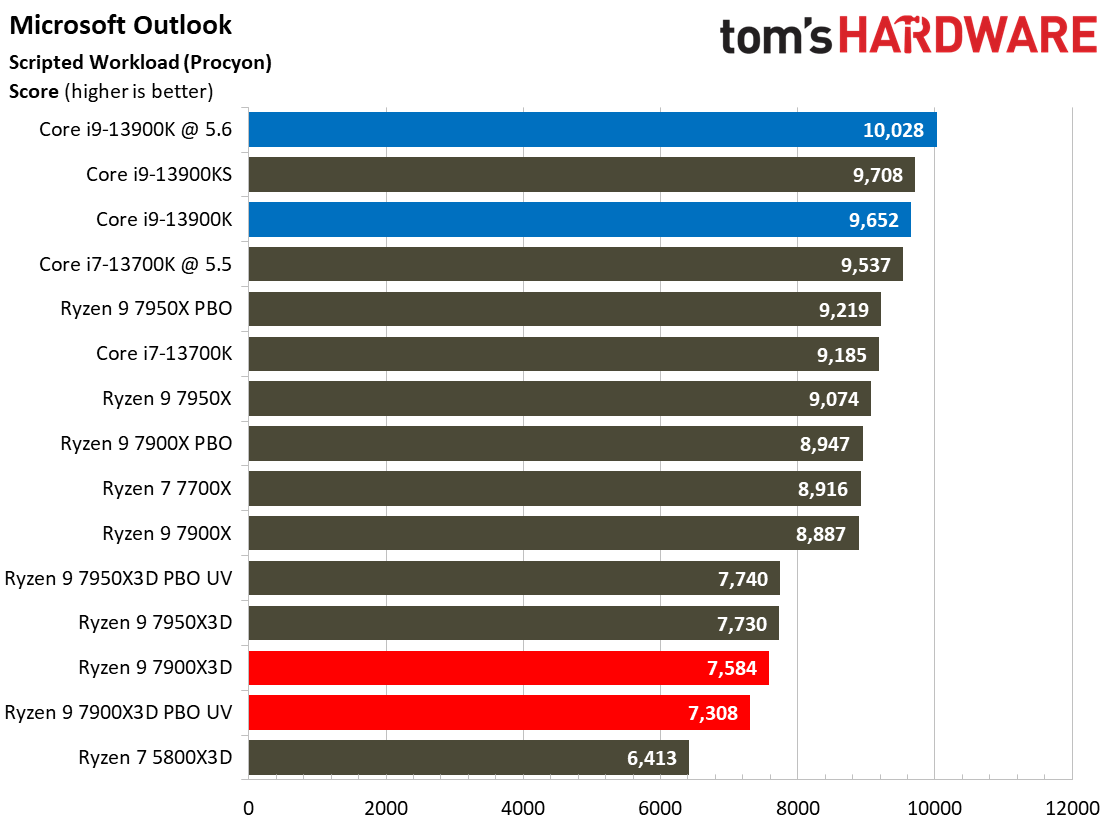
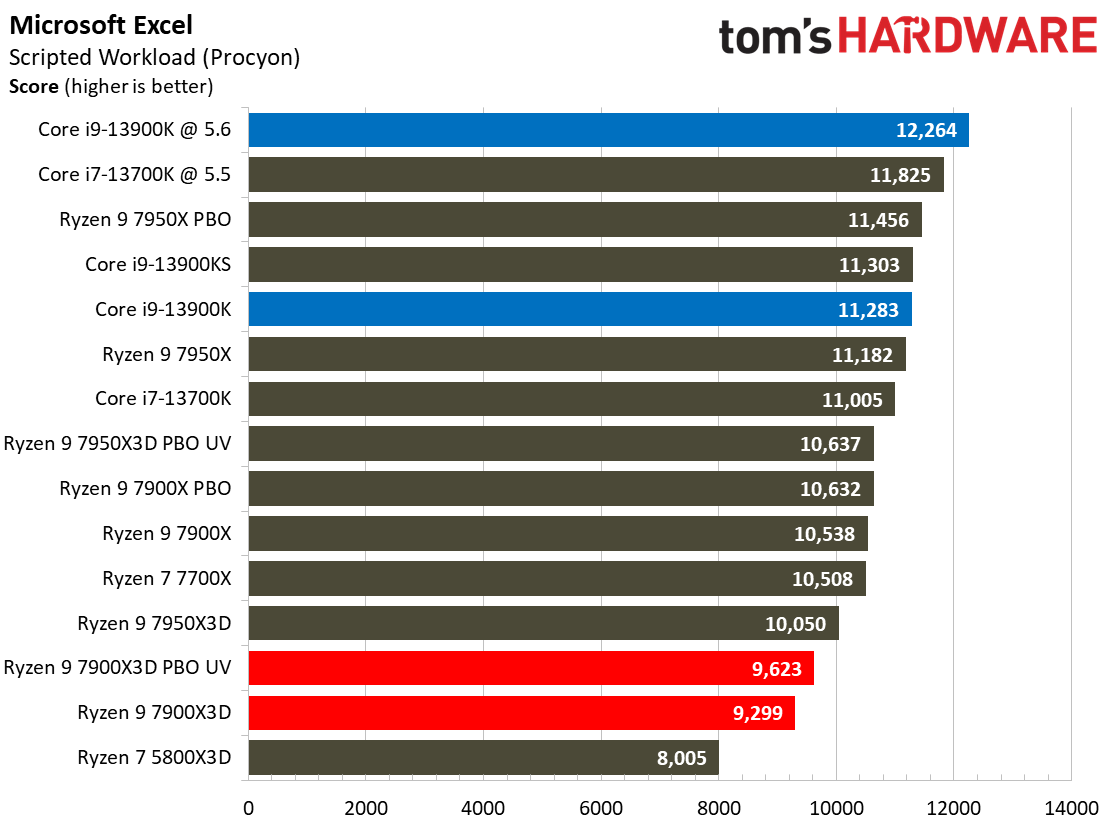
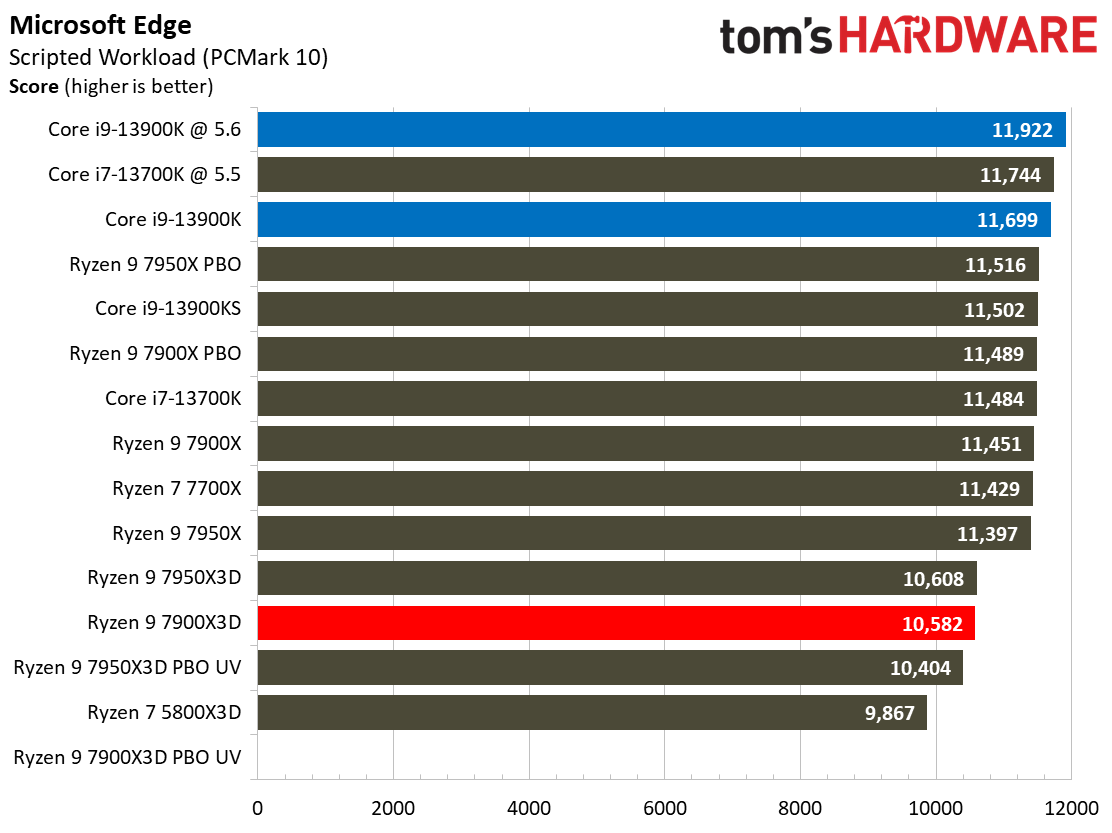
The Ryzen 9 7900X3D doesn't deliver enough performance to justify its price tag in this category of benchmarks, you'll find similar or better performance from much lower-priced alternatives.
Compilation, Compression, AI Chess Engines, AVX-512 Performance on AMD Ryzen 9 7900X3D
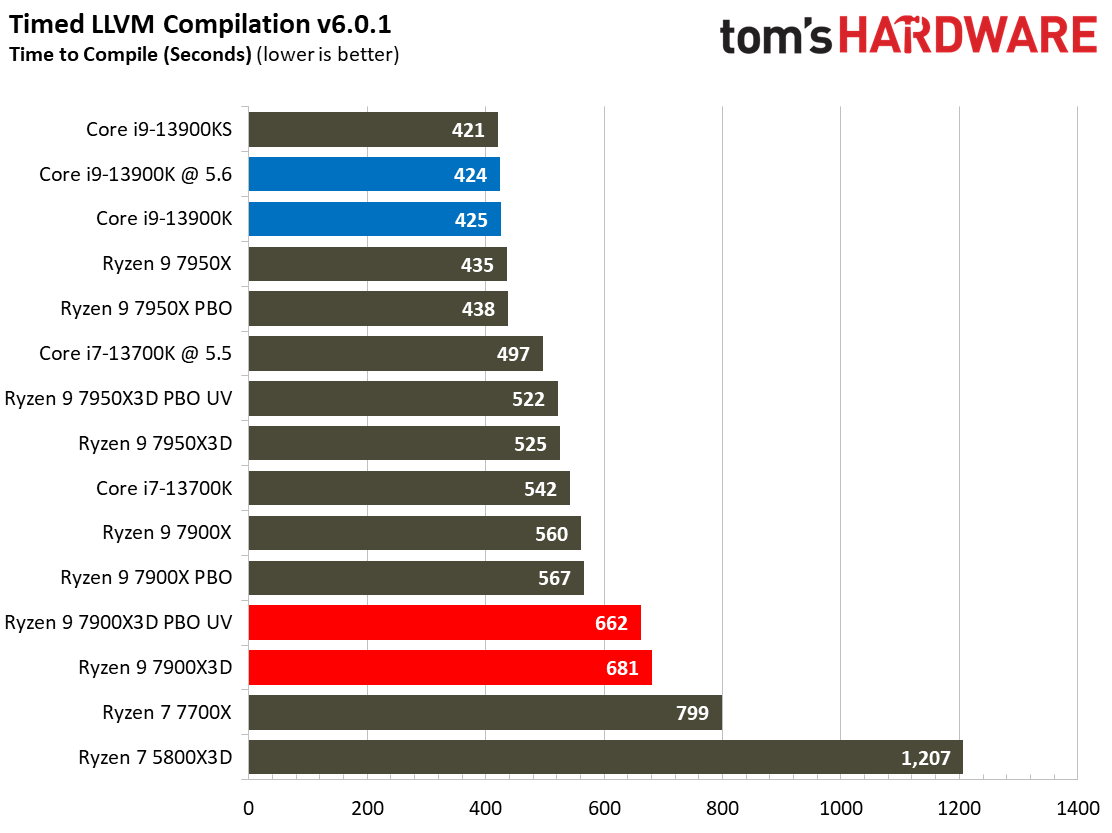
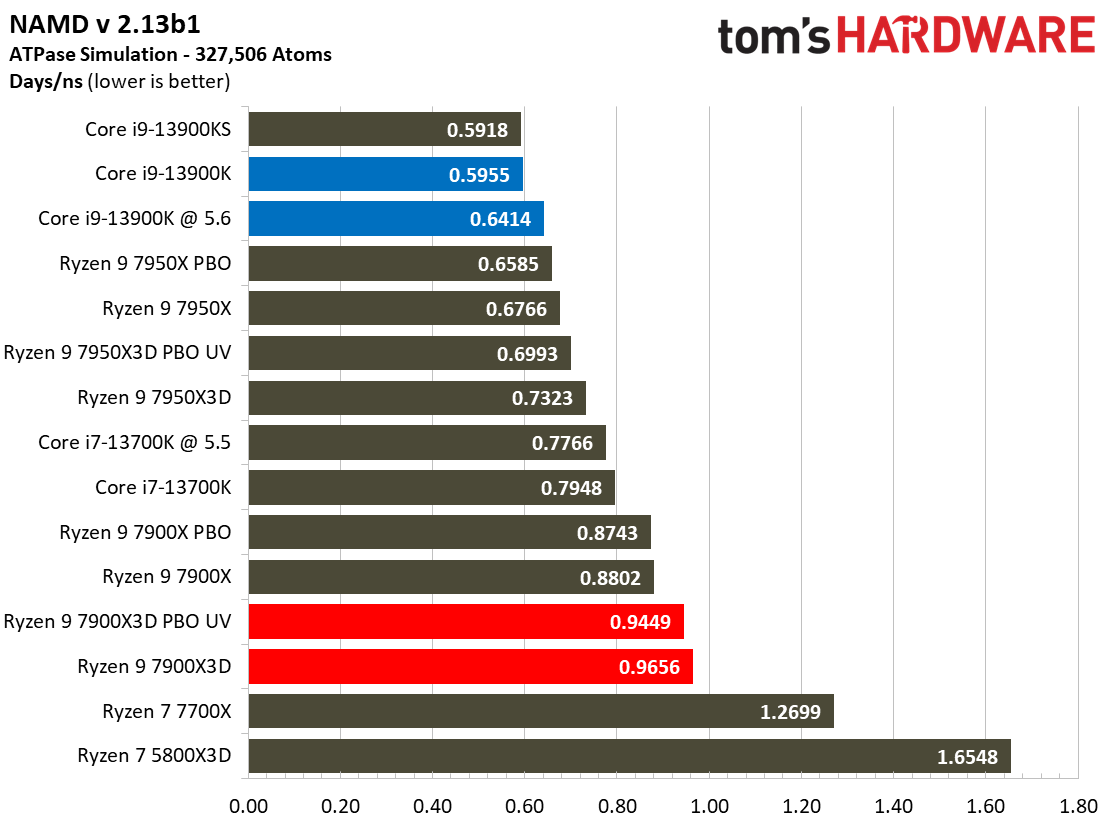
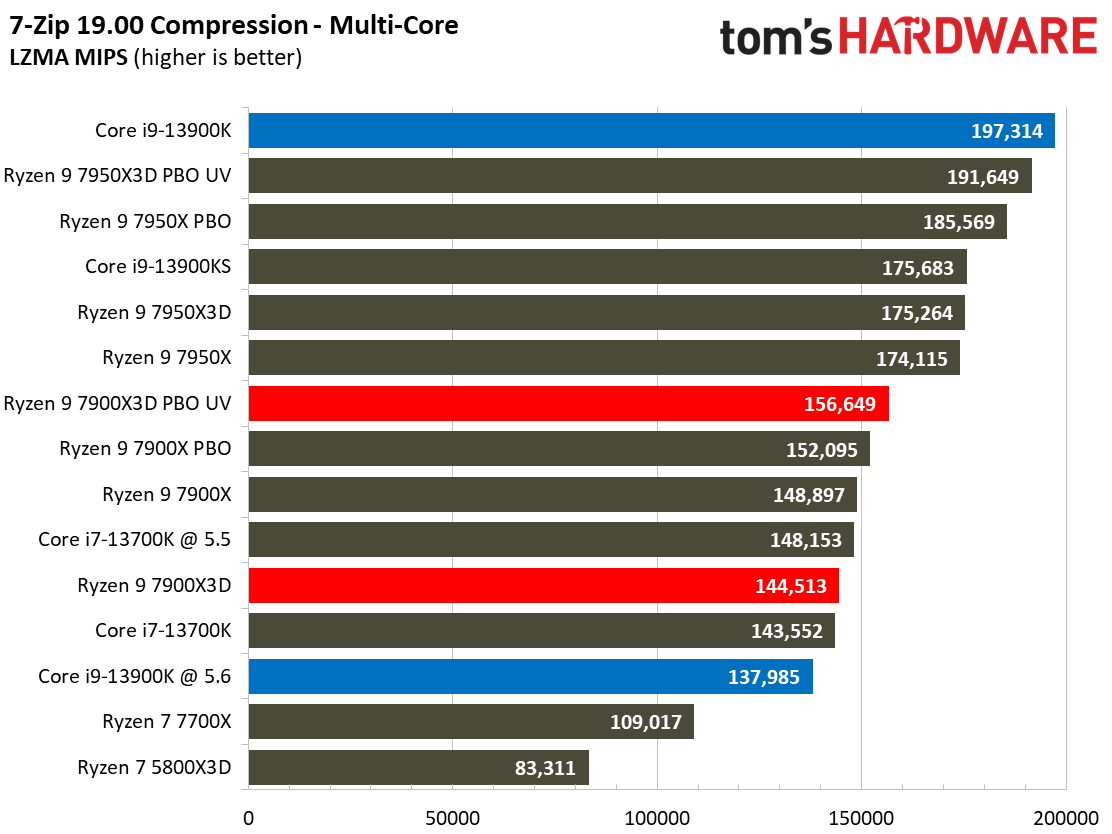
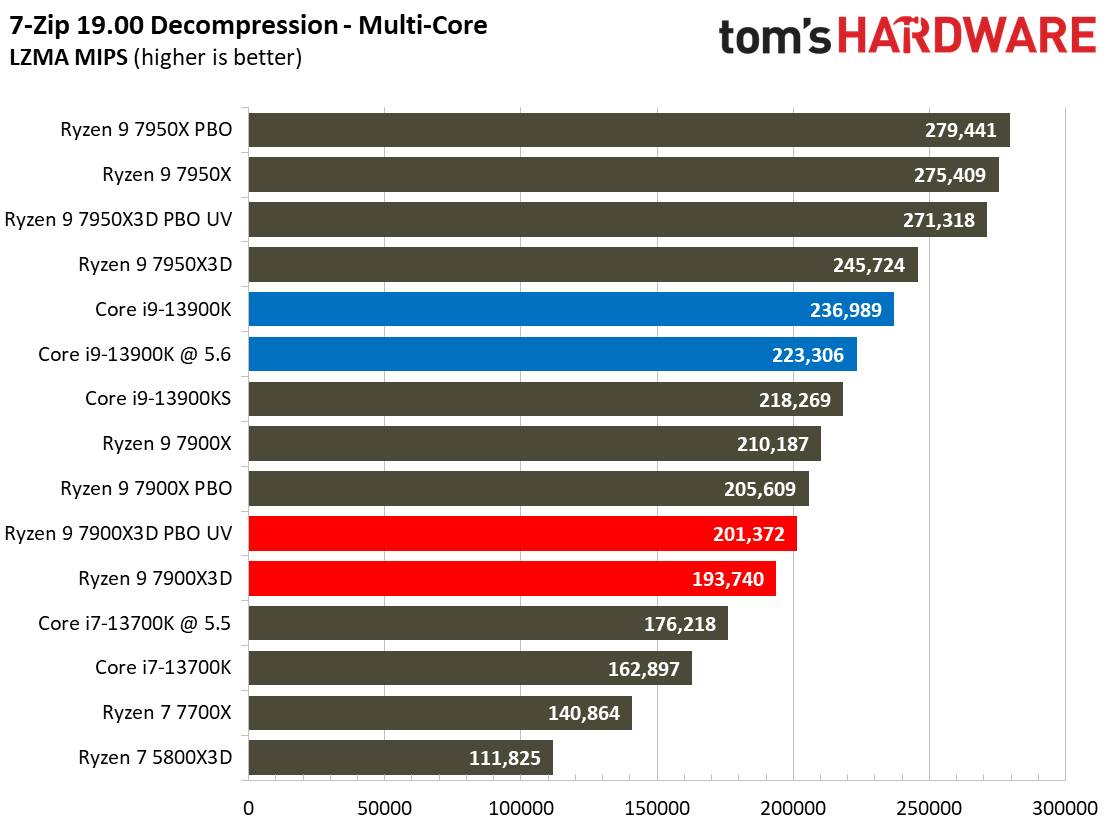
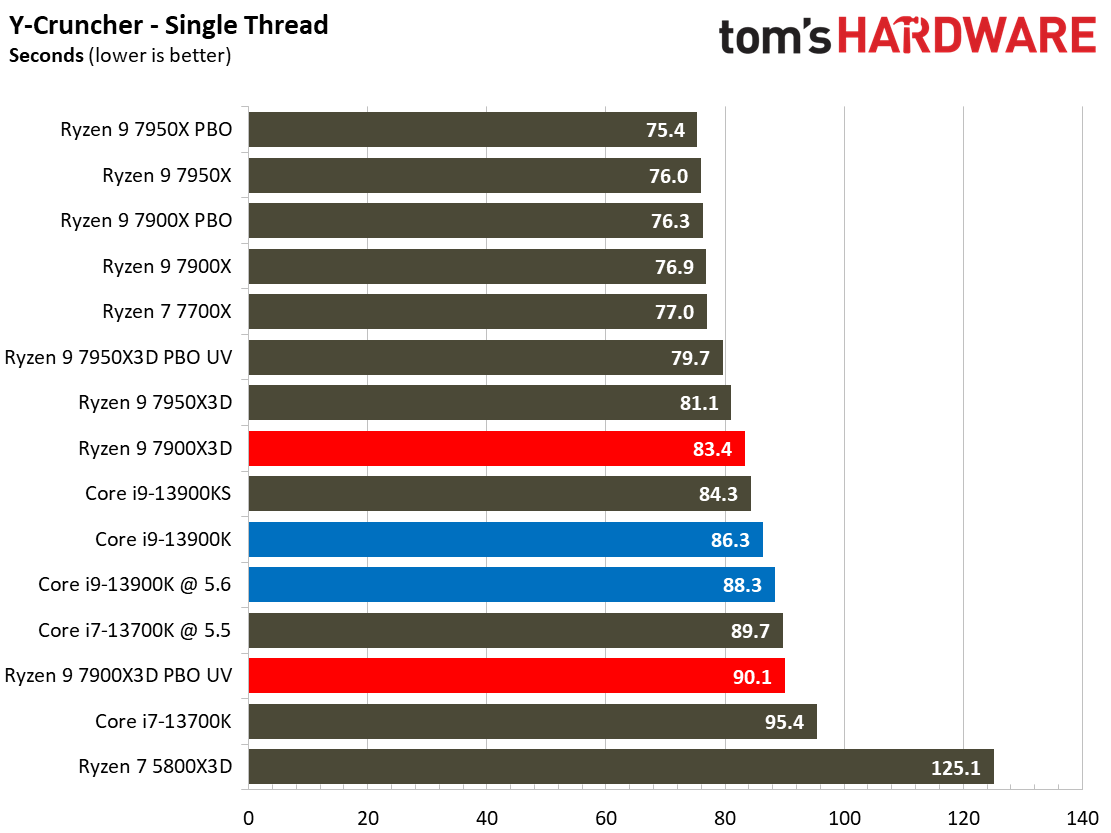
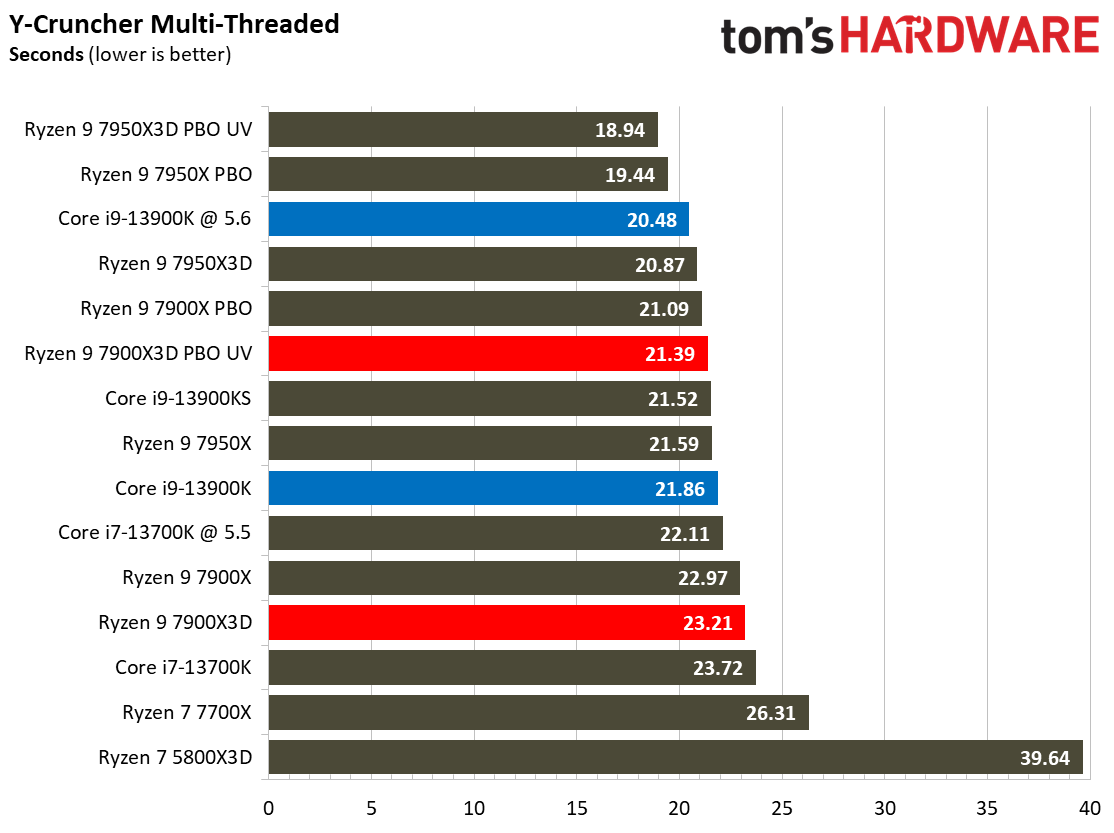
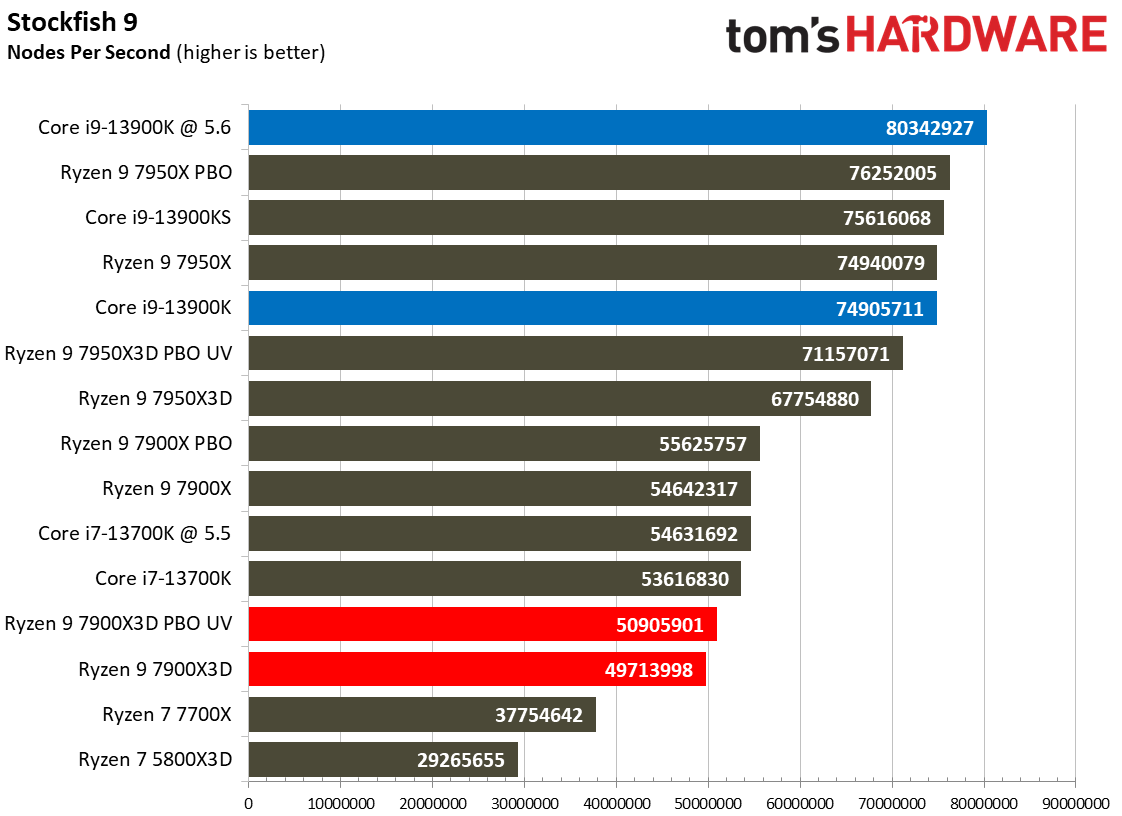
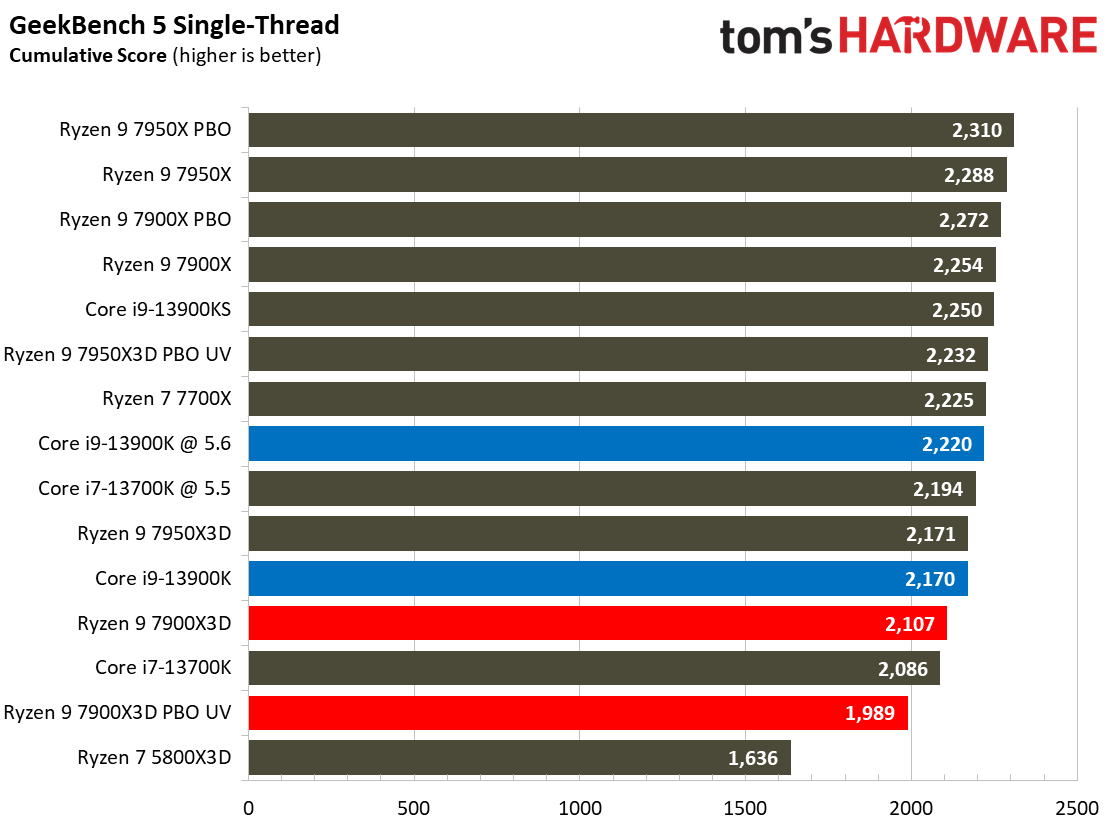
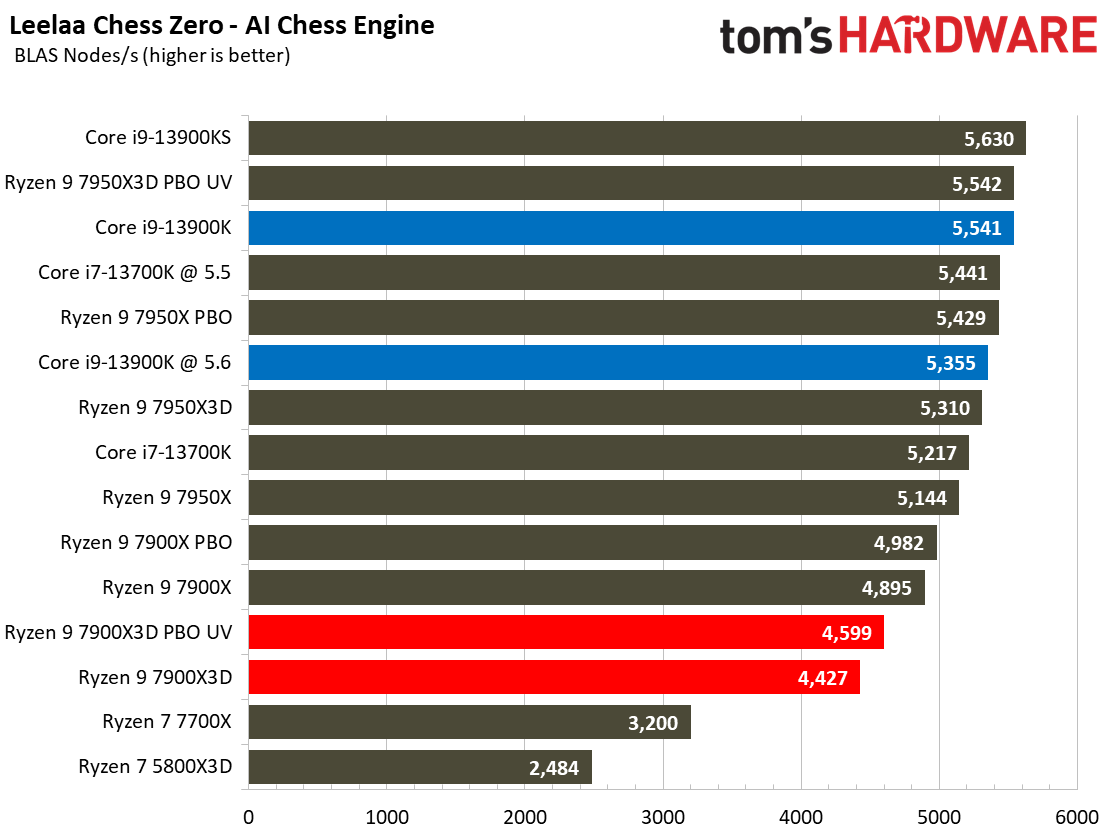
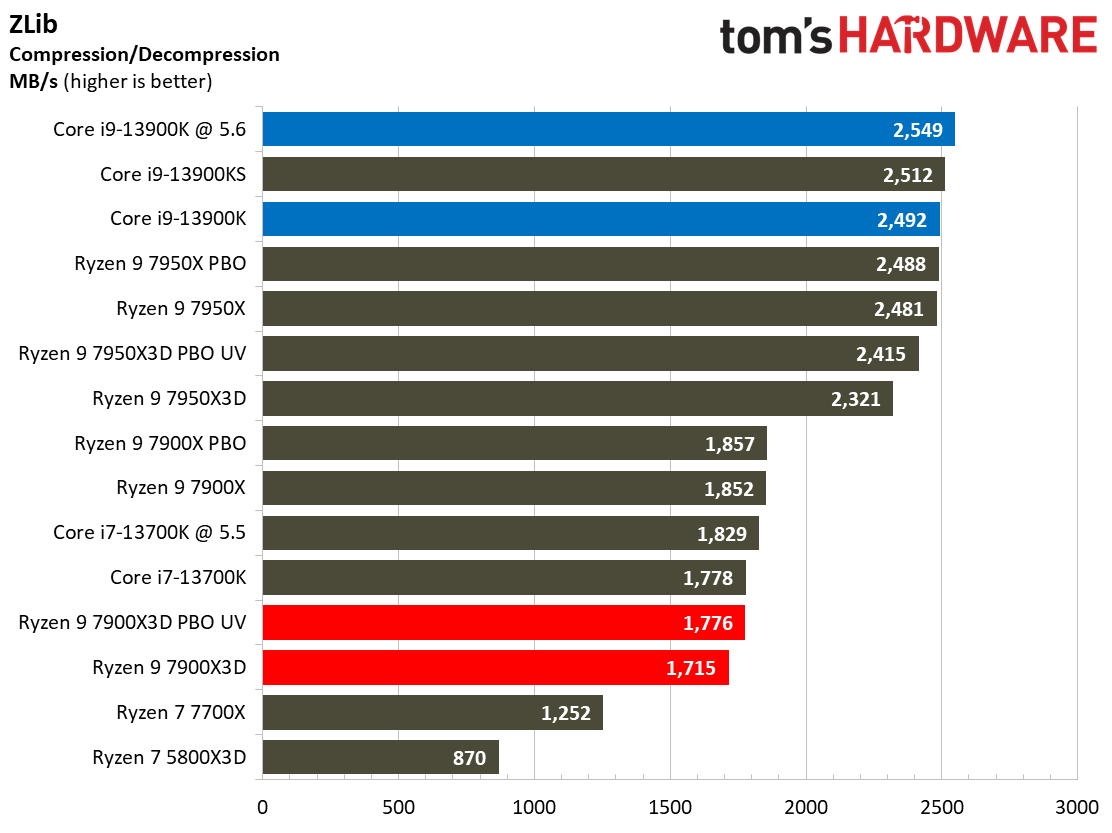
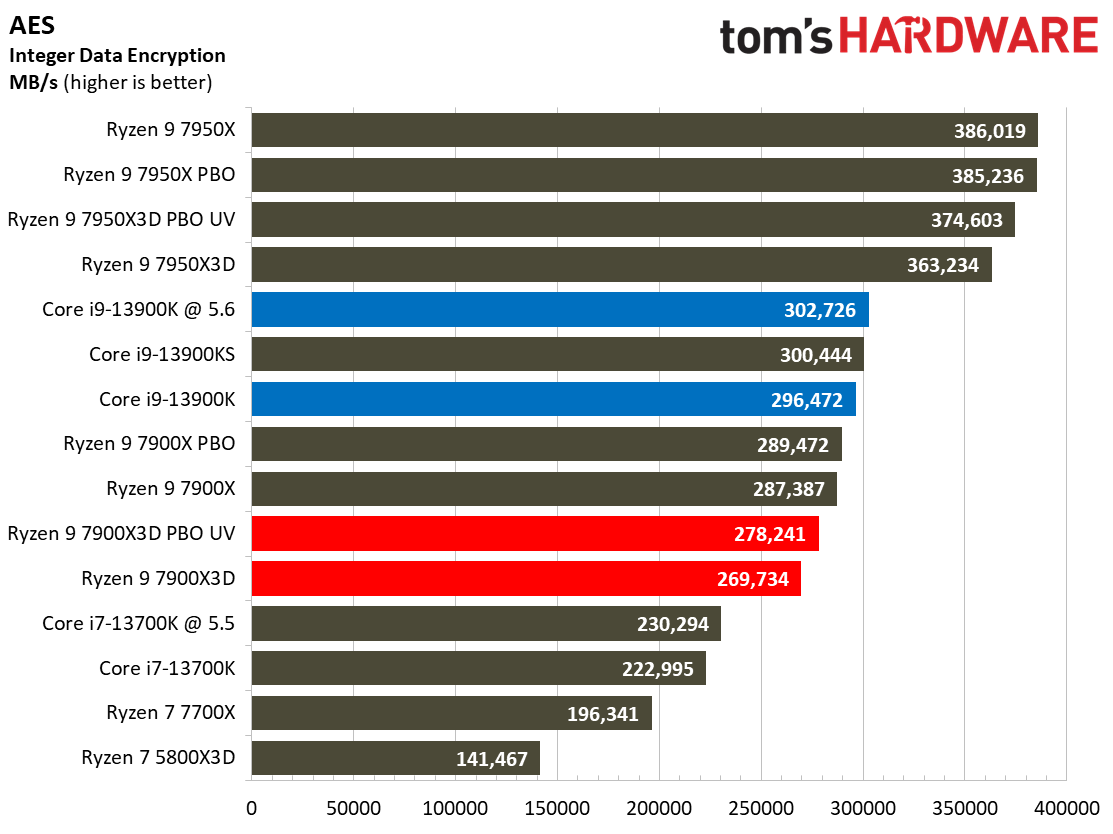
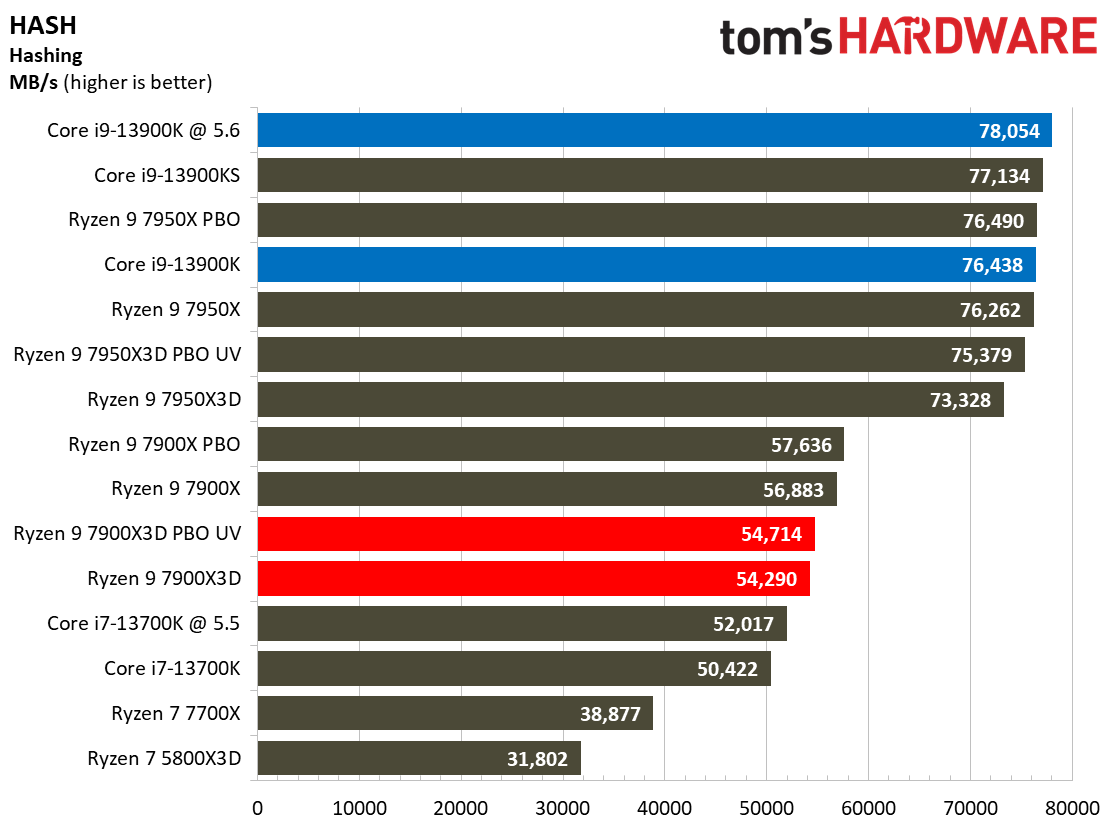
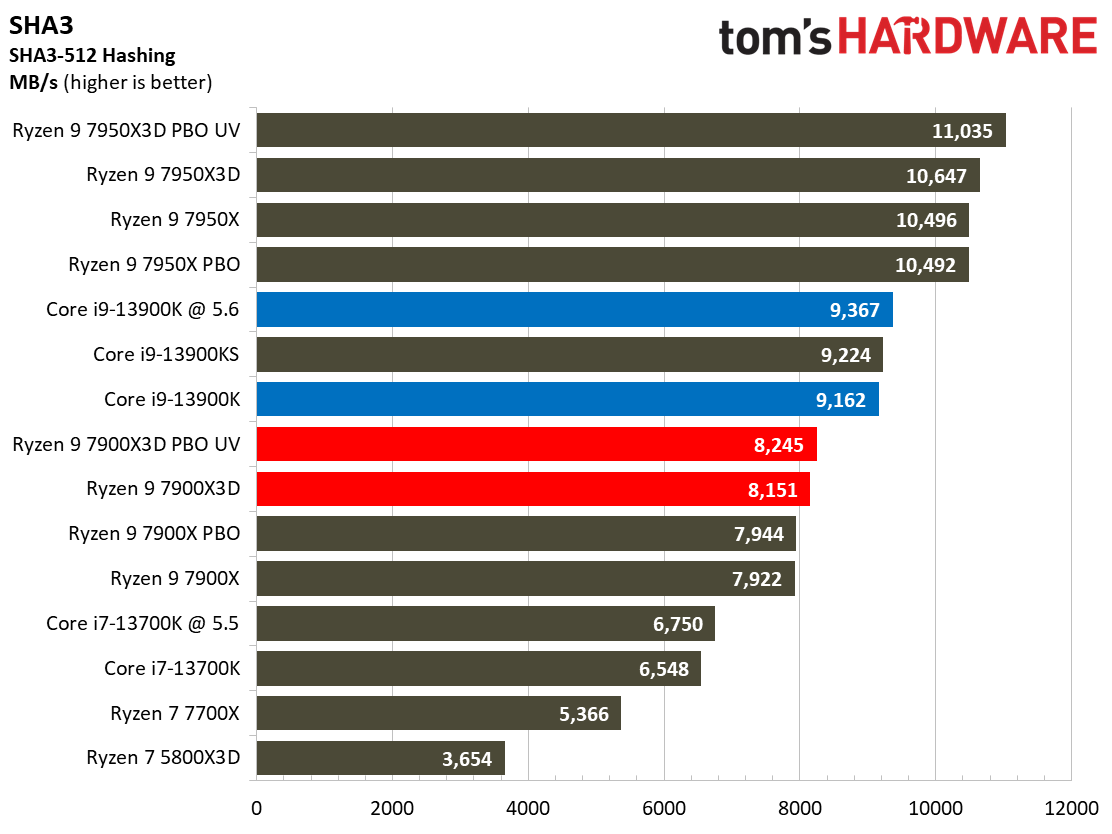
This selection of tests runs the gamut from the exceedingly branchy code in the LLVM compilation workload to the massively parallel molecular dynamics simulation code in NAMD to encryption and compression/decompression performance.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
The demanding Y-cruncher benchmark computes Pi with the AVX instruction set and has optimizations for both Intel and AMD’s architectures. The Ryzen 9 7900X3D again fails to impress in these heavy workloads — aside from encryption workloads, you're much better looking to lower-priced alternatives for these types of applications.
- MORE: Best CPU for gaming
- MORE: CPU Benchmark Hierarchy
- MORE: Intel vs AMD
- MORE: How to Overclock a CPU
Current page: AMD Ryzen 9 7900X3D Productivity Benchmarks
Prev Page AMD Ryzen 9 7900X3D Gaming Benchmarks Next Page Challengers On All Sides
Paul Alcorn is the Editor-in-Chief for Tom's Hardware US. He also writes news and reviews on CPUs, storage, and enterprise hardware.
-
Brian D Smith -No support for DDR4 memoryReply
LOL...that's like saying a horse cannot use an elephant's saddle. Seriously, why even say that as a negative? Oh...it's Paul. -
Giroro I question the point of a non-flagship gaming CPU when nobody is making a non-flagship gaming GPU.Reply -
logainofhades ReplyGiroro said:I question the point of a non-flagship gaming CPU when nobody is making a non-flagship gaming GPU.
The 7900xt, 4070ti, and 4080 are not flagship models. That would be the 7900xtx and the 4090. -
Metteec Brian D Smith: I get your point, but the Intel i9-13900K (the competitor to the Ryzen 9 7900X3D) supports both DDR4 and DD5. Therefore, Paul's feedback on this particular issue is warranted. AMD's design decision to switch exclusively to DDR5 is a detractor to many buyers, including myself, who would have upgraded their CPUs but can't because they would have to invest in DDR5. Conversely, Intel has eased the transition its 12th generation processor by offering compatible motherboards with either DDR4 or DDR5.Reply
I would guess that Intel's 14th generation will ditch DDR4 for good, but as of now, DDR4 compatibility is one thing that the i9-13900K has going for it over the Ryzen 9 7900X3D.
Disclosure: I hold positions in both Intel and AMD stock and use predominantly AMD products. -
2Be_or_Not2Be I wonder how the upcoming single-CCD 7800X3D will perform. I like that it's a single-CCD CPU vs the dual-CCD in the 7950/7900X3D. If it can boost to 5.6GHz, despite the official boost rating only showing 5.0GHz, then that could potentially be the best of both worlds (gaming & application, when app not limited by # of cores).Reply -
2Be_or_Not2Be ReplyMetteec said:Disclosure: I hold positions in both Intel and AMD stock and use predominantly AMD products.
Disclosure: I am currently losing money with positions in both Intel and AMD stock and use predominantly AMD products. :) -
Maebius My crystal ball foresees that after a while (a few months) , the 7900X3D will be very very closely (street)priced to the 7800X3D.Reply -
jeremyj_83 Reply
13th Gen supports DDR4 because it is socket compatible with 12th Gen. Making 13th Gen DDR5 only would have meant that Z690 (and other 12th Gen chipsets) only supported 1 CPU version. As of late Intel has made it such that chipsets support 2 generations of CPUs. When 12th Gen came out, it made sense for there to be DDR4 support as DDR5 was at a huge price premium. Fast forward to now and the price premium over DDR4 is much lower, still not 1:1 but..., so supporting 2 memory types is only for socket compatibility for Intel's standard 2 generations. Had Intel gone DDR5 only on 13th Gen we probably would have seen DDR5 prices drop much faster than they already are.Metteec said:Brian D Smith: I get your point, but the Intel i9-13900K (the competitor to the Ryzen 9 7900X3D) supports both DDR4 and DD5. Therefore, Paul's feedback on this particular issue is warranted. AMD's design decision to switch exclusively to DDR5 is a detractor to many buyers, including myself, who would have upgraded their CPUs but can't because they would have to invest in DDR5. Conversely, Intel has eased the transition its 12th generation processor by offering compatible motherboards with either DDR4 or DDR5.
I would guess that Intel's 14th generation will ditch DDR4 for good, but as of now, DDR4 compatibility is one thing that the i9-13900K has going for it over the Ryzen 9 7900X3D.
Disclosure: I hold positions in both Intel and AMD stock and use predominantly AMD products. -
Roland Of Gilead Reply
Agree with you for the most part, but this idea that DDR5 is a killer for any consumers and having to go with AMD (without choice) for Zen4/AM5 doesn't add up. DDR4 support for Intel's current 13th Gen ends with Raptor. (maybe a Raptor -s not known yet). Meteor or next desktop is exclusively DDR5. Add to that, that AMD will support maybe 3/4 new CPU's on the same socket. Intel don't do that. The cost upfront, of maybe 100-150, sure does make up for not having to upgrade on Intel every two years.Metteec said:Brian D Smith: I get your point, but the Intel i9-13900K (the competitor to the Ryzen 9 7900X3D) supports both DDR4 and DD5. Therefore, Paul's feedback on this particular issue is warranted. AMD's design decision to switch exclusively to DDR5 is a detractor to many buyers, including myself, who would have upgraded their CPUs but can't because they would have to invest in DDR5.
For what it's worth, I'd rather have a socket that lasts 4-5 years, and allow for simple drop in upgrades, that are and can be substantive. -
DavidLejdar I am avoiding the 7900X3D. Some games like to use up to 8 cores (when they are available), and the 6+6 setup means that some workload gets directed to 2 additional cores on the second CCD. This doesn't mean a stutter-fest. But what's the point (for gaming as such), when the 7800X3D may actually deliver better gaming performance, having 8 cores with 3D V-Cache?Reply
I think it is fair to point out that the CPU goes only with DDR5. But it would also be fair to run some tests comparing gaming performance of e.g. the 13900K with DDR4 and DDR5, as the charts seem to be presenting the performance with DDR5 only, which then makes it a somewhat moot point to say: "And this one can use DDR4 as well, which is a huge plus.", without then elaborating whether a DDR4 rig does deliver the same performance as a cheaper CPU with DDR5 perhaps may, etc.Metteec said:I would guess that Intel's 14th generation will ditch DDR4 for good, but as of now, DDR4 compatibility is one thing that the i9-13900K has going for it over the Ryzen 9 7900X3D.
