Enermax Platimax D.F. 1200W PSU Review
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Load Regulation, Hold-Up Time & Inrush Current
To learn more about our PSU tests and methodology, please check out How We Test Power Supply Units.
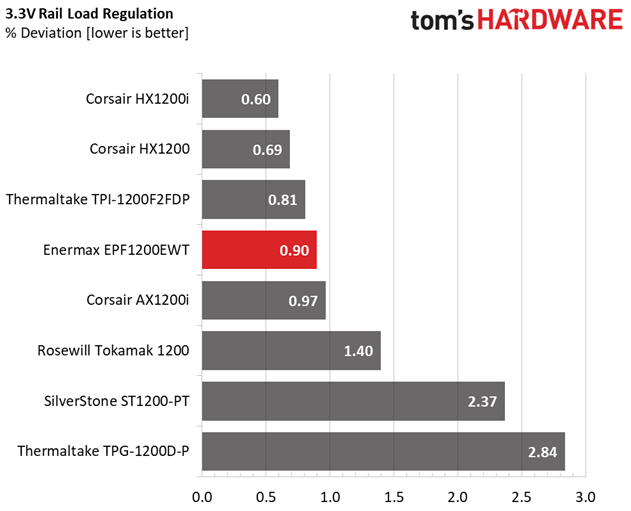
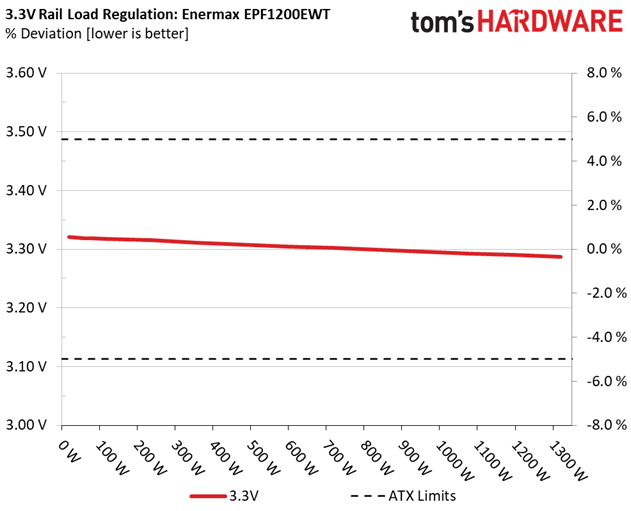
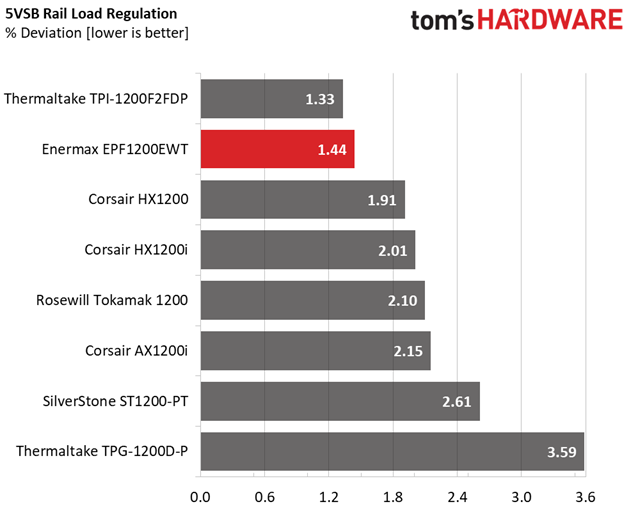
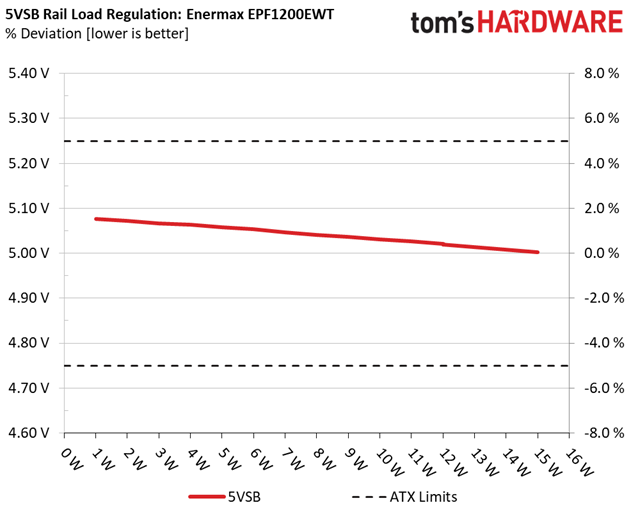
Primary Rails And 5VSB Load Regulation
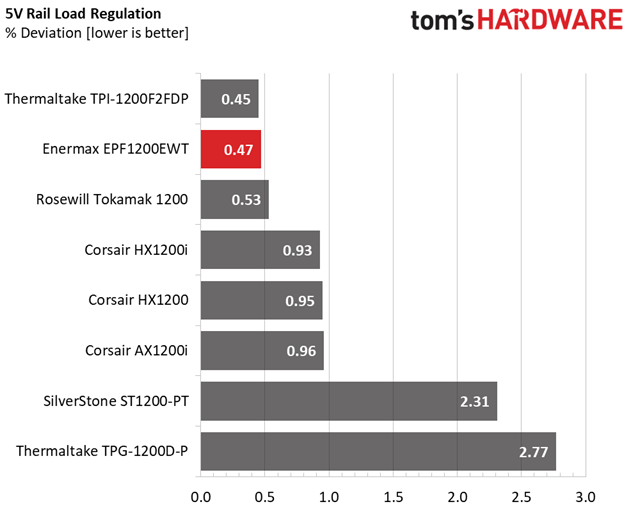
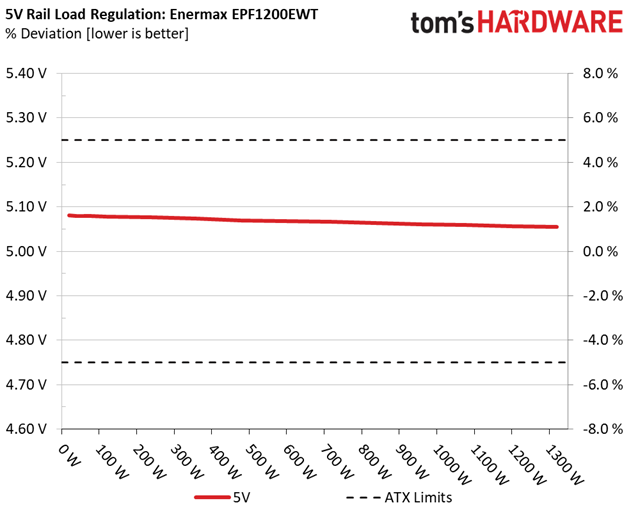
Load Regulation testing is detailed here.
Hold-Up Time
Our hold-up time tests are described in detail here.
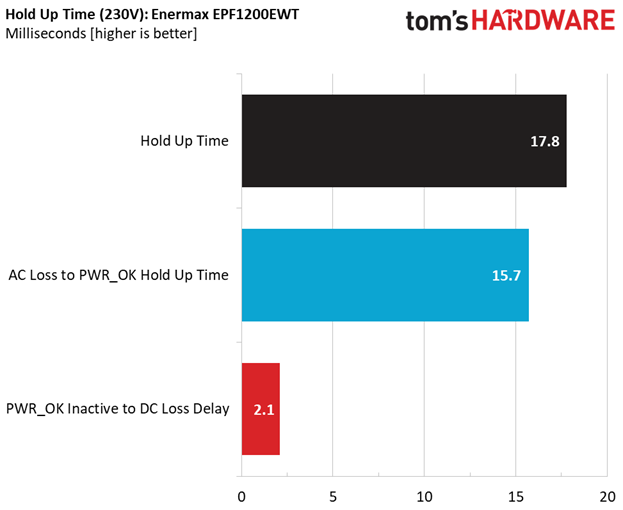
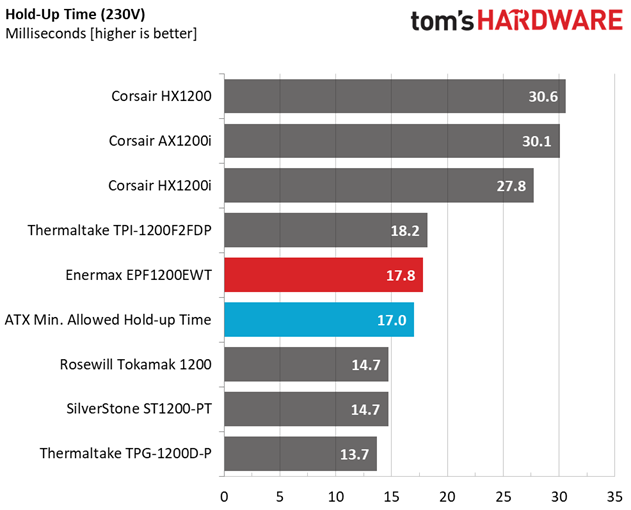
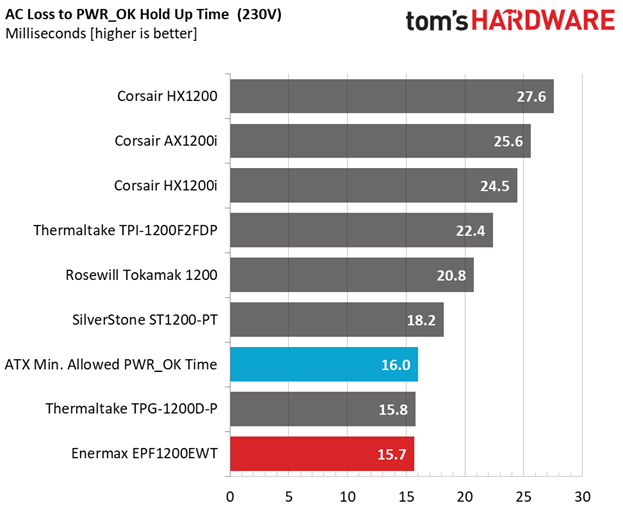
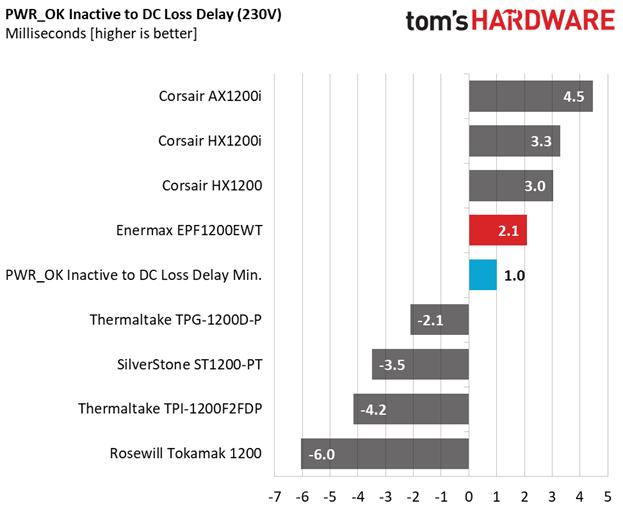
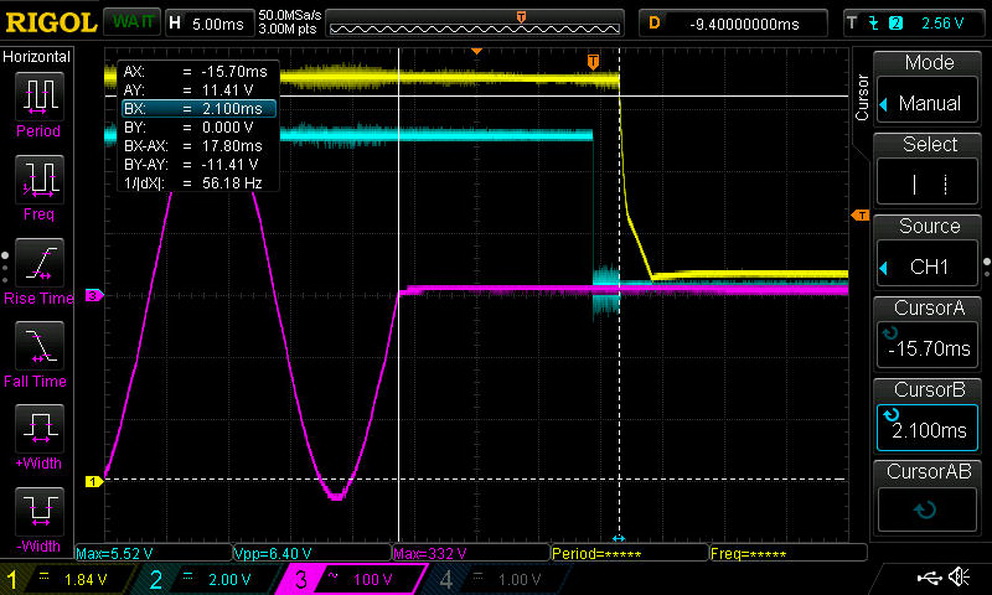
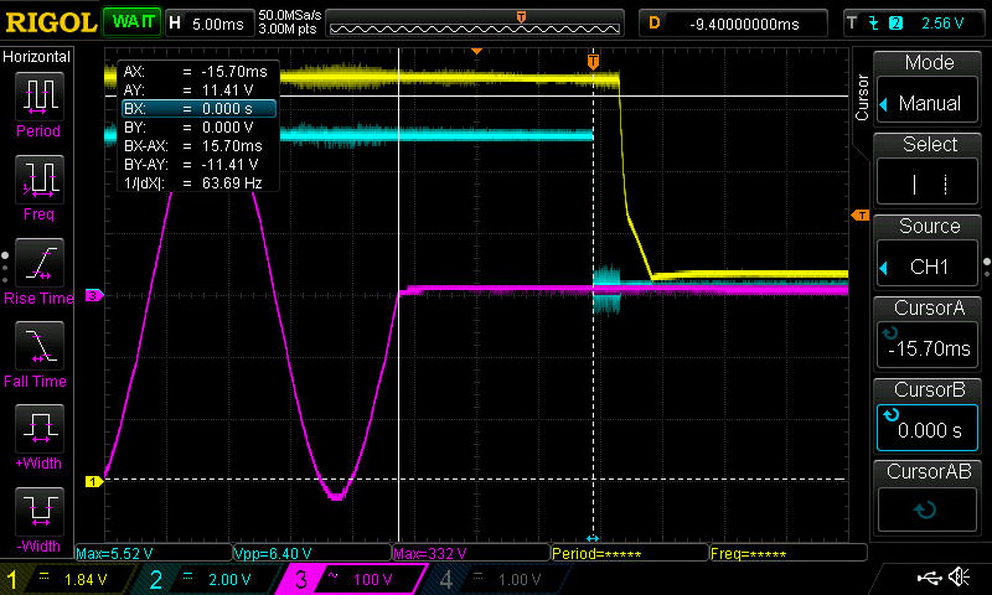
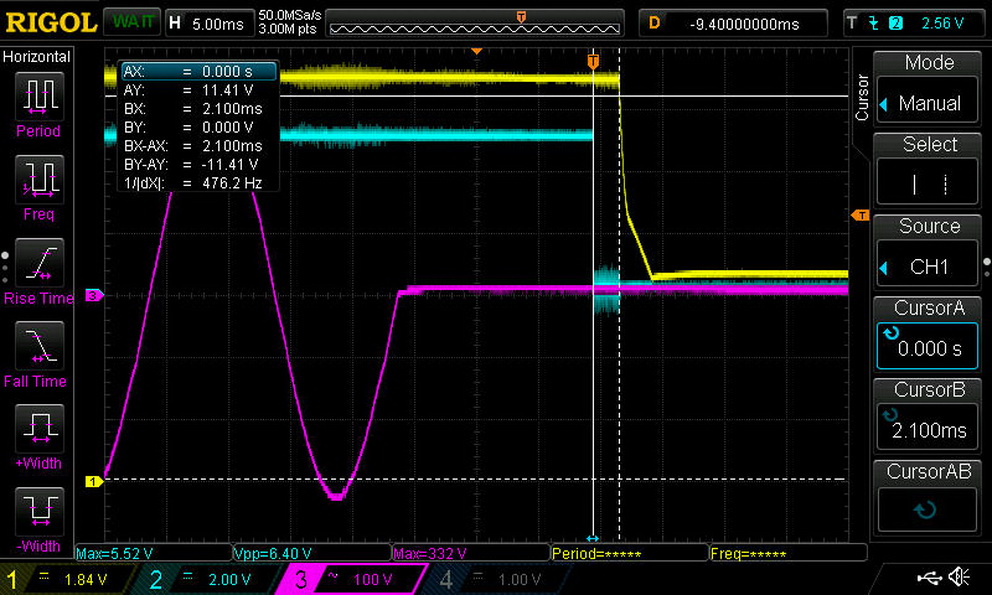
The hold-up time we measure satisfies the ATX spec's demands. Moreover, the power-good signal is accurate and only a hair away from 16ms. We don't have a problem when the power-good signal is a little lower than it should be, but we do take issue when it's inaccurate, making the system's motherboard believe it's receiving proper voltage levels when it's not.
Inrush Current
For details on our inrush current testing, please click here.
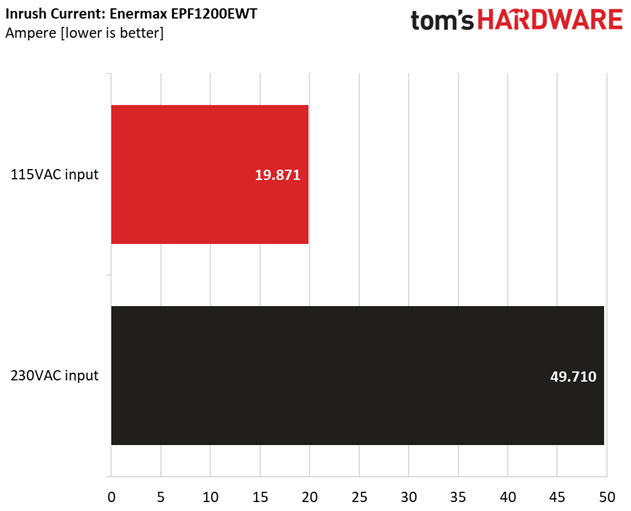
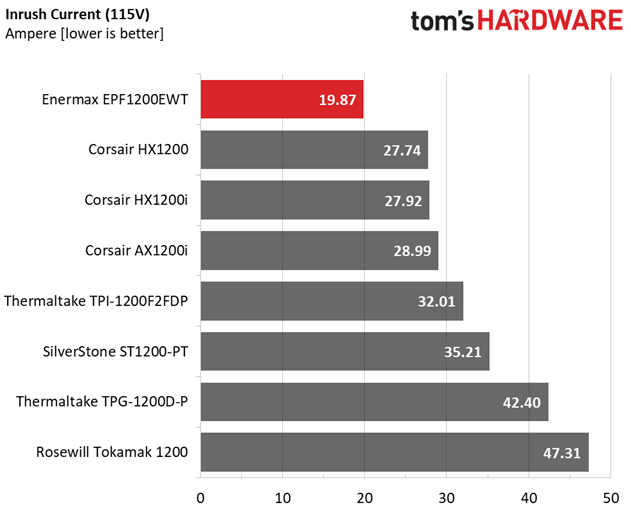
The inrush current is pretty low with both voltage inputs.
Load Regulation And Efficiency Measurements
The first set of tests reveals the stability of the voltage rails and the EPF1200EWT's efficiency. The applied load equals (approximately) 10 to 110 percent of the PSU's maximum load in increments of 10 percentage points.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
We conducted two additional tests. During the first, we stressed the two minor rails (5V and 3.3V) with a high load, while the load at +12V was only 0.1A. This test reveals whether a PSU is compatible with Intel's C6/C7 sleep states or not. In the second test, we determined the maximum load the +12V rail could handle with minimal load on the minor rails.
| Test # | 12V | 5V | 3.3V | 5VSB | DC/AC (Watts) | Efficiency | Fan Speed | PSU Noise | Temps (In/Out) | PF/AC Volts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8.176A | 1.968A | 1.989A | 0.989A | 119.994 | 89.032% | 0 RPM | <6.0 dB(A) | 48.33°C | 0.982 |
| 12.035V | 5.078V | 3.318V | 5.058V | 134.776 | 38.18°C | 115.22V | ||||
| 2 | 17.371A | 2.955A | 2.984A | 1.188A | 239.713 | 91.969% | 0 RPM | <6.0 dB(A) | 49.17°C | 0.992 |
| 12.021V | 5.076V | 3.315V | 5.054V | 260.645 | 38.54°C | 115.05V | ||||
| 3 | 26.922A | 3.450A | 3.472A | 1.387A | 359.197 | 92.021% | 1105 RPM | 31.8 dB(A) | 38.76°C | 0.994 |
| 12.005V | 5.073V | 3.311V | 5.047V | 390.344 | 49.81°C | 114.98V | ||||
| 4 | 36.561A | 3.945A | 3.993A | 1.587A | 479.649 | 92.059% | 1105 RPM | 31.8 dB(A) | 39.06°C | 0.996 |
| 11.992V | 5.070V | 3.308V | 5.041V | 521.022 | 50.49°C | 114.85V | ||||
| 5 | 45.843A | 4.934A | 4.994A | 1.788A | 599.801 | 91.726% | 1105 RPM | 31.8 dB(A) | 39.67°C | 0.997 |
| 11.982V | 5.068V | 3.304V | 5.036V | 653.908 | 51.40°C | 114.74V | ||||
| 6 | 55.061A | 5.923A | 5.996A | 1.988A | 719.933 | 91.010% | 1105 RPM | 31.8 dB(A) | 40.62°C | 0.997 |
| 11.989V | 5.066V | 3.302V | 5.031V | 791.044 | 54.33°C | 114.66V | ||||
| 7 | 64.268A | 6.914A | 7.004A | 2.189A | 839.688 | 90.154% | 1230 RPM | 36.5 dB(A) | 41.89°C | 0.998 |
| 11.990V | 5.063V | 3.299V | 5.026V | 931.393 | 57.89°C | 114.48V | ||||
| 8 | 73.609A | 7.906A | 8.011A | 2.391A | 960.183 | 89.385% | 1330 RPM | 36.0 dB(A) | 43.18°C | 0.998 |
| 11.979V | 5.061V | 3.296V | 5.021V | 1074.210 | 61.54°C | 114.37V | ||||
| 9 | 83.291A | 8.404A | 8.504A | 2.391A | 1079.515 | 88.503% | 1410 RPM | 37.6 dB(A) | 45.35°C | 0.998 |
| 11.970V | 5.059V | 3.293V | 5.020V | 1219.744 | 66.55°C | 114.16V | ||||
| 10 | 92.846A | 8.903A | 9.028A | 2.999A | 1199.973 | 87.437% | 1410 RPM | 37.6 dB(A) | 46.03°C | 0.998 |
| 11.958V | 5.056V | 3.290V | 5.003V | 1372.384 | 71.73°C | 114.05V | ||||
| 11 | 102.952A | 8.905A | 9.037A | 3.000A | 1319.896 | 86.295% | 1625 RPM | 42.1 dB(A) | 47.79°C | 0.998 |
| 11.949V | 5.055V | 3.287V | 5.001V | 1529.516 | 74.87°C | 113.85V | ||||
| CL1 | 0.744A | 16.005A | 15.999A | 0.000A | 143.069 | 83.059% | 0 RPM | 0 dB(A) | 48.25°C | 0.987 |
| 12.031V | 5.069V | 3.312V | 5.112V | 172.249 | 46.09°C | 115.15V | ||||
| CL2 | 100.011A | 1.001A | 0.999A | 1.000A | 1210.027 | 87.632% | 1430 RPM | 37.1 dB(A) | 47.23°C | 0.998 |
| 11.965V | 5.062V | 3.293V | 5.038V | 1380.807 | 72.93°C | 114.07V |
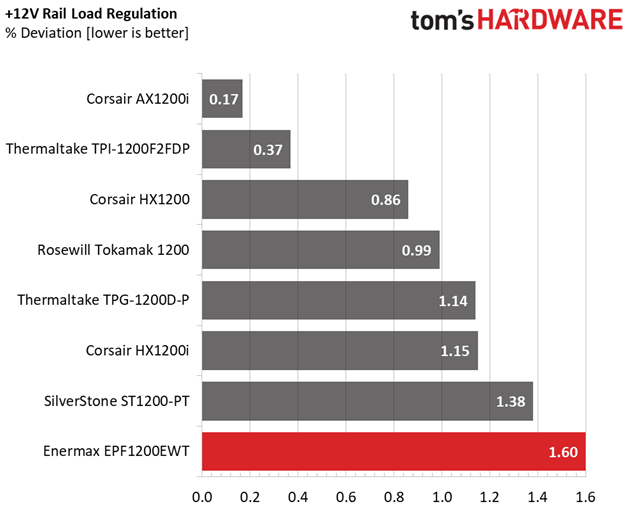
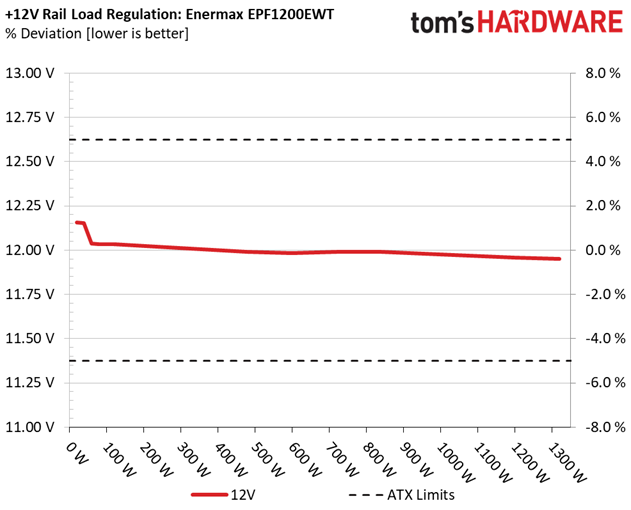
Load regulation on the +12V rail is pretty tight. However, there is a large voltage drop with 40W and 60W load. And since we take the 40W load test as point zero, that's why the deviation on this rail reaches a not-so-impressive 1.6%. If we took the voltage level at +12V with 60W load as reference, the deviation would be 0.66%. We use 40W as the reference in our reviews, though, and it wouldn't be right to make an exception here. CWT should probably take a look at its platform and figure out why there's a weird voltage drop at such a light load level.
The EPF1200EWT easily clears the 80 PLUS Platinum certification's 20% load requirement. However, it falls short in the 50% and full load tests. We collect data at a very high ambient temperature, though, and this plays a key role in efficiency performance.
Another problem is that the fan fires up at a very high initial speed (1100 RPM). In other words, the transition from passive to active mode is noticeable. This transition should be smoother, with the fan spinning slowly at first, even if it means interrupting passive operation sooner. Fortunately, the fan doesn't accelerate to full speed, even under 100% load. It's only if you push the PSU beyond its nominal capacity that you'll cause the fan to top out.
MORE: Best Power Supplies
MORE: How We Test Power Supplies
MORE: All Power Supply Content
Current page: Load Regulation, Hold-Up Time & Inrush Current
Prev Page Teardown & Component Analysis Next Page Efficiency, Temperature & Noise
Aris Mpitziopoulos is a contributing editor at Tom's Hardware, covering PSUs.
-
Soaptrail The DFR would not be that bad at adding dust to the case if it does it each time you start your PC. If DFR kicks in each time you resume from sleep i do not expect to see dust all over the case but if DFR is only activated once or twice a year then yes you will be adding dust to the case assuming it actually detaches from the PSU.Reply -
love4earthwk I'm afraid Teardown video is about thermaltake grand rgb.Reply
Enermax platimax df 1200w video is uploaded in Aris's youtube channel
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UYHaJDsd9QI -
Aris_Mp Yes there is a problem with the video. We are working on it! I am sorry for the confusion!Reply -
bettsar I prefer to read the teardown analysis. I usually find that to be the most interesting part of the power supply reviews. Thanks for the high quality work that you do in putting these together.Reply


