Nvidia GeForce GTX 1050 3GB Review: (Mostly) Faster Than 1050 2GB
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Results: Power, Clock Rates, and GPU Temperature
Slowly but surely, we’re spinning up multiple Tom’s Hardware labs with Cybenetics’ Powenetics hardware/software solution for accurately measuring power consumption.
Powenetics, In Depth
For a closer look at our U.S. lab’s power consumption measurement platform, check out Powenetics: A Better Way To Measure Power Draw for CPUs, GPUs & Storage.
In brief, Powenetics utilizes Tinkerforge Master Bricks, to which Voltage/Current bricklets are attached. The bricklets are installed between the load and power supply, and they monitor consumption through each of the modified PSU’s auxiliary power connectors and through the PCIe slot by way of a PCIe riser. Custom software logs the readings, allowing us to dial in a sampling rate, pull that data into Excel, and very accurately chart everything from average power across a benchmark run to instantaneous spikes.
The software is set up to log the power consumption of graphics cards, storage devices, and CPUs. However, we’re only using the bricklets relevant to graphics card testing. Nvidia’s GeForce GTX 1050s get all of their power from the PCIe slot, while our Asus Radeon RX 560 requires a single six-pin auxiliary connector.
Idle
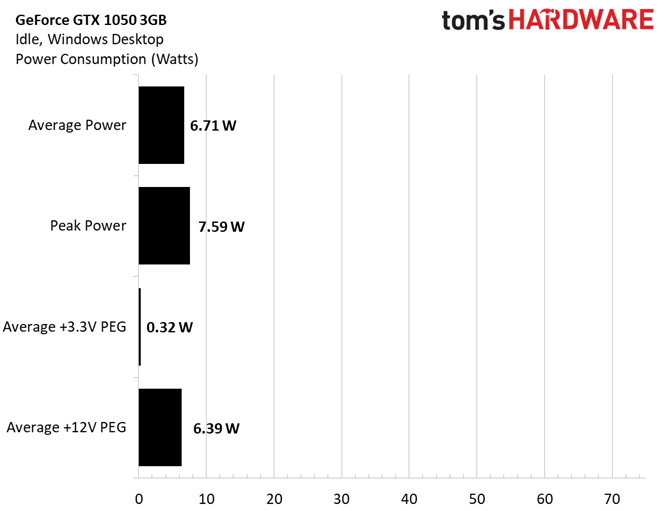
Sitting on the Windows desktop, driving a single QHD monitor, Nvidia’s GeForce GTX 1050 3GB averaged less than 7W, spiking about 1W higher during our 10-minute data collection window.
The card’s fan barely spun up (there is no semi-passive mode) and its GPU only got a little warmer than our ambient environment.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Gaming
The built-in benchmark of Metro: Last Light Redux gives us a consistent sequence that can be looped as many times as needed to generate good data.
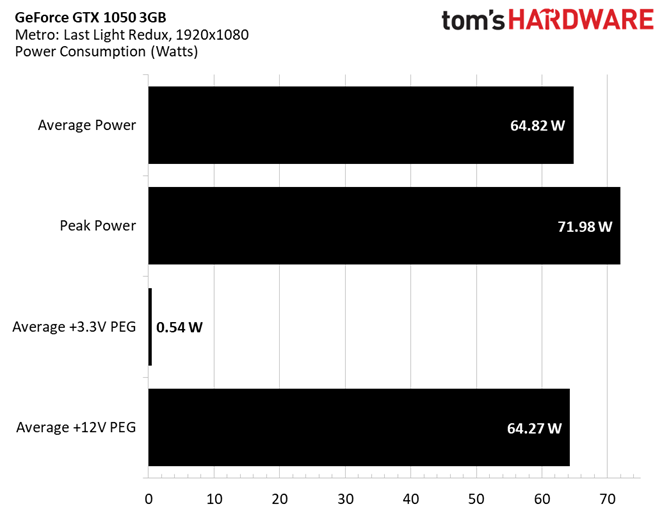
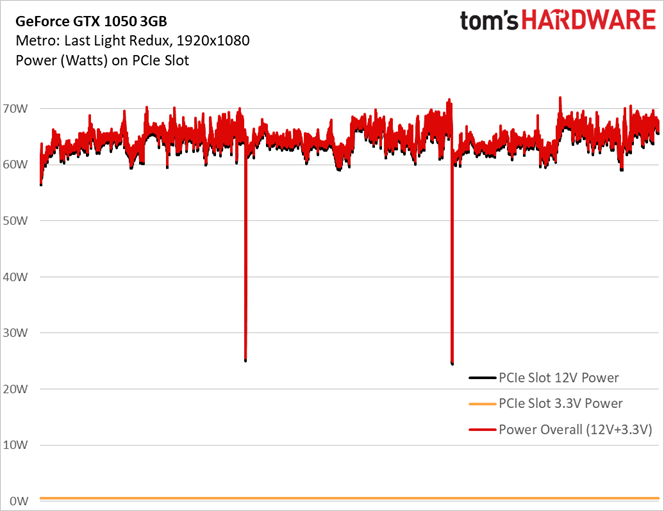
An almost-65W average landed well below the 1050 3GB's 75W total board power rating (though our peak power reading gets quite a bit closer at 72W).
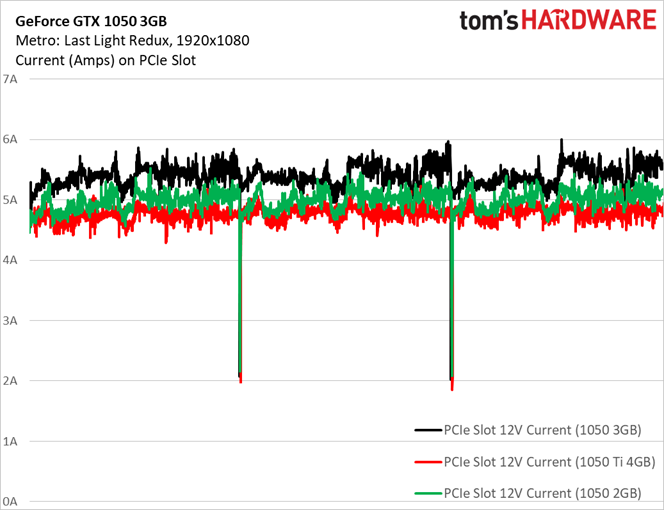
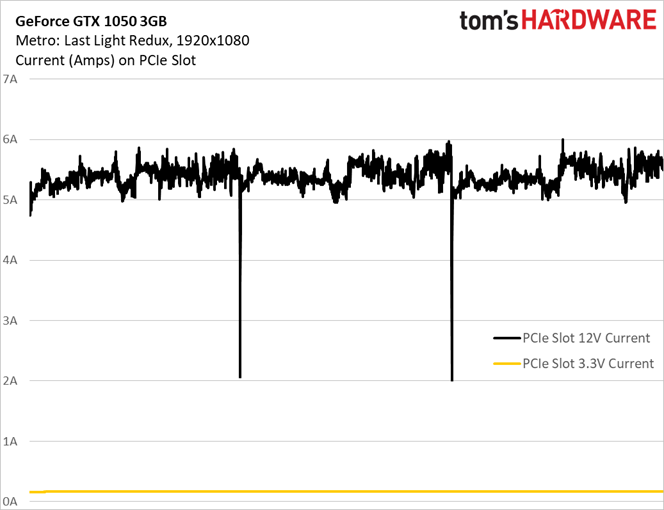
Interestingly, although we observed an average current draw of 5.39A on the 12V rail through three runs of the Metro benchmark, there were some spikes that exceeded the PCI-SIG’s 5.5A ceiling. For comparison, check out the same data next to current draw from GeForce GTX 1050 Ti 4GB and GeForce GTX 1050 2GB:
Those two notable dips are indicative of brief pauses between test runs. Otherwise, the data clearly shows our GeForce GTX 1050 3GB sample pulling more current from the PCIe slot than it should.
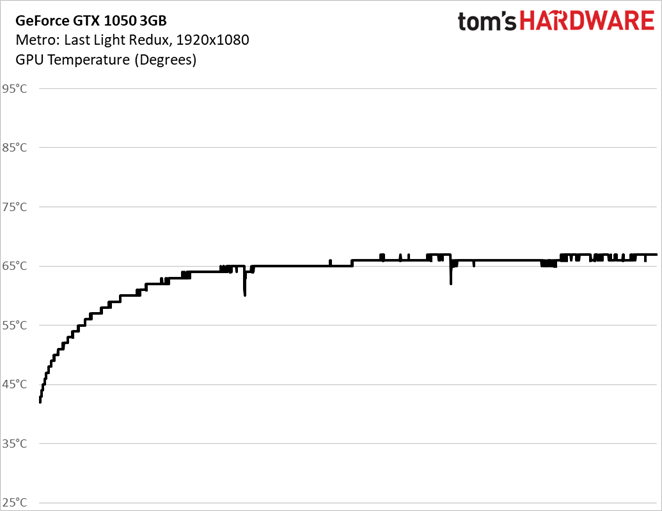
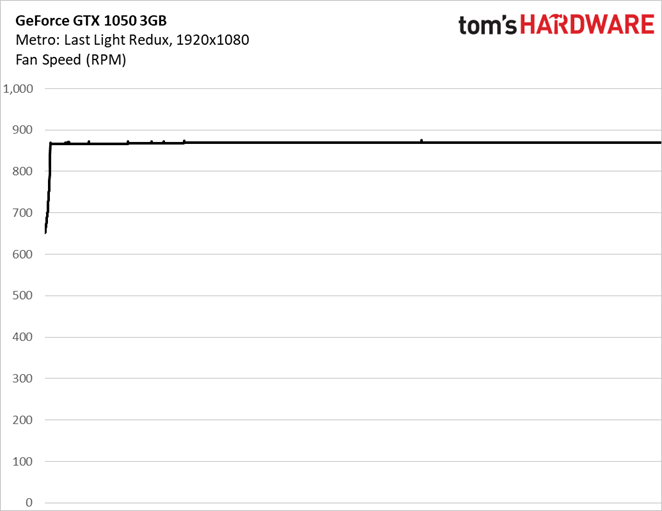
The card’s fan speed does ramp up in response to increased thermal load, even though Nvidia’s GP107 processor never heats up much more than 65°C.
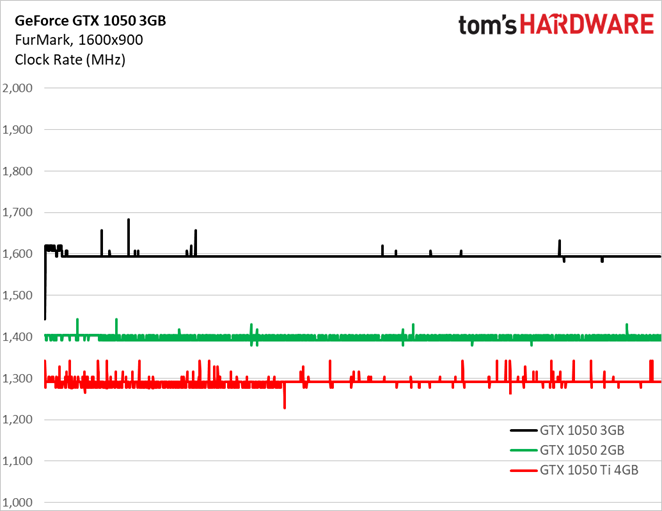
FurMark
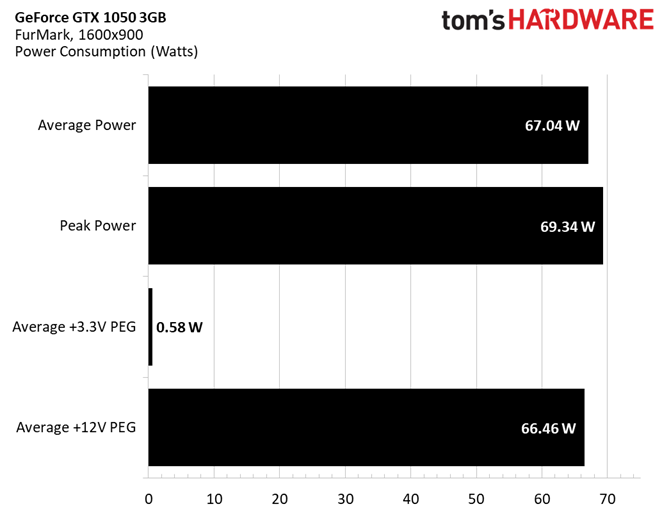
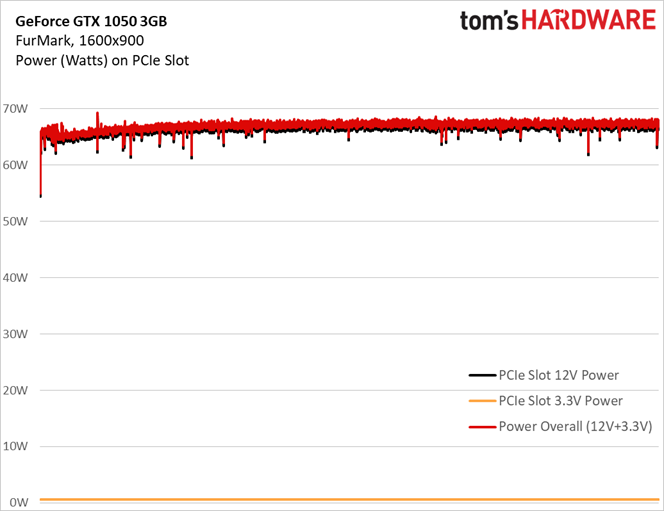
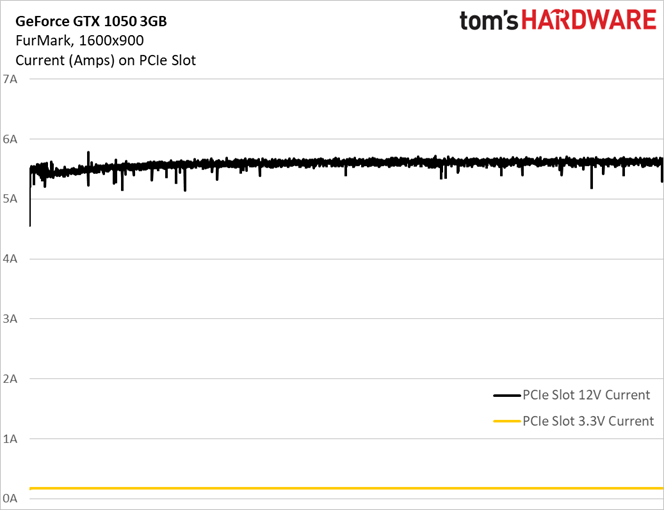
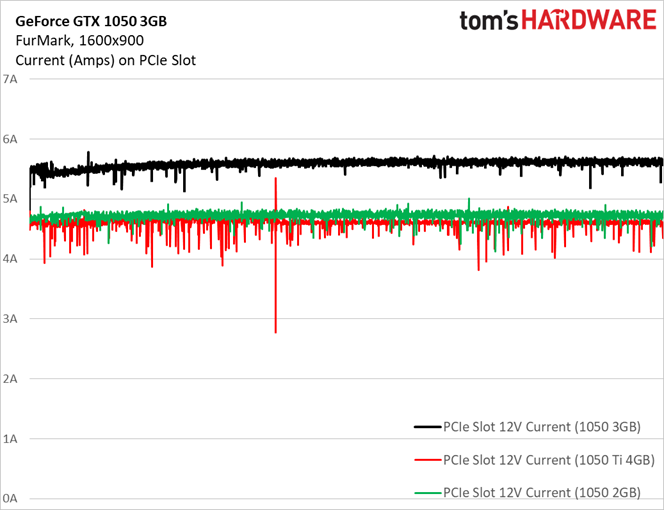
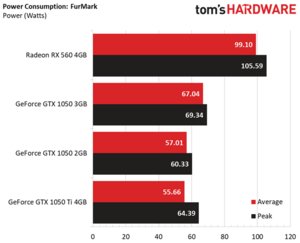
A more consistent workload is less susceptible to power consumption spikes (even if the task is as taxing as FurMark). GeForce GTX 1050 3GB doesn’t exceed 70W.
This time, average current draw of 5.58A does exceed the official 5.5A ceiling.
Again, putting all three GeForce GTX 1050s on one graph shows current draw from the 1050 3GB higher than it should be.
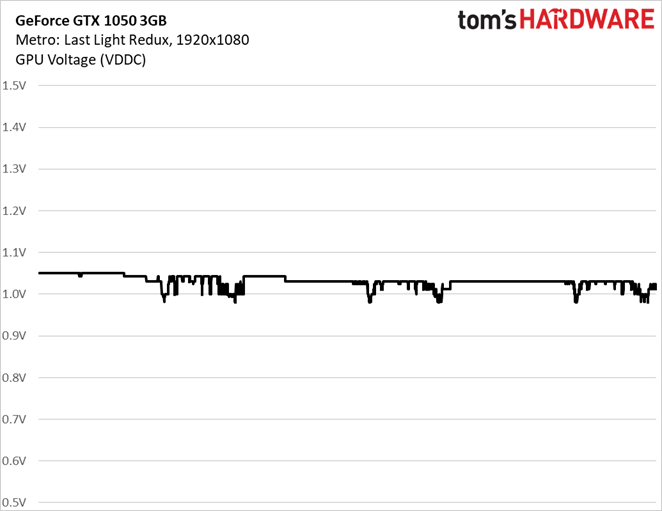
Voltage was pulled back to avoid violating Nvidia’s power limit, and core clock rate consequently dropped to about 1595 MHz. For comparison, the GPU voltage during our Metro run remained above 1.0V, and the core clock rate stuck right around 1771 MHz.
Comparing All Of The Cards
AMD’s Radeon RX 560 was easily the most power-hungry card in our gaming and stress test workloads. Between the GeForce GTX 1050s, though, Nvidia’s new 3GB card came closest to the company’s 75W rating (as you might have guessed from our current draw data).
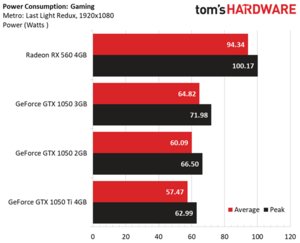
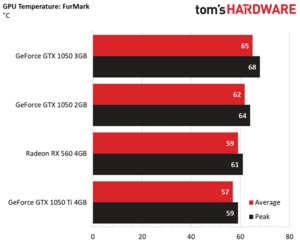
GeForce GTX 1050 3GB also ran the warmest across both of our benchmarks.
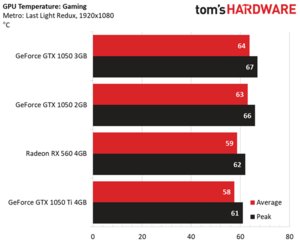
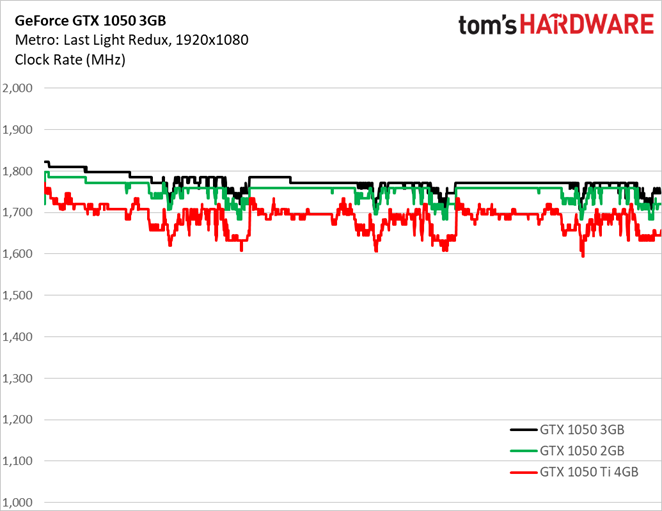
Nvidia pushes the GeForce GTX 1050 3GB’s clock rate a bit higher than what we got out of GeForce GTX 1050 2GB through our Metro: Last Light Redux workload.
Meanwhile, GeForce GTX 1050 Ti 4GB, with its 768 CUDA cores and 128-bit memory bus, doesn’t need to operate at aggressive frequencies to lay down better performance than the other two cards. It took a bigger clock rate hit in gaming scenarios to avoid violating its power limit.
FurMark makes each card’s respective ceiling much more obvious. Given their power limits, GeForce GTX 1050 3GB sustained roughly 1.6 GHz, the 1050 2GB was allowed right around 1.4 GHz, and 1050 Ti 4GB topped out around 1.3 GHz.
MORE: Best Graphics Cards
MORE: Desktop GPU Performance Hierarchy Table
MORE: All Graphics Content
Current page: Results: Power, Clock Rates, and GPU Temperature
Prev Page Results: Rise of the Tomb Raider, StarCraft II, and The Witcher 3 Next Page Conclusion-
caledbwlch Any chance we can get a comparison of the 1050 3GB with the memory overclocked in comparison to the 1050 Ti?Reply -
dudmont These 1050s are begging for some OEM to add a 6pin PCIE connector and rework the power limits on the cards. With good cooling, I'm betting 2GHZ isn't out of the question, with a good GPU.Reply -
King_V bit_userReply
Well, our somewhat opposing speculations when the 3GB version announced pretty much are BOTH confirmed with this test.
Sometimes it achieves parity with the 1050Ti, and sometimes it dips below 1050 performance.
Depends on the game.
One thing neither of us considered in our conversation - the need for higher clocks pushes up power consumption to the point where spikes occasionally exceed the specs for the PCIe slot.
Still, the results are interesting - and my curmudgeonly side somewhat objects to the idea of cutting memory bandwidth and compensating for it by cranking up the power. -
Giroro Since this is basically an overclocked 1050 ti with one memory chip missing, I figure it should be no problem to overclock any 1050 Ti to the same rate as the 1050 3GB.Reply -
BulkZerker @redgarlReply
Second paragraph of the article.
"According to our sources, it really doesn’t. Slowly but surely, GeForce GTX 1050 3GB cards will start replacing 2GB boards, particularly as the 512MB memory chips used on those 2GB implementations become harder to source. " -
cangelini Reply21079032 said:Any chance we can get a comparison of the 1050 3GB with the memory overclocked in comparison to the 1050 Ti?
I've been playing with this a bit. Wanted to get the GDDR5 fast enough to give 112 GB/s but realistically it's going to take down-clocking the 1050 2GB, overclocking the 3GB card, and then seeing what difference the missing ROP partition/L2 makes. Will continue trying to come up with a good comparison. -
cangelini Reply21079785 said:Better to test the real product when it shows up. Things must be slow at Tom's.
It *is* a real product. There's a model number and everything :) I've been itching to do something with graphics for months!