HP's Z400 Workstation Runs The Tom's Hardware Gauntlet
We've recently put a lot of effort into designing a custom benchmark suite for testing workstation-class hardware. It's a work in progress, first used to test Intel's Xeon 5600-series CPUs. Today we have some results gleaned from HP's Z400 workstation.
Benchmark Results: Scientific Tests
One of the other major uses for workstation-class PCs is in the scientific, CAD, and engineering markets. We’re working on tests to fill in this part better, but to start with we’ve used a standard Euler3D engineering benchmark.
Euler3D Benchmark
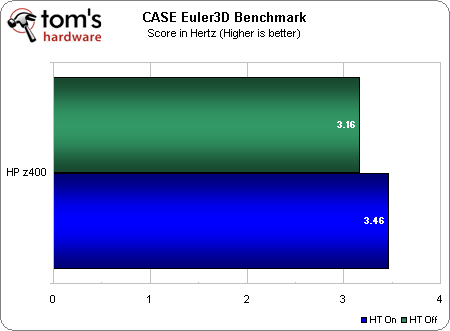
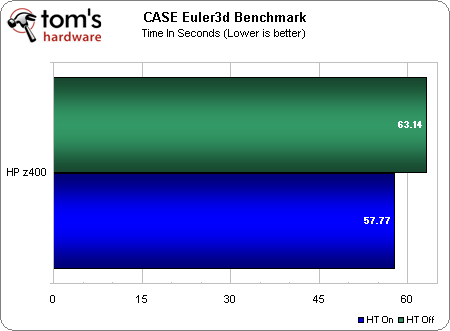
This Euler3D benchmark was developed by the Computational AeroServoElasticity (CASE) Lab at Oklahoma State University’s Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. The test simulates iterations of a computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) airflow problem over a NACA 445.6 aeroelastic test wing at Mach 0.5 (half the speed of sound).
The test reports two figures: the number of iterations the test completes per second (reported in Hertz) and the amount of time necessary to complete the benchmark (in seconds).
The Euler3D benchmark only gains about 9.5% from Hyper-Threading, but is fully threaded. This is indicative of another possible bottleneck that prevents us from realizing a more substantial gain--or perhaps Hyper-Threading simply isn't able to stretch its feet here due to more complete utilization of each physical core by each thread of the benchmark.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Benchmark Results: Scientific Tests
Prev Page Benchmark Results: Digital Audio Workstation Next Page Conclusion-
haplo602 hmm ... I wonder if you could make a D3D/OGL comparison test in some 3D modeling software ? I don't actualy know if any of them supports both APIs.Reply
BTW you dual PCIex16 comment is wrong. There were dual PCIex16 slots in HP workstations since xwX400 models (6400,8400,9400). -
Draven35 Some of the other models have dual x16 slots... but they are rare in baseline models. At some point we'll look at how well an SLI config works in workstation OpenGL tests.Reply
3dsMax uses Direct3D (and OpenGL), but prefers Direct3D (it is 'recommended' by Autodesk on my GTX 460-equipped primary machine...), but Maya does not, it requires OpenGL.
As for whether HT should be disabled? Still questionable. If you're doing animation, and have HT off, you'll gain some interactivity when working, but as soon as you need a test render you'll be losing time. If your 3D application does multithreaded interactiivty tasks, then you're better off with HT on- for instance, the VPR interactive shading mode in Lightwave 10. Its largely dependent on how your software responds to what, and hopefully we'll have more answers on that with the next workstation we look at. -
Draven35 It came that way! The other models in the z-series have better cable management even, specially with the shrouds.Reply -
HibyPrime Lets see.Reply
2GB Ram - Not even close to be considered a usable workstation. - Nevermind, I messed up. I didn't see the (x3)
250GB main/2TB raid 0 - raid 0 setups in workstations are used for scratch disks, and thats it - storage is too risky. 2x 250GB in raid 0 makes much more sense cost wise as you'll never use more than 500GB on a scratch disk, with a 1TB for temporary storage. I say temporary because a workstation is just that, once the work is done (and during) it's backed up and rarely used again.
Creative Labs X-Fi Titanium PCIe - Any Audio professional needing sound quality is going to be using almost exclusively external hardware. The analog outputs all anyone else is going to need.
Who ever chose the specs for this machine needs to be shot. -
MU_Engineer This was an interesting review, but the real machine to test would have been the dual-processor Z800. The big advantages of a workstation are better reliability and stability than a standard desktop and the ability to use multiple processors and more RAM than a typical desktop. Perhaps a Z400 vs. Z800 test would have been interesting as there were a mix of poorly-threaded and well-threaded applications in the test.Reply -
warezme This machine is pathetic. Any decently configured OC'ed quadcore i7 will run circles around this thing, ugh.Reply -
Draven35 It was agreed to start with a z400... the workstation tests were actually developed on this machine, hence why it has a Gen 1 board. Mayhap we'll look at a z800 later.Reply
Most video editors use a RAID array for their video files unless they are just editing DV. HD footage shot on a decent quality camera would quickly overwhelm your proposed 500GB array- the raw P2 footage alone for my film project was 350 GB, and that's before the scratch files generated for color correction and transition renders- and the P2 footage is pretty strongly compressed for semi-pro camera footage. (40 Mb/s) If you're editing uncompressed 1080 HD, you're dealing with 124 MB per second of video. With a larger array, a system like this could be set up for editing uncompressed HD with the simple addition of a BlackMagic Decklink in one of its HD flavors, or the HD version of the Avid Mojo if you prefer to work in something like Media Composer. With the transition of TV to HD, more and more projects are being finished for HD in an attempt to future-proof them- which has actually been going on for about five years before the transition. If you want to see something truly horrible, look at the data rates required for 2k or 4k playback...
HP doesn't sell their machine configured with any kind of professional audio interfaces. They submit their machines for certification by Avid, and the 'full' Pro Tools (Pro Tools HD) comes from Avid on a z800.The audio interface choice for the system was either the Creative card, or the onboard RealTek codec, because that's what HP had and could configure a system with.
You'll find a surprising number (like, most) audio guys including musicians these days working with a mix of software and hardware, and the mixing is done on a computer, not on external hardware. There are audio interfaces with two, four, six, eight and more inputs... my personal music workstation has eight analog inputs, plus ADAT and S/PDIF in. (Note, I need more like twice that in inputs.) You need all these input to capture multiple instruments on completely independent tracks simultaneously , so that they can be given separate effects and the mix can be adjusted on each track. (That's right, you can capture all those tracks at the same time.) Some of these audio interfaces are an internal card , some are an internal card plus an external breakout box (M-Audio Delta series, MOTU 2408, etc), and most are USB or firewire external (Presonus, TASCAM, Echo, Digidesign, Focusrite, et al) boxes with all the hardware located within it. In addition, many have PCI or PCIe DSP accelerator cards from UAD or TC electronic for effects processing and synthesis. -
cadder ReplyThe big advantages of a workstation are better reliability and stability than a standard desktop
I'm not sure I understand this. A machine built with the best enthusiast-class hardware should be basically 100% reliable. The most unreliable part is the hard drive. This machine uses Seagate hard drives, probably the most unreliable brand of drives. This machine also uses an HP motherboard, and HP is below average in reliability in their retail products. Should we expect the workstation components to be better? As for stability, it's using the same OS that everybody else has access to.
All of our CAD machines here use i5/750 CPU's, aftermarket coolers, 8GB, Gigabyte motherboards, a Velociraptor or SSD for the boot drive, a WD Black for the storage drive, ATI FireGL video cards, Win7 Pro 64bit. The machines run at 3.5GHz 24/7 with no problems. I add 2 cooling fans to each case and that in conjunction with the aftermarket cooler keeps things running real cool.