Intel Announces Cascade Lake: Up to 56 Cores and Optane Persistent Memory DIMMs
Xeon D-1600, New SSDs, and 100Gb Ethernet
Xeon D-1600
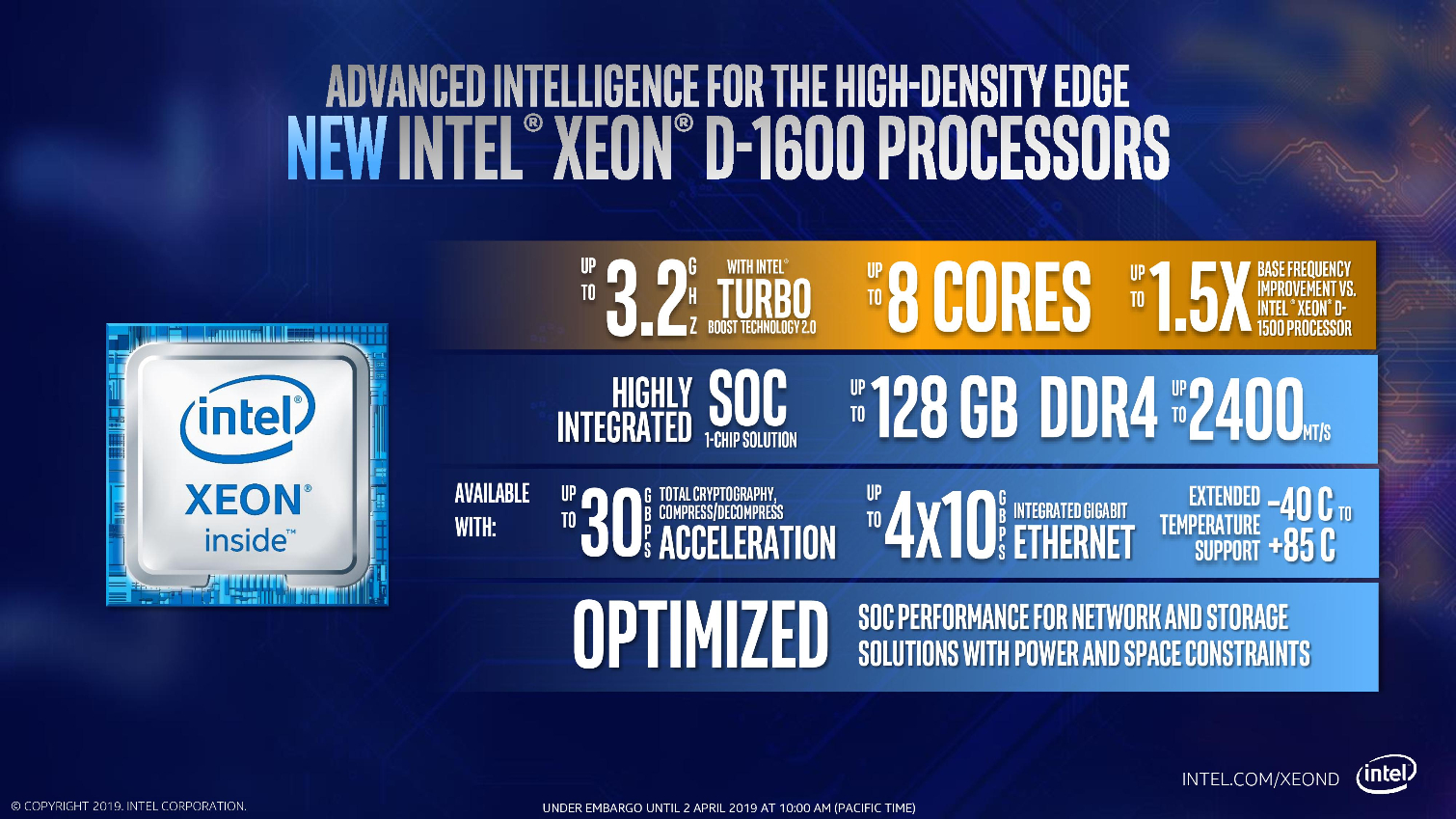
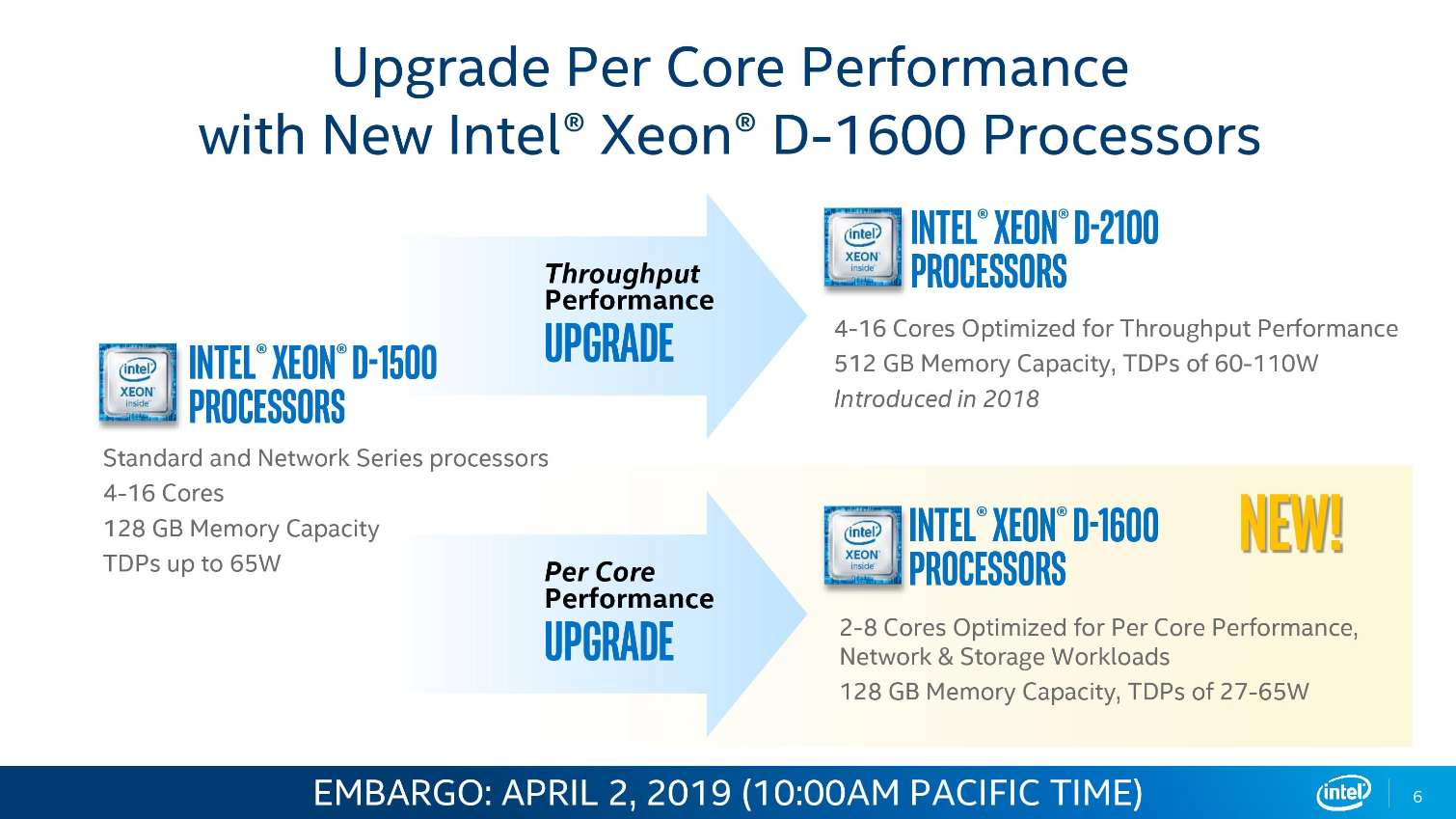
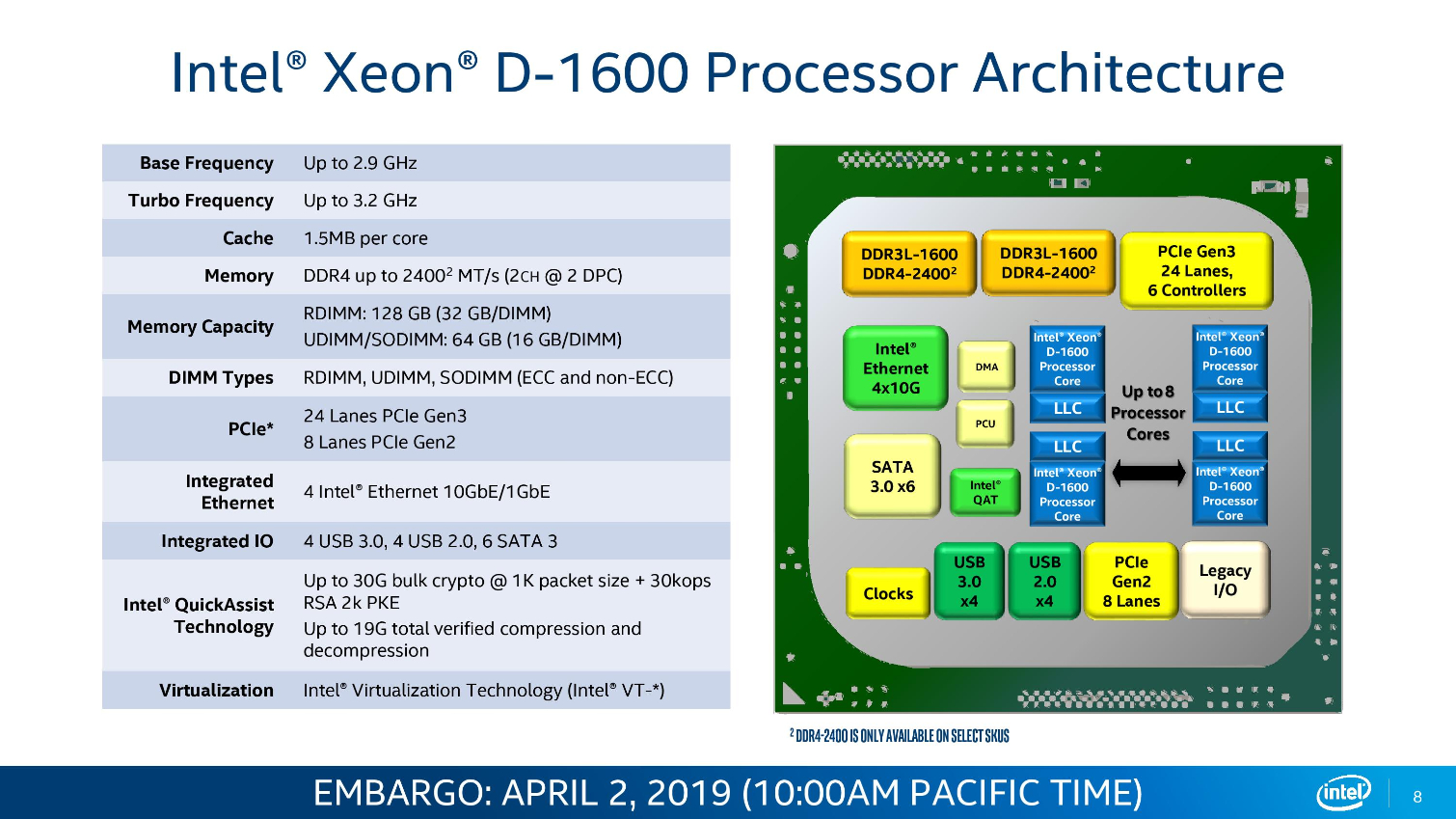
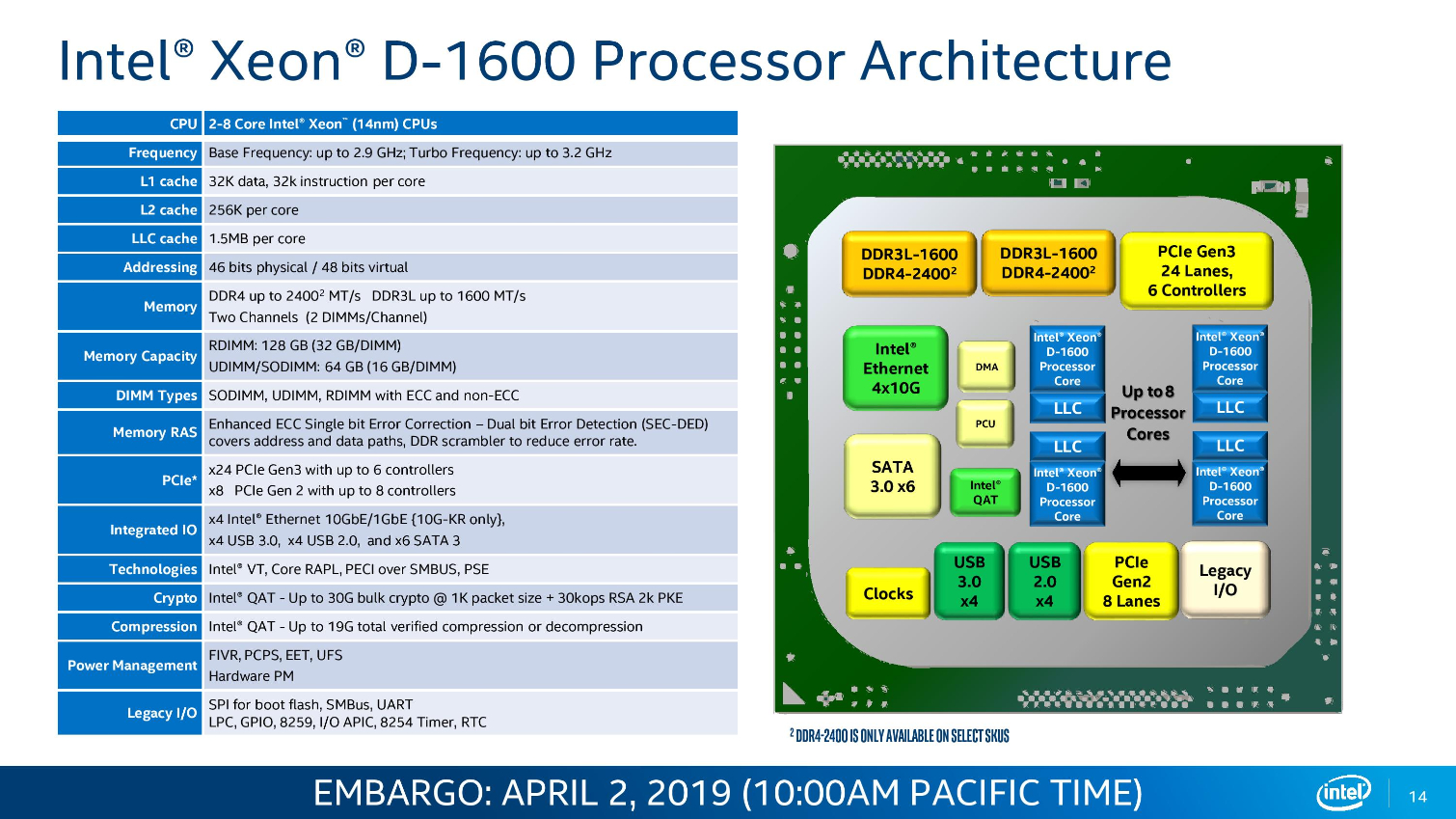
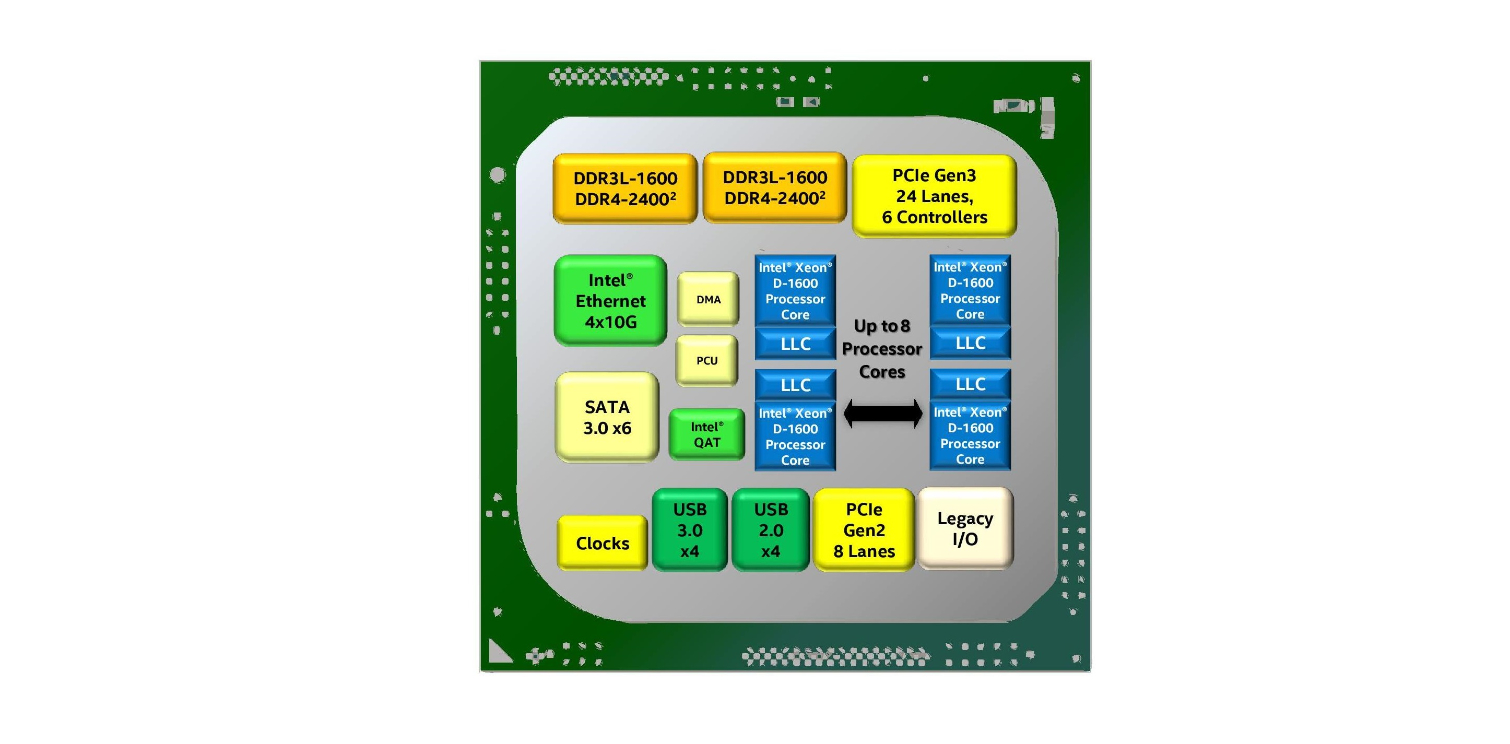
Intel's Xeon D-1600 series slots in as the SoC (System On Chip) solution for power and space-constrained environments, which is critical for Intel's 5G ambitions. These chips find their way into a range of devices, but edge processing for 5G networks is a specific target with this new generation of SoCs.
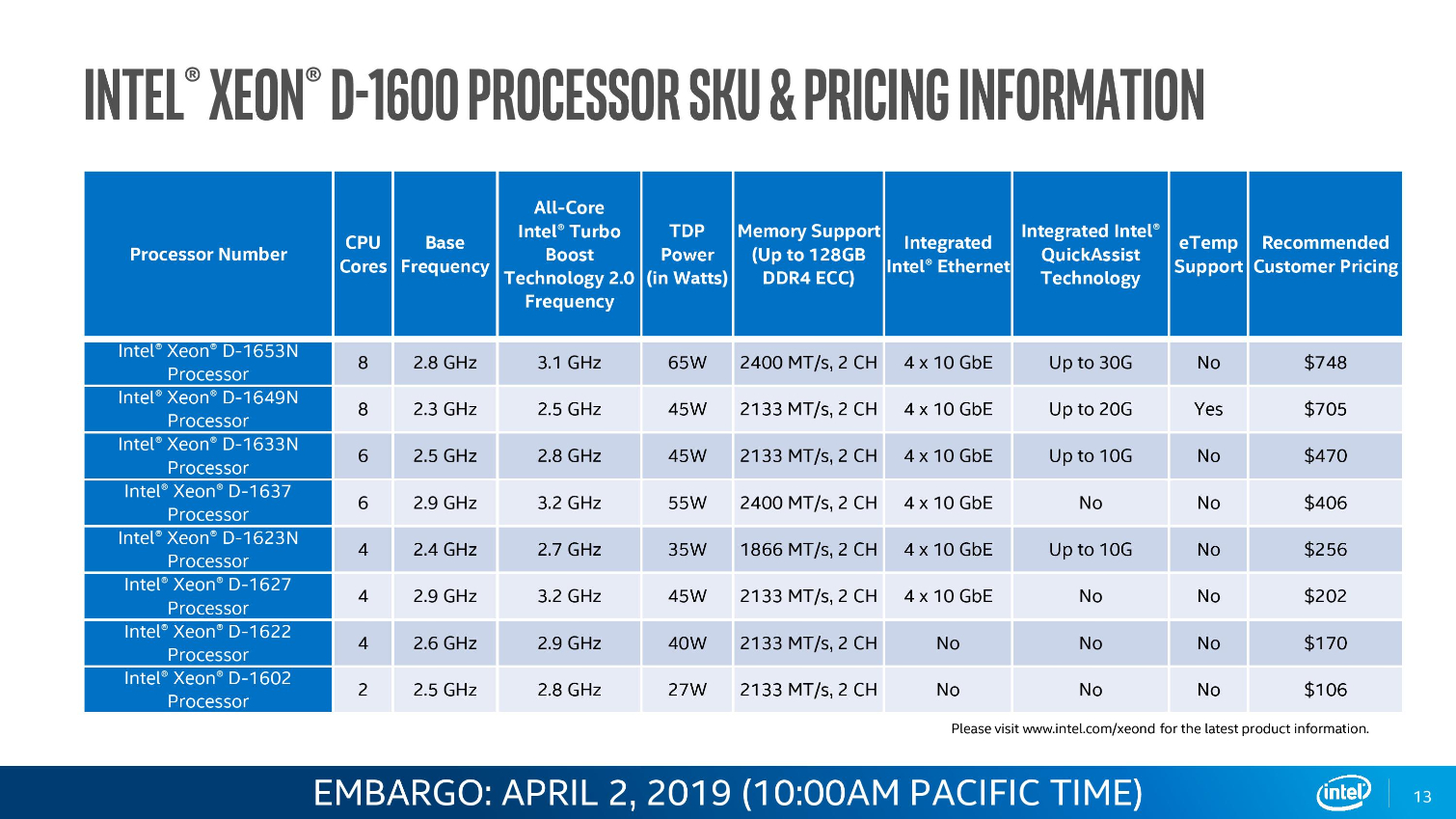
Xeon D-1600 pricing spans from $106 to $748, highlighting that this broad stack of Xeon D-1600 processors, which slot in under the throughput-optimized D-2100 series, addresses a plethora of different use-cases.
The Broadwell-based D-1600 lineup spans up to eight cores and supports up to 128GB of dual-channel DDR4 clocked at (up to) 2400 MT/s, while the D-2100 series spans from four cores to 16 and supports up to 512GB of memory.
Critically, the D-1600 SoCs also come equipped with (up to) an integrated quad-10GBe interface. The Xeon D-1600 processors span from a 27W TDP up to 65W, making them well-suited for a diverse number of power-constrained applications. Core counts span from two to eight cores, with clock speeds ranging from a 2.5GHz base frequency to a 3.2 GHz boost.
Intel Columbiaville 800 Series Ethernet Adapters
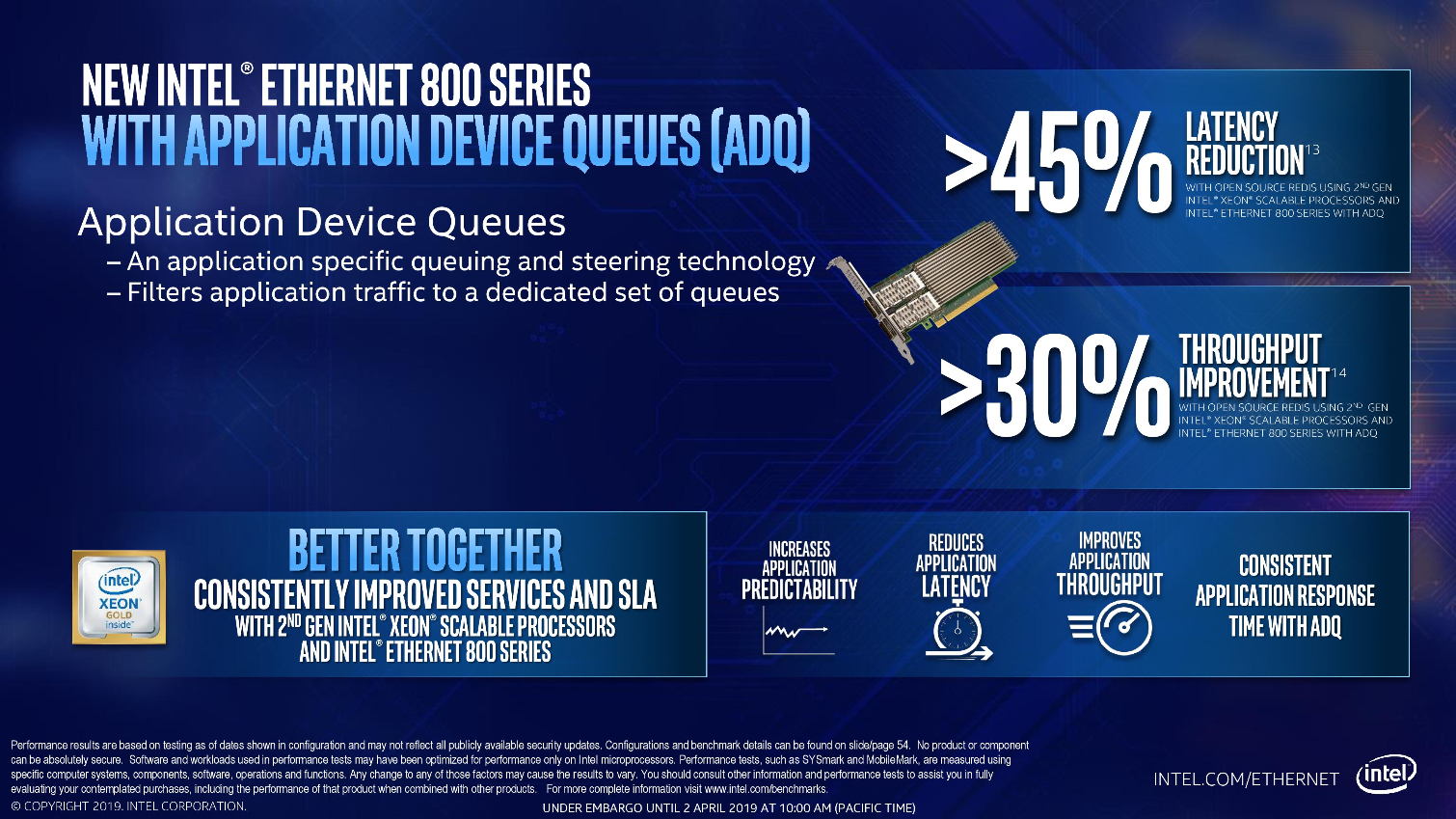

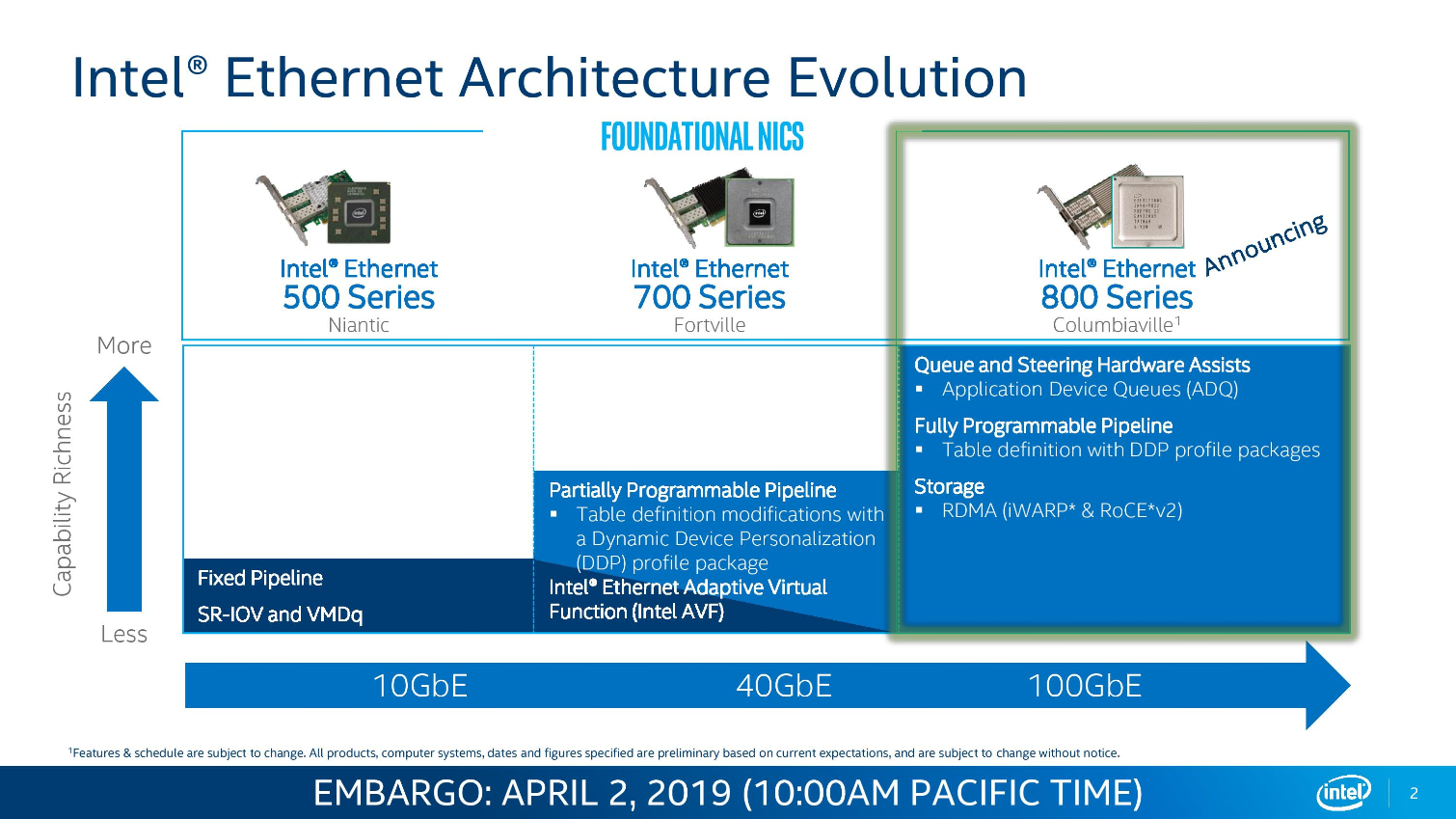
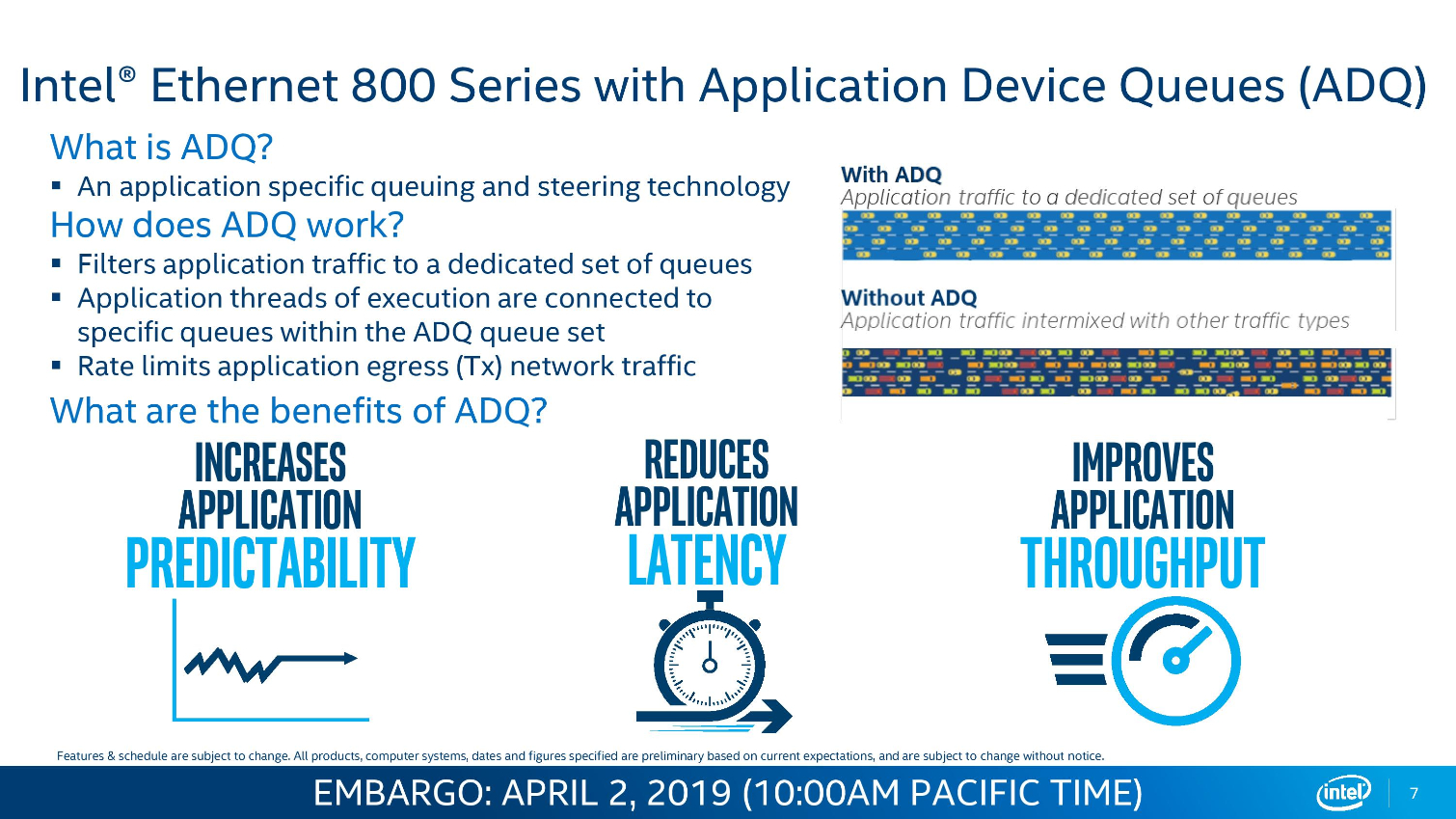
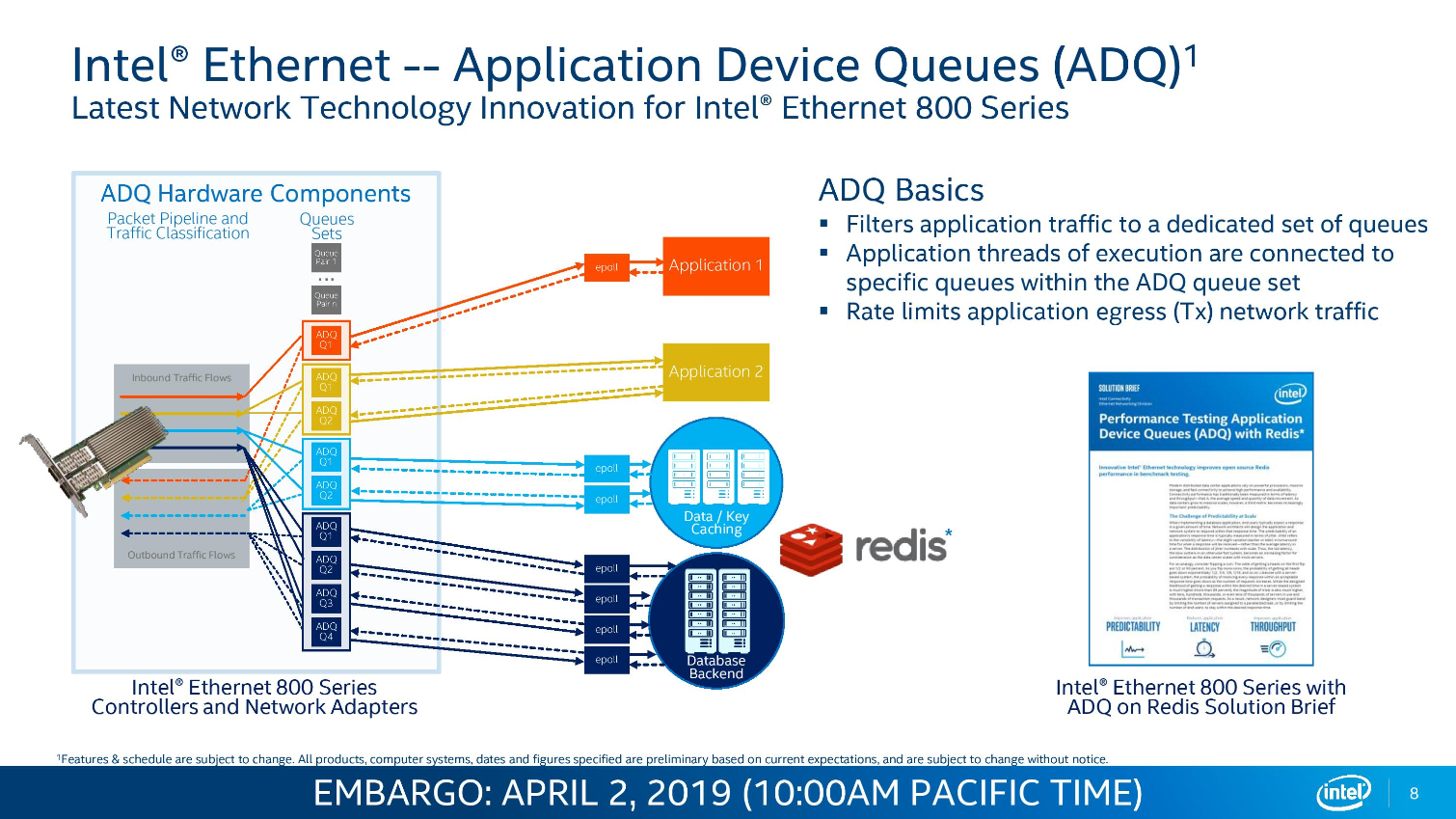
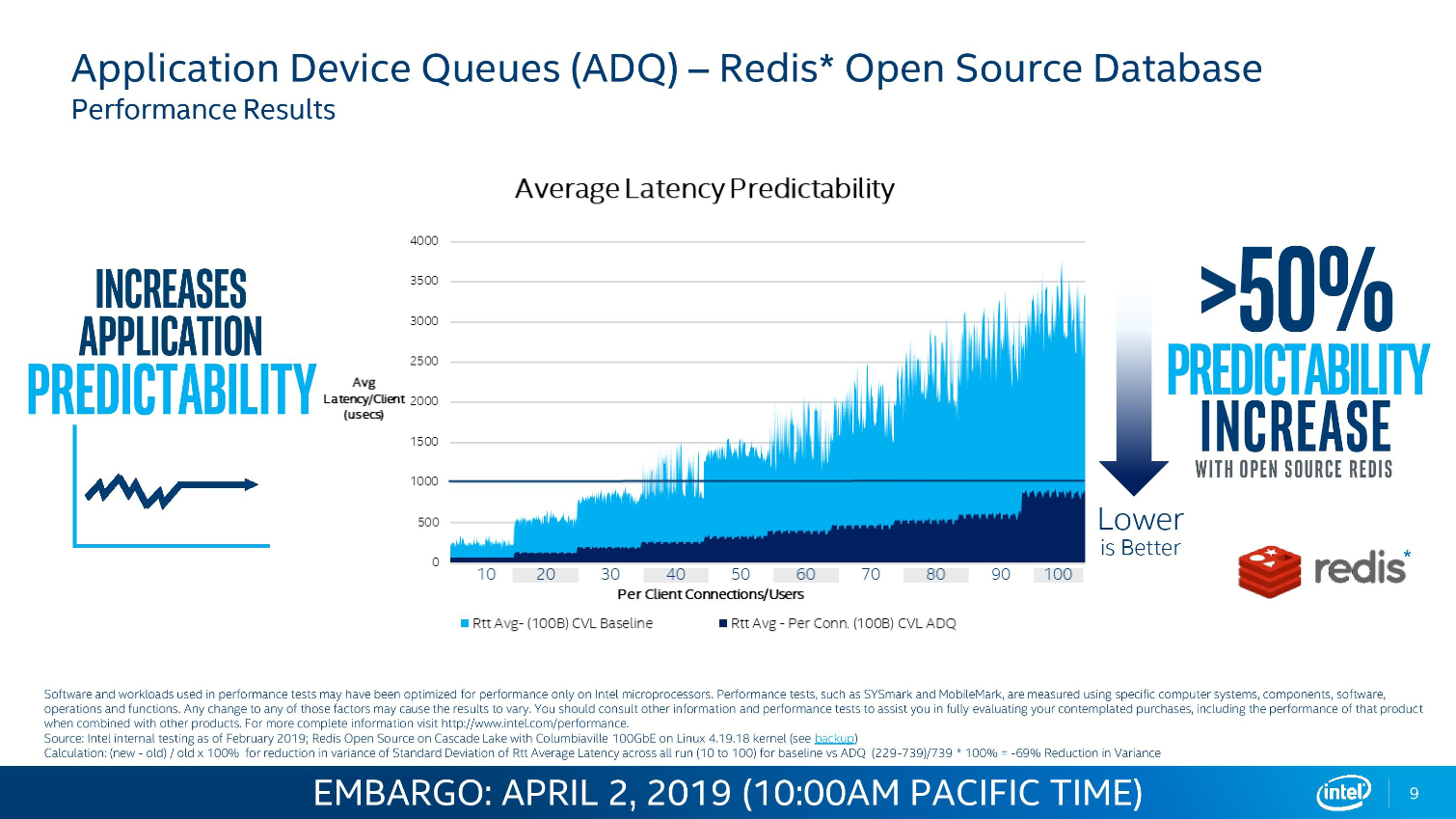
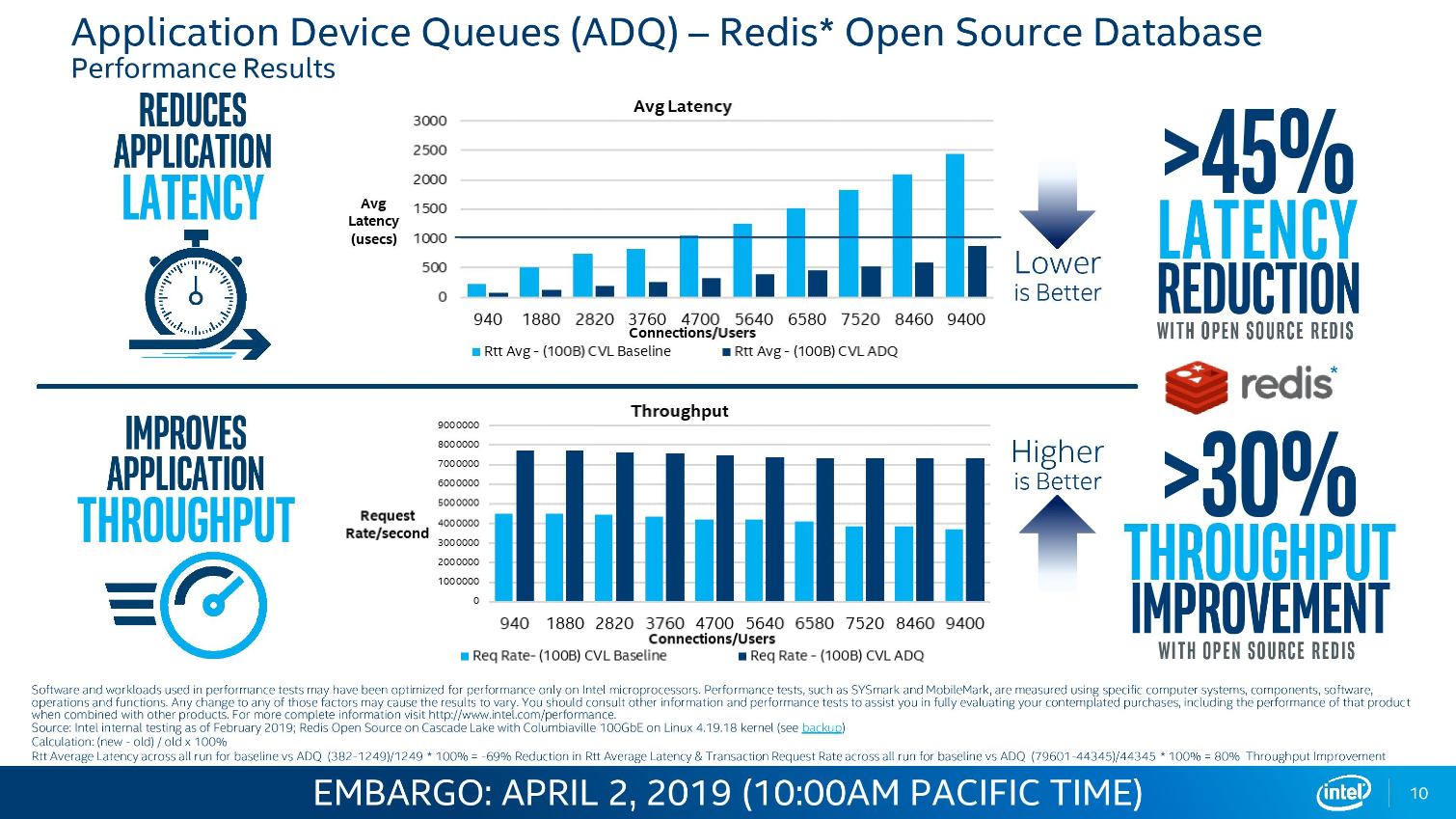
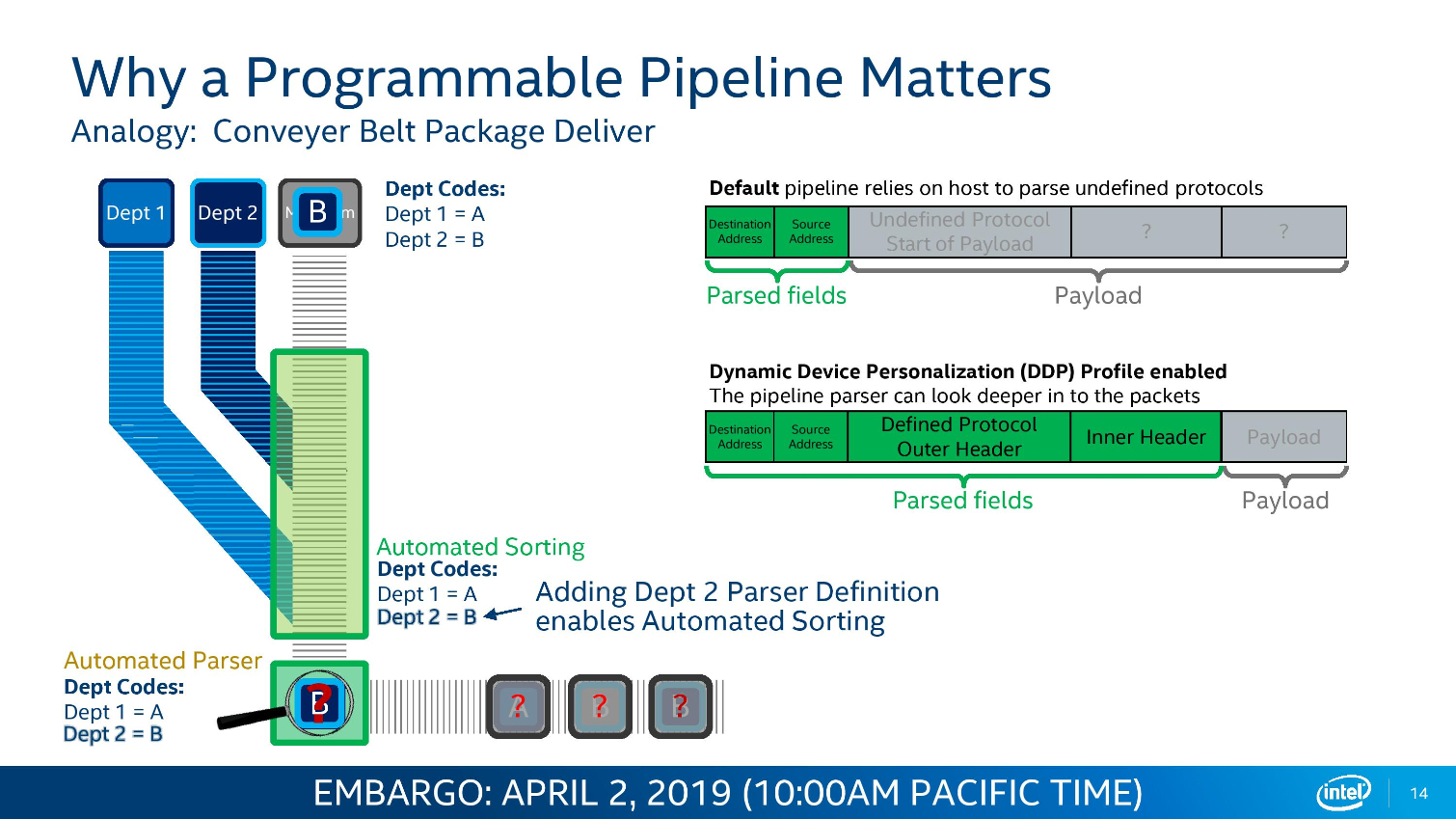
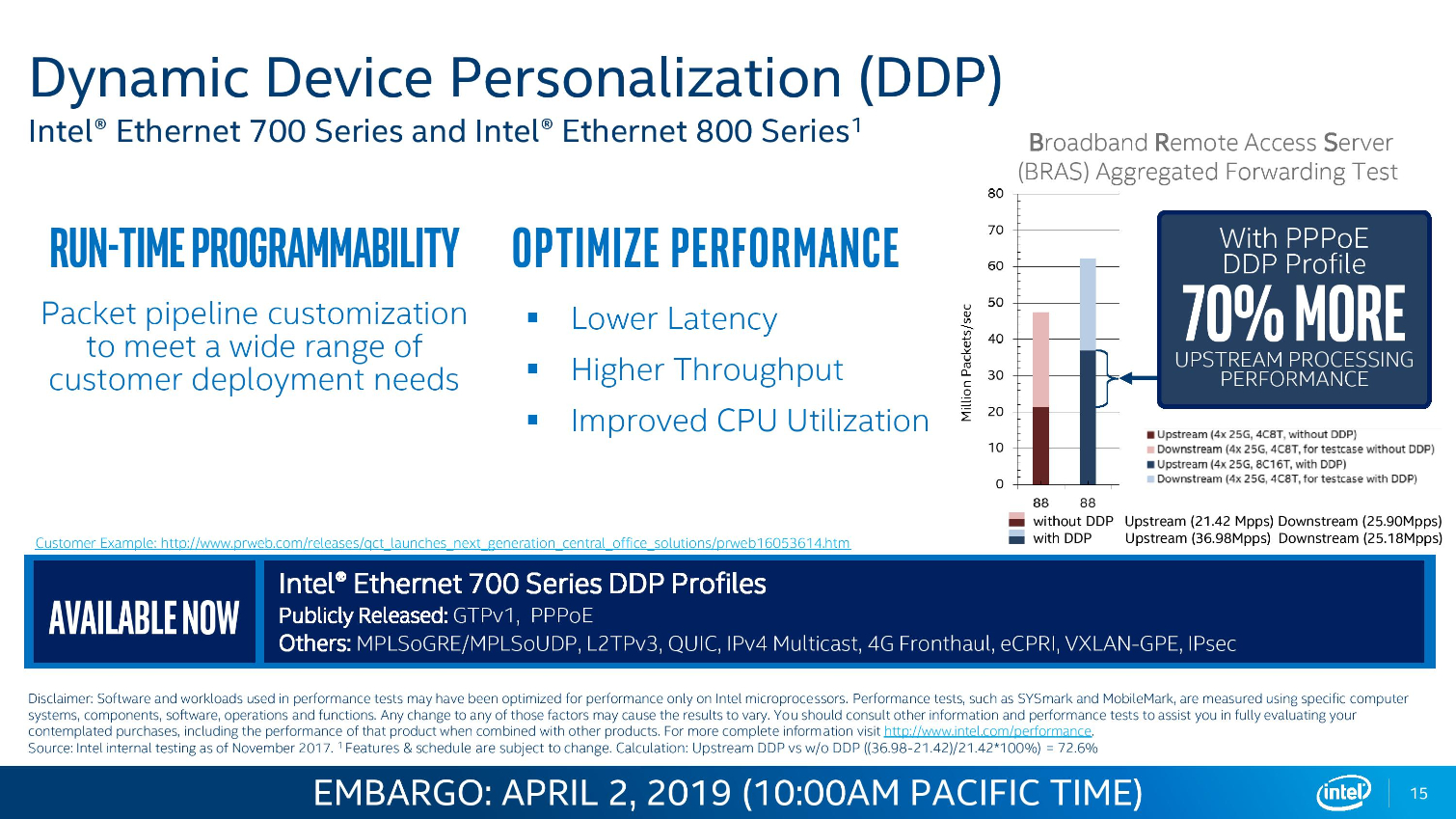

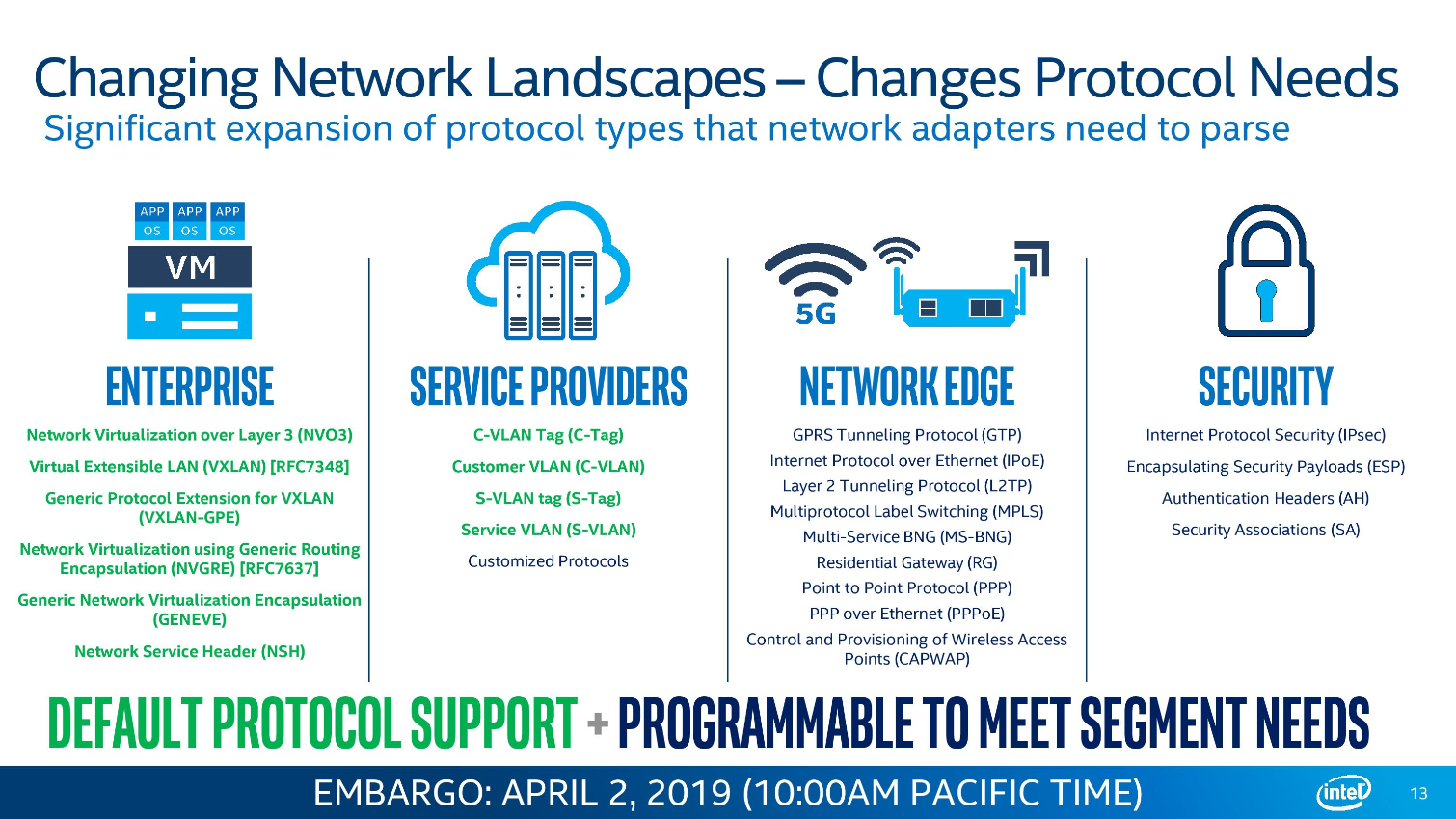
Intel's Ethernet adapters don't draw as many flashbulbs, but they serve as a key strategic asset for the company. Intel's new 800 Series adapters offer up to 100Gbps port speeds and support the new ADQ (Application Device Queue) feature that partitions network traffic into dedicated swim-lanes to boost performance significantly. The adapters also support Dynamic Device Personalization (DPP) profiles that enable smart packet sorting to route data intelligently. These adapters also support RDMA via iWARP and RoCE v2.
Intel hasn't released pricing information for the cards yet, which are sampling to customers, but expects them to launch in Q3 2019.
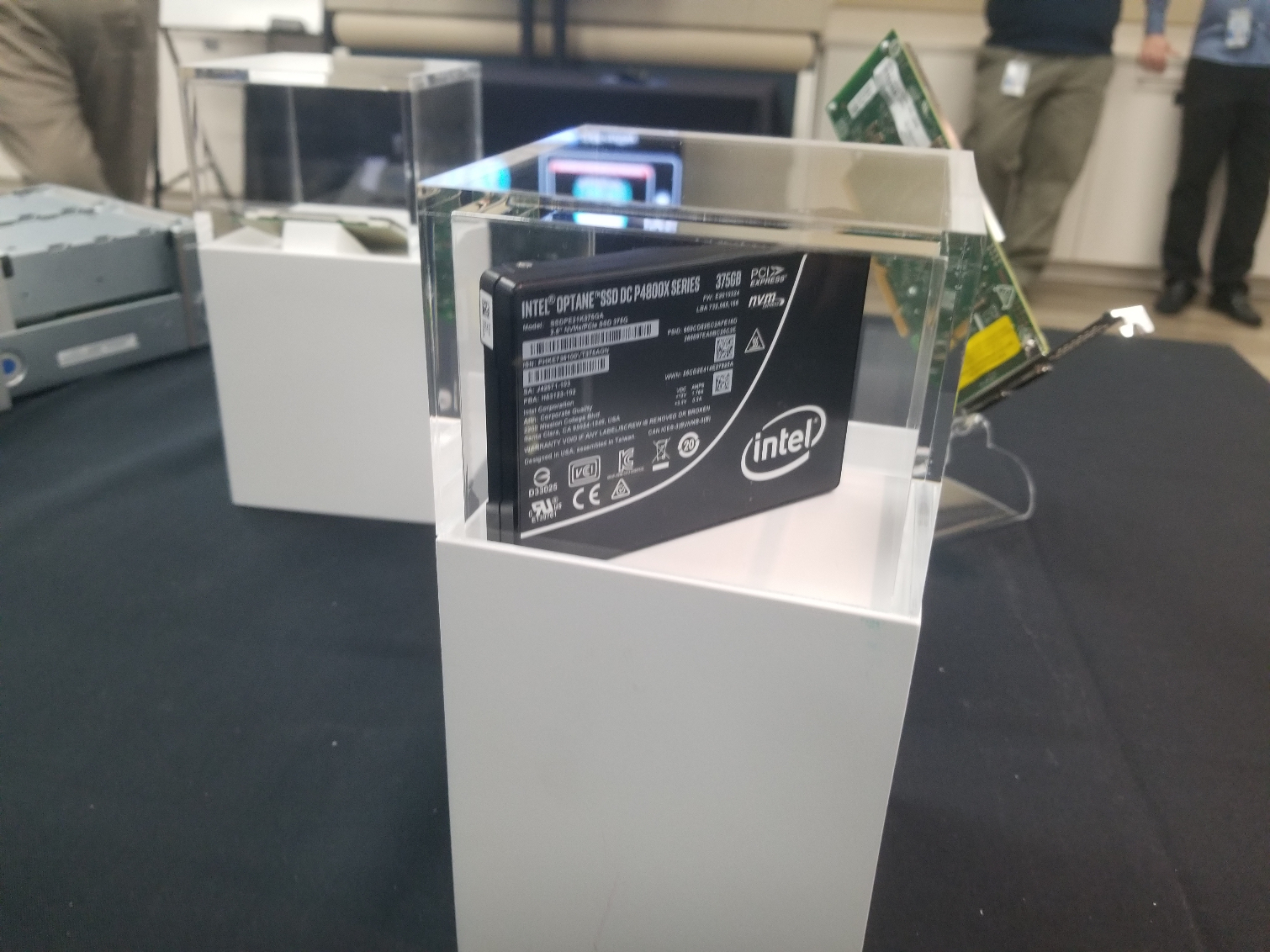
Intel Optane SSD DC D4800X and D5-P4326
Intel announced its new DC D4800X Optane SSDs, which provide dual port functionality that provides multiple pathways into the storage device. This feature provides redundancy, failover, and multi-pathing capabilities for mission-critical applications.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Intel also announced the D5-P4326 SSD. This new SSD adheres to the new standardized ESDF "ruler" form factor and boosts capacity by switching to QLC (Quad-Level Cell) flash. Even though we've seen Intel's MLC variants of these drives demoed for years, these new models are the first for the general market.
The denser flash enables up to 30.72TB per ruler, and up to 1PB of storage per 1U server. Random read/write speeds weigh in at 580,000/11,000 IOPS, while sequential read/write performance lands at 3,200/1,600 MB/s. As expected, QLC flash results in reduced endurance of 0.9 DWPD (Drive Writes Per Day), but this should be sufficient for warm and cold data storage.
Intel hasn't released performance or pricing specifics of its new dual port Optane SSDs, but we'll update as more information becomes available.
Also, stay tuned for our deep-dive analysis of Intel's new 10nm Agilex FPGAs.
Current page: Xeon D-1600, New SSDs, and 100Gb Ethernet
Prev Page Optane DIMMs Have Bright Prospects
Paul Alcorn is the Editor-in-Chief for Tom's Hardware US. He also writes news and reviews on CPUs, storage, and enterprise hardware.