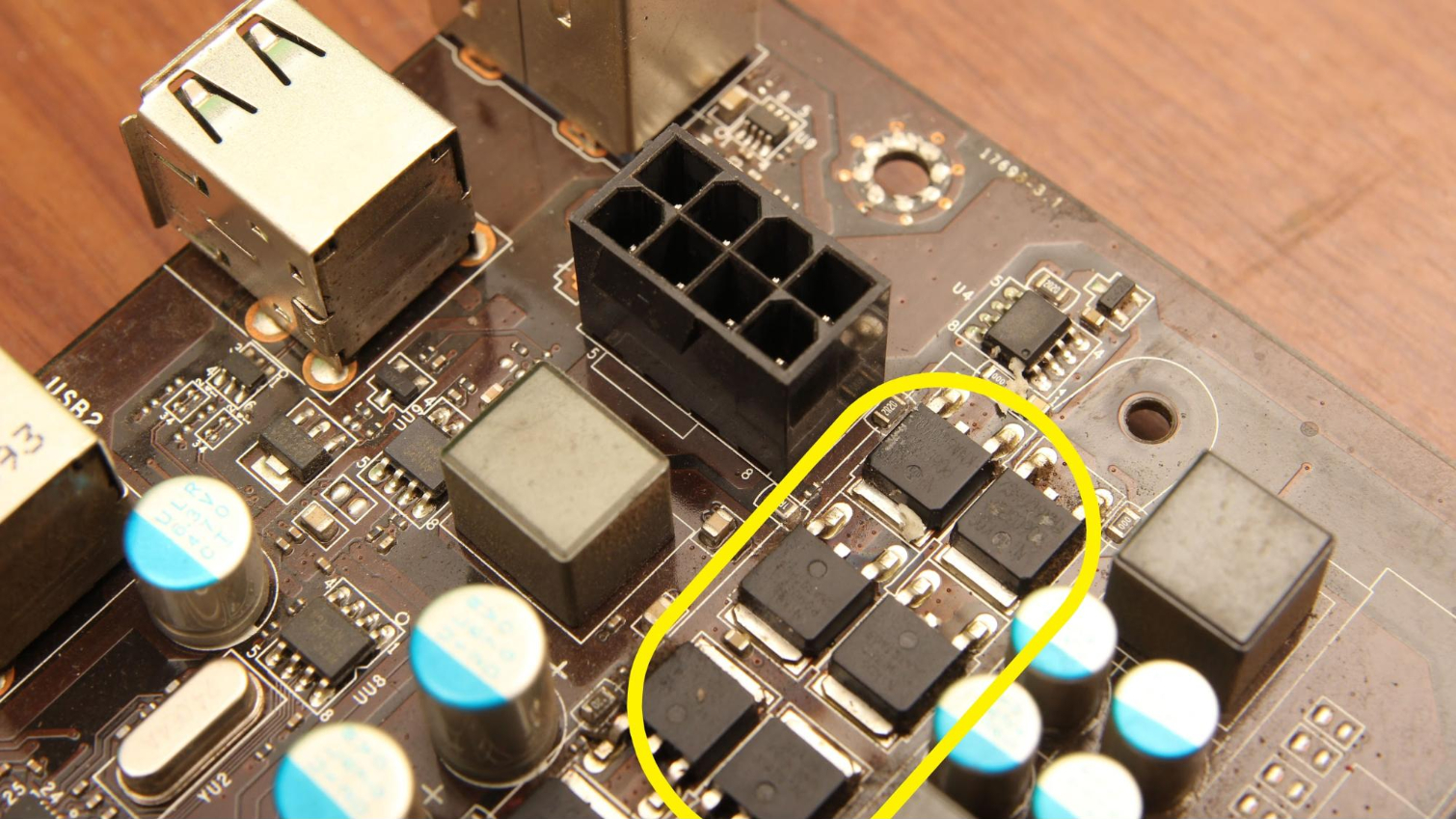
What Is a MOSFET? A Basic Definition
MOSFET stands for metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor. In the PC world, you’ll find these electrical components on a desktop or laptop motherboard, as well as a desktop power supply unit (PSU).
Motherboard MOSFETs
On a PC, MOSFETs help make up the VRM (voltage regulator module), which controls how much voltage other components on the motherboard, like the CPU or graphics card, receive.
PC components like CPUs and graphics cards have strict operating voltages, so a motherboard’s VRM helps make sure this isn’t exceeded. MOSFETs are important to VRM functionality and have an impact on the amount of heat being generated by a VRM while it’s doing its job. MOSFETs can get quite toasty if you’re using a powerful graphics card, and a motherboard’s heatsink helps cool the MOSFETs and, thus, the VRM. In addition to keeping the overall system safe, keeping MOSFETs cool is also important for any type of overclocking.
How Do They Work?
MOSFETs are like switches that go on and off based on a signal from an integrated circuit (IC) called the PWM chip / controller. MOSFETs switch on and off quickly, allowing high current to flow through in short bursts. This, along with other parts of the VRM, controls voltage sent to other PC components on the motherboard.
To keep motherboard MOSFETs cool during extreme overclocking, PC enthusiasts often use waterblocks. Vendor EK also makes Monoblocks, which is a shared CPU and MOSFET waterblock.
MOSFETs and Power Supplies
MOSFETs perform a similar function on PC power supplies.They’re used in convertors and regulator circuits for switching purposes in switched-mode power supplies (SMPS).
In an SMPS, energy is pulled from an AC socket before its broken down into small packets with the MOSFETs acting as switchers. Those packets are then carried via capacitors, inductors and more electric components capable of storing energy. Ultimately, the packets merge into one for a single, and steady, output.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
This article is part of the Tom's Hardware Glossary.
Further reading:
- Dissecting the Modern Motherboard: Connectors, Ports & Chipsets Explained
- Best Motherboards
- Best Power Supplies

Scharon Harding has over a decade of experience reporting on technology with a special affinity for gaming peripherals (especially monitors), laptops, and virtual reality. Previously, she covered business technology, including hardware, software, cyber security, cloud, and other IT happenings, at Channelnomics, with bylines at CRN UK.
-
TJ Hooker ReplyPC components like CPUs and graphics cards have strict operating voltages, so a motherboard’s VRM helps make sure this isn’t exceeded. MOSFETs are important to VRM functionality and have an impact on the amount of heat being generated by a VRM while it’s doing its job. MOSFETs can get quite toasty if you’re using a powerful graphics card, and a motherboard’s heatsink helps cool the MOSFETs and, thus, the VRM. In addition to keeping the overall system safe, keeping MOSFETs cool is also important for any type of overclocking.
This paragraph is sort of misleading. Your motherboard VRMs have nothing to do with your graphics card, and vice versa. -
MeeLee Moss is like grass, but smaller. And fet is like a mix of get and fat.Reply
Is like a cow, eating grass makes you fat. -
bit_user Reply
Ha ha!MeeLee said:Moss is like grass, but smaller. And fet is like a mix of get and fat.
Is like a cow, eating grass makes you fat.
I only clicked this article for the comments. Thanks for not disappointing.
: )