Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Nvidia RTX 4060 Ti AI Performance
GPUs are also used with professional applications, AI training and inferencing, and more. Along with our usual professional tests, we've added Stable Diffusion benchmarks on the various GPUs. AI is a fast-moving sector, and it seems like 95% or more of the publicly available projects are designed for Nvidia GPUs. Those Tensor cores aren't just for DLSS, in other words. Let's start with our AI testing and then hit the professional apps.
We're using Automatic1111's Stable Diffusion version for the Nvidia cards, while for AMD we're using Nod.ai's Shark variant — we used the automatic build version 20230521.737 for testing, launched with "--iree_vulkan_target_triple=rdna3-7900-windows" as recommended by AMD, or "rdna2-unknown-windows" for the RX 6000-series (that's the default). The Nvidia GPUs were tested after replacing the default CUDA DLL files with newer versions, as recommended by Nvidia.
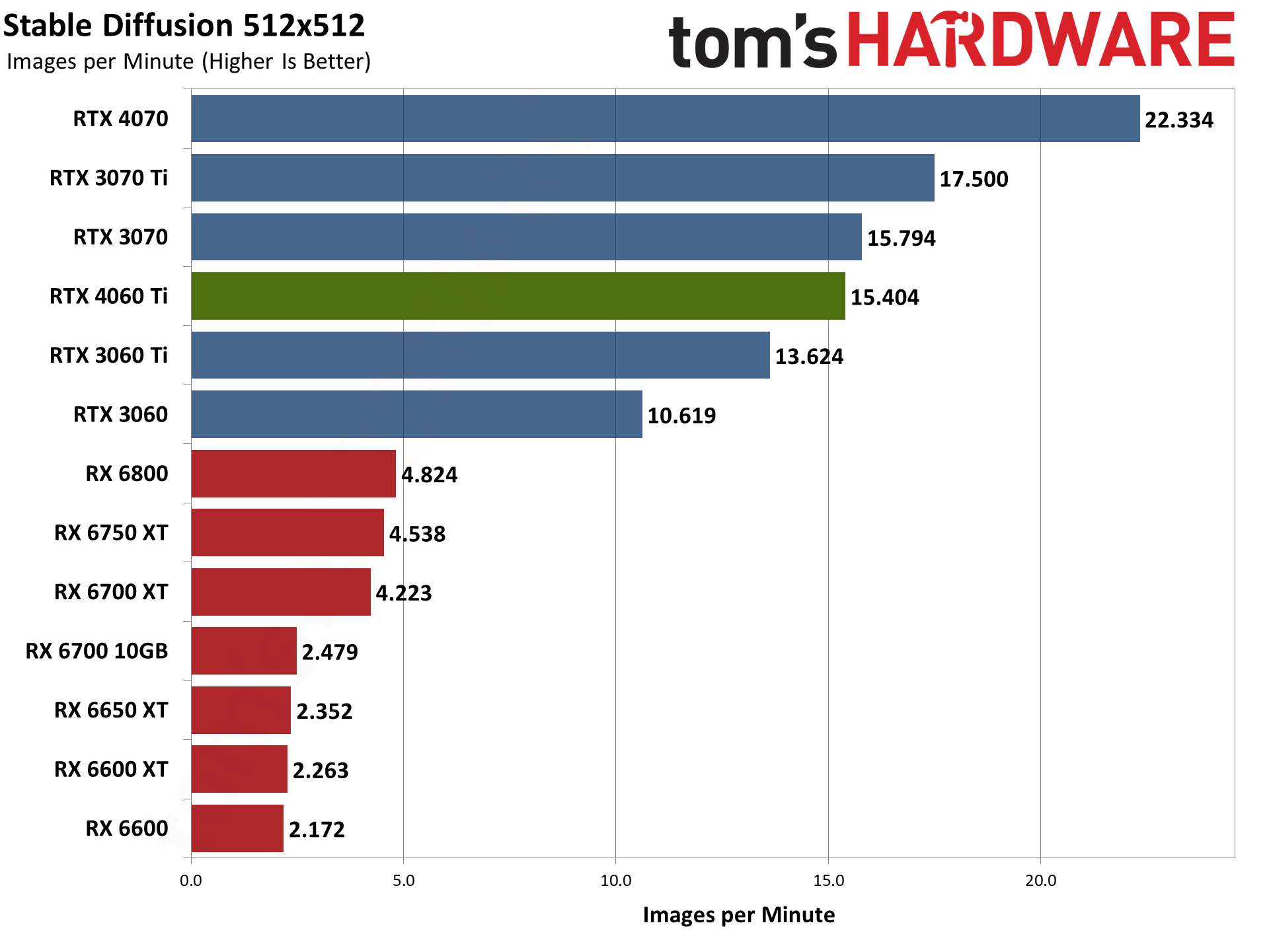
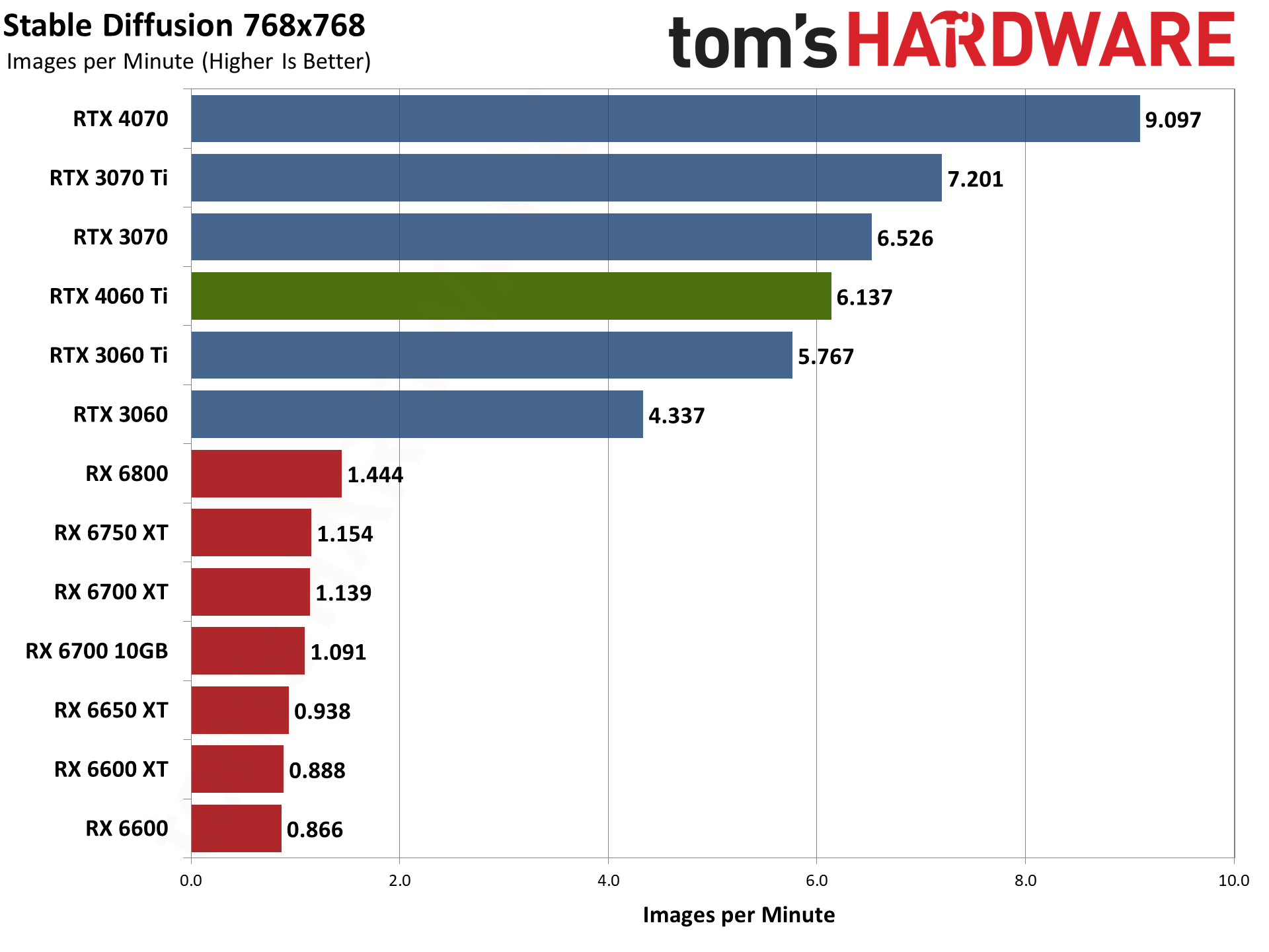
This particular sort of workload is ideally suited to the tensor cores in Nvidia's RTX GPUs. The RTX 3060 more than doubles the Stable Diffusion throughput of the RX 6800 for 512x512 images, and triples the 768x768 performance. We do need to mention that Nod.ai doesn't have "tuned" performance for 768x768, at least with the version of Shark Stable Diffusion that we used, and that's likely a factor. Still, we've been waiting to see improved 768x768 throughput for several months now.
The RTX 4060 Ti takes up its standard position in the charts otherwise, with performance just a bit below the RTX 3070 but also a bit ahead of the RTX 3060 Ti. Like many other workloads, Stable Diffusion is perfectly fine with using the larger L2 cache to overcome the reduction in memory bandwidth.
There are other AI workloads, particularly those that use LLMs (Large Language Models) where VRAM capacity can be more important that computational performance. For example, when we last poked around with running a local chatbot, some of the models required 10GB or even 24GB of VRAM just to run — and there are even larger models for Nvidia's A100/H100 data center GPUs and DGX servers.
Nvidia RTX 4060 Ti Professional Workloads
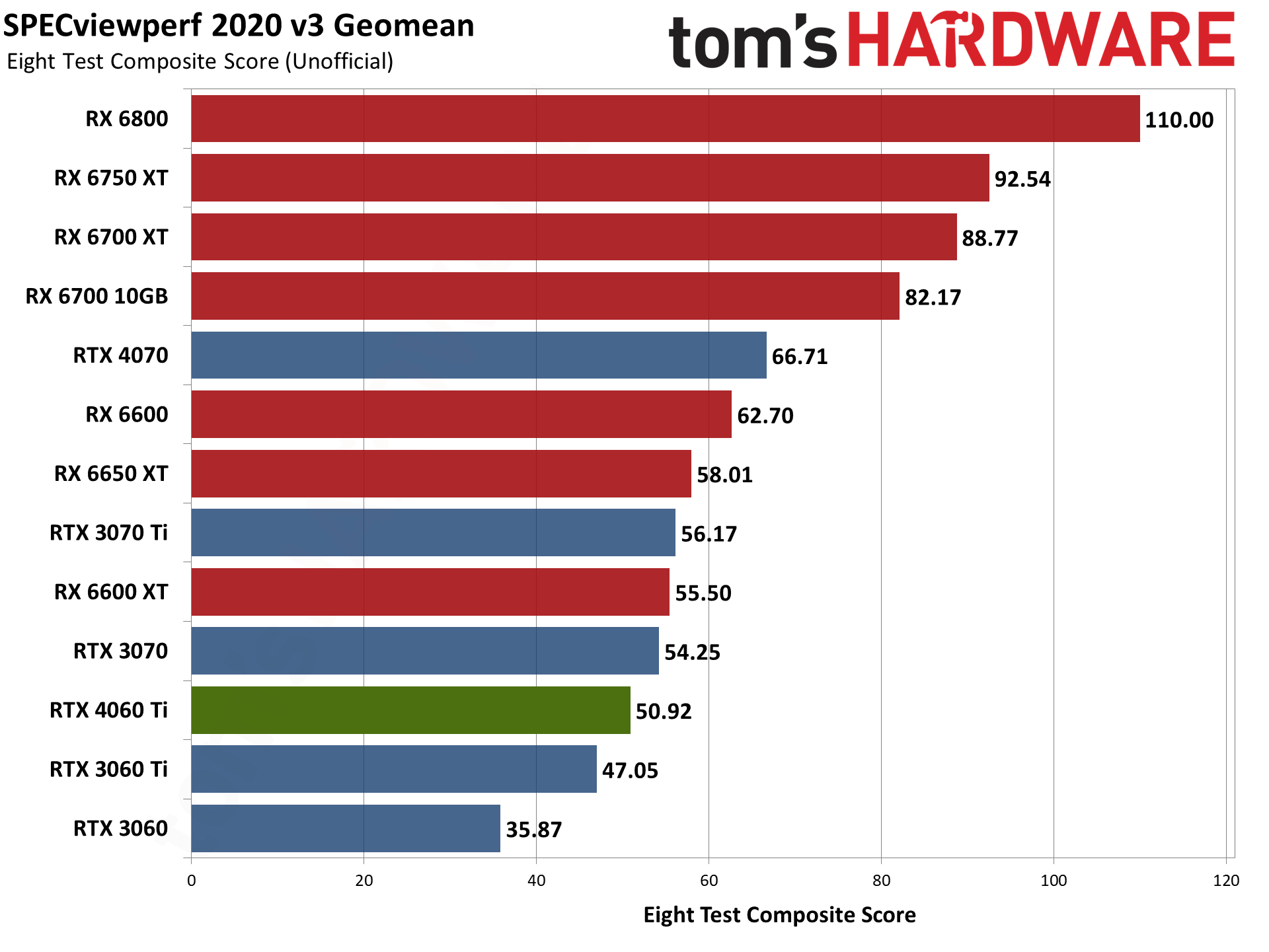
SPECviewperf 2020 consists of eight different benchmarks, and we use the geometric mean from those to generate an aggregate "overall" score. Note that this is not an official score, but it gives equal weight to the individual tests and provides a nice high-level overview of performance. Few professionals use all of these programs, however, so it's typically more important to look at the results for the application(s) you plan to use.
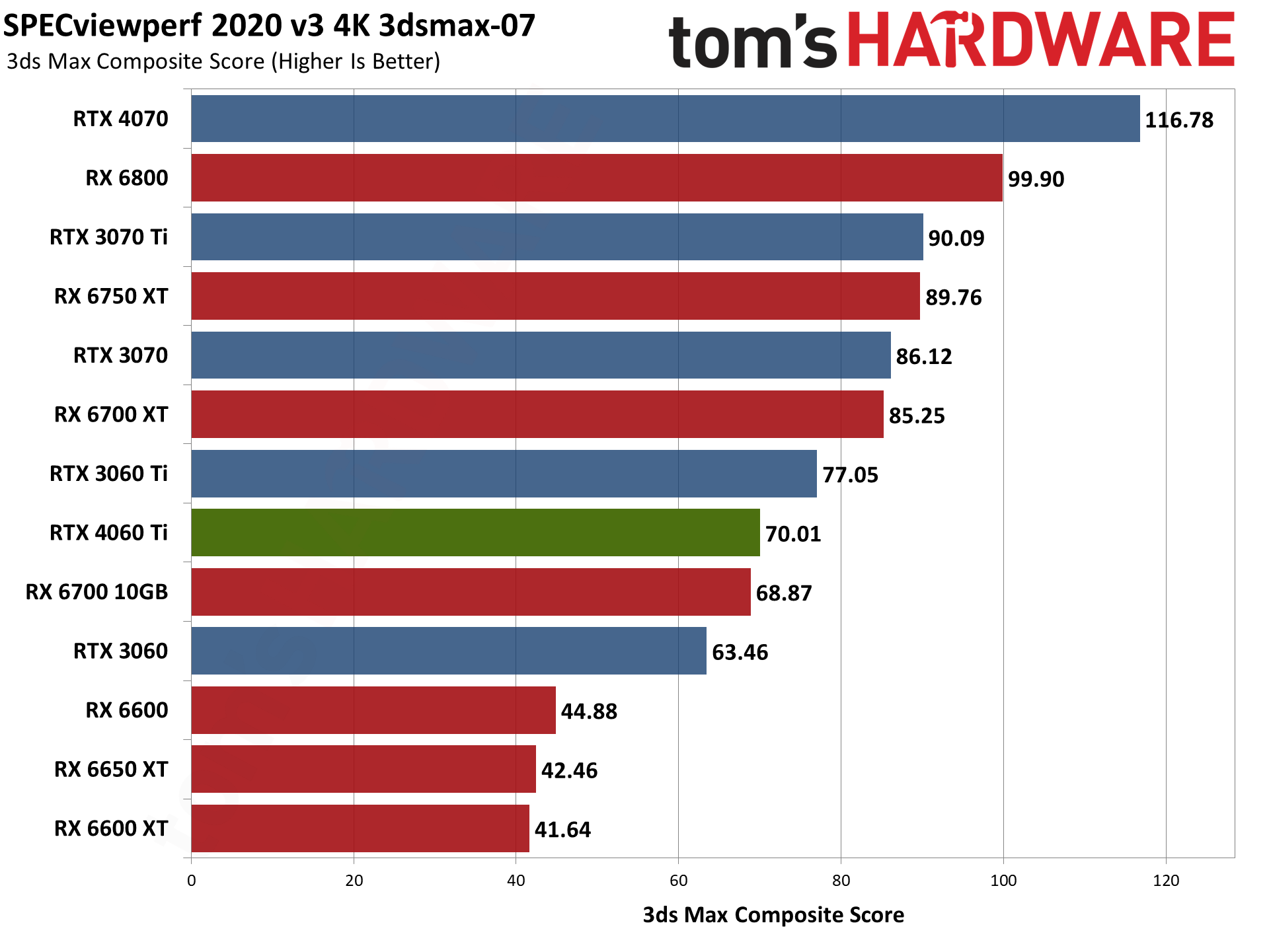
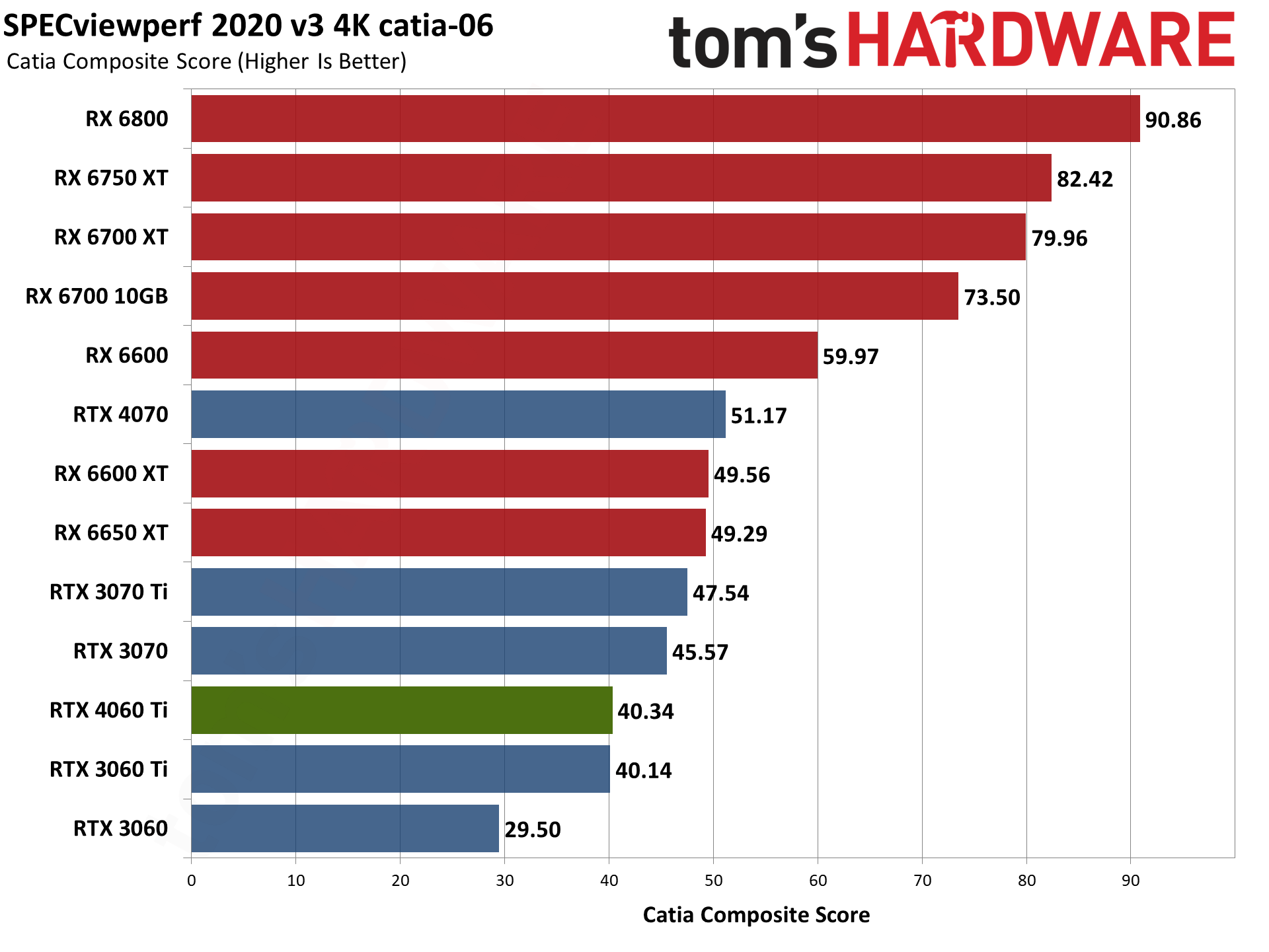
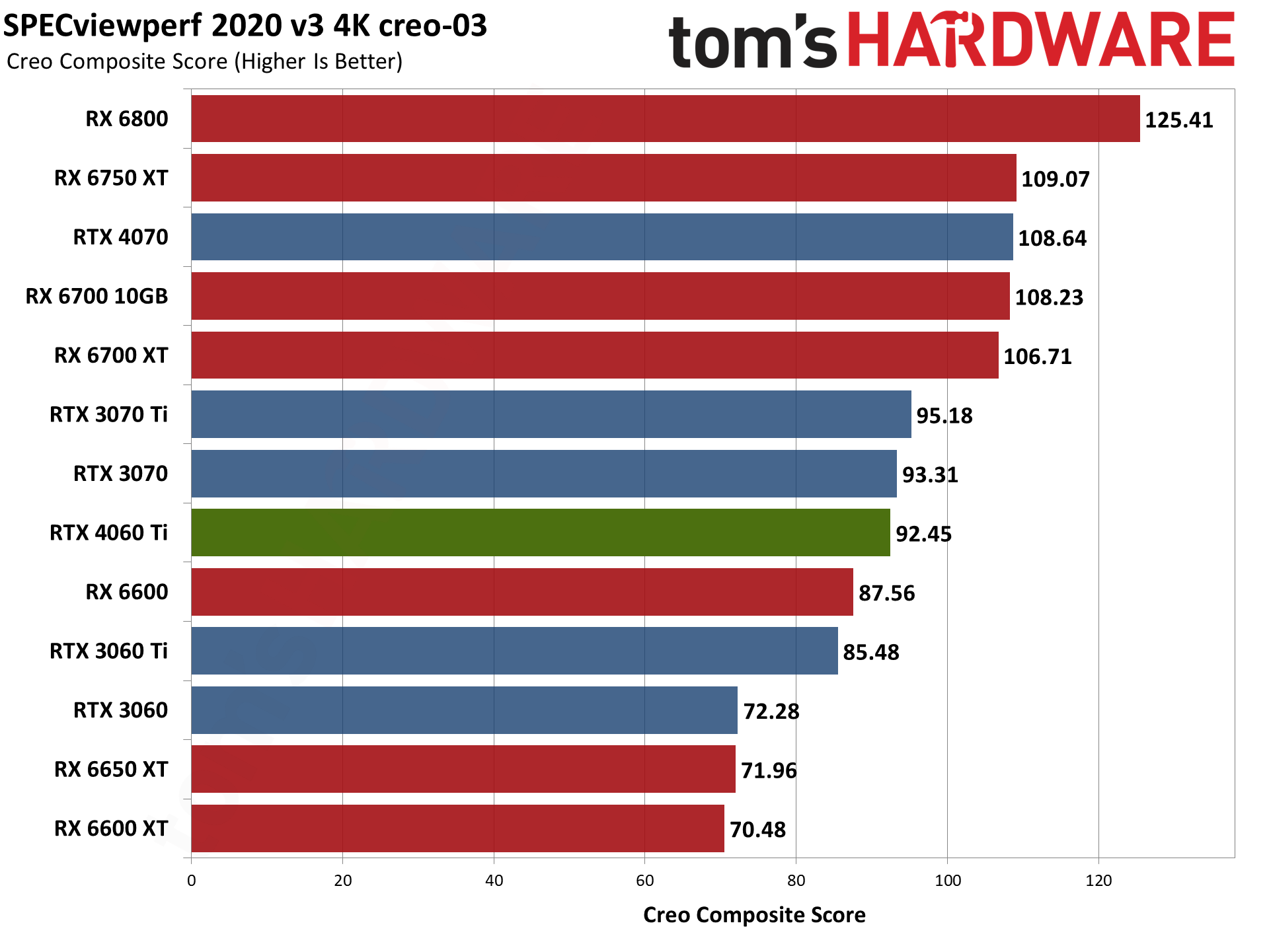
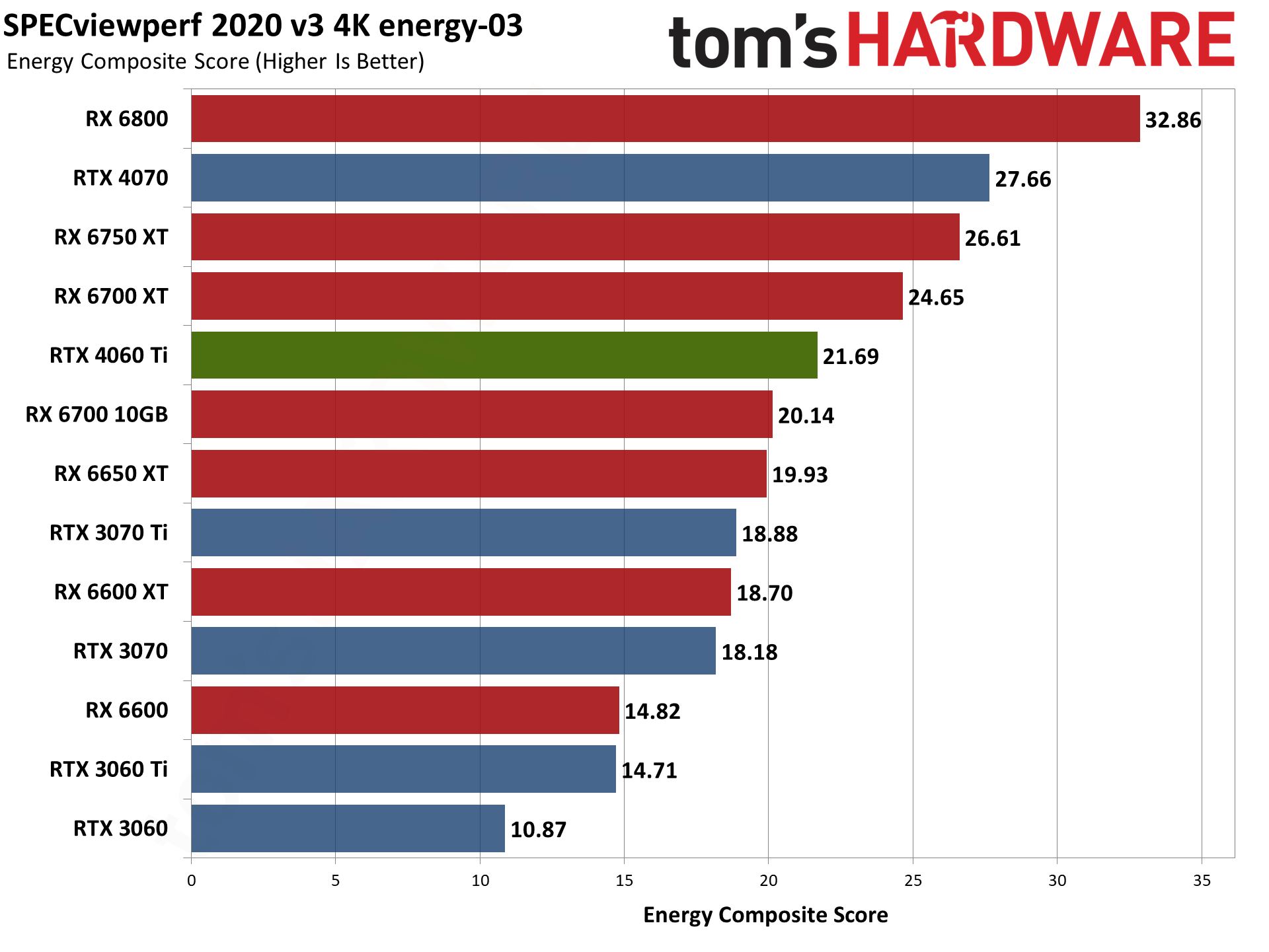
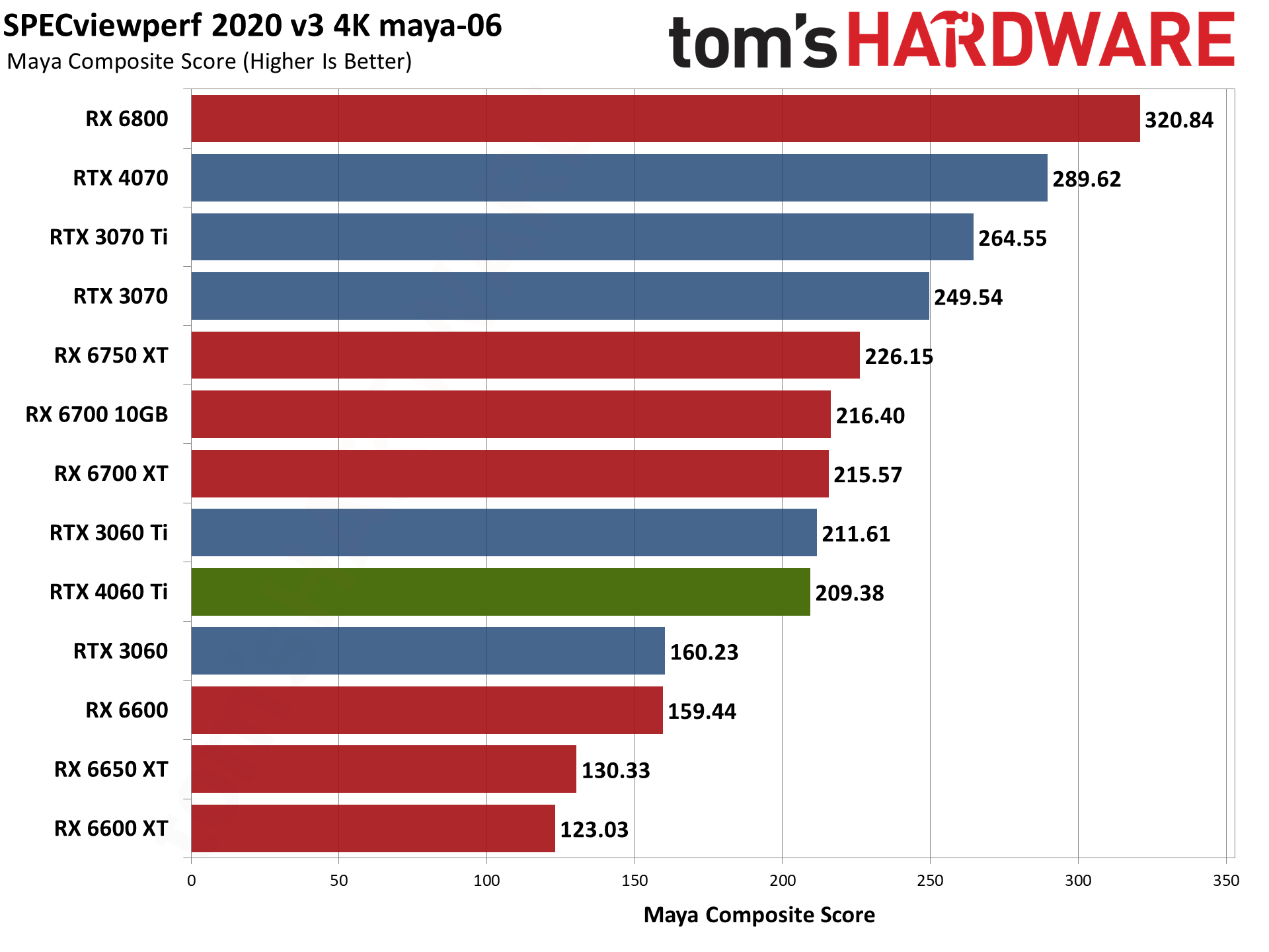
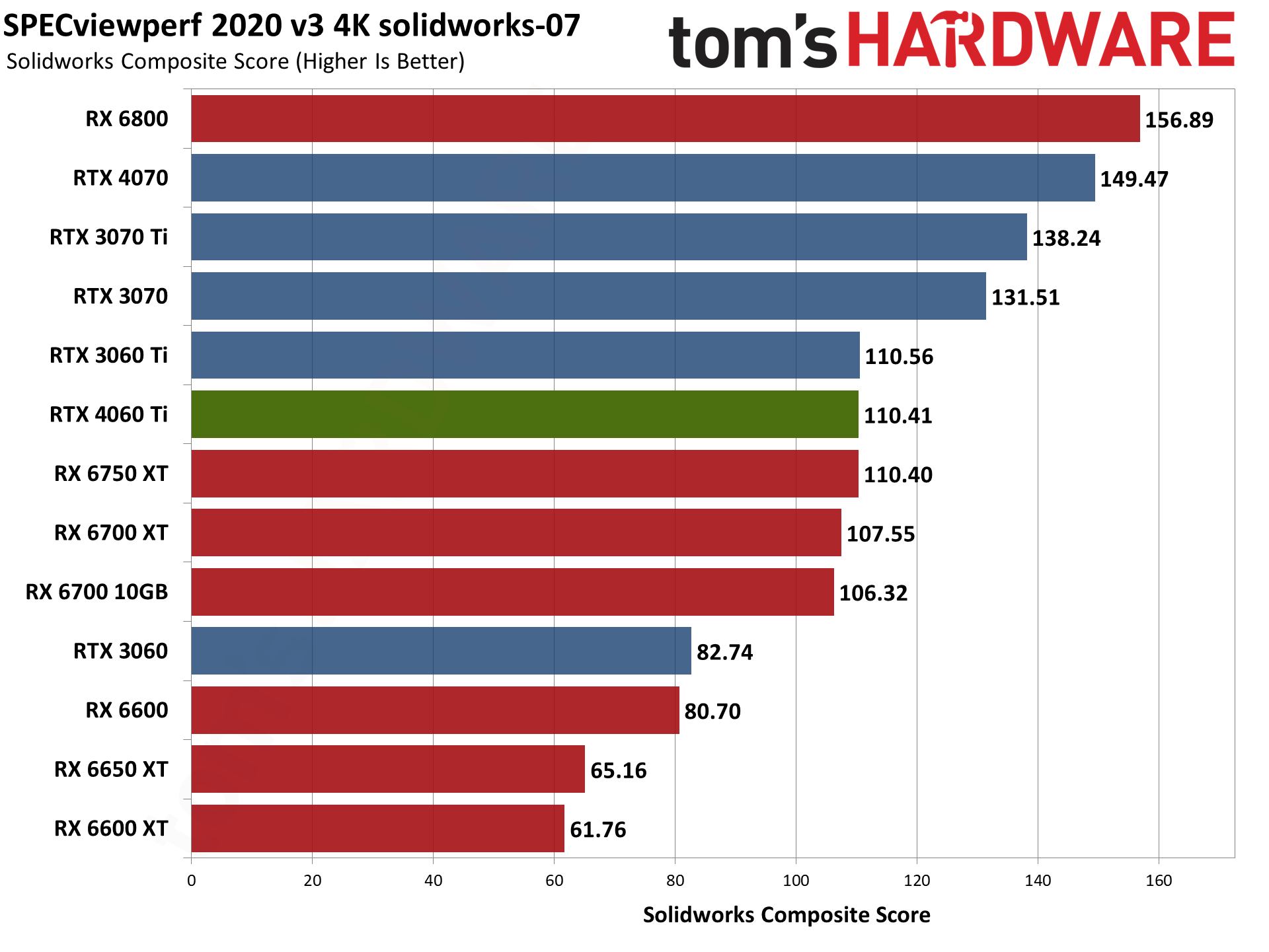
Nvidia's RTX 4060 Ti does battle with the RTX 3060 Ti here, winning in some tests and losing in others. Overall, it lands between the 3060 Ti and 3070 once again, but 3D Studio Max as an example either prefers the higher raw memory bandwidth of the 3060 Ti, or else it's simply better tuned for the Ampere architecture.
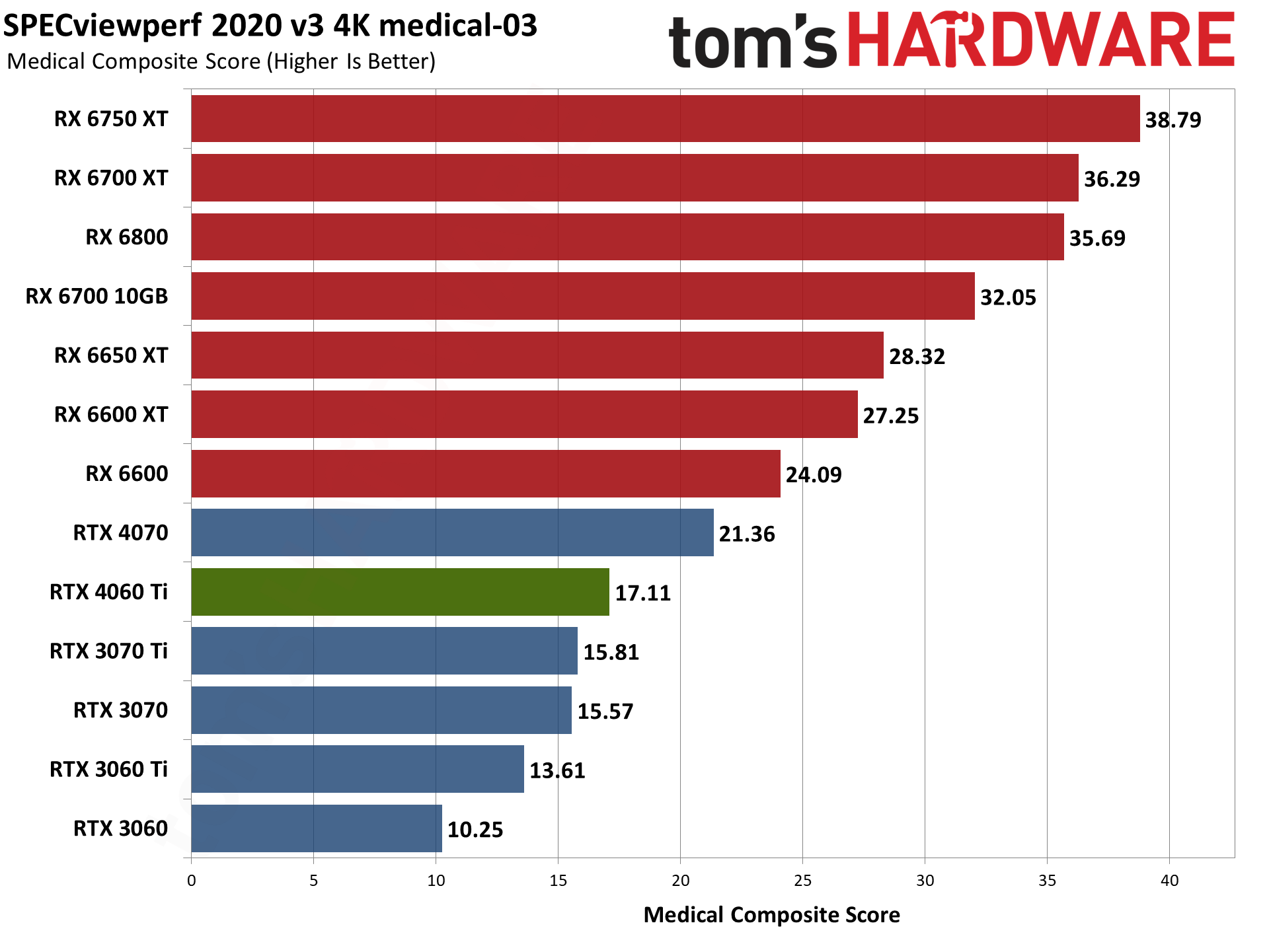
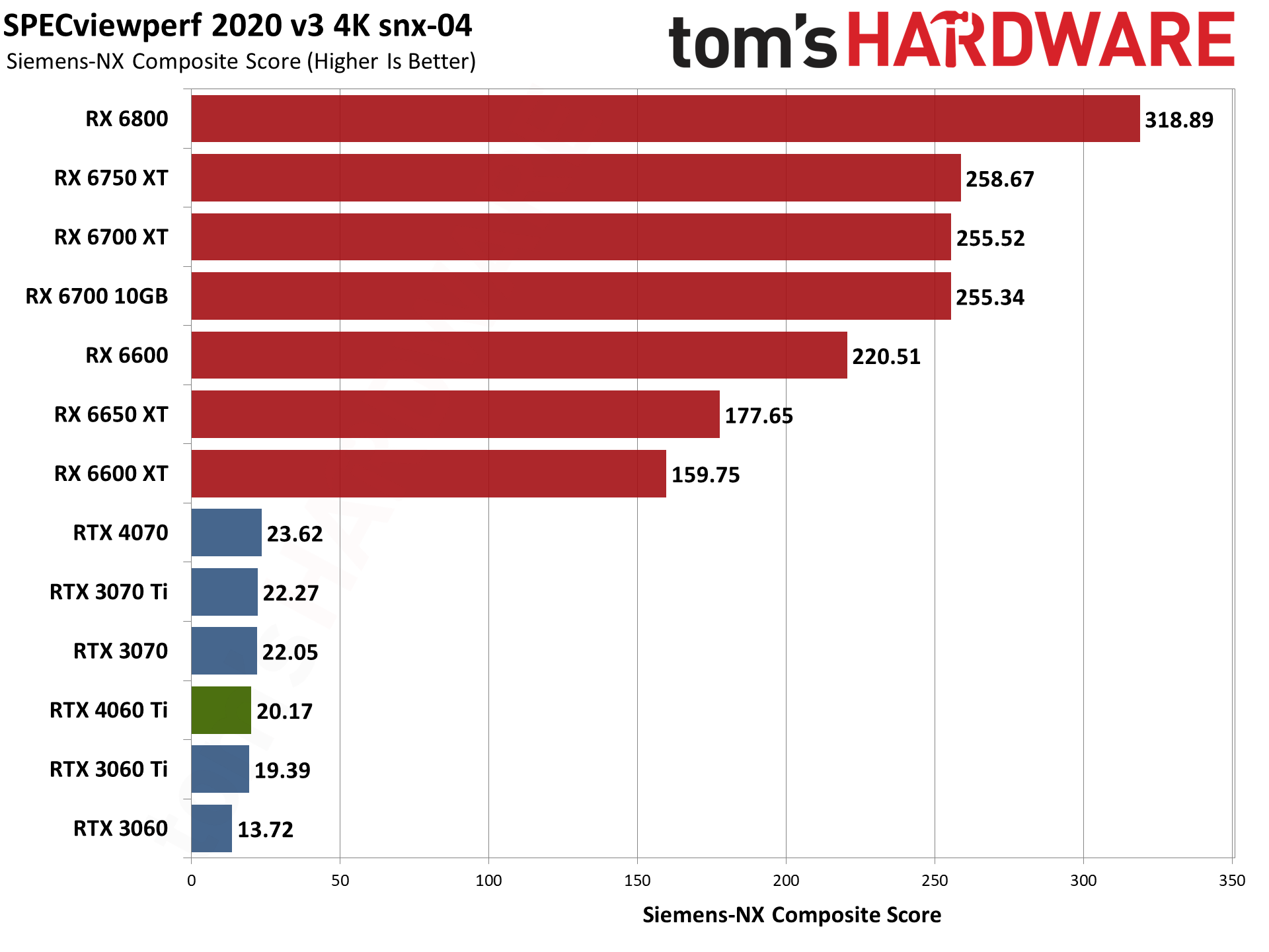
For its part, AMD released drivers that provided a substantial boost to SPECviewperf scores last year. AMD GPUs score particularly well in snx-04 (or if you prefer, Nvidia's consumer RTX cards do very poorly). AMD also tends to score higher in catia-06, creo-03, energy-03, and medical-03, while Nvidia GPUs do better in 3dsmax-07 — with maya-06 and solidworks-07 being more neutral.
To match the RX 6000-series GPUs in some workloads, you'd need one of Nvidia's professional cards. (Also: No, I'm not sure why the RX 6600 performed so well. I tested it alongside the RX 6600 XT and RX 6650 XT within the past 24 hours, and it simply performed better for some reason.) Anyway, if you use any of these applications on a regular basis, that could be enough to sway your GPU purchasing decision.
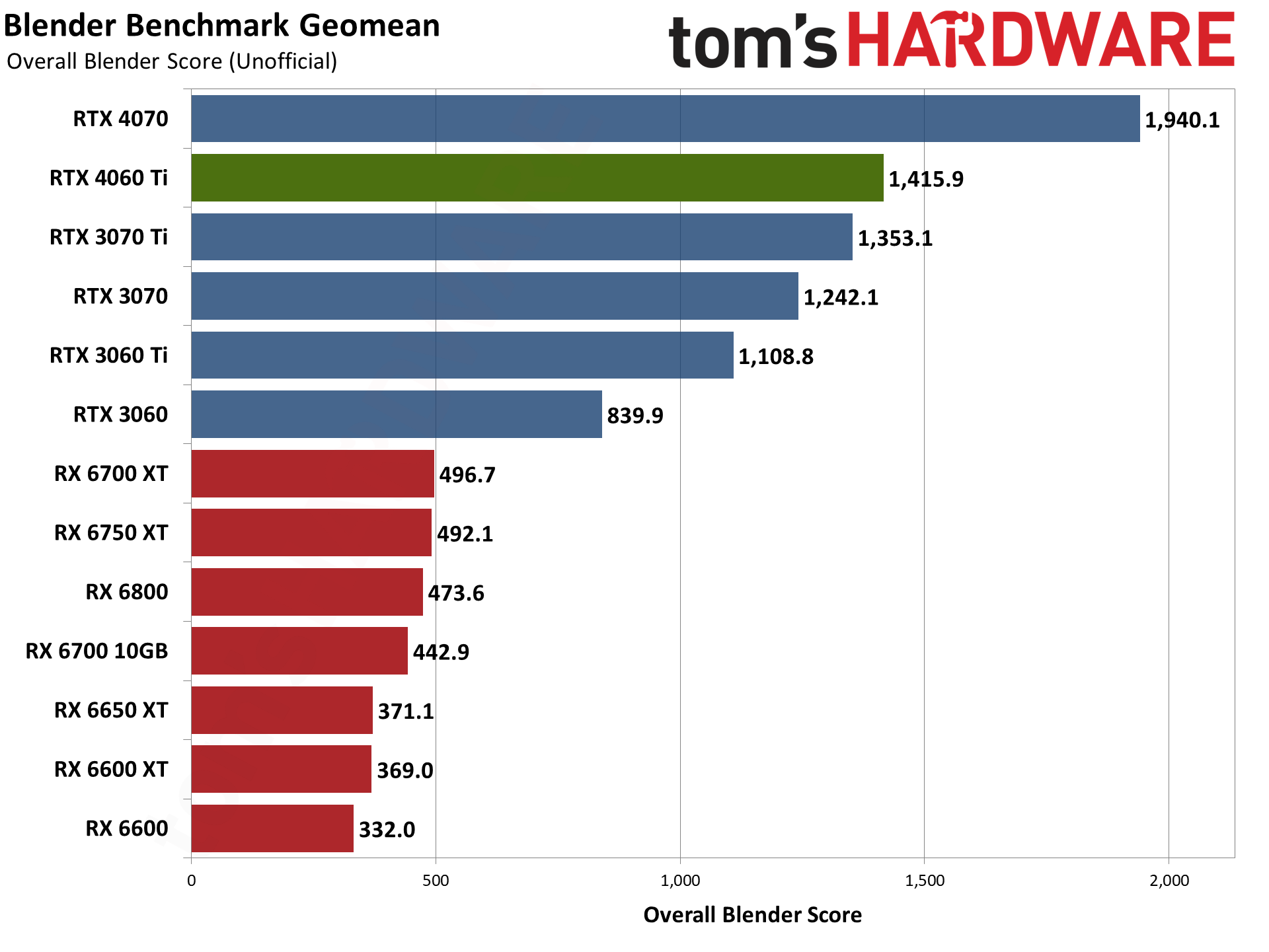
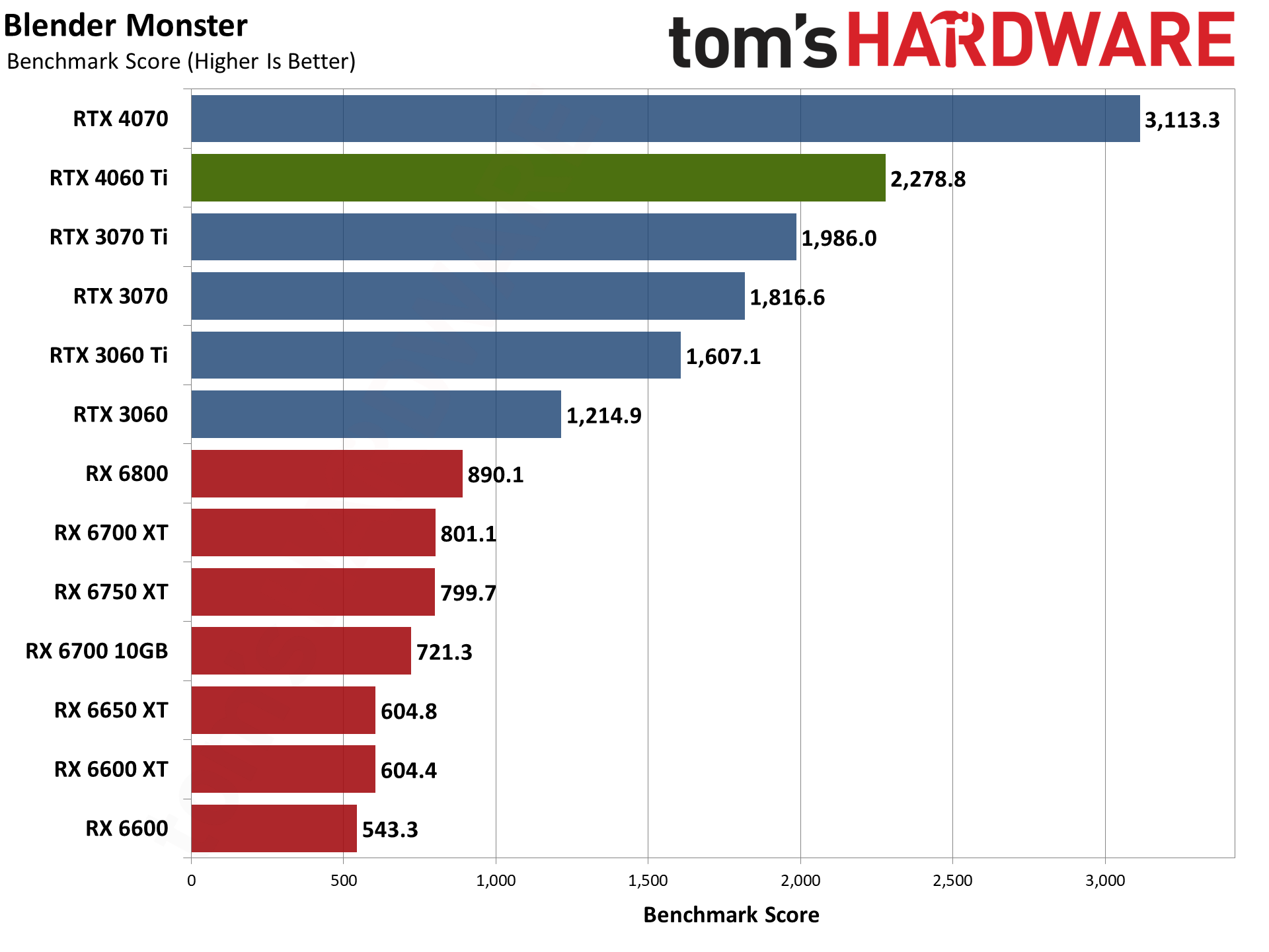
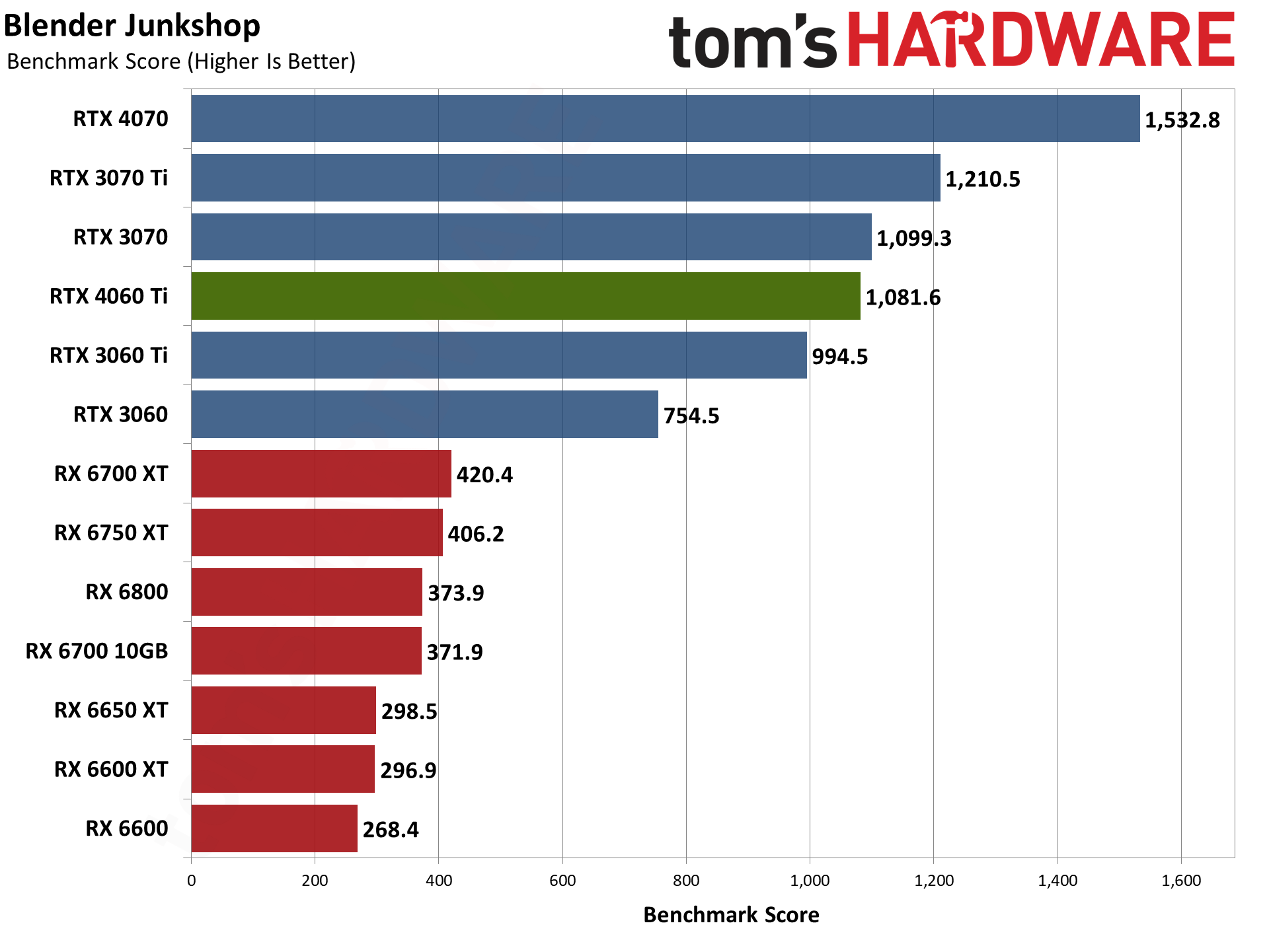
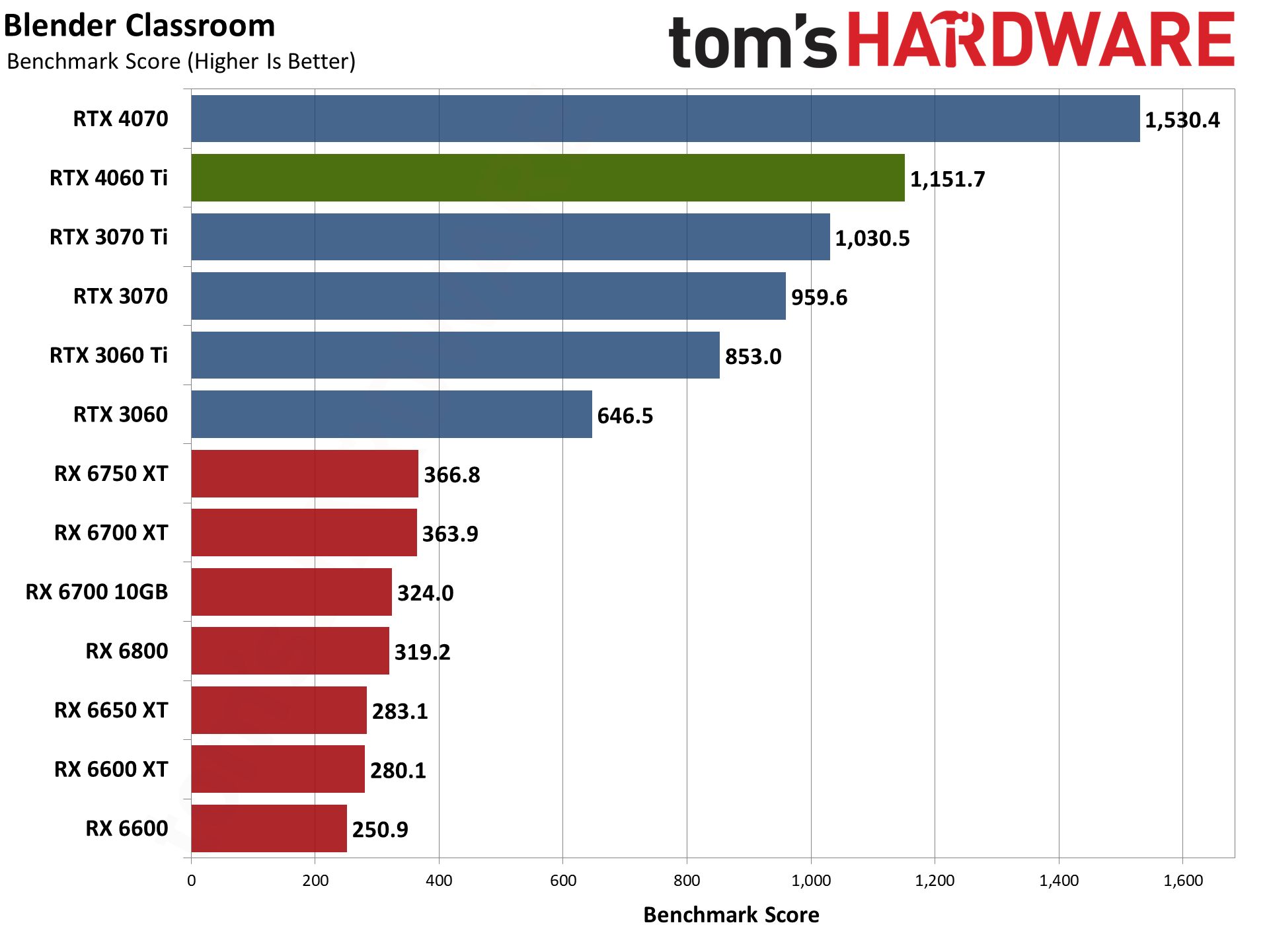
Moving on to 3D rendering, Blender is a popular open-source rendering application, and we're using the latest Blender Benchmark, which uses Blender 3.50 and three tests. Blender 3.50 includes the Cycles X engine that leverages ray tracing hardware on AMD, Nvidia, and even Intel Arc GPUs. It does so via AMD's HIP interface (Heterogeneous-computing Interface for Portability), Nvidia's CUDA or OptiX APIs, and Intel's OneAPI — which means Nvidia GPUs have some performance advantages due to the OptiX API.
The RTX 4060 Ti falls just behind the RTX 3060 in the Junkshop scene, but then it performs better than the RTX 3070 Ti in Monster and Classroom. AMD GPUs don't do nearly as well, and even the RTX 3060 comes out ahead of the RX 6750 XT and RX 6800. (And again, we have a case where one of AMD's GPUs seems to underperform, as normally the RX 6800 should be a bit faster.) Overall, Blender performance ends up being a strong point for the RTX 40-series GPUs.
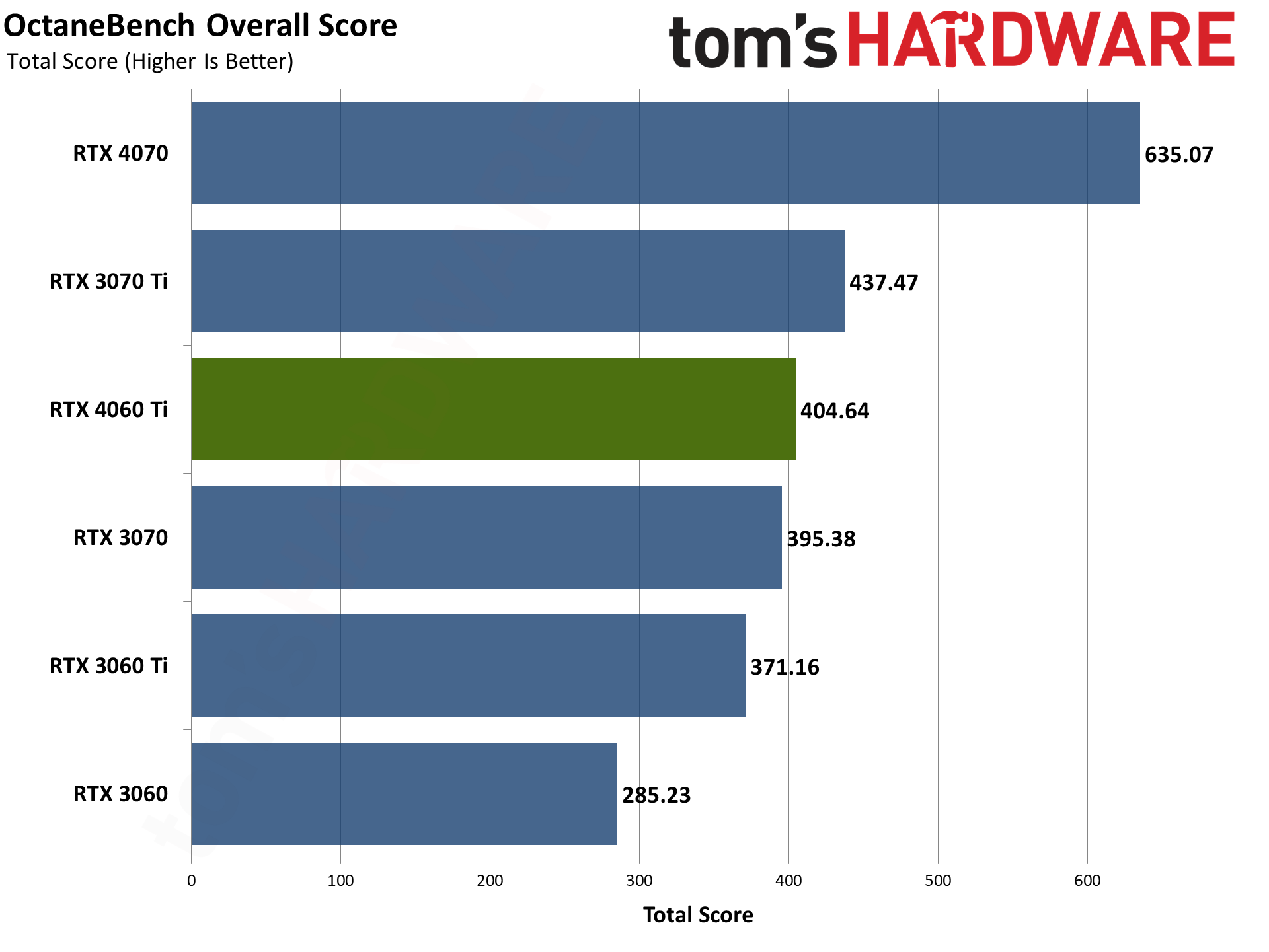
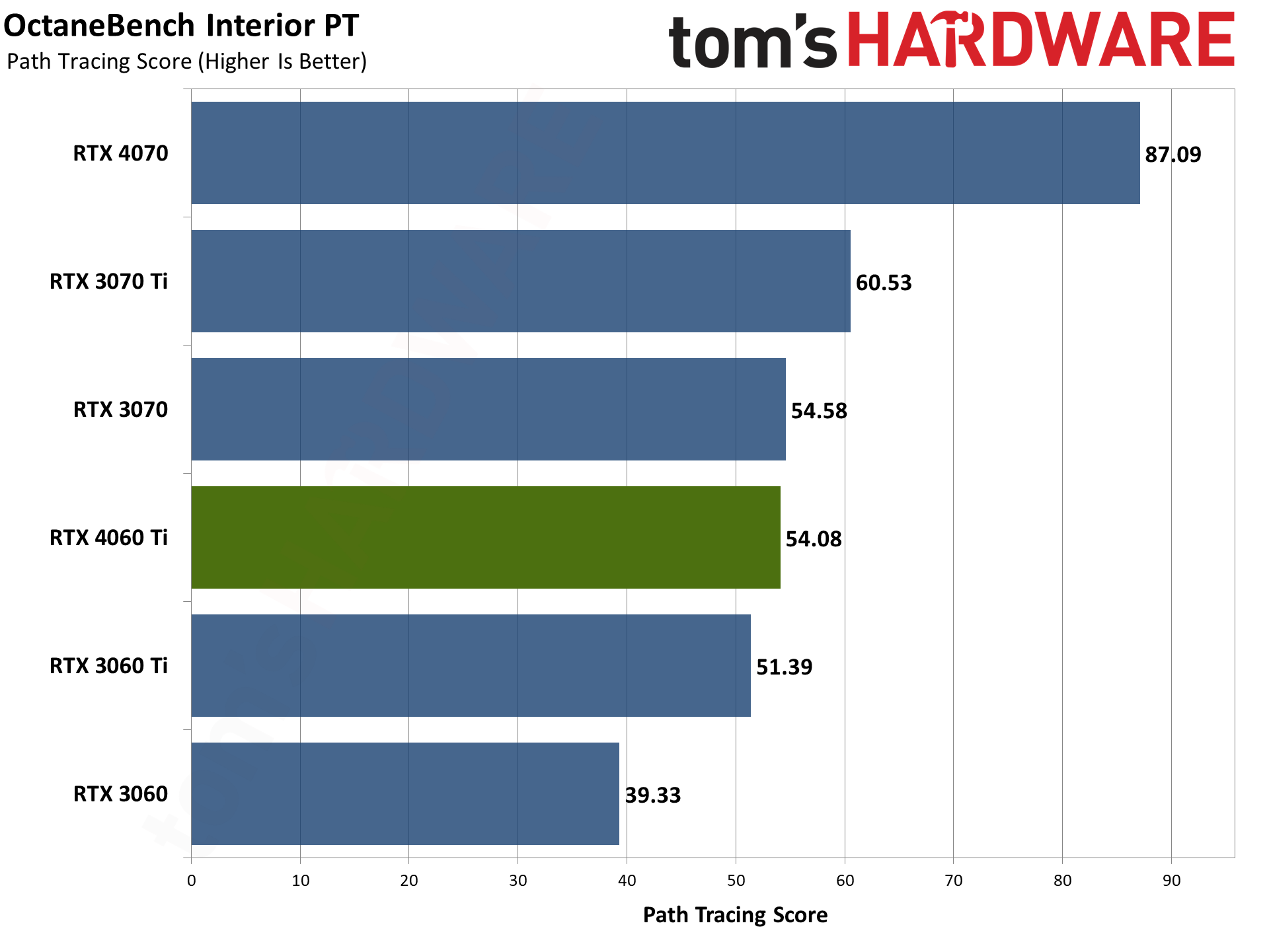
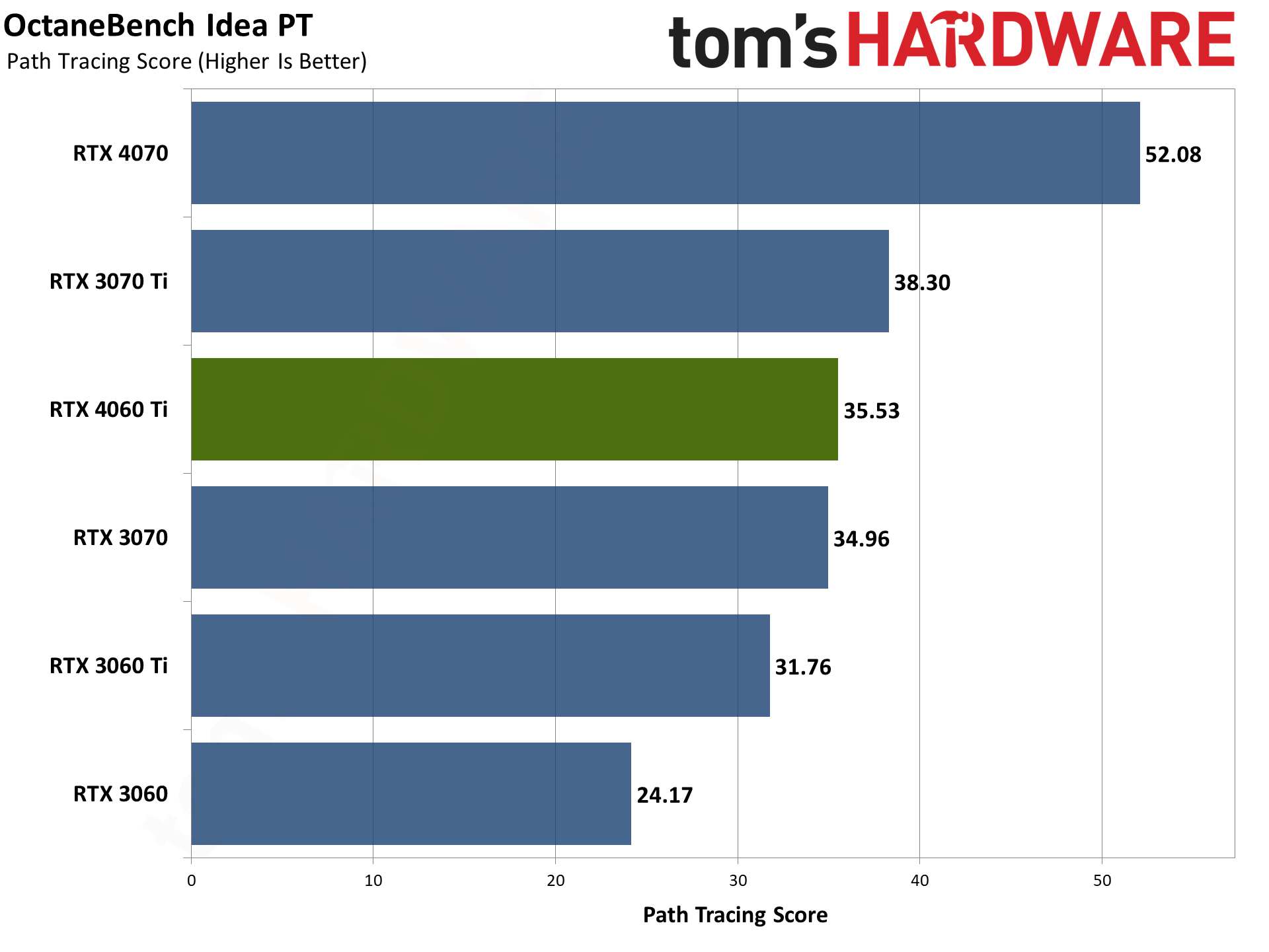
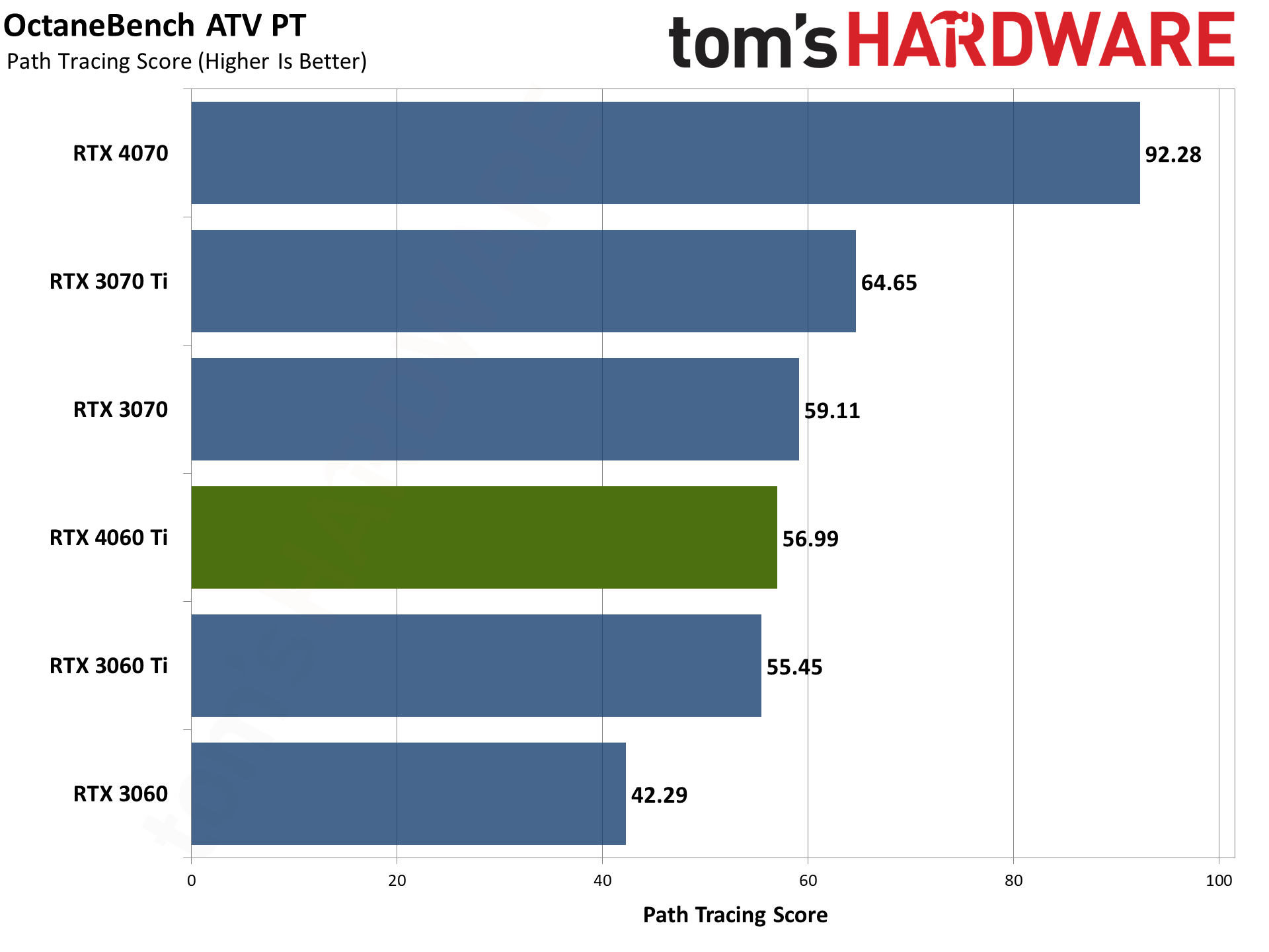
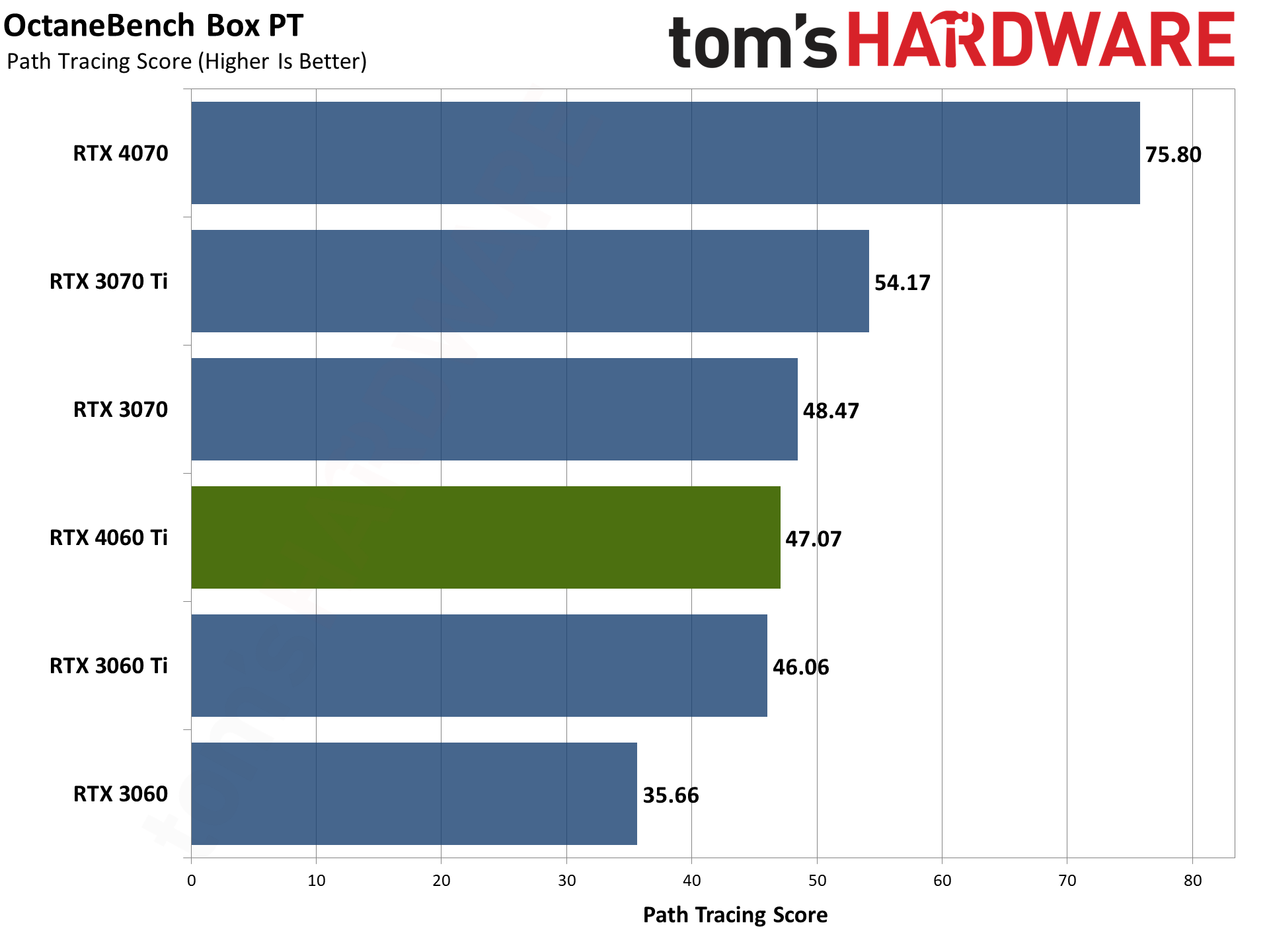
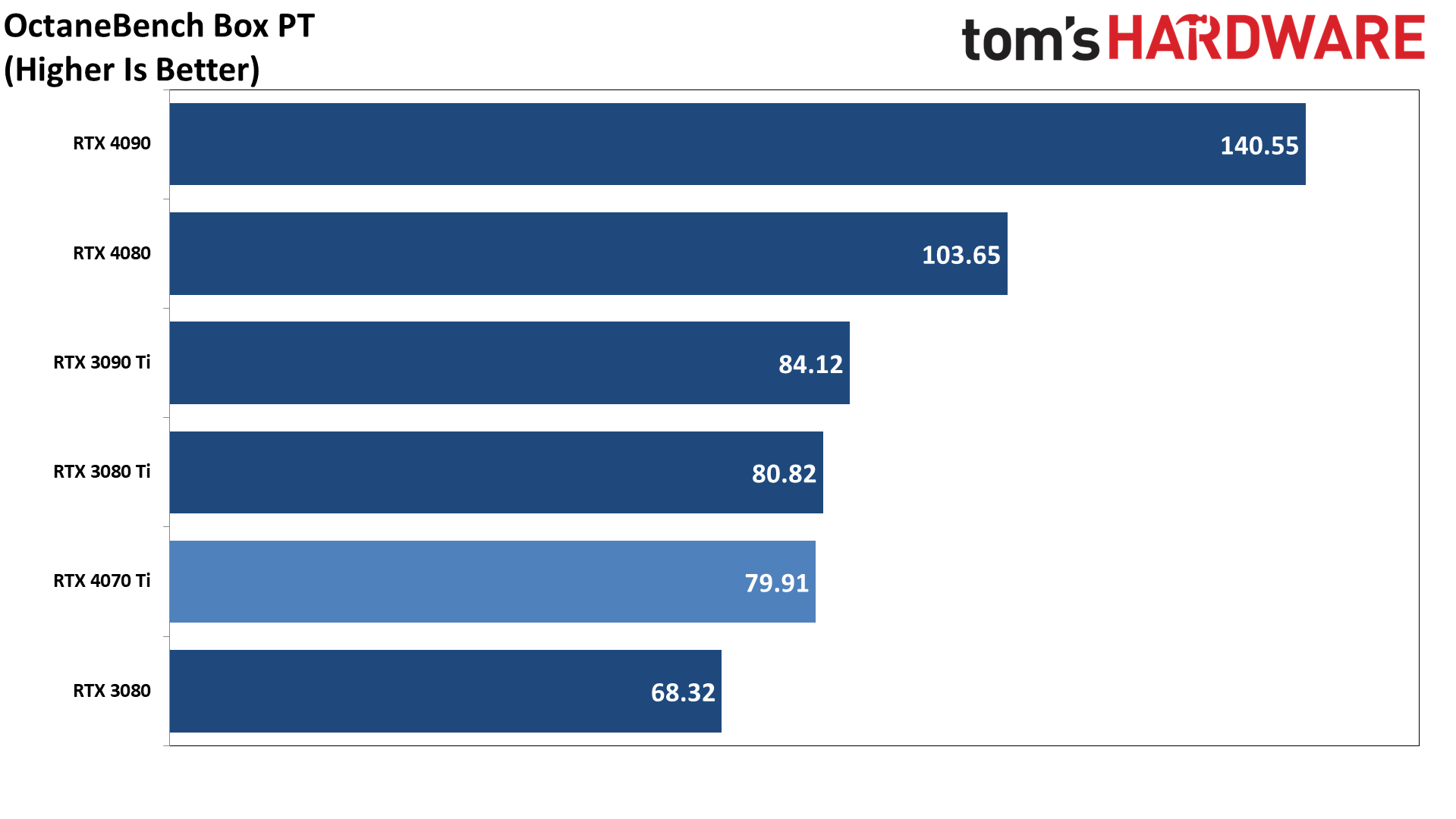
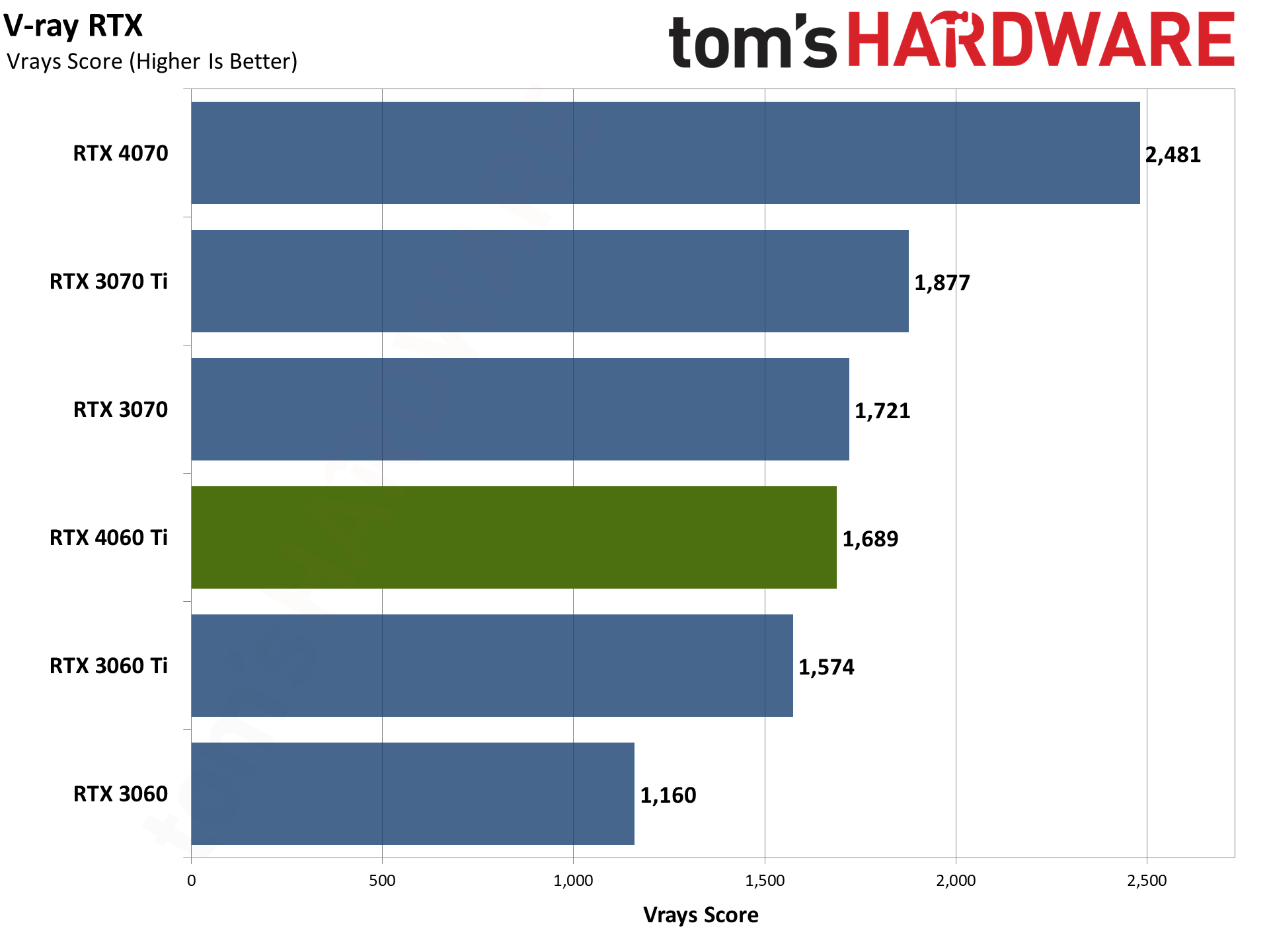
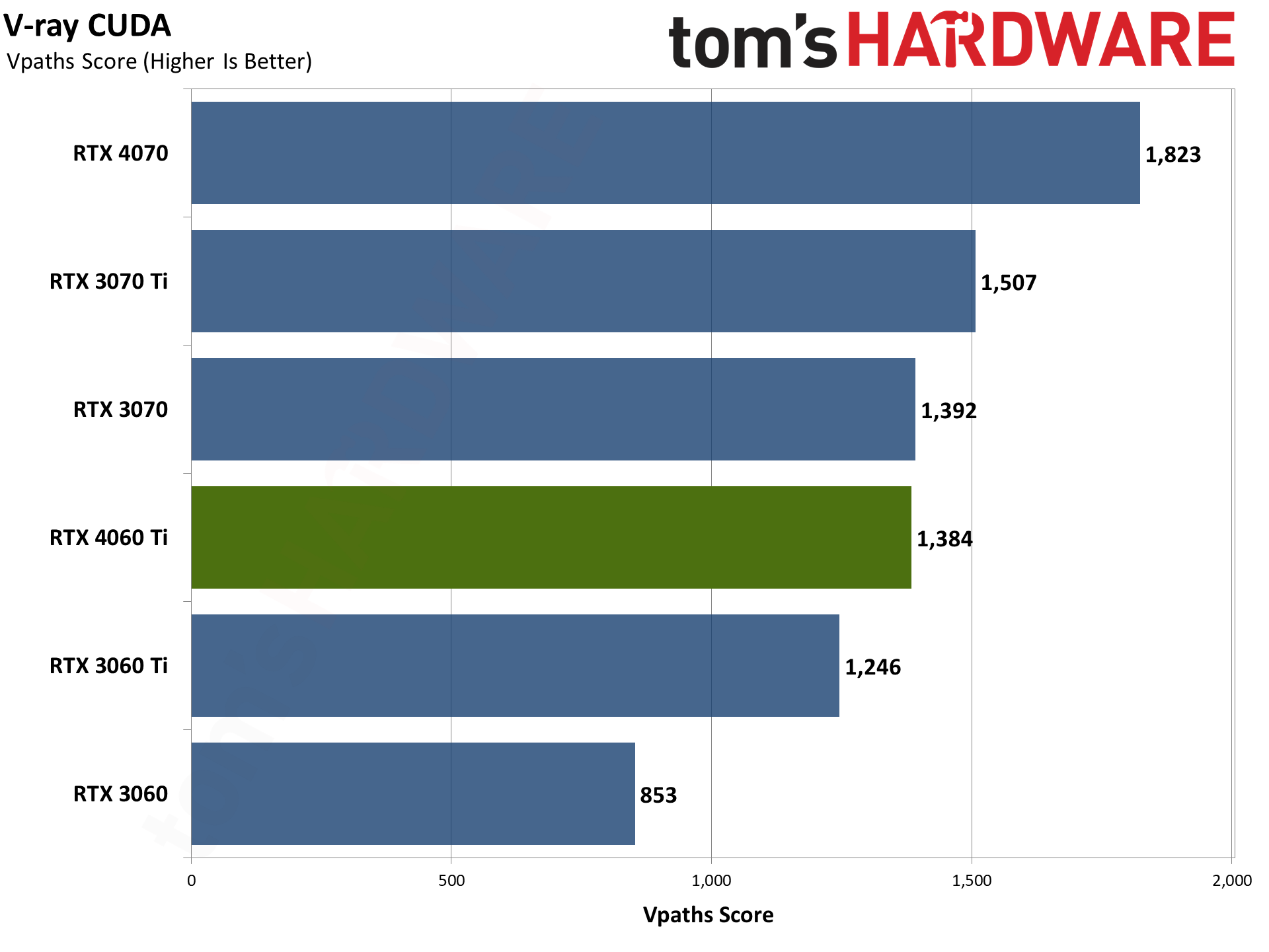
Our final two professional applications only have ray tracing hardware support for Nvidia's GPUs. OctaneBench puts the RTX 4060 Ti roughly on par with the RTX 3070 (slightly ahead overall), while V-ray has the 4060 Ti trailing by just a hair. The RTX 4070 meanwhile delivers substantially higher performance than the 4060 Ti in these tests.
- MORE: Best Graphics Cards
- MORE: GPU Benchmarks and Hierarchy
- MORE: All Graphics Content
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: GeForce RTX 4060 Ti: Professional Content Creation and AI Performance
Prev Page GeForce RTX 4060 Ti: DLSS Upscaling and Frame Generation Next Page GeForce RTX 4060 Ti: Power, Clocks, Temps, and Noise
Jarred Walton is a senior editor at Tom's Hardware focusing on everything GPU. He has been working as a tech journalist since 2004, writing for AnandTech, Maximum PC, and PC Gamer. From the first S3 Virge '3D decelerators' to today's GPUs, Jarred keeps up with all the latest graphics trends and is the one to ask about game performance.
-
lmcnabney 3.5 stars for what is a fairly negative review.Reply
Who is the target for this product? A console will perform better for the same money and eliminate the cost of the rest of the computer. -
DSzymborski Replylmcnabney said:3.5 stars for what is a fairly negative review.
Who is the target for this product? A console will perform better for the same money and eliminate the cost of the rest of the computer.
Presumably people who want a computer that can do the stuff a console can and still do the other things that a console doesn't do all that well. -
bourgeoisdude Reply
It also costs more :)HKTacticblade said:RX 6800 16GB from previous gen is already better.
Seriously though, I keep waiting for a card around this price point to upgrade to, as I have the 1070 ti, but I keep getting disappointed. I am considering AMD as a protest to what I consider the NVIDIA name tax, but frankly I am skeptical that they will do much better with their 7600 (XT) or 7700 (XT). I play enough older games that I also lean away from Intel. I guess I'm just hanging on to Pascal for a bit longer. -
J_E_D_70 WTH is going on. The $500 2070 Super 8GB from four (!!!) years ago crushes 1080p and is highly competent at 1440p. Two generations later a 4060ti should be equivalent to what... a 2080 or higher? Guess they really have hit a wall.Reply -
dk382 FYI, the professional/content creation portion of the review is for the 4070. Looks like you forgot to replace it with the 4060 Ti's data in the template.Reply -
evdjj3j Reply
I came here to say the same thing.lmcnabney said:3.5 stars for what is a fairly negative review.
Who is the target for this product? A console will perform better for the same money and eliminate the cost of the rest of the computer.
"RTX 4060 Ti comes in just ahead of the RTX 3070 at 1080p, but falls behind the RTX 3060 Ti at 1440p and 4K."
"Being faster than the RTX 3070 is at least something, but the lead is very slim, and the RTX 3060 Ti isn't far behind either. Gen on gen, we're looking at native performance that's only 13% faster with the RTX 4060 Ti."
That's not 3 1/2 starts worthy.
I'm getting the impression that Tom's doesn't want to bite the had that feeds it. -
peachpuff Reply
Maybe it's out of 10 stars? 🤔lmcnabney said:3.5 stars for what is a fairly negative review.
-
bit_user Reply
I also noticed that, but the article text explains it:dk382 said:FYI, the professional/content creation portion of the review is for the 4070. Looks like you forgot to replace it with the 4060 Ti's data in the template.
Note: We're still retesting some of the cards and so the ProViz and AI results aren't quite ready yet. Check back later today... the charts and text below are placeholders from the RTX 4070 launch. -
btmedic04 So more or less 3070 performance for $100 less now, or 3070 performance with double the vram for the same launch price as the 3070 next month. Yeah no thanks. Insane that nvidia thinks they can charge essentially the same price on 3 year old performanceReply
