Radeon HD 5550 And 5570: Pumped Up With GDDR5
AMD quietly introduced its new Radeon HD 5550 and prepped the Radeon HD 5570 GDDR5 to follow. We examine the performance of these two stealth-launched models to see if they have what it takes to replace a couple of power contenders in the sub-$100 market.
The Radeon HD 5550 Architecture
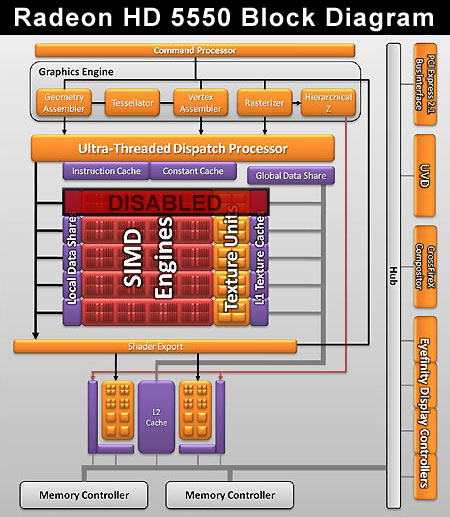
We’ll start by looking at a block diagram of the new Radeon HD 5550. The GPU is actually the same RV830-based silicon used in the Radeon HD 5570/5670, but with some functionality disabled.
In the big scheme of things, not much is changed. The only notable modification is that the Radeon HD 5550 GPU has four single-instruction multiple-data (SIMD) engines, while the Radeon HD 5570/5670 has five. Each SIMD engine features four texture units and 16 stream processors, and each stream processor has five ALUs (AMD calls them stream cores). Therefore, the Radeon HD 5550 GPU has 320 stream cores and 16 texture units, compared to the Radeon HD 557/5670’s 400 stream cores and 20 texture units. Aside from this 20% reduction, nothing else has been disabled. The Radeon HD 5550 sports the same dual 64-bit memory controllers sharing two render back-ends as the Radeon HD 5570/5670. Each render back-end contains four color render output units (ROPs) resulting in a total of eight ROPs and a combined 128-bit memory interface.
The end result is that the Radeon HD 5550 GPU is quite powerful for a low-end part (certainly a lot more powerful than the Radeon HD 5450 and its 80 stream cores). Often, when low-end GPUs are designed, the render back-ends are sacrificed. But the Radeon HD 5550 maintains the same ROP count as the Radeon HD 5570 and 5670. To get the whole story though, let’s look at the complete list of specifications:
| Header Cell - Column 0 | Radeon HD 5550 | Radeon HD 5570 | Radeon HD 4670 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shader Processors: | 320 | 400 | 320 |
| Texture Units: | 16 | 20 | 32 |
| Color ROPs: | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Fabrication process: | 40 nm | 40 nm | 55 nm |
| Core Clock: | 650 MHz | 650 MHz | 750 MHz |
| Memory Clock: | 900 MHz DDR3900-1000 MHz GDDR5 | 900 MHz DDR3900-1000 MHz GDDR5 | 1000 MHz DDR3 |
| Memory Bus: | 128-bit | 128-bit | 128-bit |
| Data Rate: | 1.8 Gb/s DDR33.6-4 Gb/s GDDR5 | 1.8 Gb/s DDR33.6-4 Gb/s GDDR5 | 2 Gb/s DDR3 |
| Compute (GFLOPs): | 352 | 520 | 480 |
| Transistors (Millions): | 627 | 627 | 514 |
| Max Power (W) | 39 | 42.7 | 59 |
| Idle Power (W) | 10 | 10 | 14 |
The numbers show us how AMD is wedging the Radeon HD 5550 into the 5000-series: by dropping the GPU's core clock in order to keep performance in line with the product’s placement. But overclockers can see the Radeon HD 5550’s potential. The RV830 GPU should be able to handle a 700 MHz operating frequency with ease, and at that speed, the Radeon HD 5550 should be quite competitive with the Radeon HD 5570.
On top of this, the GDDR5 version of the Radeon HD 5550 offers more than twice the memory bandwidth of AMD's Radeon HD 5570 DDR3. It’s quite possible that could offset the core clock (and possibly the 80-core advantage) of the Radeon HD 5570. If this proves to be the case in the benchmarks, budget-oriented gamers will have an attractive board to tweak and tune. Of course, it'd be a little awkward for AMD, with the Radeon HD 5550 DDR5 and Radeon HD 5570 DDR3 performing uncomfortably similarly. We’ll keep our eyes on these two cards in the upcoming test results.
Finally, let's take a look at the new GDDR5-based Radeon HD 5570 and see how it stacks up against the Radeon HD 5670 and Radeon HD 5570 DDR3:
| Header Cell - Column 0 | Radeon HD 5670 | Radeon HD 5570 GDDR5 | Radeon HD 5570 DDR3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shader Processors: | 400 | 400 | 400 |
| Texture Units: | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Color ROPs: | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Core Clock: | 775 MHz | 650 MHz | 650 MHz |
| Memory Clock: | 1000 MHz GDDR5 | 900-1000 MHz GDDR5 | 900 MHz DDR3 |
| Memory Bus: | 128-bit | 128-bit | 128-bit |
| Data Rate: | 4 Gb/s GDDR5 | 3.6-4 Gb/s GDDR5 | 1.8 Gb/s DDR3 |
| Compute (GFLOPs): | 620 | 520 | 520 |
| Transistors (Millions): | 627 | 627 | 627 |
| Max Power (W) | 61 | 42.7 | 42.7 |
| Idle Power (W) | 14 | 10 | 10 |
Armed with the same GDDR5 memory as the next-highest model in AMD's Radeon HD 5000 family, the only functional difference between the Radeon HD 5570 and 5670 is 125 MHz of core clock speed. The Radeon HD 5570 GDDR5 might reach Radeon HD 5670 performance when overclocked, but 775 MHz on the core might be a bit of a stretch without a voltage increase. We’ll see how things turn out when we try our hand at overclocking these cards.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: The Radeon HD 5550 Architecture
Prev Page Enter The Radeon HD 5550 Next Page HIS Radeon HD 5550 DDR3 And GDDR5Don Woligroski was a former senior hardware editor for Tom's Hardware. He has covered a wide range of PC hardware topics, including CPUs, GPUs, system building, and emerging technologies.
-
welshmousepk crysis 2 'on the horizon'?Reply
either you have not heard the terrible news, or you are a far more patient man than I. -
gkay09 No surprises IMO as it was the same with the HD 4650/ 4670...the 1GB DDR2 was slower than the 512MB DDR3...Reply -
You've mixed up the HIS5550 and HIS5570 end-on port pictures I think. You state the 5550 GDDR5 has no VGA and one is shown and vice-versa for the 5570 GDDR5. In fact it looks like quite few of the pictures are misplaced.Reply
-
edlight When you do the HQV tests, could you investigate drivers? They have a desktop color and a video (movies) section. With my 4670, it's not always clear which videos the video section works on. It varies between Win 7 and XP. Basically it works on movies in the overlay, and/or players with hardware acceleration turned on. In Win 7 it works on the flash videos, in XP it doesn't. In XP in video you can adjust Gamma, in Win 7 you can't. In XP the brightness etc. adjustment in video is independent from the desktop. In Win 7 desktop adjustments to brightness etc. affect the videos, even in the overlay. In XP the Dynamic Contrast button is there, but does nothing.Reply
After driver 10.4, in XP, video brightness and other adjustments just don't work. If you want to adjust the video you have to go back to 10.4.
Contrast this with nvidia. As far as I know, their drivers work properly, with Gamma adjustment for video, and video brightness etc. separated from desktop brightness etc.
But, in the last nvidia drivers I tried, there are problems with profiles. While you're in video, you can't save the settings as a profile. You have to go to desktop. Then you can save them. You used to be able to right-click on the tray icon and select your profiles. In the last nvidia driver I checked, you couldn't do that. At least you can do that in the ATI drivers. You can't sort the darn things, though.
So, to select a profile in nvidea you'd always have to open the control panel. In ATI, if you've come upon a dark video and you have several profiles to try on it, it's fast and easy by right-clicking in the tray.
I don't think the programmers actually use the control panels themselves. Such awful logic!
One last thing I'd like to know from the coming article is if the nvidia video section works on flash videos (with the 10.1 flash) in XP. It must in Win 7. -
dconnors welshmousepkcrysis 2 'on the horizon'? either you have not heard the terrible news, or you are a far more patient man than I.Reply
I would say anything under a year is "on the horizon" so a March 2011 street date lines up pretty well with that statement.
-Devin -
Onus I would like to have seen the HD4670 in the benchmarks; I think that is more likely competition than the HD4650, which was beaten pretty badly.Reply -
Belardo Yeah, the 4670 does belong on this benchmark article, but for the most part - the 5570 OC is on par with a standard 4670. Give or take.Reply
But what really belongs here is the 5450!
That would show how much MORE powerful the 5550/70 cards are... Yeah I know, about 4x... but still it should be there. Maybe the 5470 will come out ;)
Current pricing of the lower 5000 & 4000 series (Order of performance)
5450 = $40~70 ($55+ = 1GB useless versions)
4650 = $50~80
5550 = $65~90 (DDR2 or DDR3 ver)
5570 = $70~90 (DDR3)
4670 = $70~90
5670 = $85~105
5750 = $125~150 (Ouch - considering they cost less to make that 4670s)
First, when it comes to DX11 games, they are too much for the 5550 and below - but under DX10 - they do pretty good. So for your $70~75, you might as WELL buy the 4670 over the 5550s and 5570-DDR3. Now if the the 5550-DDR5 sells for the same price or less of a 4670, then it maybe worth it.
Considering the age of these cards, the 5670 should be $80~90... as it doesn't touch the $100 4850! But the 4850 & 57xx requires more power/bigger PSUs.
A non-eyeinfinity version of a 5750 for $100 would be a sweat card to get that would hammer the nail into the 4800 series.