DIY Solar-Powered PC: Solar Components
Component And Vendor Detail Listing
We used numerous components for the construction of our solar power generator.
All of these ingredients were used in our solar power generator.
We were ably and substantially assisted by Wagner & Co Solartechnik in the practical construction of this project. They also made a wide range of components available to use as we worked through the details.
In contrast to PCs, where individual components may be purchased separately and safely assumed to interconnect and interoperate, we learned that building a solar power generator is somewhat more difficult. To begin with, we performed numerous calculations to help us determine the proper types and power ratings for the battery, power cables, and voltage regulator we used.
It's also necessary to include protective components - for example, fuses - to make sure that variations in the power generation system don't deliver spikes or surges that might otherwise damage electrical components.
We used standard automotive fuses rated up to 25 A to protect our gear
Sizing Our Power Cables: Only 2.6% Energy Loss
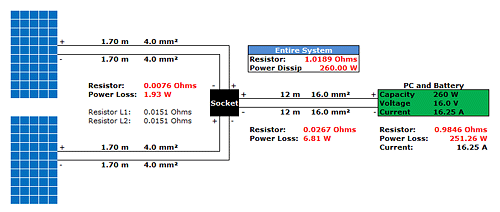
Both of our solar arrays combine to produce a nominal maximum power output of 260 Watts with output voltage of around 16 volts. The distance between the solar panels on the roof and our desktop PC ran about 40 feet (12 meters). Because we need separate leads for positive and negative polarities, this doubles the transmission length to nearly 80 feet (24 meters). In this case the electrical resistance of the cable plays a major role in ensuring that as little power as possible is wasted from end to end. That's why we used heavy duty cable with a cross-section of nearly 0.024 in2 (16 mm2) which is approximately 5 gauge AWG cable; by contrast lamp cord (the type of cable used for many A/C appliances) is only 16 gauge with a cross-section of only 1.31 mm2.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Heavy-duty power cable is 12 times thicker than lamp cord
Our readers can't help but notice that the color of our wiring is green and yellow. This color coding is normally associated with ground wire (PE, protective earth) applications. For ferrying conventional solar power direct current, blue is used for minus and red for positive voltage. We decided to use the green-yellow coated cable because it's much more efficient at carrying current than cables in other colors. Otherwise, construction details remain the same, no matter what color your cables might be.
Laying our heavy duty power cable
If we had used ordinary 1.5 mm2 power cable for this application - it's probably what runs between the wall-sockets and the circuit box in your house - power loss from the cable alone would have amounted to 22.3%. For our particular installation, this would mean a significant power loss of 58 Watts.
Left, 2.5 mm2 power cable normally used for solar power; right, 16 mm2 power cable.
Solar power vendors typically won't tolerate energy losses greater than 3% from power cables. With our tenfold increase in thickness to 16 mm2 energy loss drops to 2.6% which amounts to 6.8 Watts for the current that this cable carries.
Current page: Component And Vendor Detail Listing
Prev Page Power Cable Drive, Continued Next Page Modular Junctions For Maximal Cabling