Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Protection Features
Check out our PSUs 101 article to learn more about PSU protection features.
|
OCP (Cold @ 29°C) |
12V: 103.4A (124.13%), 11.996V |
|
OCP (Hot @ 40°C) |
12V: 103A (123.65%), 12.022V |
|
OPP (Cold @ 30°C) |
1315.41W (131.54%) |
|
OPP (Hot @ 41°C) |
1238.41W (123.84%) |
|
OTP |
✓ (185°C @ 12V Heat Sink) |
|
SCP |
12V to Earth: ✓ |
|
PWR_OK |
Proper operation |
|
NLO |
✓ |
|
SIP |
Surge: MOV |
This PSU's OCP triggering points are at reasonable levels at 12V, which goes for the OPP's triggering point as well. On the other hand, the minor rails have sky-high OCP points, which can be a problem, especially under high operating temperatures. There is no need for such high power levels on the minor rails, especially at 3.3V.
DC Power Sequencing
According to Intel’s most recent Power Supply Design Guide (revision 1.4), the +12V and 5V outputs must be equal to or greater than the 3.3V rail at all times. Unfortunately, Intel doesn't mention why it is so important to always keep the 3.3V rail's voltage lower than the levels of the other two outputs.
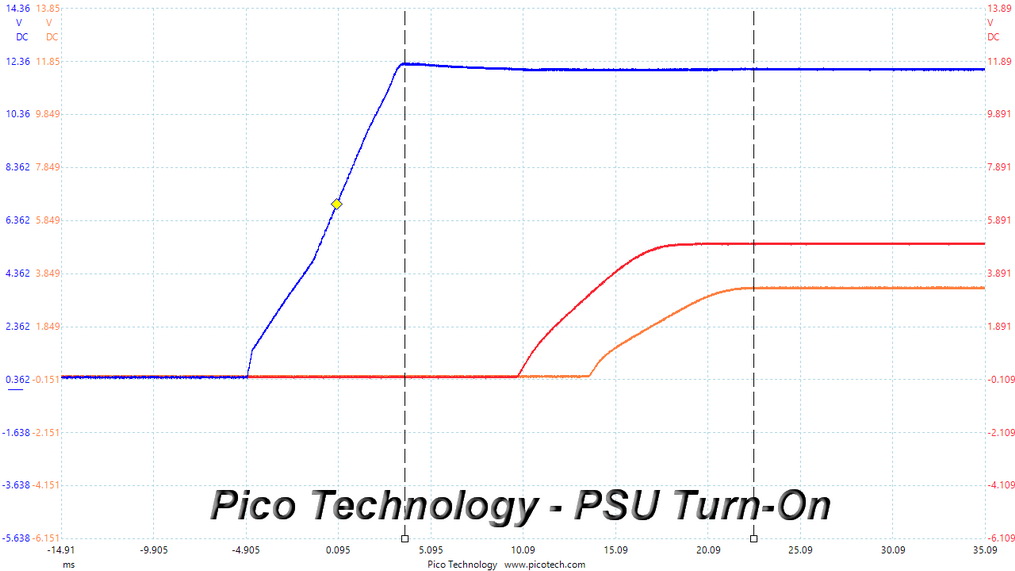
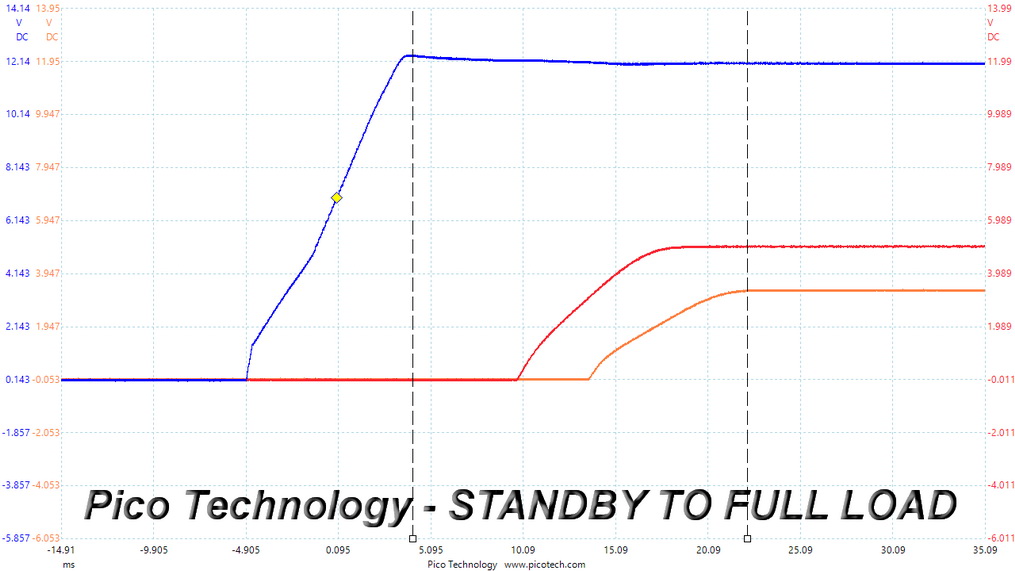
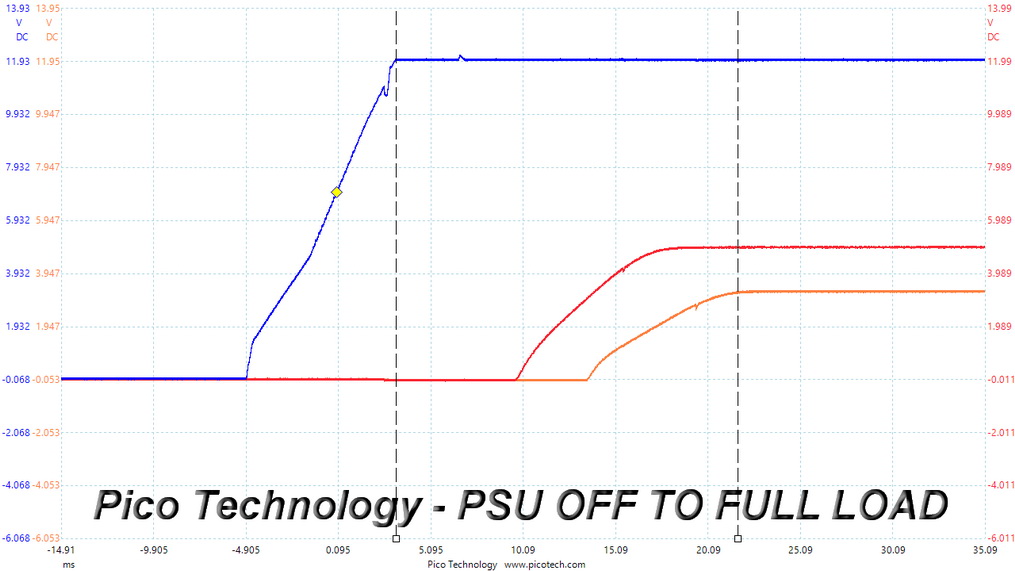
Regardless, there are no problems here since this PSU's 3.3V rail is always lower than the other two.
Cross Load Tests
To generate the following charts, we set our loaders to auto mode through custom-made software before trying more than 25,000 possible load combinations with the +12V, 5V, and 3.3V rails. The deviations in each of the charts below are calculated by taking the nominal values of the rails (12V, 5V, and 3.3V) as point zero. The ambient temperature during testing was between 30 to 32 degrees Celsius (86 to 89.6 degrees Fahrenheit).
Load Regulation Charts
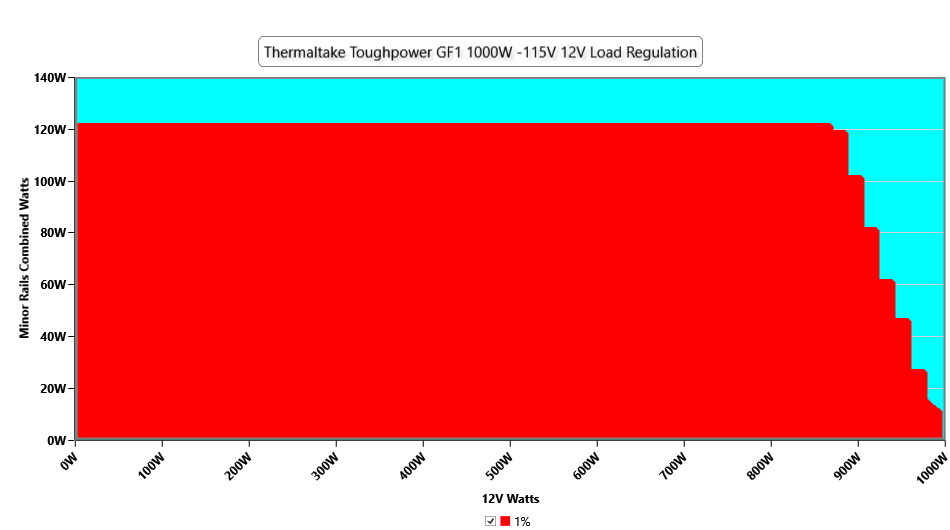
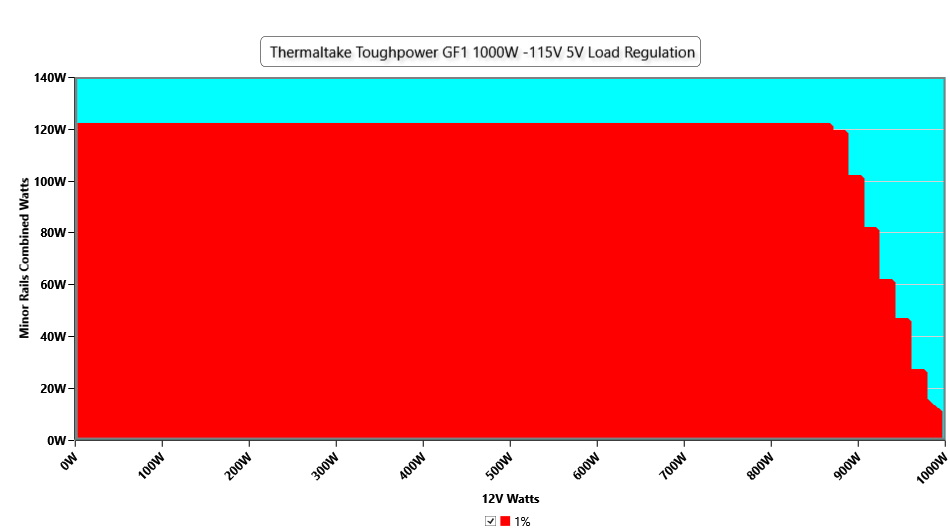
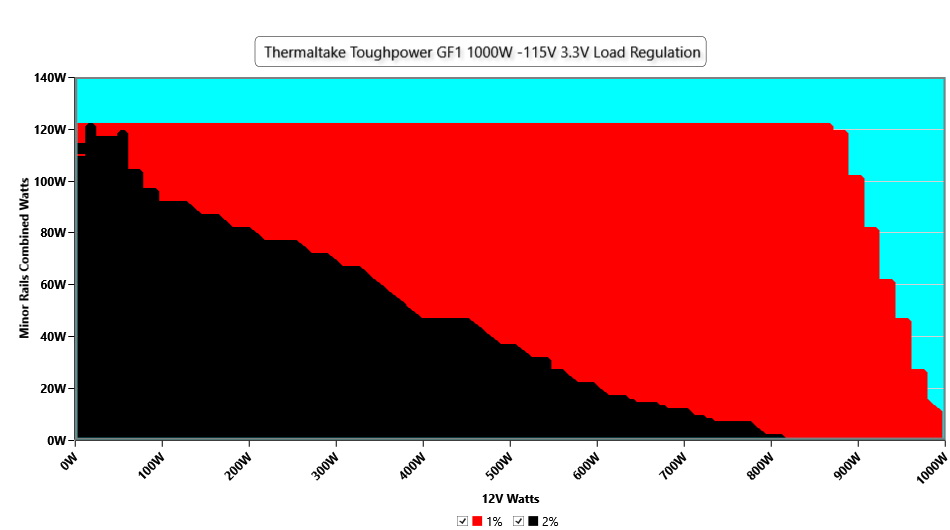
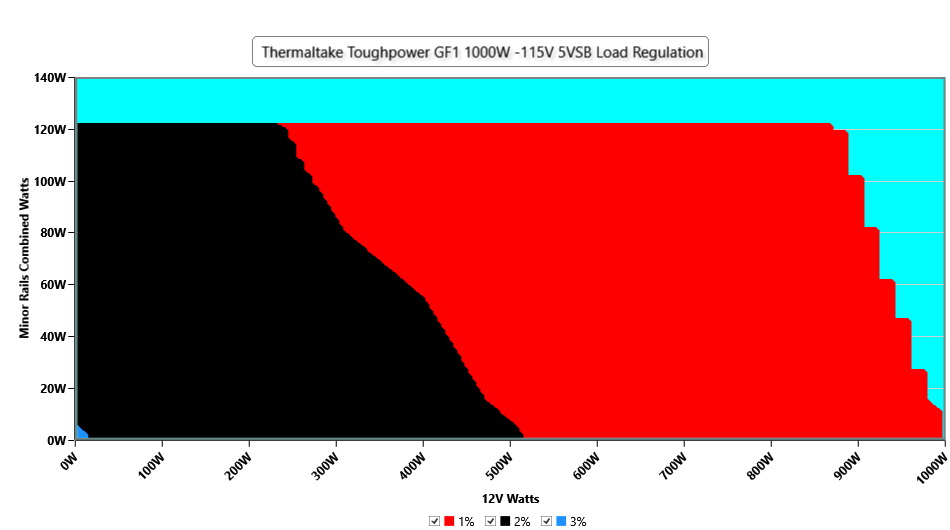
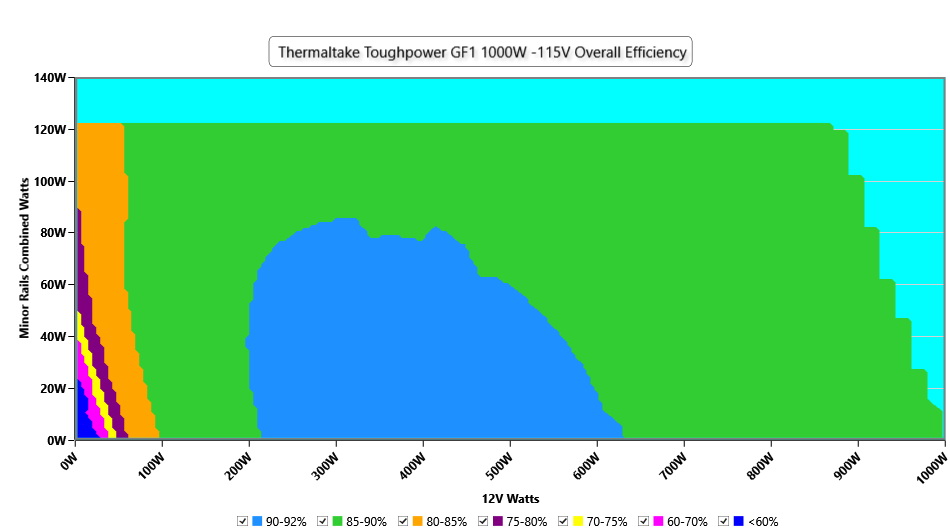
Efficiency Graph
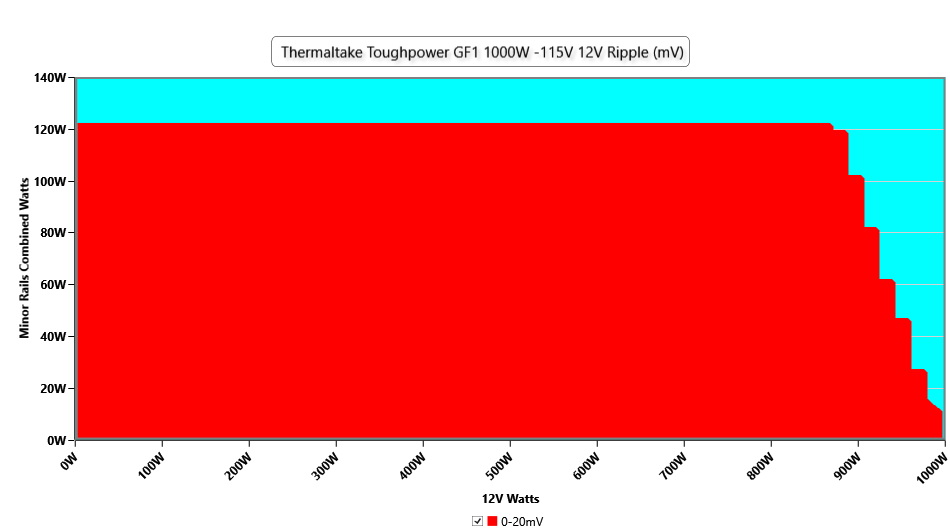
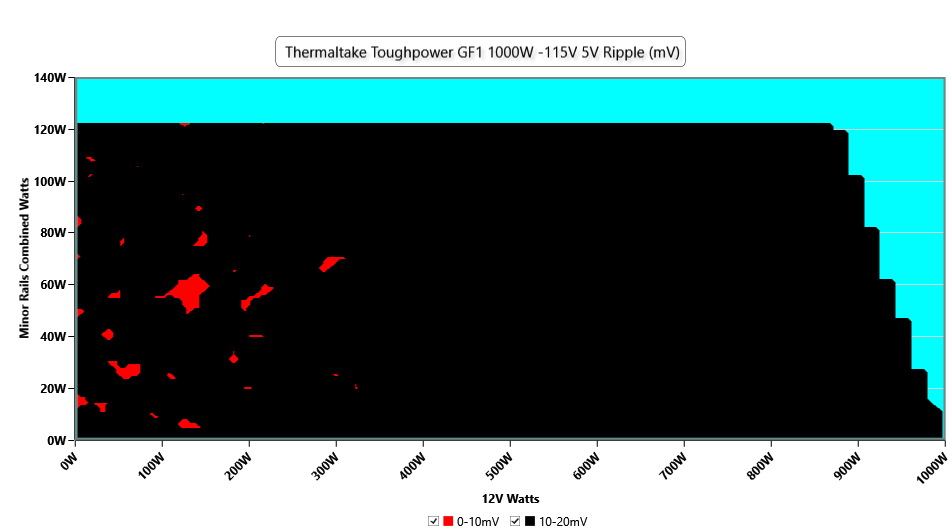
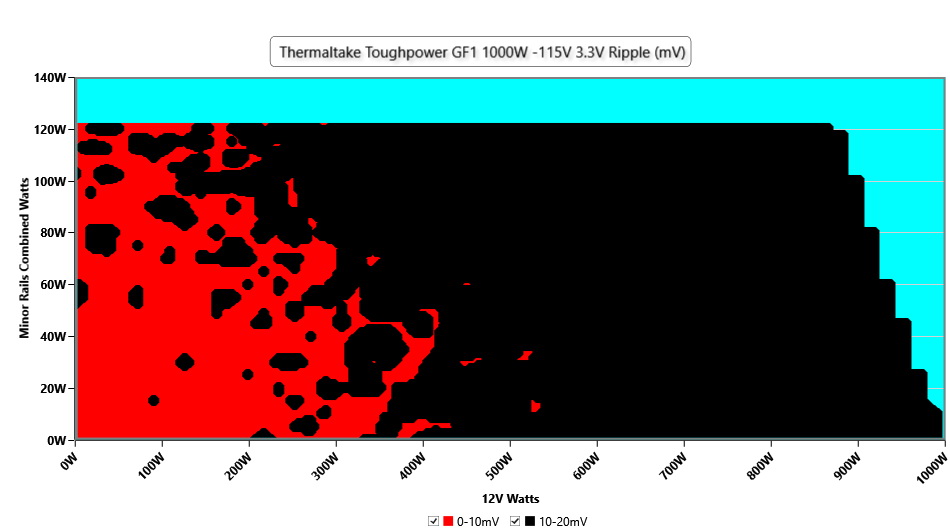
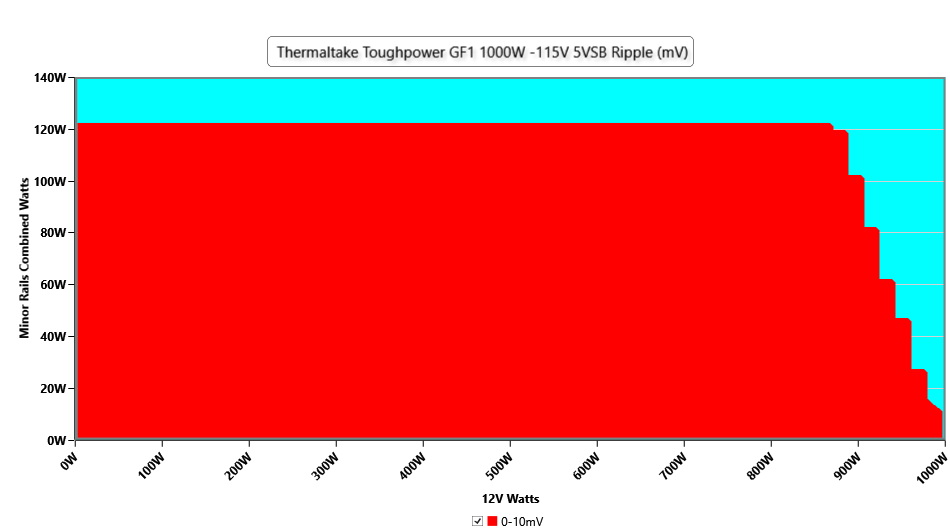
Ripple Graphs
The lower a power supply's ripple, the more stable the system will be and the less stress will also be applied to its components.
Infrared Images
To get the following images, we apply a half-load for 10 minutes with the PSU's top cover and cooling fan removed before taking photos with a modified FLIR E4 camera able to deliver an IR resolution of 320x240 (76,800 pixels).
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
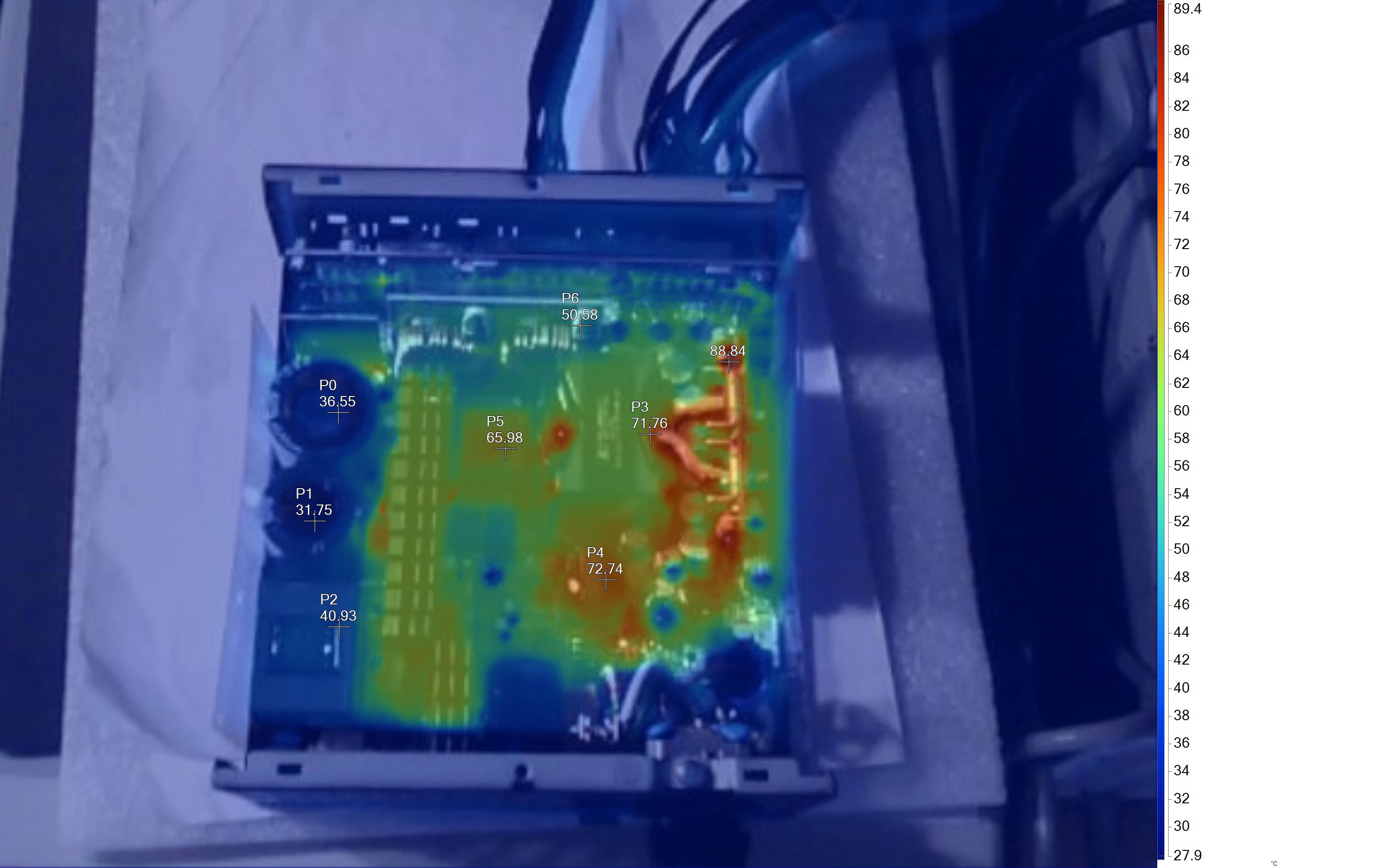
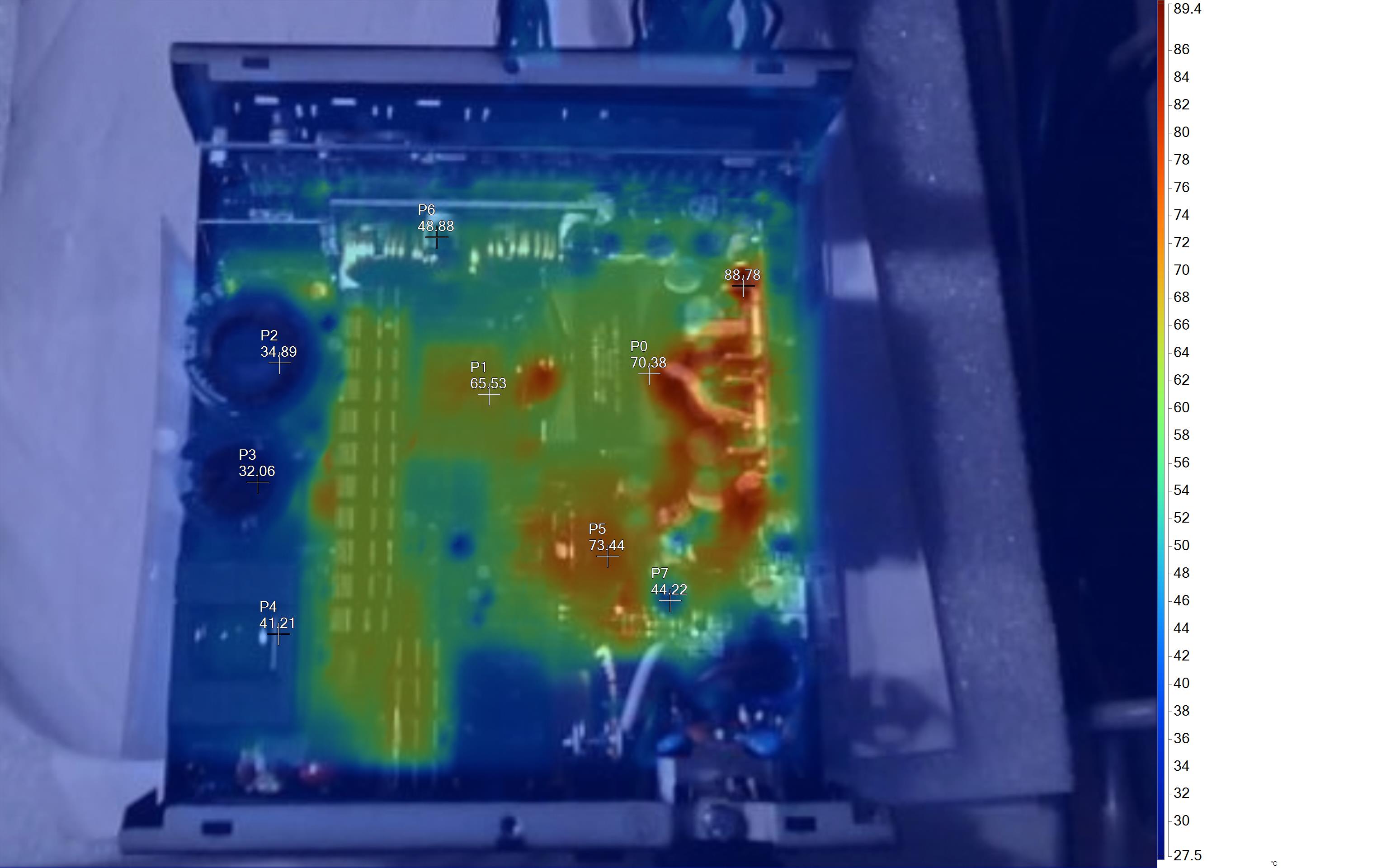
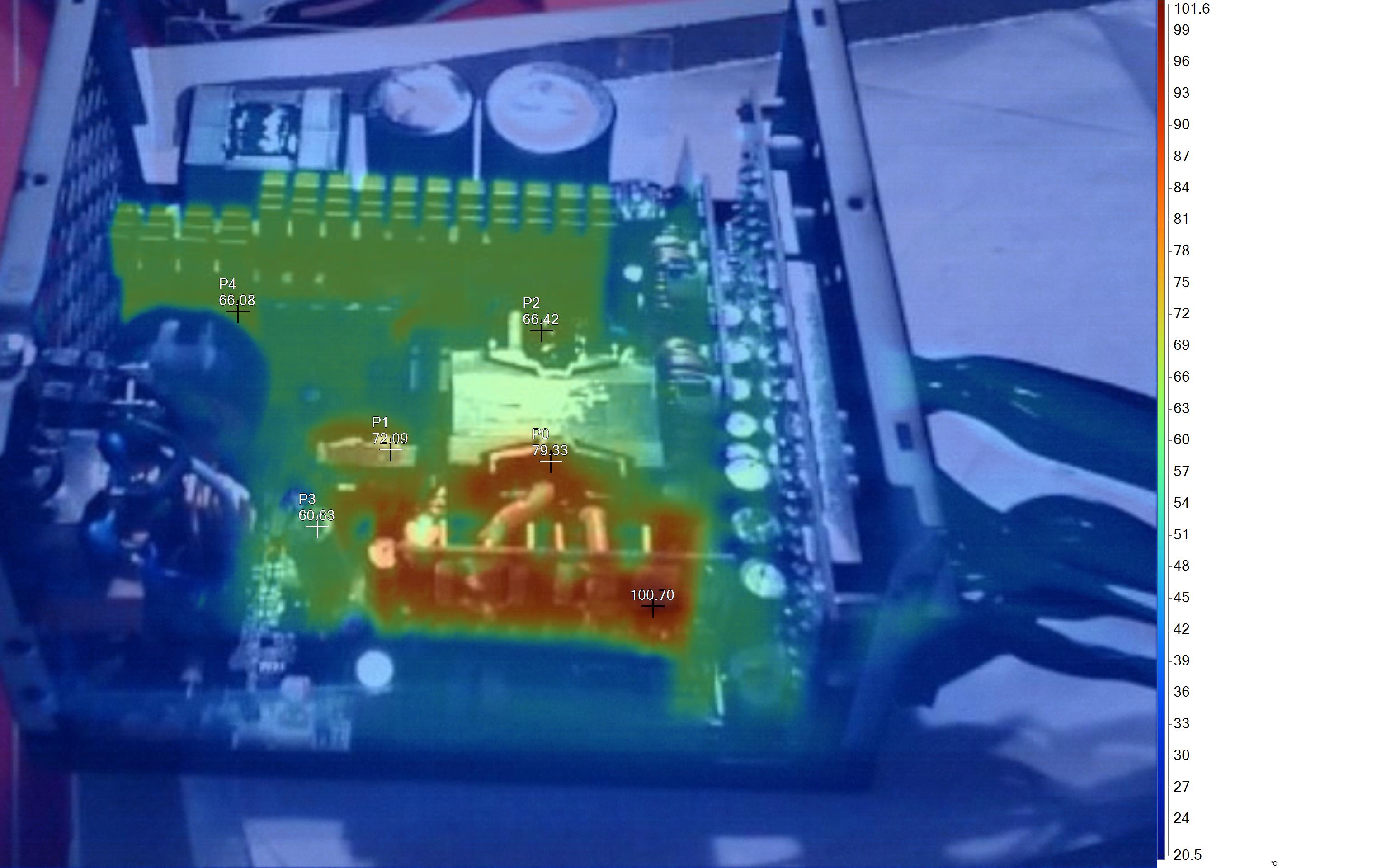
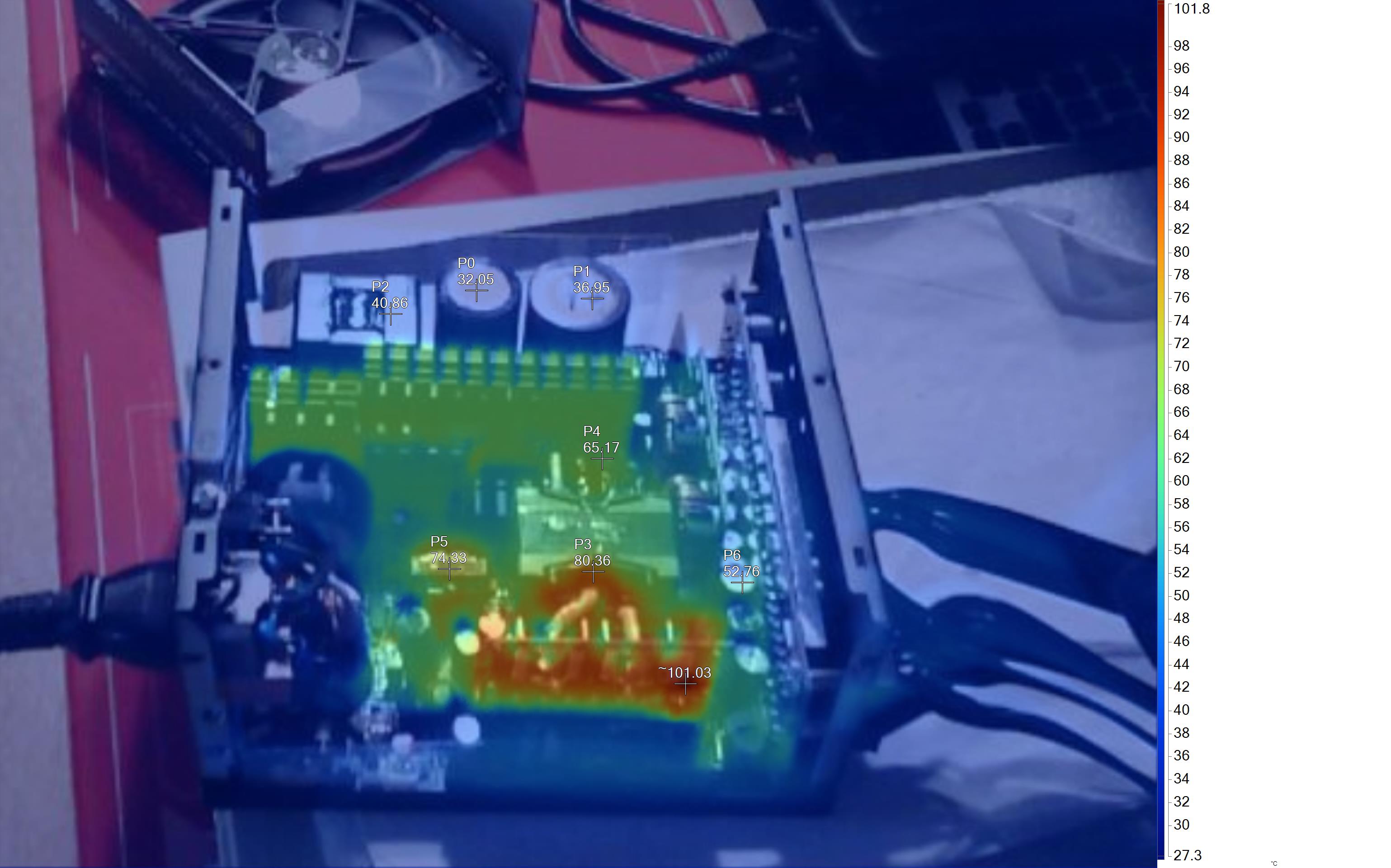
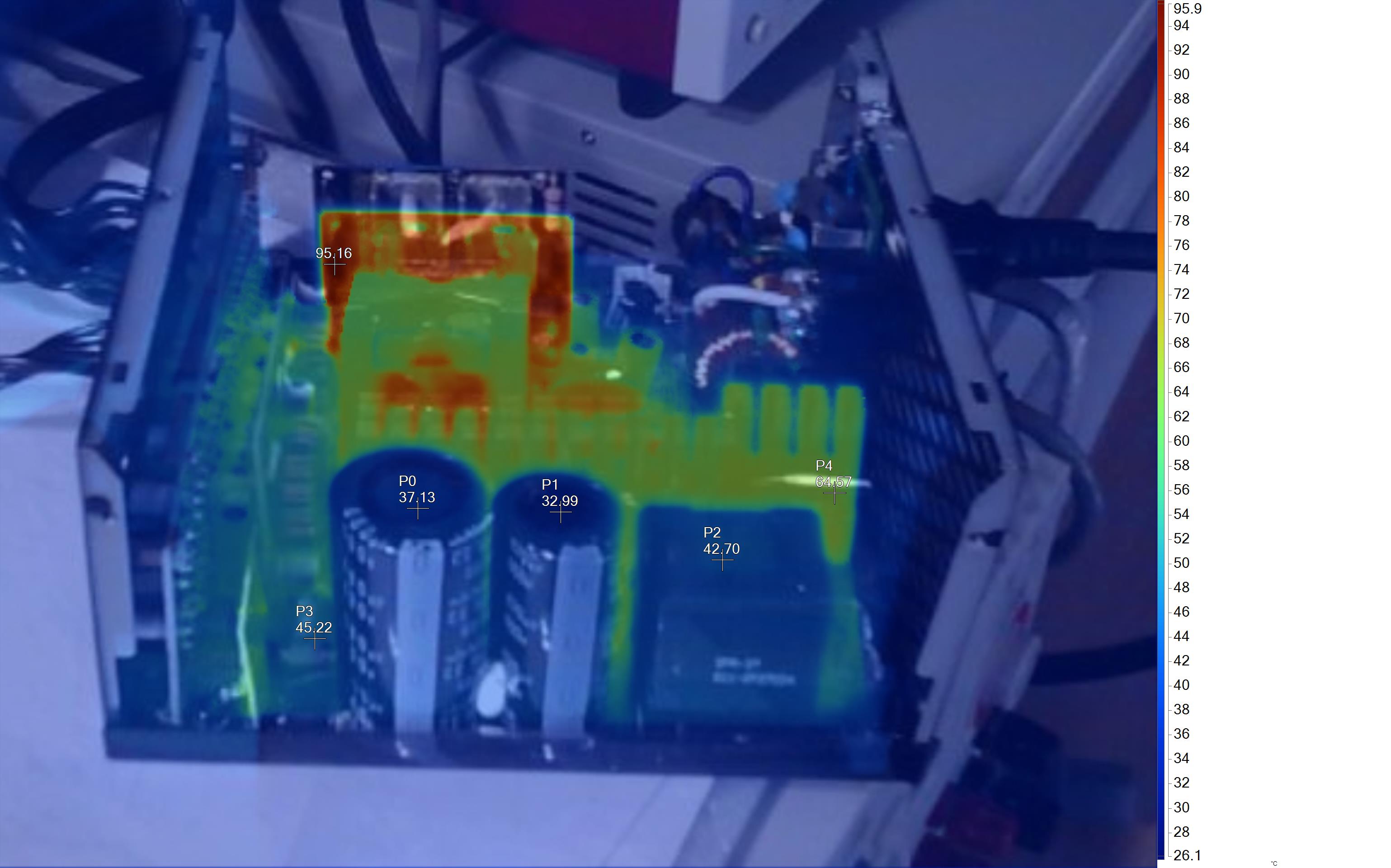
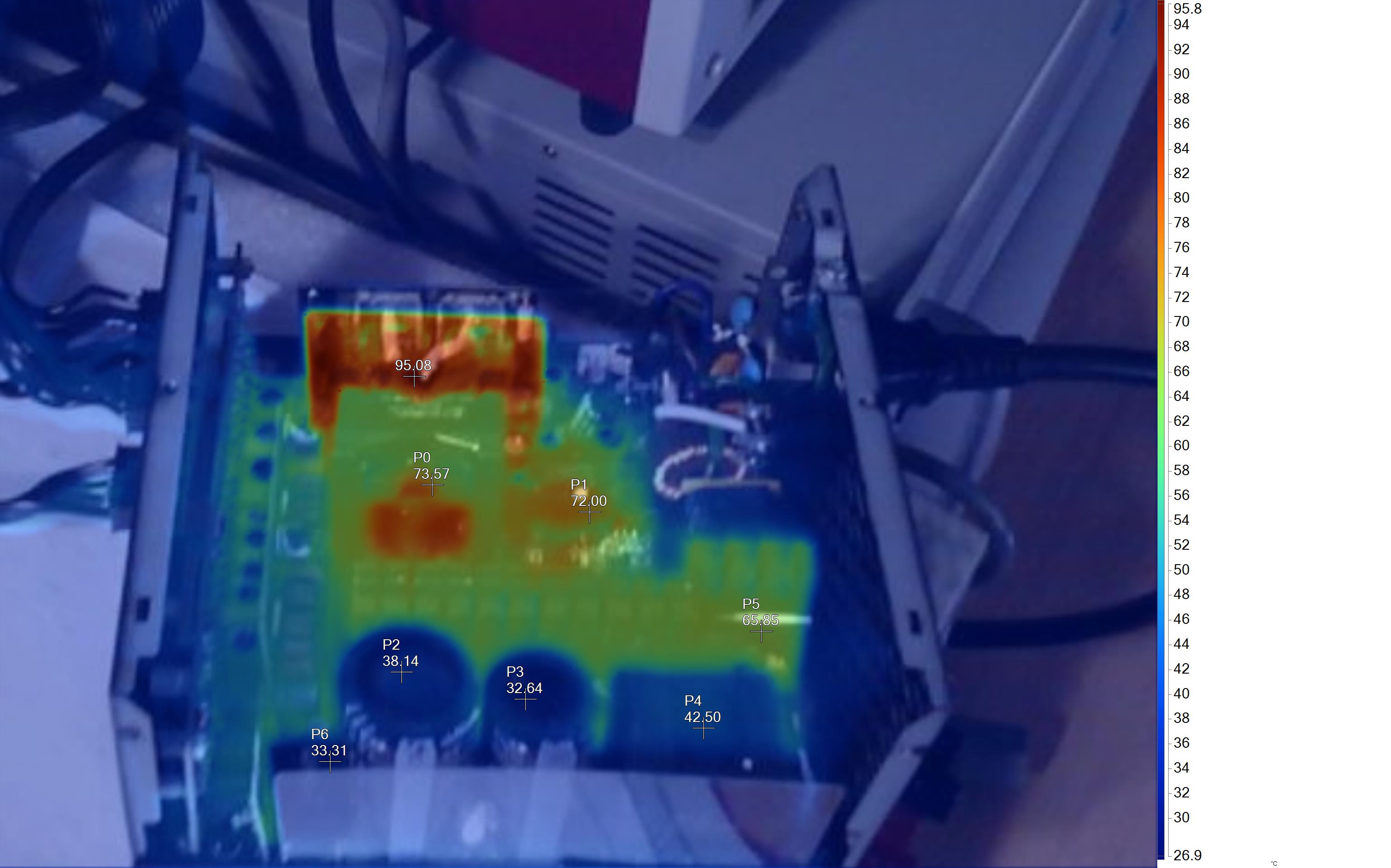
The hottest part on this unit is the board hosting the 12V FETs. The thick cables connecting this board with the main transformer also have increased temperatures.
MORE: Best Power Supplies
MORE: How We Test Power Supplies
MORE: All Power Supply Content
Current page: Protection Features, DC Power Sequencing, Cross-Load Tests and Infrared Images
Prev Page Load Regulation, Hold-Up Time, Inrush & Leakage Current, Efficiency and Noise Next Page Transient Response Tests, Timing Tests, Ripple Measurements and EMC Pre-Compliance Testing
Aris Mpitziopoulos is a contributing editor at Tom's Hardware, covering PSUs.