Wireless Range Extender 101
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Configuration
Most range extenders offer one of two configuration methods. The first and by far the simplest uses WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup), which involves pressing physical buttons on the wireless access point and range extender in order to securely pair the two devices. WPS provides easy setup but offers limited configuration options without further tweaking. Power users are better served walking through the manual configuration method, which typically involves a fairly straightforward setup process:
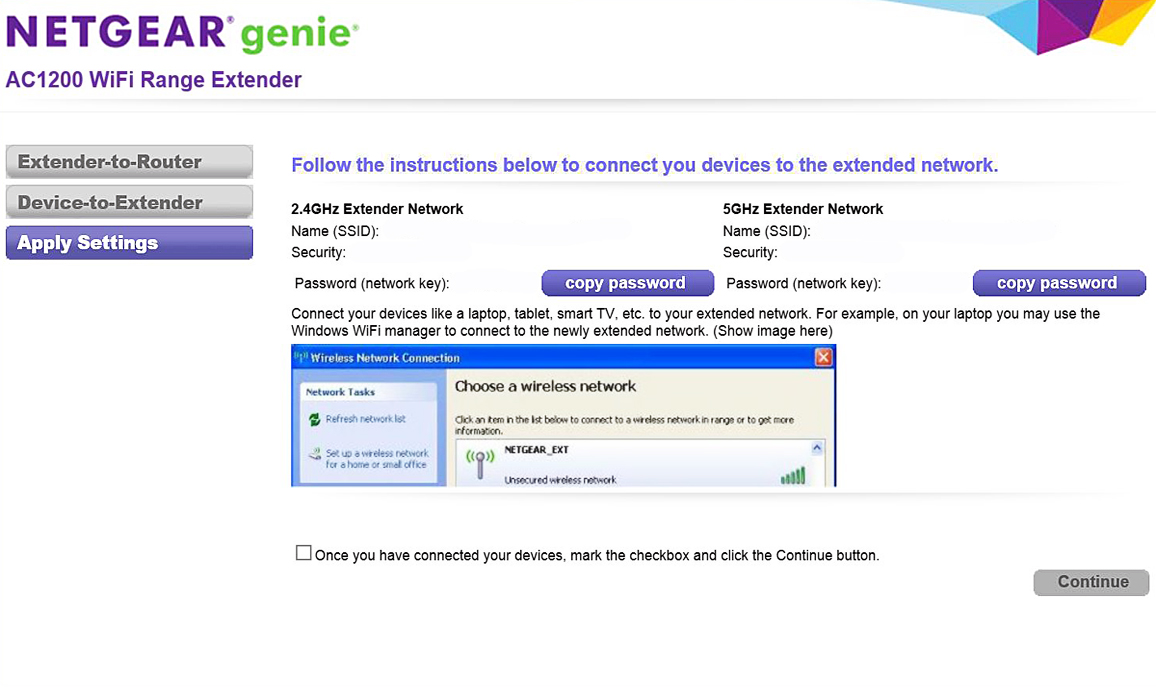
- Connect your computer to the range extender using a wired or wireless interface.
- Access the configuration website by name or IP address.
- Configure the range extender to connect to your existing wireless network – preferably using both 2.4 and 5GHz connections.
- Set up a new SSID for both frequencies.
- Connect your wireless clients to the new range extender SSIDs.
The most difficult step in configuring your range extender is usually connecting to the configuration page, particularly after the device has been connected to your network and it pulls an IP address using DHCP. Most range extenders offer a method of connecting to your range extender without having to guess at the IP address. One of the most common methods used to provide access to your range extender configuration is using a DNS domain name (such as myrangeextender.com) that resolves only if your computer is connected to the range extender. Other devices use the Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) standard, which allows your computer to recognize the range extender as a configurable wireless networking device. In some cases, you may have to look through your router’s DHCP client table, but you should consult your range extender’s documentation in order to determine the preferred method of accessing the configuration page.
It’s worth noting that a wireless range extender functions differently than an access point configured using Wireless Distribution System (WDS). WDS functions at a lower level – using the devices radios but not Wi-Fi – and is typically vendor-specific. Wireless range extenders use existing Wi-Fi networks, allowing them to support connection to any wireless access point that supports the proper bands.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
-
James Mason I bought a media bridge for my bitcoin miners so I could put them in the kitchen where it's cooler and there is more free outlets and also it's on a different circuit than the rest of my apartment. Of course I only spent like $40 on it because bitcoin mining isn't super internet intensive. These extenders are more expensive than alot of routers though, so they don't exactly seem worth it.Reply -
wtfxxxgp I still see the relative value of the smaller, outlet-based units. These are useful because of one main issue: ease of use. The only real short-coming is that they require all parts of your house to be on the same circuit, which in some cases is not the case. I don't want a long story just to be able to get internet or network access to every room in my house - I want a simple solution that works and doesn't cost me an arm and a leg. My experience with a unit I bought has been amazing - I do not know why I kept forking out money on USB-based wi-fi dongles for my gaming PC in the past. It took me literally 2 minutes to connect my PC to my network in a "wired" fashion and my ping and stability since doing that has been outstanding. I highly recommend those units, especially if you have more than 1 PC that requires networking in your house, and you want to be able to go to any room with a wi-fi-reliant device and get a strong wi-fi signal. No hectic cables, no fuss, no insane costs and the best part is, if you move, they move.Reply -
LostAlone ReplyI still see the relative value of the smaller, outlet-based units. These are useful because of one main issue: ease of use. The only real short-coming is that they require all parts of your house to be on the same circuit, which in some cases is not the case. I don't want a long story just to be able to get internet or network access to every room in my house - I want a simple solution that works and doesn't cost me an arm and a leg. My experience with a unit I bought has been amazing - I do not know why I kept forking out money on USB-based wi-fi dongles for my gaming PC in the past. It took me literally 2 minutes to connect my PC to my network in a "wired" fashion and my ping and stability since doing that has been outstanding. I highly recommend those units, especially if you have more than 1 PC that requires networking in your house, and you want to be able to go to any room with a wi-fi-reliant device and get a strong wi-fi signal. No hectic cables, no fuss, no insane costs and the best part is, if you move, they move.
I absolutely agree with this. Powerline adapters are amazing things, a substantially better answer than wifi for a lot of typical stuff like media streaming and reasonably high-traffic internet use. They aren't without their problems (our ones needs the occasional reset) but they really are a better answer in so many homes where wifi is spotty. -
bliq ReplyI still see the relative value of the smaller, outlet-based units. These are useful because of one main issue: ease of use. The only real short-coming is that they require all parts of your house to be on the same circuit, which in some cases is not the case. I don't want a long story just to be able to get internet or network access to every room in my house - I want a simple solution that works and doesn't cost me an arm and a leg. My experience with a unit I bought has been amazing - I do not know why I kept forking out money on USB-based wi-fi dongles for my gaming PC in the past. It took me literally 2 minutes to connect my PC to my network in a "wired" fashion and my ping and stability since doing that has been outstanding. I highly recommend those units, especially if you have more than 1 PC that requires networking in your house, and you want to be able to go to any room with a wi-fi-reliant device and get a strong wi-fi signal. No hectic cables, no fuss, no insane costs and the best part is, if you move, they move.
I absolutely agree with this. Powerline adapters are amazing things, a substantially better answer than wifi for a lot of typical stuff like media streaming and reasonably high-traffic internet use. They aren't without their problems (our ones needs the occasional reset) but they really are a better answer in so many homes where wifi is spotty.
we actually use a PLN kit that has a 802.11N access point on the remote side built into the remote side plug. I think it cost $29. works perfectly (although our new router has such good range I don't actually think we need it anymore). -
Rookie_MIB I just picked up an Amped wireless range extender, and I have to admit, it's a pretty effective piece. I was having intermittent signals in the back of the facility (we use Square card readers with cellphones for CC transactions...) and the device would go offline since it was pretty far from the front router (about 200ft away).Reply
Put in one of the 'high power' extenders in (broadcasts at 600mw (!!!!) and actually placed it right beside the existing router, and have 70% signal strength all the way to the back now. Pretty darn impressive. -
melanfred I purchased a Netgear pair of Powerline + Access Point. This was a great solution. The Netgear boxes are small and unobtrusive, and I can get > 20 Mbps at the farthest reaches of my house. No problems with Roku, the signal is strong and consistent. Very little resetting needed,maybe once every 3 months, I reset the access point. The pair only cost $70, this was a much better solution than a WiFi extender. Just place the units about 40 feet apart, preferably on the same circuit. A light will change color to show you if you are connected at the highest speed.Reply -
Travis Hershberger Range extenders can be a good solution in a home where you only need a single one to get good coverage over the entire property. They absolutely kill performance when more than a single one is used, each extender is going to cut throughput by half. Add the fact of current WiFi standards all being half-duplex and you get abysmal performance real quick.Reply