Mobo Makers Try Again with Intel's 925X and 915P Chipsets
Hot Property: Pentium 4 Processor 560
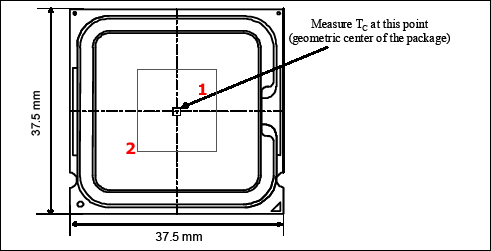
The key temperature value for manufacturers is Tc.
The Pentium 4 Prescott is without doubt controversial, as the high power loss still verges on record-breaking. The versions with 2.8 to 3.2 GHz clock rates are now widely available in the shops - preferably bundled with a matching cooler. All Prescott CPUs are famous for reaching above-average temperatures when in operation, so that a sufficiently powerful cooler along with decent housing ventilation are absolute necessities.
The 3.4 GHz version is a rarity, and there is a waiting list for the 3.6 version. We are actually starting to think that Intel prefers to send the two really "hot" models to system manufacturers, so that they can build complete systems that are guaranteed to meet Intel specifications. As shown in the specification, the versions up to 3.2 GHz can convert a maximum of 84 W into thermal power, whereas the 3.4 and 3.6 GHz versions can manage up to 115 W.
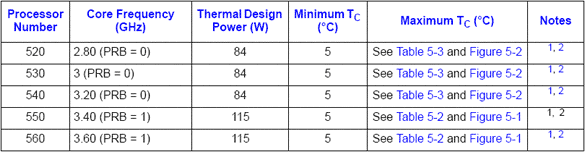
The fastest P4 processors can convert an impressive 115 W into thermal power.
Platform Requirement Bit
The platform requirement bit, the PRB for short, is used to prevent motherboards being overloaded (not every board is bound to support the fast model). If this is used (for Model 550 and 560), the BIOS will know that the increased demands have to be met. If this is not guaranteed, then the processor will start with the smallest multiplicator (x14).
Protective Mechanisms
To ensure that the CPU can also cope with the comparatively high power load indefinitely, Intel has taken measures to accommodate the heat levels. The first is the well-known thermal monitoring mechanism, which modulates the clock rate flexibly when the PROCHOT signal (processor hot) is activated and, if necessary, carries out the duty cycles.
When the maximum chip temperature is reached, boards should also be able to shut down for safety reasons, which brings us to the second protective mechanism: the THERMTRIP signal is activated after a maximum temperature level is reached. According to the datasheet, this limit is approximately 20°C higher than the case temperature of the Tcase processor. THERMTRIP causes the whole system to switch off, in order to prevent damage to the processor.
Stay on the Cutting Edge
Join the experts who read Tom's Hardware for the inside track on enthusiast PC tech news — and have for over 25 years. We'll send breaking news and in-depth reviews of CPUs, GPUs, AI, maker hardware and more straight to your inbox.
Current page: Hot Property: Pentium 4 Processor 560
Prev Page Not Much Luck This Time With Nine Boards For LGA775 And DDR2 Next Page Emergency Disconnection By Means Of The THERMTRIP SignalMost Popular

