Samsung 750 EVO SSD Review
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
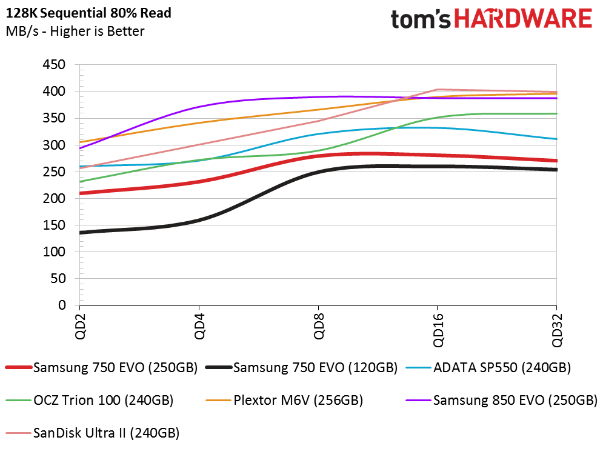
Mixed Workload And Steady State Testing
80 Percent Sequential Mixed Workload
Our mixed workload testing is described in detail here, and our steady state tests are described here.
Sequential mixed workloads prove problematic for both 750 EVOs. Frankly we were expecting higher performance, particularly for the higher-capacity model that fared so well in the sequential read and write tests. After all, Samsung SSDs often lead the way in this metric, as you can see from the 250GB 850 EVO (the purple line).
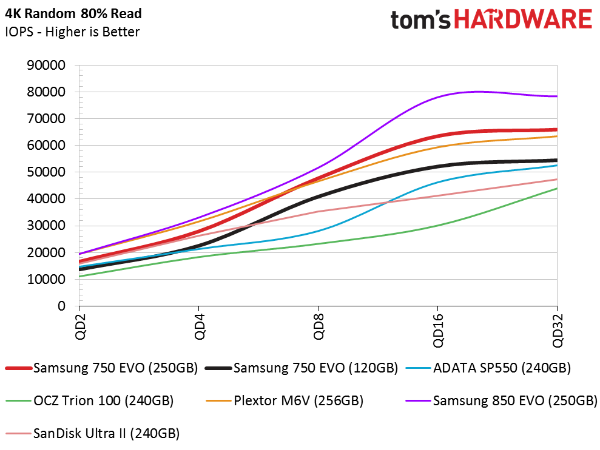
80 Percent Random Mixed Workload
The 750 EVOs appear stronger in the random mixed workload test. We see the 250GB model trailing Samsung's 250GB 850 EVO by a small margin while outperforming a number of other SSDs. The 120GB drive lands in the middle of the pack. To be fair, though, it's being compared to SSDs with two times the flash density.
Sequential Steady State
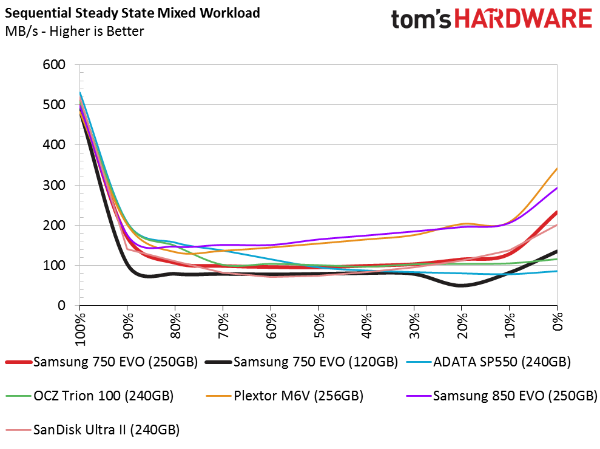
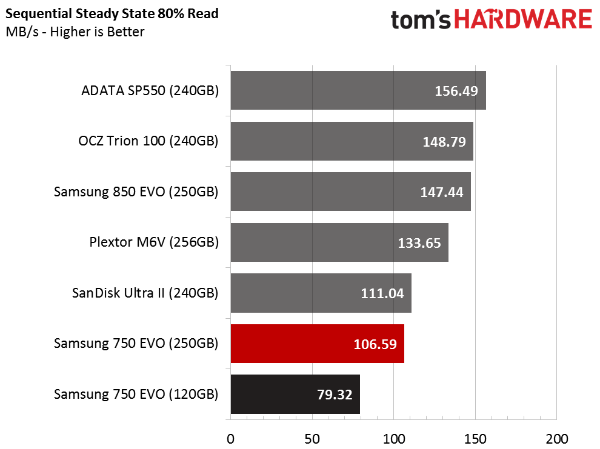
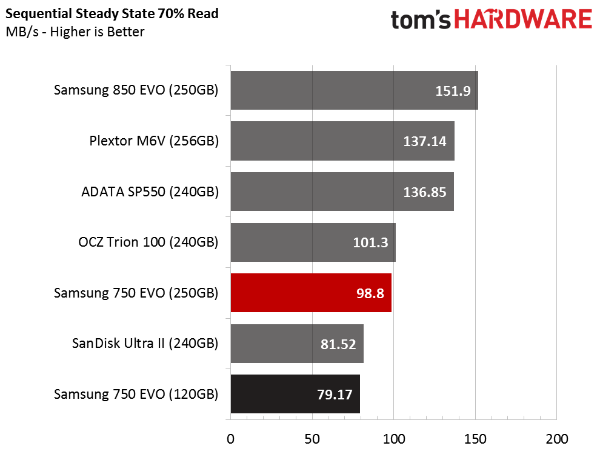
TLC-based SSDs rarely fare well under steady state conditions. Samsung's 850 EVO is the sole exception. It's the only drive we tested that delivers performance comparable to Plextor's M6V with MLC flash.
The 750 EVOs do well against competing TLC-based drives, but fall short of the mid-market leader.
Random Write Steady State
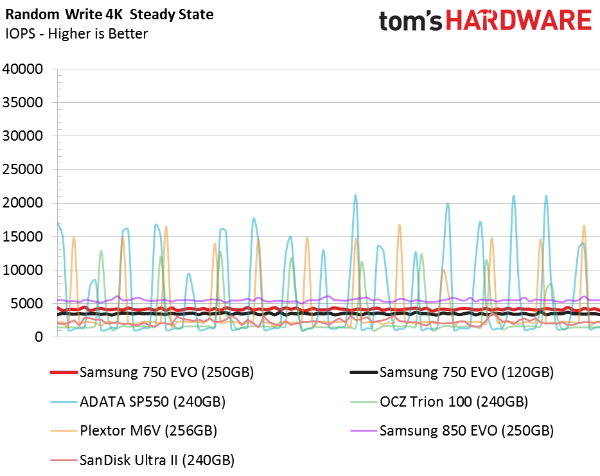
The random write steady state test shows that the 750 EVOs are very consistent. Their overall write performance isn't as high as the 850 EVO, but the line graph is as straight as an arrow. Though they're not ideal for RAID, these drives would at least serve up a solid experience striped together in an array. Samsung's asking price will ultimately determine if this is a path that makes financial sense over a single, larger SSD.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Mixed Workload And Steady State Testing
Prev Page Performance Testing Next Page Real-World Software Performance
Chris Ramseyer was a senior contributing editor for Tom's Hardware. He tested and reviewed consumer storage.
-
SteelCity1981 wow the battery life benchmarks on the 750 EVO is highly impressive, it make the 850 EVO's look power hungry. i wasn't expecting to see that at all esp from a non 3D V-NAND SSD. So if getting the most out of your battery life in your portable pc device is very important to you, then def the 750 EVO is the way to go.Reply -
araczynski Of course they're intending these for system integrators, who get a marketing bullet point at a reduced price, and while their lifespan is inferior, the eventual failures will fall out of the integrator's default warranty period ("not our problem, buy a new one from us"). Personally I think this is a cheap move to milk consumers. Samsung should stick to the middle/high level stuff while they still have a good reputation at quality.Reply -
Gam3r01 ReplyOf course they're intending these for system integrators, who get a marketing bullet point at a reduced price, and while their lifespan is inferior, the eventual failures will fall out of the integrator's default warranty period ("not our problem, buy a new one from us"). Personally I think this is a cheap move to milk consumers. Samsung should stick to the middle/high level stuff while they still have a good reputation at quality.
While I do enjoy recommending Samsung's high end drives, I dont see this as milking customers. I would be more comfortable seeing a 750 evo inside a low budget system than kingston's SSD Now! drives. They saw a market in low cost, cheaper made drives. I am happy to see Samsung moving their old tech into this area. Its not the fastest, nor the highest quality drive, but it fits.
I dont see Samsung's quality reputation getting hurt any time soon. -
phoenix32x I am confused. How is this good/better or useful? The 250GB 850 EVO is quite often available for $80. $5 less for inferior flash with less endurance. I don't get the point I guess.Reply -
Gam3r01 Reply17524941 said:I am confused. How is this good/better or useful? The 250GB 850 EVO is quite often available for $80. $5 less for inferior flash with less endurance. I don't get the point I guess.
I see the price dropping once it becomes available. Otherwise I agree it wont have a place at that price. -
Darkbreeze At twenty bucks less it makes sense, otherwise, it would be worth the extra twenty bucks simply for the longevity. Especially when the Sandisk Ultra II has similar performance to the 850 EVO in most capacities for a lower price.Reply -
joex444 Replywow the battery life benchmarks on the 750 EVO is highly impressive, it make the 850 EVO's look power hungry. i wasn't expecting to see that at all esp from a non 3D V-NAND SSD. So if getting the most out of your battery life in your portable pc device is very important to you, then def the 750 EVO is the way to go.
You're absolutely not wrong that the 750 seems to give about an hour more battery life than the 850 does, but let's remind ourselves that these plots were made starting at 500 minutes not 0 minutes. That's inherently deceptive, and obviously THG would say it's meant to show the variation more clearly, but the fact is that the bar looks like it's 70% longer (170 apparent units versus 105 apparent units), we should divide the values to reveal the true benefit: 10.7%. I may not be that inclined to get up in a tizzy about an extra 10% or an extra hour -- particularly when the 850 already allows 10 hours of usage -- but an extra 70% would be truly outstanding. Alas, that 70% is merely deceptive non-zero starting points on a graph. -
Math Geek endurance is not that bad really unless you try to use it as a torrent drive or something silly like that. during the 3 yr warranty period for the 120 gb drive, you'd have to write 32 GB per day to the drive to reach the 35 TB TBW. sure the initial windows install and program installations will take up a bit of this but once that is done, day to day use won't get anywhere near this number for the average user.Reply
double this amount for the 250 GB drive since it has the same 3 yr warranty but a 70 TBW and you're even further than breaking this threshold. even storing data on it won't do much since this is usually written once and then read over and over. the reading of the data does not go against this TBW rating.