Intel Core i5-13400F Review: Leading Value Gaming at $200
Mid-range gaming has a new champion.
The $221 Intel Core i5-13400 comes armed with ten cores and 16 threads, but you can also buy the chip as a graphics-less Core i5-13400F model that delivers identical performance for $196, giving AMD's Ryzen 7000 lineup stiff competition — particularly in the mid-range tier where AMD's chips suffer the most from high platform pricing.
The Core i5-13400/F is a solid improvement over the previous-gen 12400 model that has long dominated our best CPUs for gaming list due to its exceptional performance and attractive pricing. This new 13th-Gen Raptor Lake chip delivers even more gaming performance than its predecessor, and Intel's addition of e-cores to its 65W Core i5 processors, a first, brings additional threaded horsepower for productivity and game streaming, too.
Intel's Raptor Lake processors have taken the lead in gaming, productivity, and value over AMD's Zen 4 Ryzen 7000 processors, coming out on top in our CPU benchmark hierarchy. The rivalry remains heated, though: AMD recently released three new 'non-X' processors, including the $229 Ryzen 5 7600 that's the 13400's closest competitor. However, although the non-X chips are a better value than AMD's X-series processors, they still have other pricing problems.
| Header Cell - Column 0 | Street/MSRP | Cores / Threads (P+E) | P-Core Base / Boost Clock (GHz) | E-Core Base / Boost Clock (GHz) | Cache (L2/L3) | TDP / PBP / MTP | Memory |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core i5-13400 / 13400F | $221 - $196 (F) | 10 / 16 (6+4) | 2.5 / 4.6 | 1.8 / 3.3 | 29.5MB (9.5+20) | 65W /148W | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-4800 |
| Core i5-12400 / F | $185 - $167 (F) | 6 / 12 (6+0) | 4.4 / 2.5 | - | 25.5MB (7.5+18) | 65W / 117W | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-4800 |
Despite Ryzen's impressive performance, the chips have been plagued by high B-series motherboard pricing and Ryzen's strict requirement for DDR5 memory, both of which lead to higher platform costs. In contrast, Intel's motherboard ecosystem remains less expensive, and the Raptor Lake chips support either value-centric DDR4 or the pricier DDR5. As our tests show, you should only buy the latter if you intend to splurge on a heavily-overclocked kit — at stock settings, a cheap DDR4 memory kit will give you roughly the same gaming performance as a pricey DDR5 kit. Additionally, DDR5 overclocking gains come with eye-pricing markups that largely aren't worth the small uplift.
Like AMD, Intel also throws in a bundled cooler with its lower-end 65W chips to sweeten the deal, and even though we generally recommend buying a better cooler than the bundled models, the Core i5-13400 cooler is at least serviceable for most users.
AMD does have three new Ryzen 7000X3D processors coming this month with its disruptive 3D V-Cache tech that delivers explosive gains in gaming performance, but those chips start at $449, so they aren't for the mid-range market. As such, the faceoff between the Core i5-13400 and the Ryzen 5 7600 will define the ~$200 AMD vs Intel segment for the year to come. Let's see who wins the battle.
Intel Core i5-13400 and 13400F Specifications and Pricing
| Header Cell - Column 0 | Street/MSRP | Cores / Threads (P+E) | P-Core Base / Boost Clock (GHz) | E-Core Base / Boost Clock (GHz) | Cache (L2/L3) | TDP / PBP / MTP | Memory |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryzen 7 5800X3D | $358 ($449) | 8 /16 | 3.4 / 4.5 | 104MB (8+96) | 105W | DDR4-3200 | |
| Ryzen 7 7700 | $329 | 8 / 16 | 3.8 / 5.3 | 40MB (8+32) | 65W / 88W | DDR5-5200 | |
| Core i5-13600K / KF | $329 (K) - $304 (KF) | 14 / 20 (6+8) | 3.5 / 5.1 | 2.6 / 3.9 | 44MB (20+24) | 125W / 181W | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-5600 |
| Core i5-12600K / KF | $250 (K) - $225 (KF) | 10 / 16 (6+4) | 3.7 / 4.9 | 2.8 / 3.6 | 29.5MB (9.5+20) | 125W / 150W | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-4800 |
| Ryzen 5 7600 | $229 | 6 / 12 | 3.8 / 5.1 | 38MB (6+32) | 65W / 88W | DDR5-5200 | |
| Core i5-13500 | $242 | 14 / 20 (6+8) | 2.5 / 4.8 | 1.8 / 3.5 | 35.5MB (11.5+24) | 65W /148W | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-4800 |
| Core i5-13400 / 13400F | $221 - $196 (F) | 10 / 16 (6+4) | 2.5 / 4.6 | 1.8 / 3.3 | 29.5MB (9.5+20) | 65W /148W | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-4800 |
| Core i5-12400 / F | $185 - $167 (F) | 6 / 12 (6+0) | 4.4 / 2.5 | - | 25.5MB (7.5+18) | 65W / 117W | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-4800 |
| Ryzen 5 5600X | $169 | 6 / 12 | 3.7 / 4.6 | - | 35MB (3+32) | 65W | DDR4-3200 |
| Ryzen 5 5600 | $149 | 6 / 12 | 3.5 / 4.4 | - | 35MB (3+32) | 65W | DDR4-3200 |
| Core i3-13100 (F) | $134 - $139 (F) | 4 / 8 (4+0) | 3.4 / 4.5 | - | 17MB (5+12) | 60W / 89W | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-4800 |
The $221 Core i5-13400 comes with six performance cores (p-cores) and four efficiency cores (e-cores) etched onto the 'Intel 7' process node, for a total of 10 cores and 16 threads. The 13400 has a $22 markup over the previous-gen Core i5-12400's $199 debut price, but now you get four e-cores instead of zero. In effect, this makes the 13400 very comparable to the $289 previous-gen Core i5-12600K, which also came with six p-cores and four e-cores.
Perhaps most importantly, you can drop down to the $196 Core i5-13400F and receive the same performance — you just lose the 24-EU integrated UHD Graphics 730 engine, so you'll need a discrete GPU.
The Core i5-13400's p-cores have a 2.5 GHz base clock and boost up to 4.6 GHz on two cores in latency-sensitive work. That's 200 MHz faster than the previous-gen 12400 but 300 MHz slower than the 12600K. The e-cores kick in for background and multi-threaded tasks with a 1.8 GHz base and 3.3 GHz boost, a 300 MHz lower boost than the 12600K. The 13400 has a 65W Processor Base Power (PBP) and 148W Maximum Turbo Power (MTP) rating. As you'll see in our power testing, we didn't see the chip exceed 110W in any of our testing, so the MTP rating is higher than needed.
Most other features, like the supported DDR4-3200 and DDR5-5600 transfer rates, 9.5 MB of L2, and 20 MB of L3 cache, are the same as the previous-gen 12600K, and with good reason — Intel uses repurposed Alder Lake silicon for some of the Core i5-13400 chips, just as it did with the Core i5-12400 processors. The two types of dies come with different core architectures, but are designed to offer the same level of performance.
As such, the Core i5-13400/F doesn't have the same amount of cache per core as the Raptor Lake Core i7 and i9 chips. Instead, each p-core has 1.25 MB of L2 cache, and the quad-core e-core cluster has only 2MB of cache — the same as Alder Lake. That stands in contrast to the higher-end Raptor models that come with 2MB of L2 per p-core and 4MB of L2 for each e-core cluster.
The C0 die is the same silicon that Intel uses for the Alder Lake Core i5 processors, making the Core i5-13400 mostly identical to the Core i5-12600K (our test subject is C0). In contrast, the B0 stepping die comes with the Raptor Cove chip architecture, but has a cut-down cache configuration to match the Alder Lake silicon.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
The Raptor Lake processors have a vastly improved voltage/frequency curve compared to Alder Lake, making them more efficient, and a special microcontroller unit (MCU) firmware that imparts caching and prefetching advantages (deep dive here). Intel says it has tuned the two die to offer the same level of performance, but it is yet to be seen if some of Raptor Lake's finer-grained MCU tuning is present in the B0 stepping chips. We're working to acquire one to put it to the test.
As before, the LGA 1700 chip is compatible with 600-series motherboards, and because the chip has a locked multiplier (no overclocking), the B- and H-series motherboards make the most sense for this class of chip. Unlike the previous-gen 65W Alder Lake processors, there is no workaround for overclocking Raptor Lake's execution cores, as Intel adjusted to prevent a workaround from the motherboard makers.
You are free to overclock the memory on B-series motherboards, but be aware that the System Agent (SA) voltage is locked, which limits DDR4 memory overclocks in the Gear 1 setting (DDR5 still overclocks well).
Gaming Benchmarks on Intel Core i5-13400 and 13400F — The TLDR
- Intel Core i5-13400 DDR5 or DDR4: Corsair H115i 280mm water cooler, power limits removed, Stock DDR5-4800 in Gear 2 / DDR4-3200 in Gear 1
- Intel Core i5-13400 DDR4-3600 / DDR5-6800: Corsair H115i 280mm water cooler, power limits removed, DDR4-3600 CL16, DDR5-6800 XMP 3.0
- AMD PBO Configs: Precision Boost Overdrive (Motherboard), Scalar 10X, DDR5-6000 EXPO
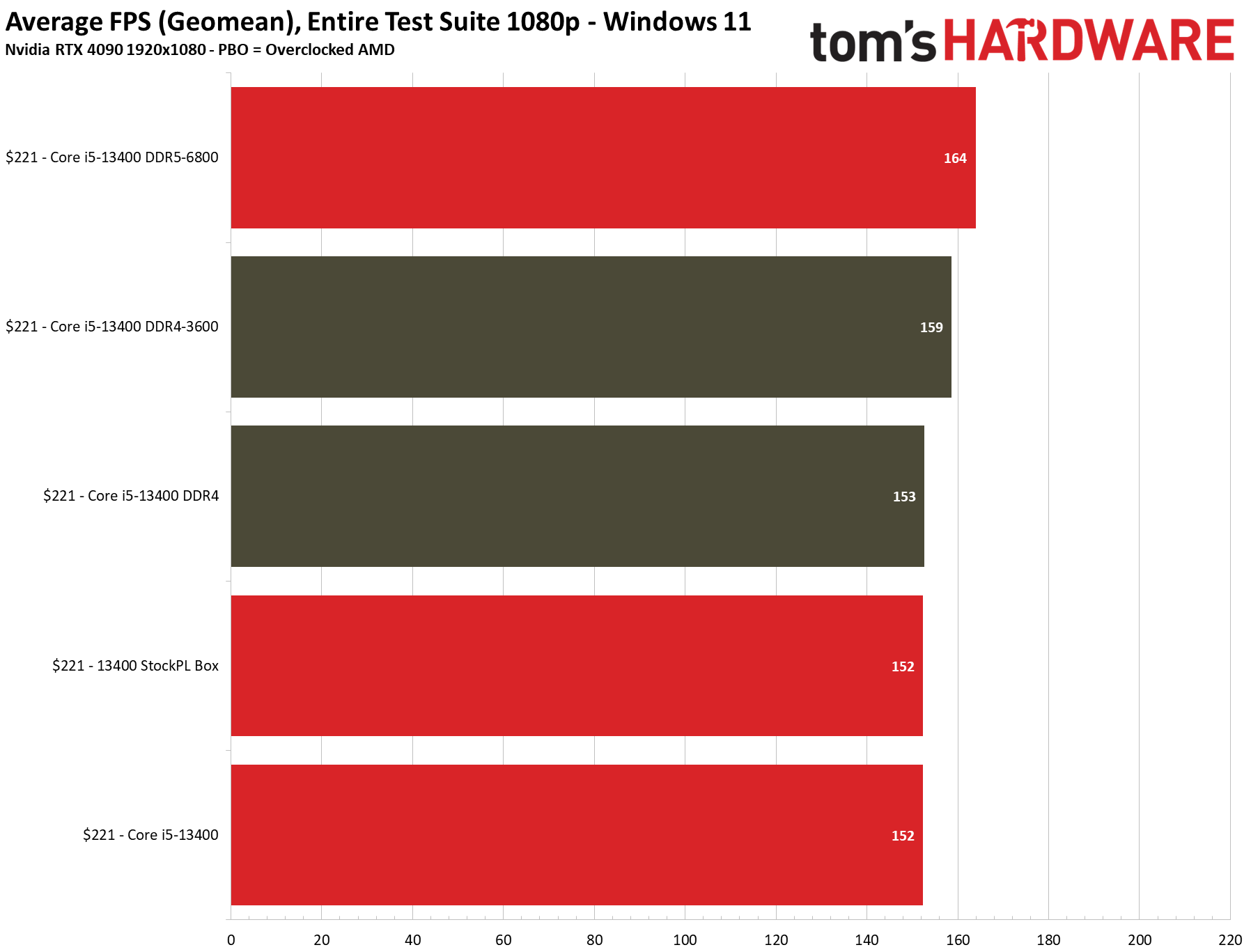
You can find the particulars of our overclock and test setup further below. Here we have the geometric mean of our gaming tests at 1080p and 1440p, with each resolution split into its own chart. We're testing with an Nvidia GeForce RTX 4090 to reduce GPU-imposed bottlenecks as much as possible, and differences between test subjects will shrink with lesser cards or higher resolutions and fidelity. You'll find further game-by-game breakdowns below.
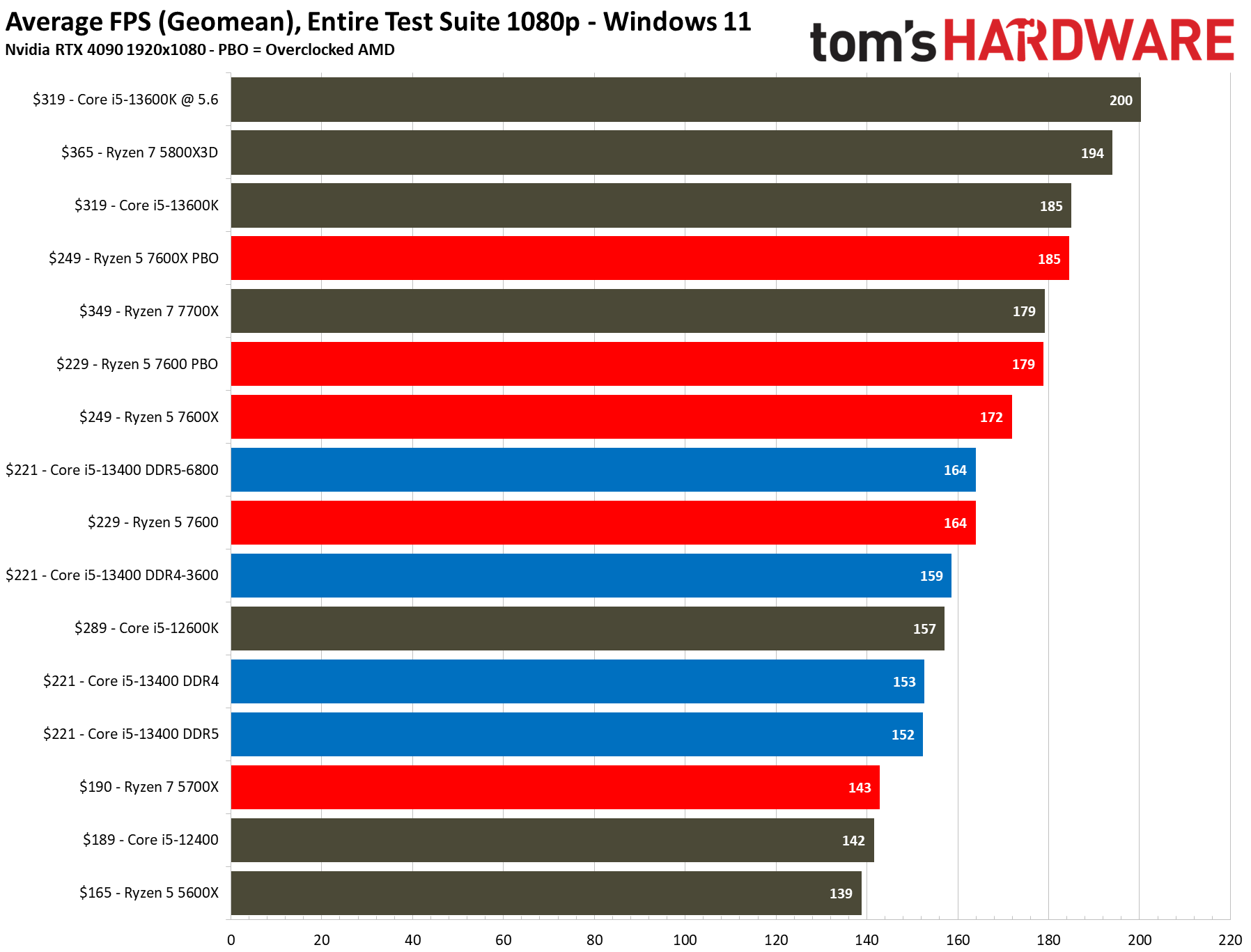
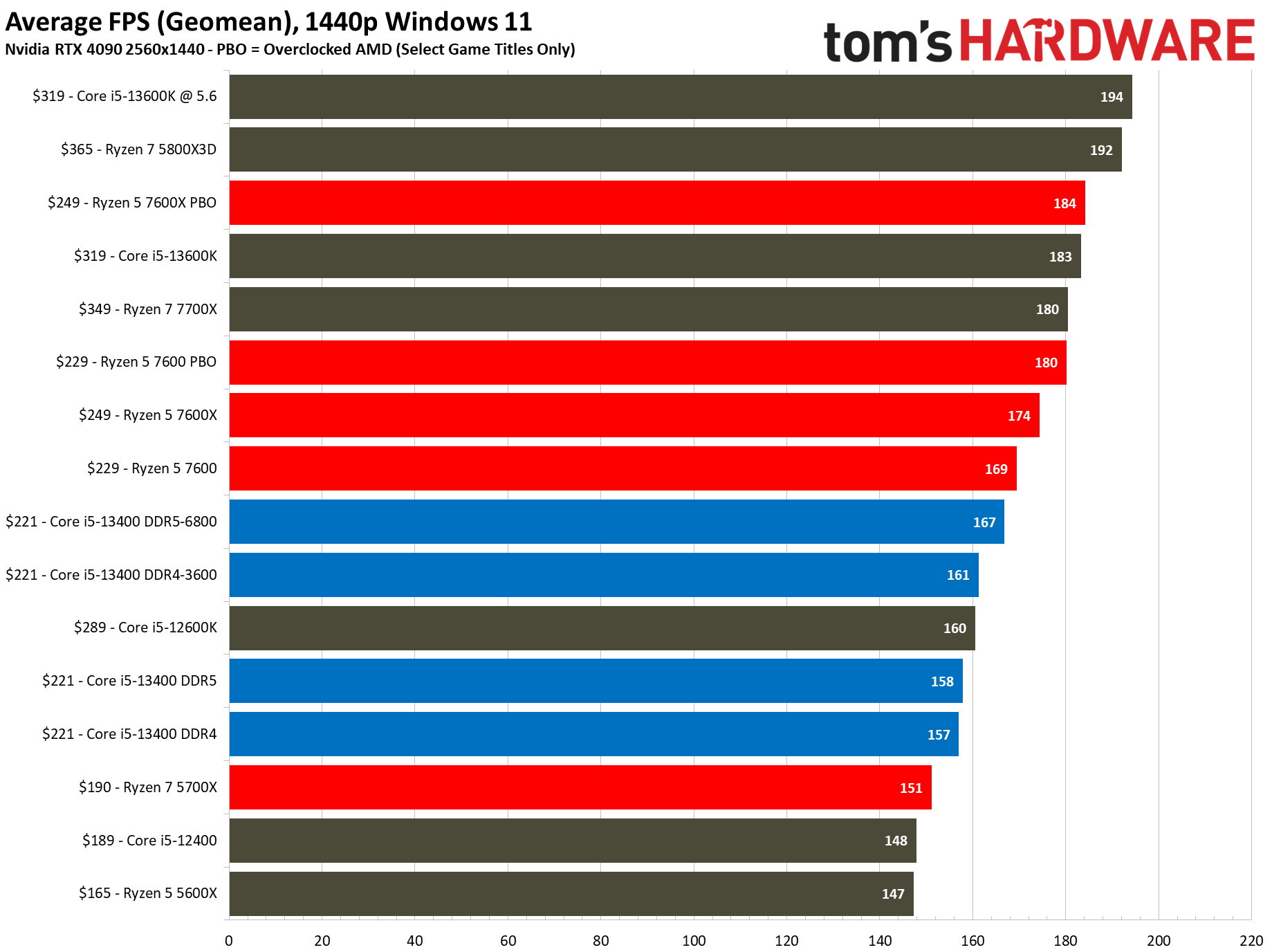
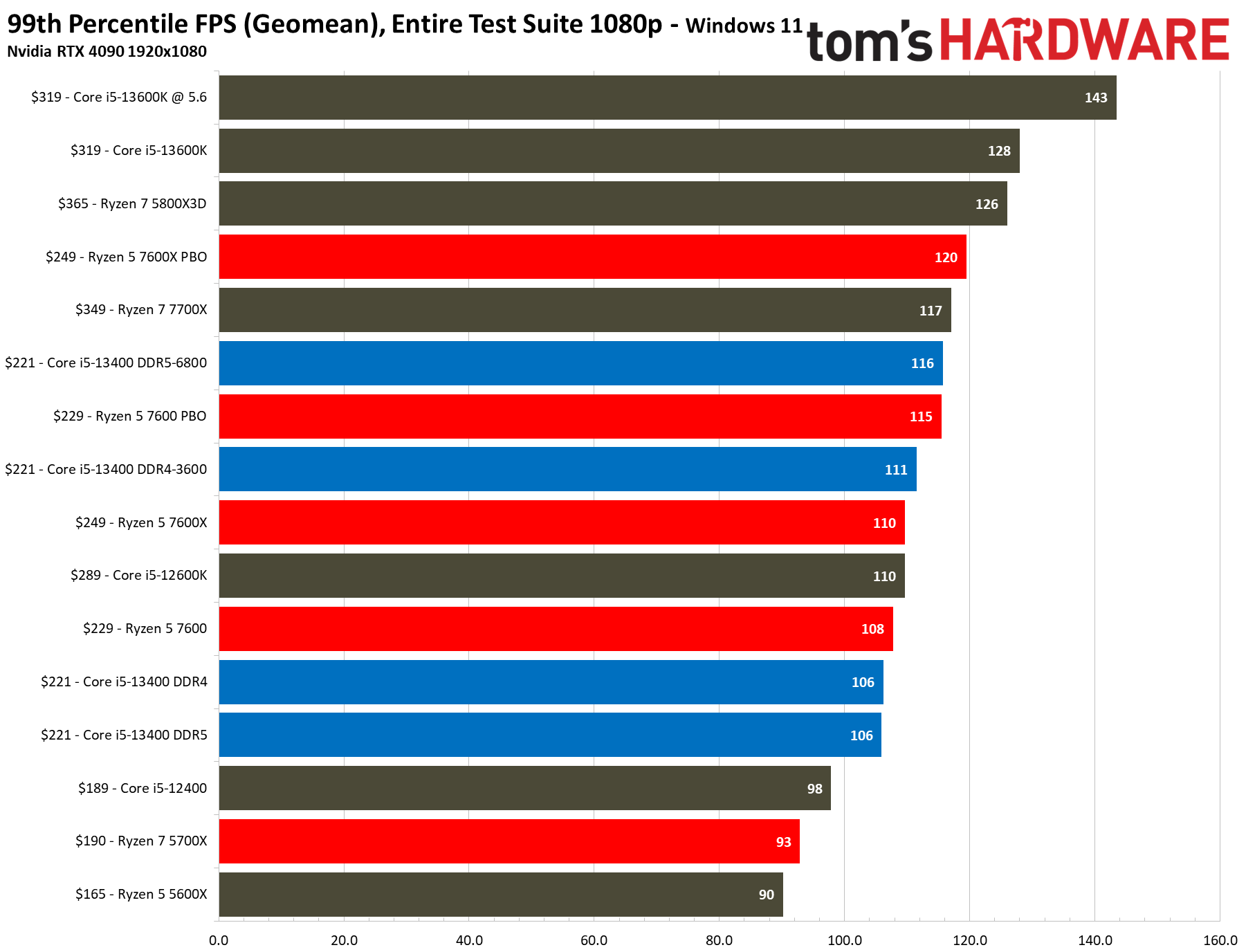
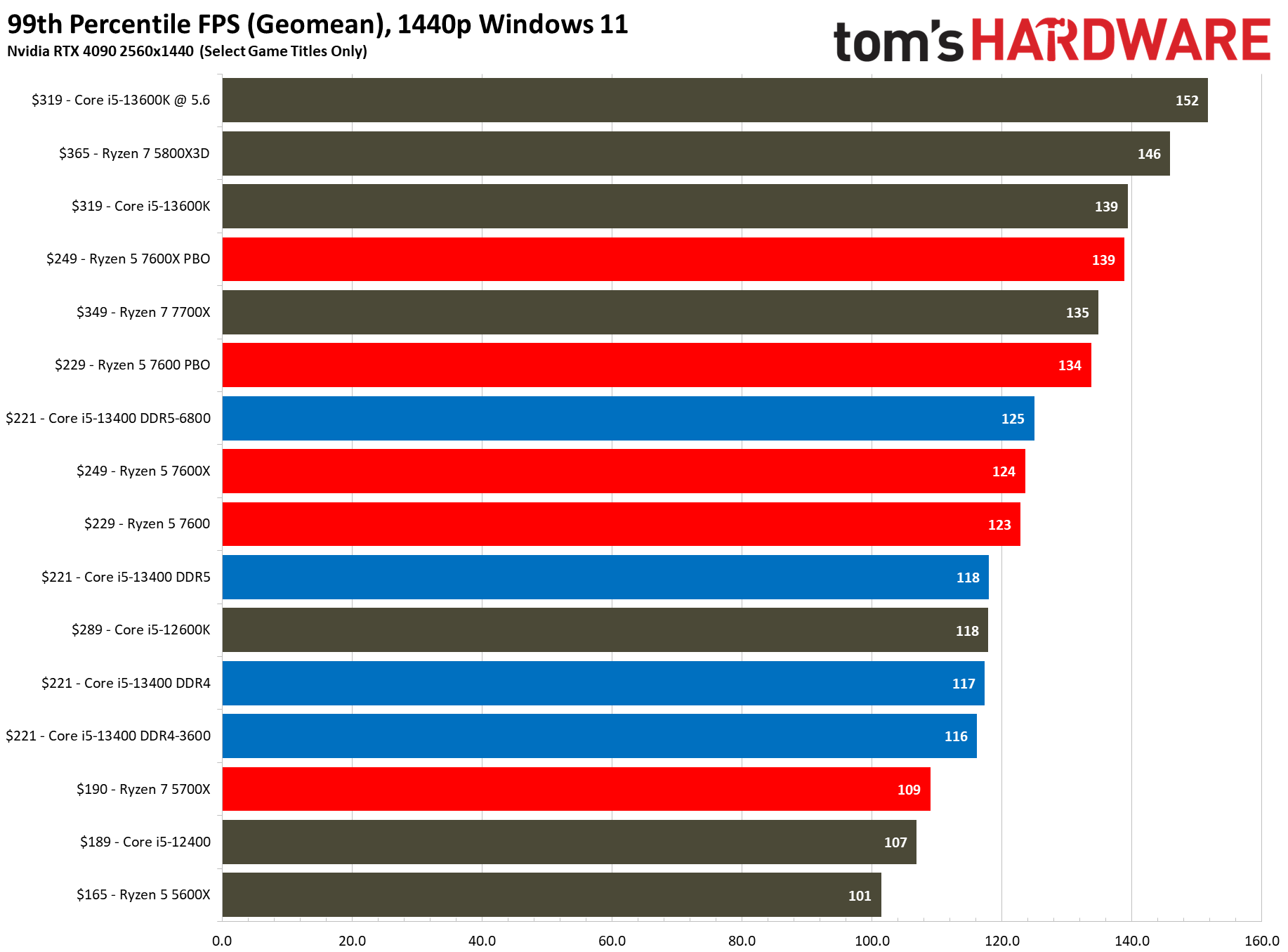
We have testing in the thermal and overclocking section that shows there is little to no performance loss in gaming if you use the 13400's included stock cooler, even with the power limits enforced — we saw no difference with the box cooler in 1080p gaming, and the stock cooler was 1.2% slower at 1440p (close enough to call a tie). To maintain a level playing field, we removed the power limits and used our H115i cooler for these tests.
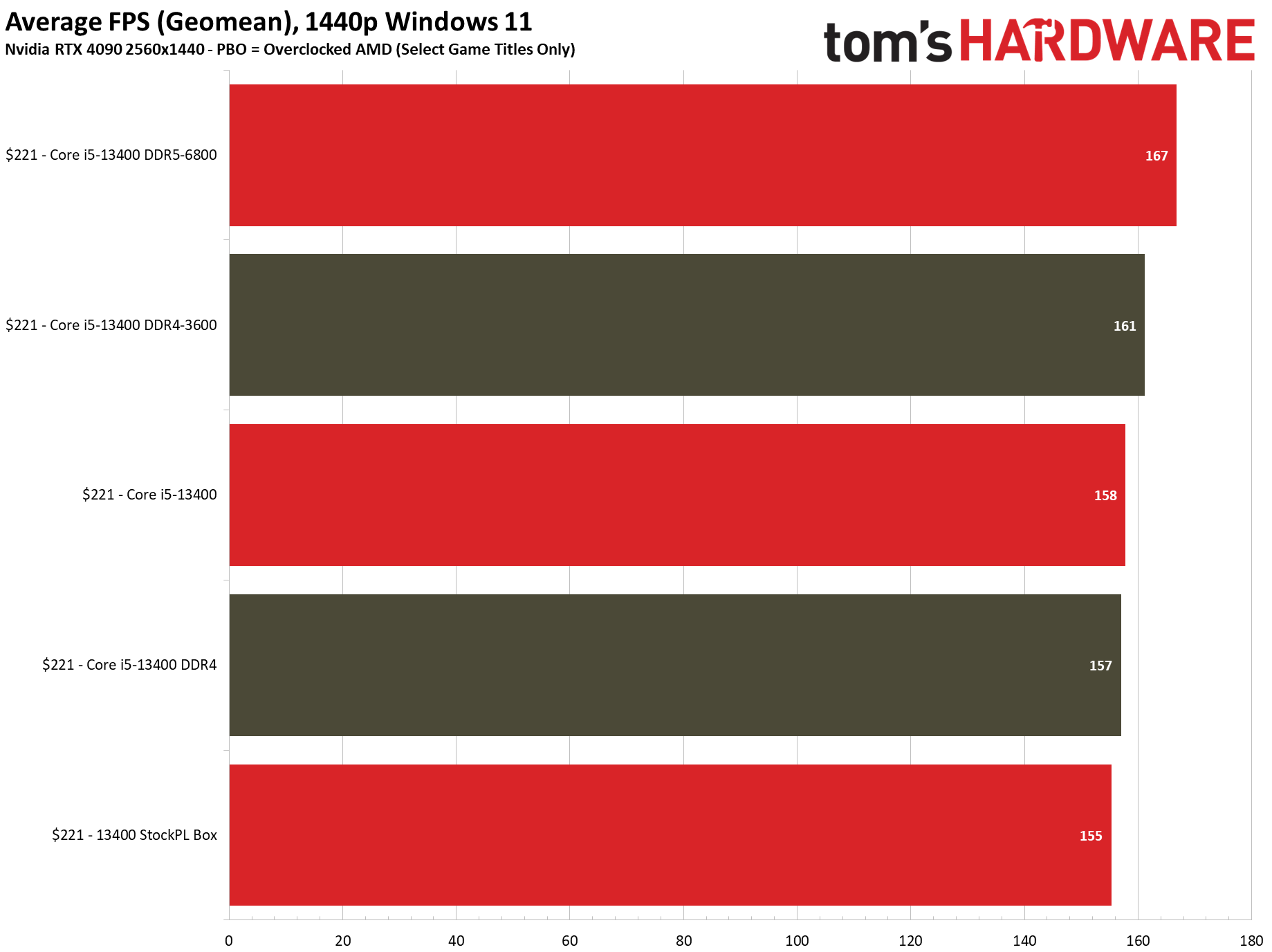
The 13400's support for DDR4 memory is key in this price range, as it still costs nearly half as much as DDR5. Overall we see a difference of 1 fps between DRR4 and DDR5, with DDR4 coming out on top by a mere 0.6% — meaning the two Core i5-13400 configs offer basically the same performance.
We did get ~3% more performance from DDR5-6800 than we did with DDR4-3600, but the DDR5 kit costs nearly three times as much as the DDR4 kit ($144 more). You could step back to a DDR5-6000 kit that 'only' costs twice as much, but neither of those DDR5 options makes much sense in this price range.
The Core i5-13400 is 7% faster than the previous-gen Core i5-12400, but despite the physical similarities between the 13400 and the 12600K, the latter is still ~3% faster on the strength of its higher clock rates. That's a pretty slim delta, though, considering the 13400's lower pricing and big improvements in productivity applications.
The stock $229 Ryzen 5 7600 is 7% faster than the stock $221 Core i5-13400 with DDR5/DDR4 in the 1080p tests. Overclocking the 7600 increases the delta over the overclocked 13400 DDR5 system to 9%, and 12% over the overclocked DDR4 config. However, the 7600 carries a ~$30 premium over the 13400F. Adding in the higher motherboard and memory costs associated with the AM5 platform also takes a toll, as you can see in our value analysis in the conclusion.
Some have pointed to the $190 Ryzen 7 5700X as an alternative here, but the Core i5-13400 is 7% faster at 1080p. Given the 5700X is only $10 less than the 13400F, comes without a cooler, has lower performance than the 13400F in productivity apps, and uses an older platform, our test data suggests it is really only a contender for an upgrader currently on an AM4 platform.
The deltas in these charts can be slim, and large deltas in individual game titles, like with the 5800X3D, impact cumulative measurements. The competition between AMD and Intel chips can vary based on the title (particularly with DDR4 vs DDR5) and the GPU you use. It's best to make an informed decision based on the types of titles you frequently play, so be sure to check out the individual tests below.
| Tom's Hardware | 1080p Game Benchmarks |
| $699 — Core i9-13900KS | 100% |
| $358 — Ryzen 7 5800X3D | 95.4% |
| $319 - Core i5-13600K | 90.9% |
| $349 — Ryzen 7 7700X | 88% |
| $249 - Ryzen 5 7600X / OC | 84.5% / 90.7% |
| $229 - Ryzen 5 7600 / OC | 80.5% / 87.9% |
| $250 - Core i5-12600K | 77.2% |
| $221 - Core i5-13400 DDR5 / DDR5-6800 | 74.9% / 80.6% |
| $221 - Core i5-13400 DDR4 / DDR4-3600 | 75.0% / 77.9% |
| $185 - Core i5-12400 | 69.6% |
Cyberpunk 2077 on Intel Core i5-13400 and Core i5-13400F
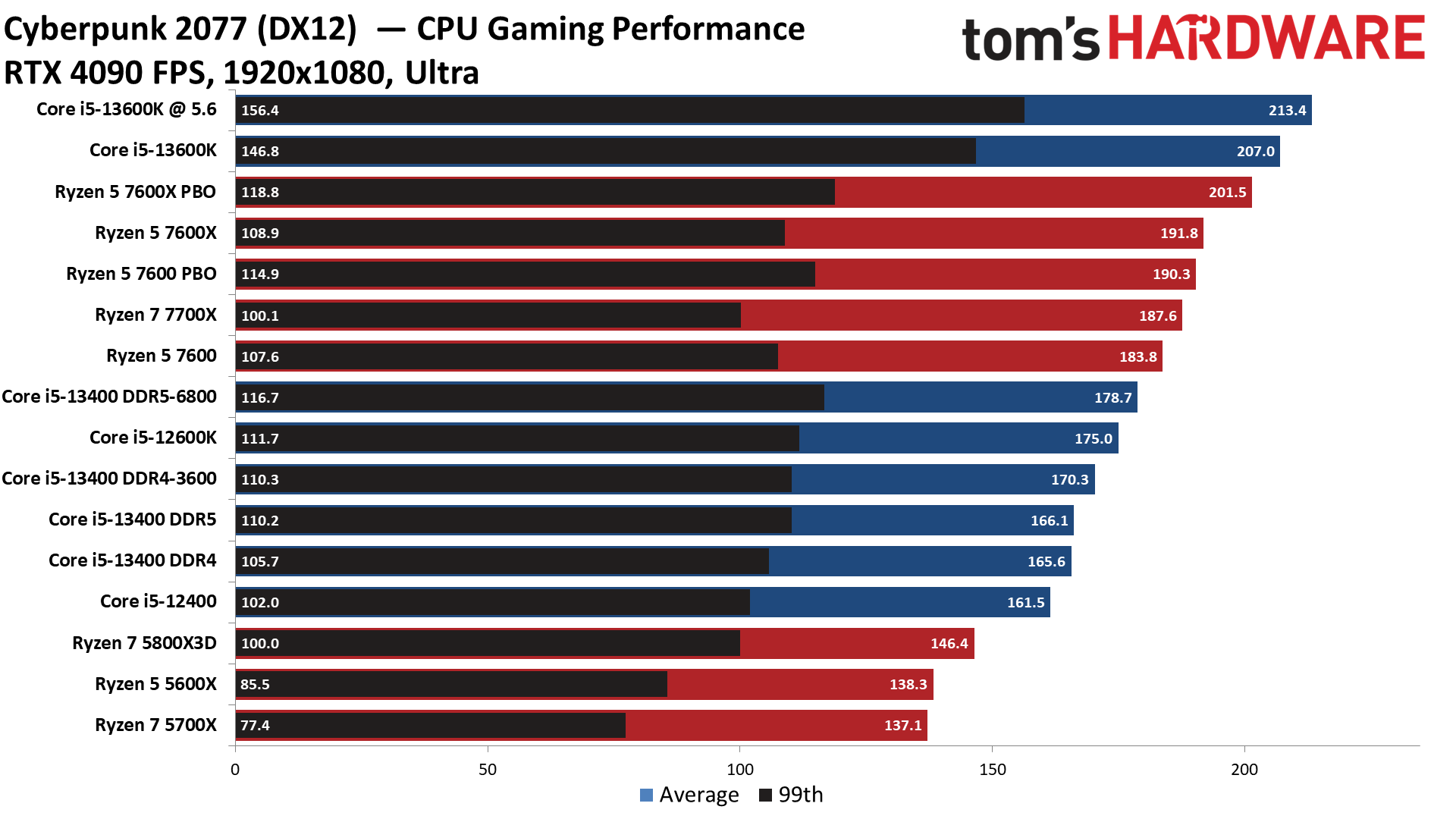
The Ryzen 5 7600 takes a strong lead in Cyberpunk 2077, while the Core i5-13400 trails across the board, even after overclocking the memory.
The Ryzen 7 5800X3D continues to not provide much performance uplift over the standard Zen 3 models, which is important to remember — not all games benefit from the 3D cache-stacking tech.
Far Cry 6 on Intel Core i5-13400 and Core i5-13400F
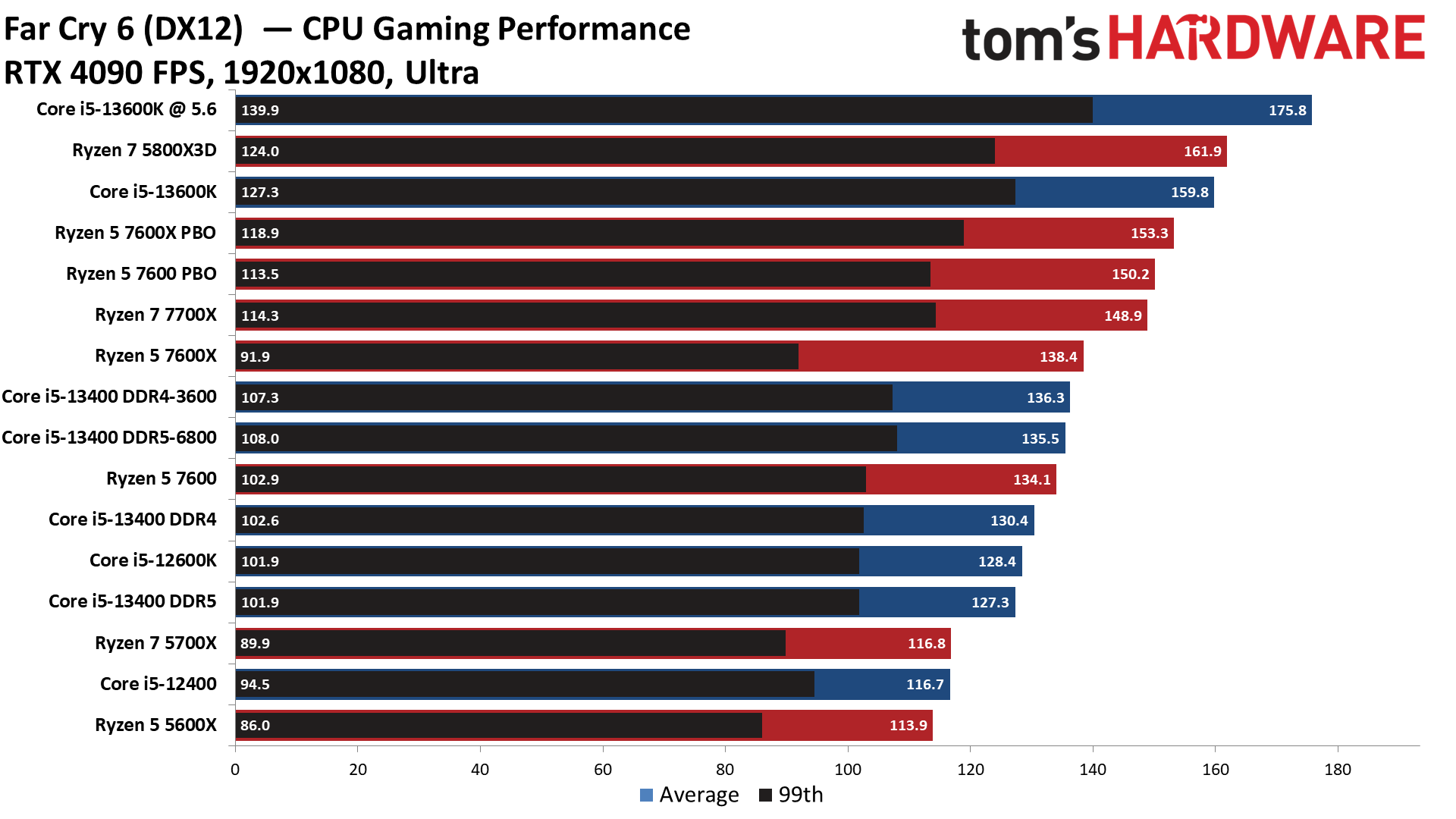
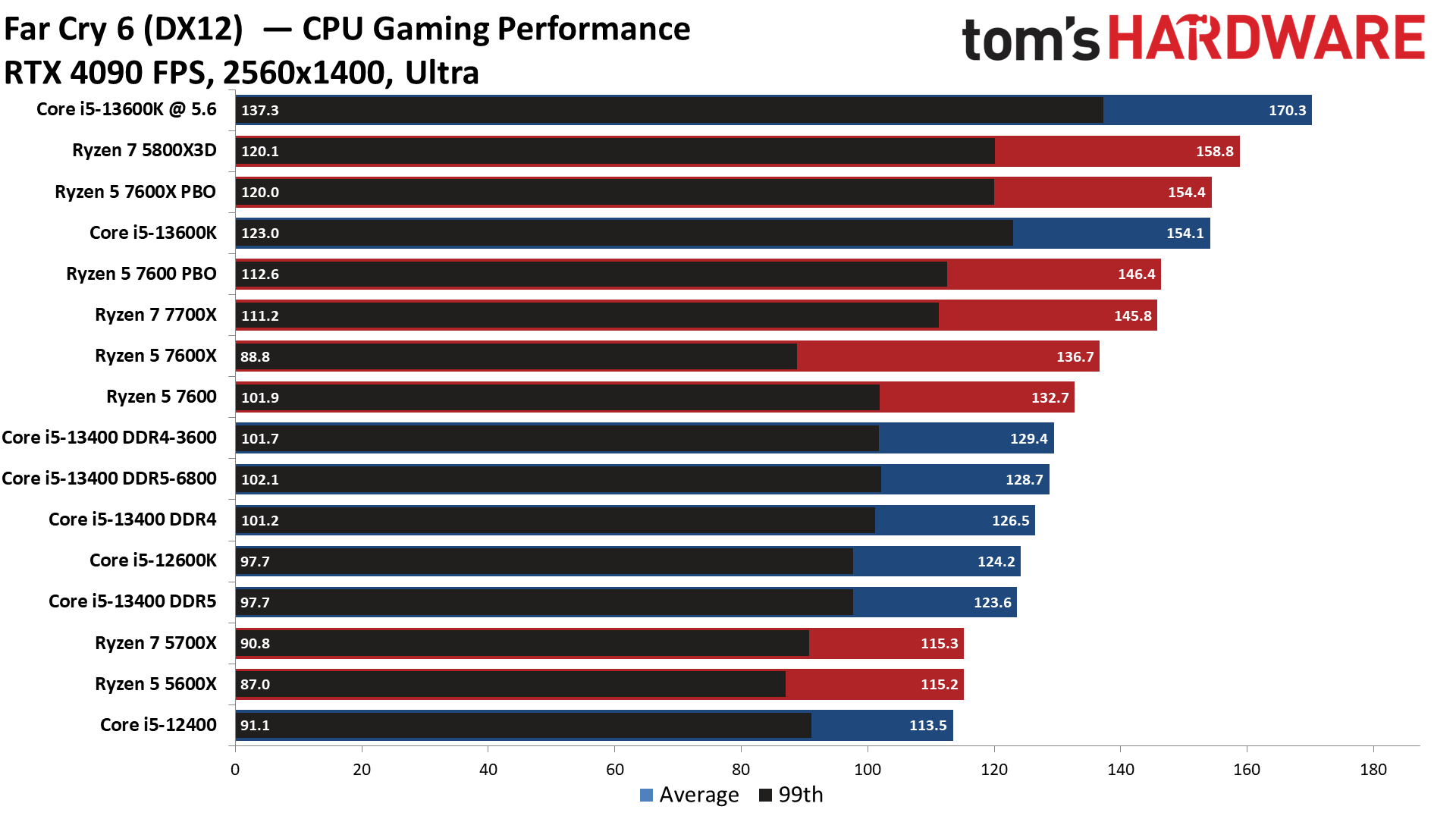
Far Cry 6 is very memory latency-sensitive, and here we can see that the DDR4 Core i5-13400 config in Gear 1 exceeds the DDR5 memory, which runs in the higher-latency Gear 2 mode, despite DDR5's throughput advantage. The DDR4 config even leads after stepping up to the relatively tame DDR4-3600 memory overclock, beating the DDR5-6800 config.
Meanwhile, the Ryzen 5 7600 edges past the Core i5-13400 in stock trim and takes an even bigger lead after overclocking.
F1 2021 on Intel Core i5-13400 and Core i5-13400F
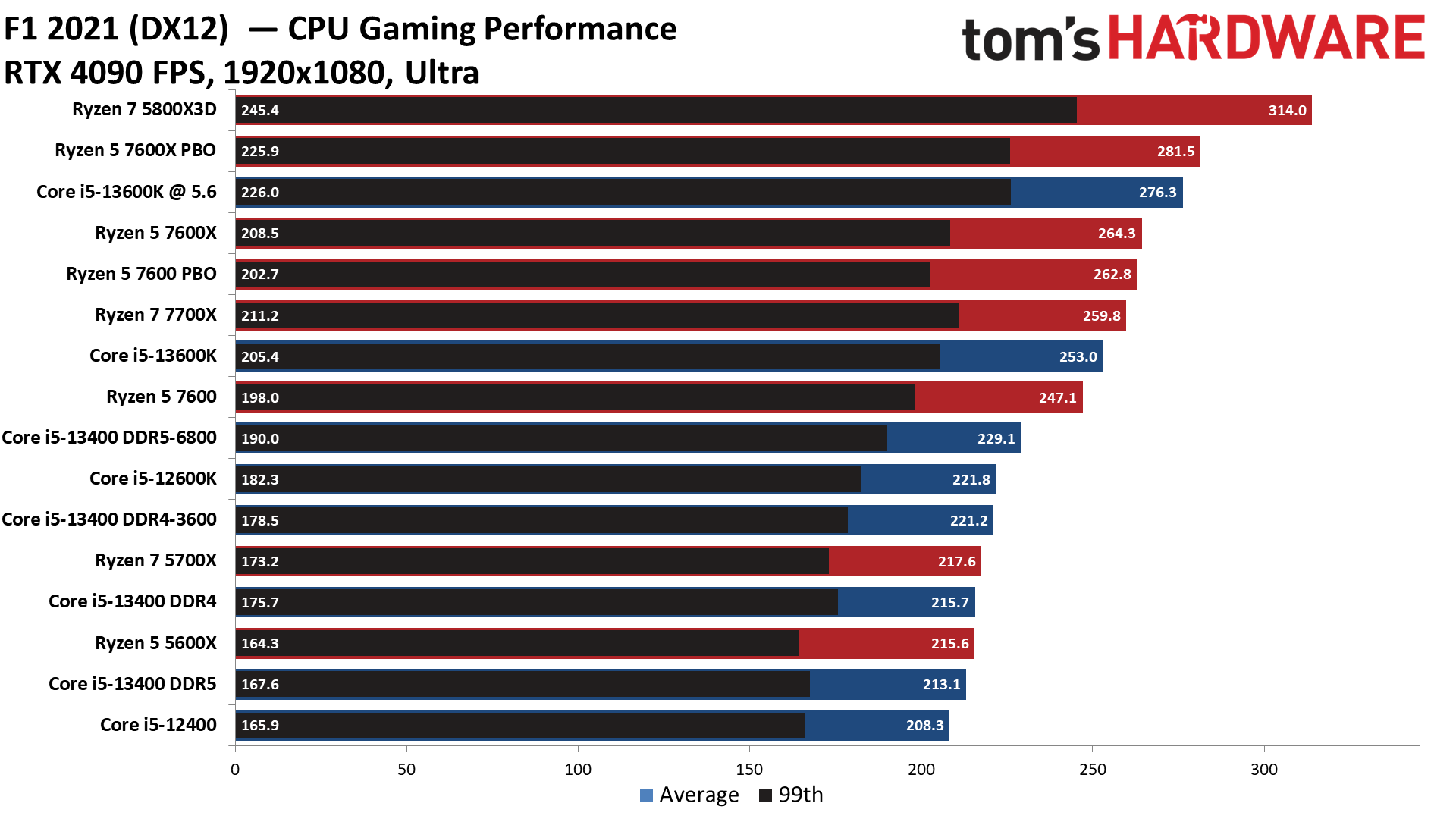
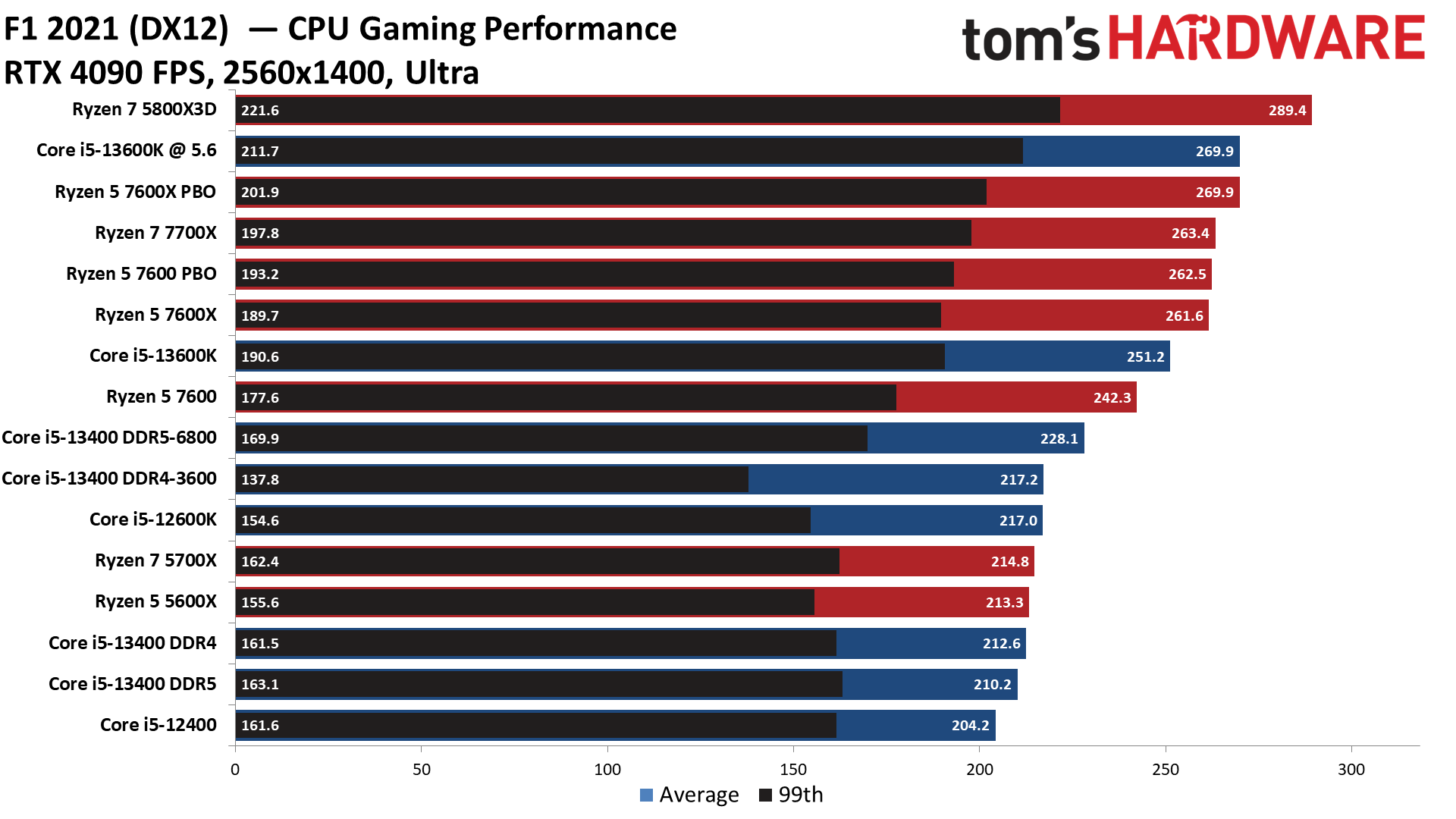
F1 2021 finds the Ryzen chips again taking substantial leads over the Core i5-13400, but that isn't entirely surprising given their higher pricing.
Hitman 3 on Intel Core i5-13400 and Core i5-13400F
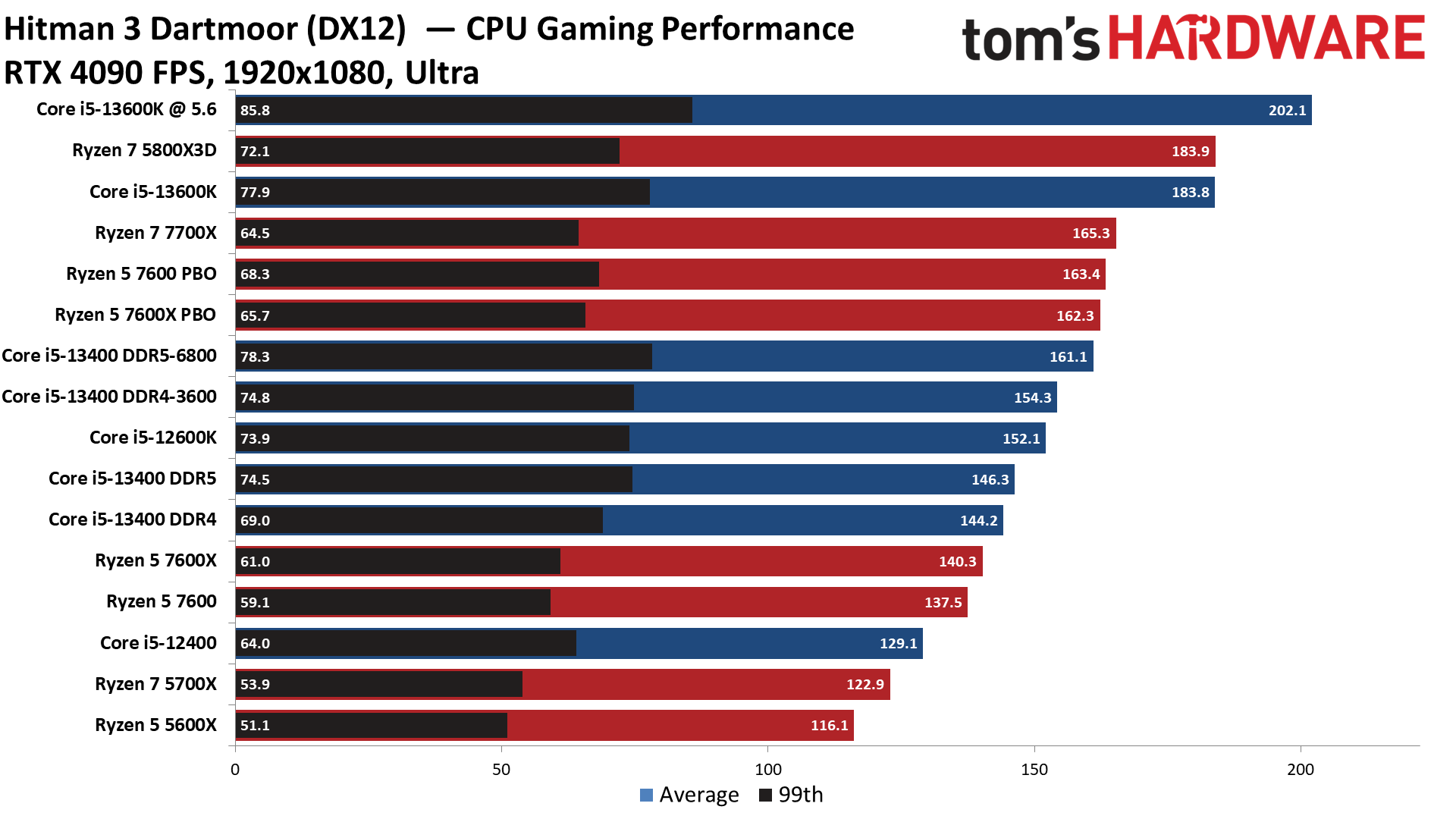
Here we can see the increased throughput of DDR5 memory having more of an impact in Hitman 3. This title also makes good use of the e-cores, thus delivering a more substantial lead over the previous-gen Core i5-12400.
Microsoft Flight Simulator 2021 on Intel Core i5-13400 and Core i5-13400F
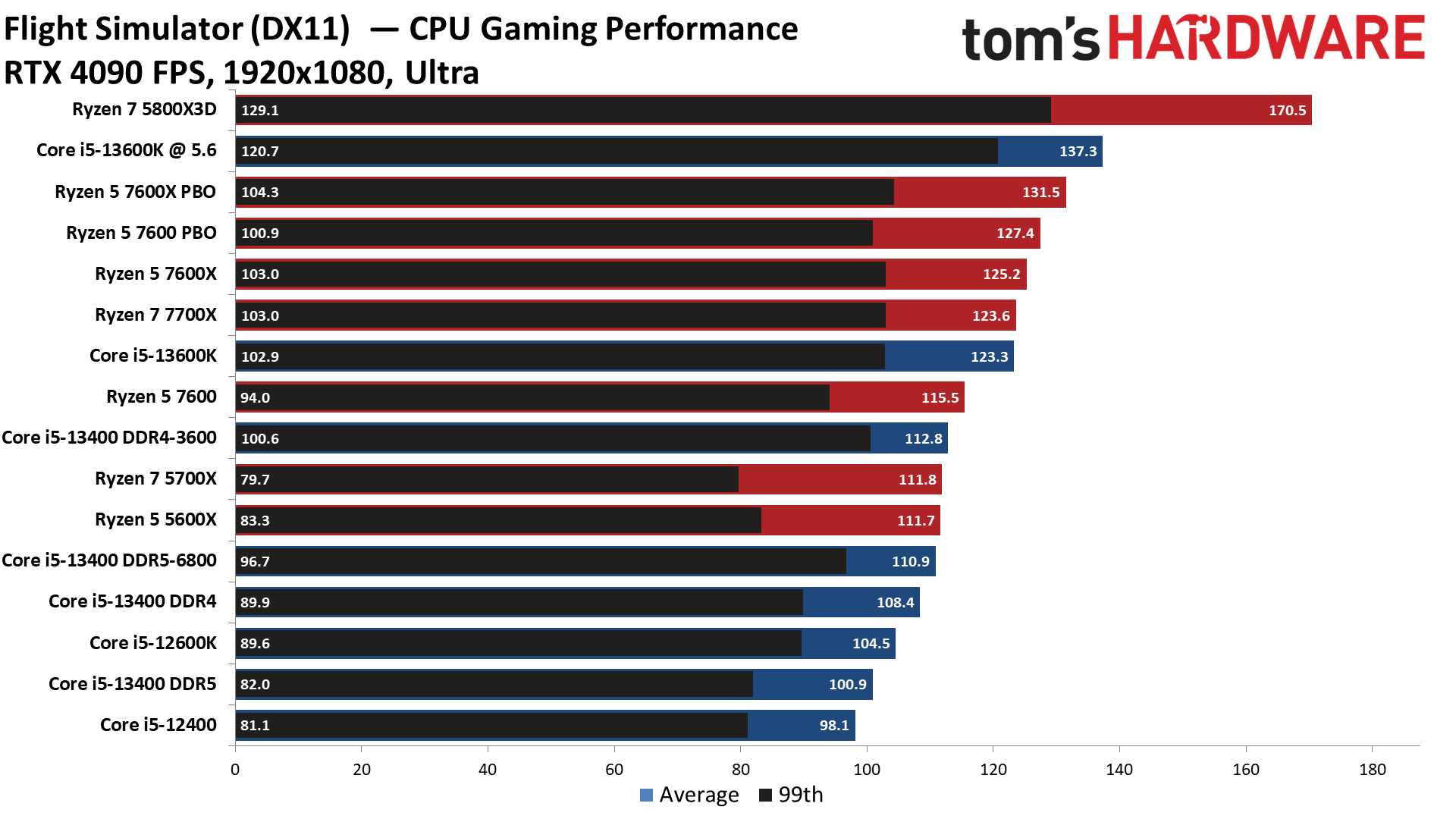
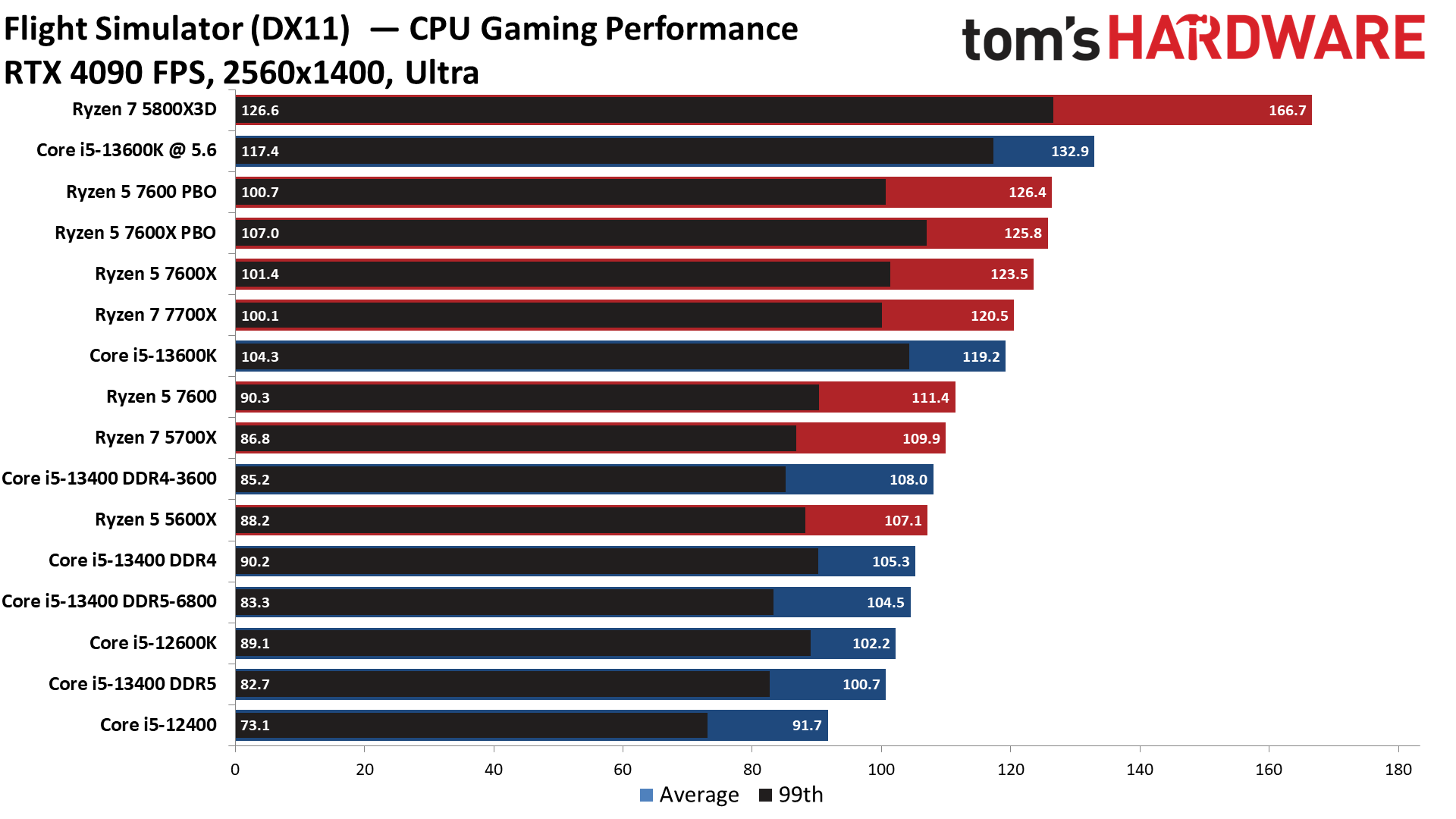
Microsoft Flight Simulator 2021 obviously benefits tremendously from L3 cache — the Ryzen 7 5800X3D is simply incredible in this title. This large advantage is amazing but doesn't represent the 5800X3D's performance in most titles. It also illustrates how outliers can make the 5800X3D seem more impressive in cumulative measurements.
Back in the more realistic land for mid-range gamers, the Core i5-13400 does much better with DDR4 memory than with DDR5, indicating that this title prefers lower latency accesses over sheer bandwidth. In fact, the Core i5-13400 with DDR4 is faster than the Core i5-12600K, which is tested with DDR5 memory.
Red Dead Redemption 2 on Intel Core i5-13400 and Core i5-13400F
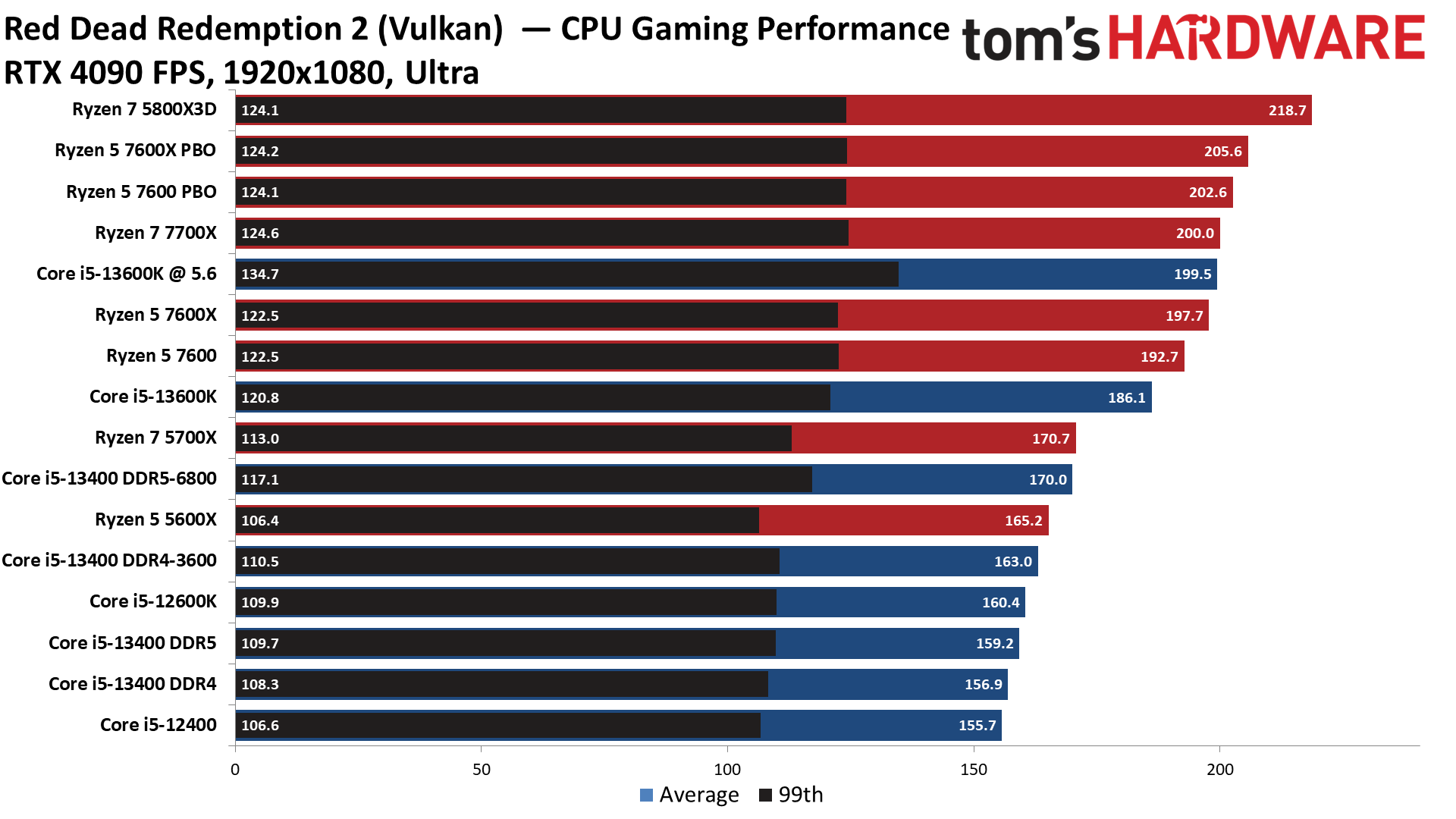
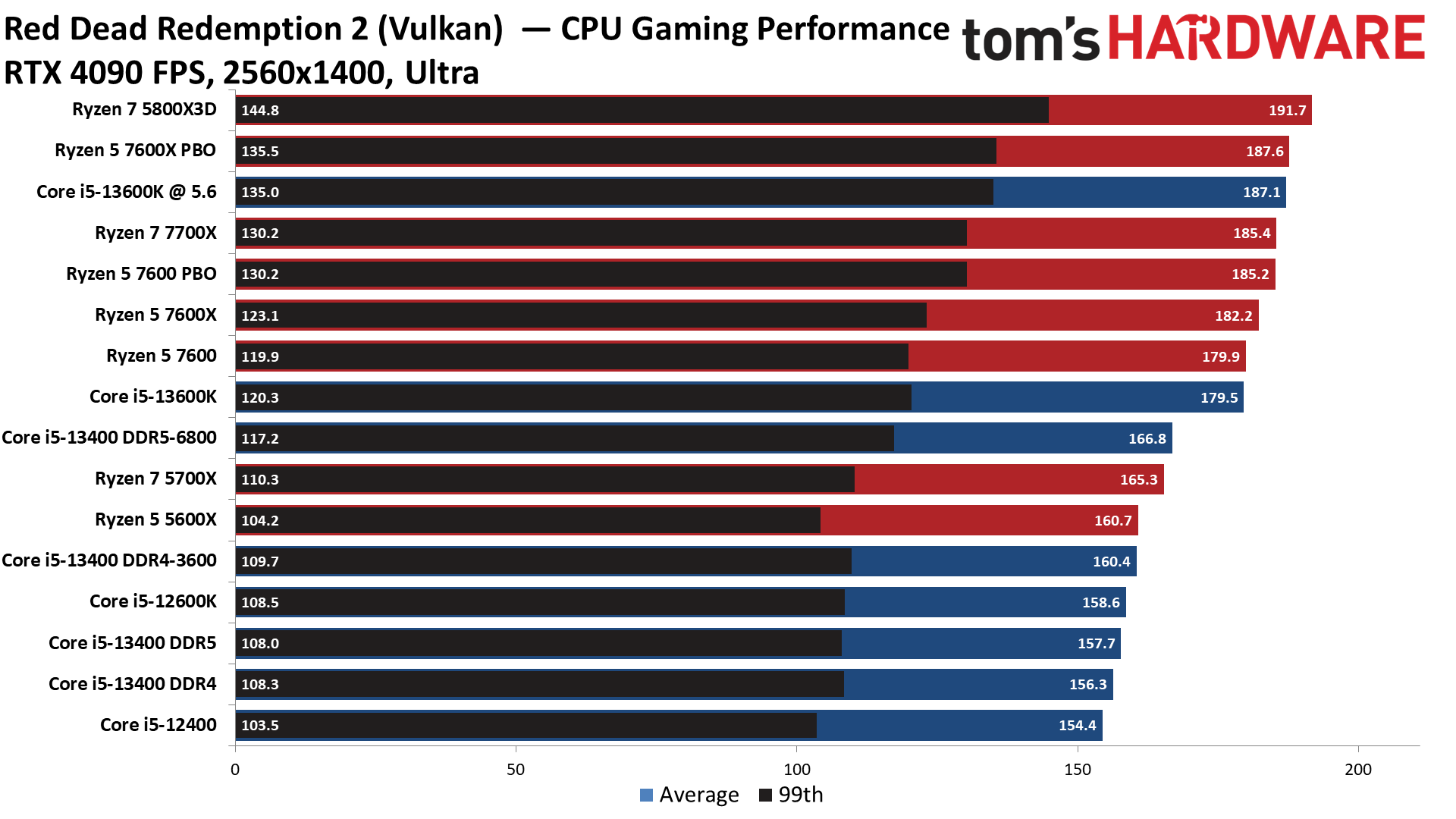
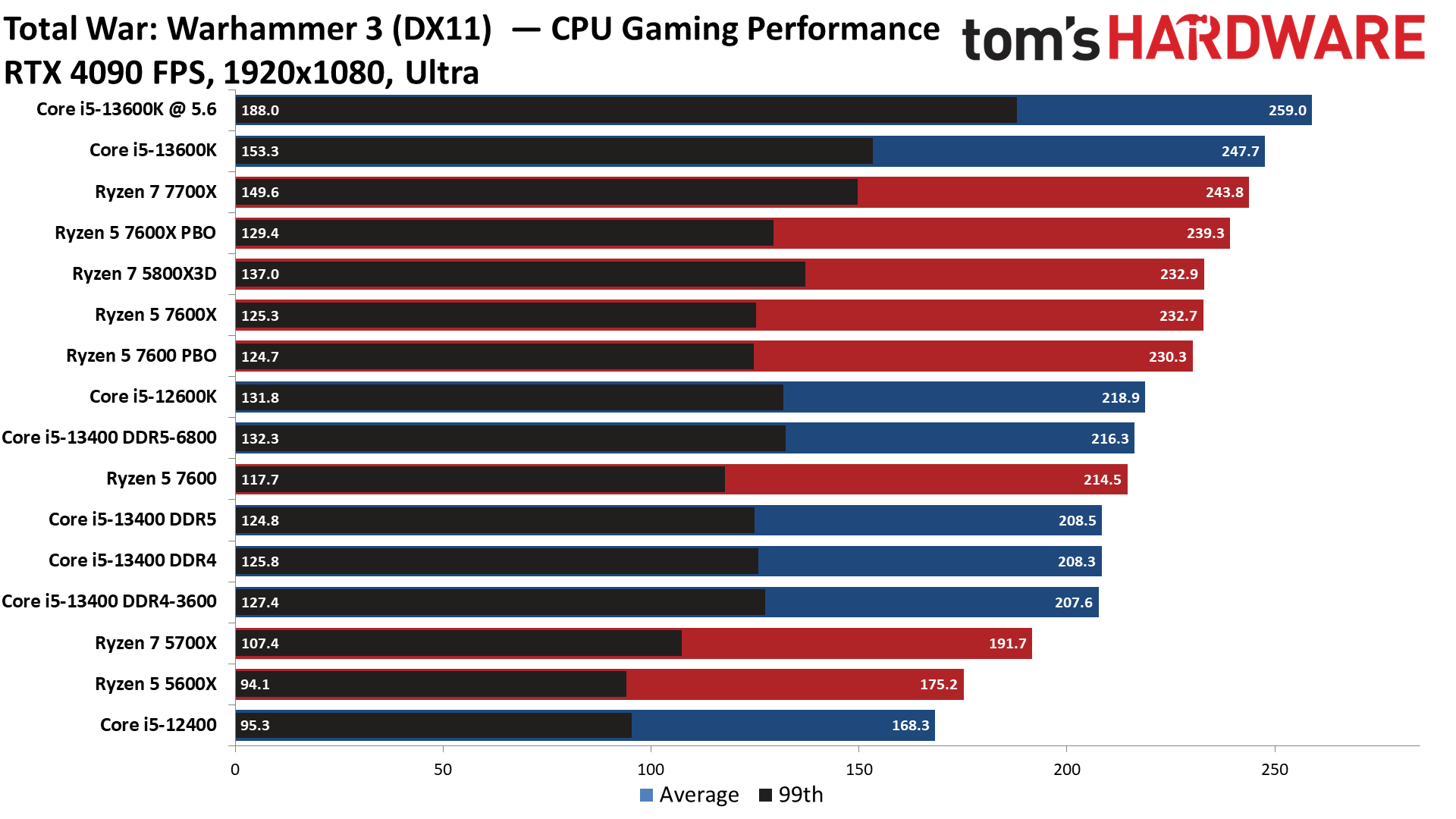
Warhammer 3 on Intel Core i5-13400 and Core i5-13400F
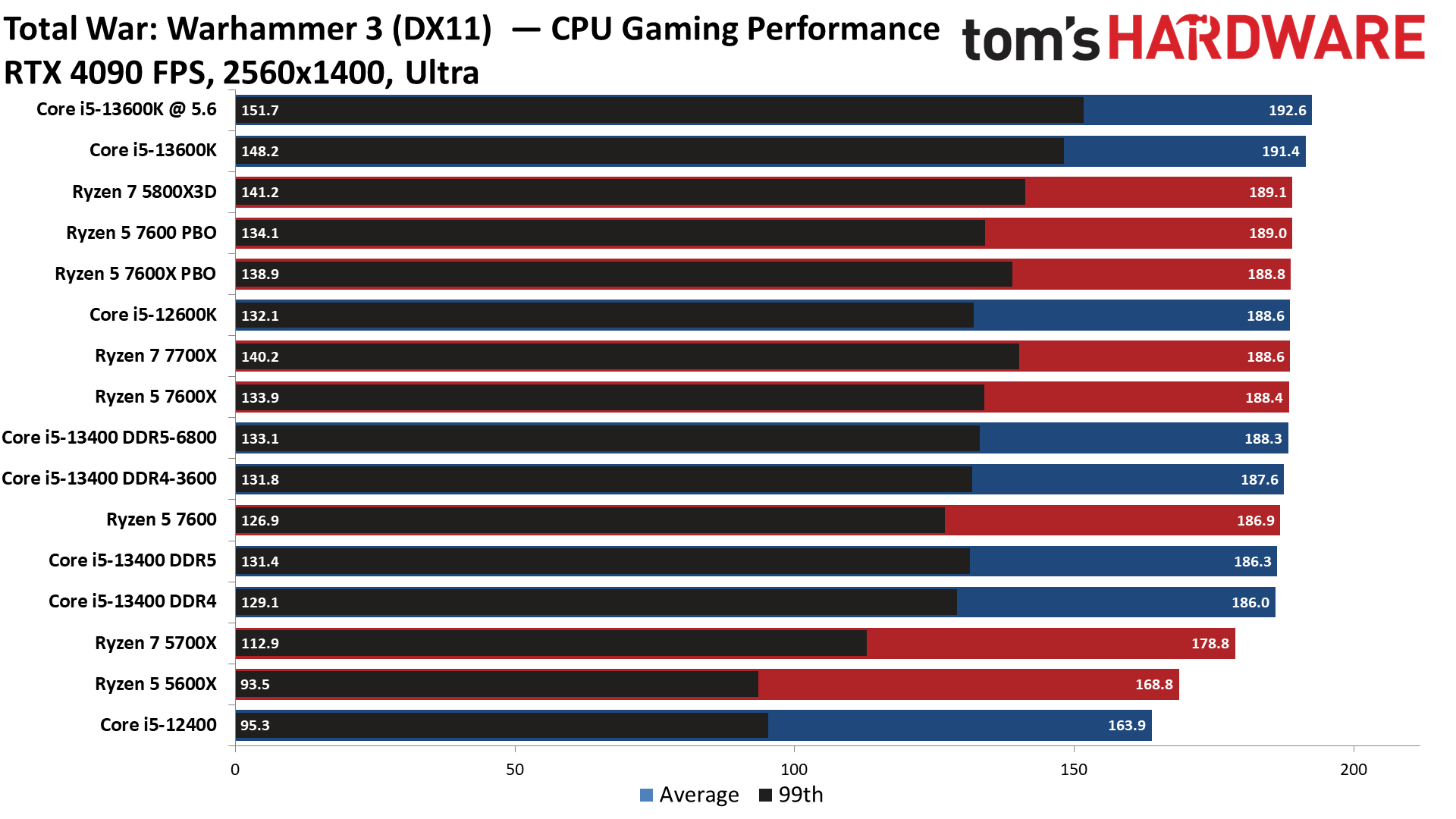
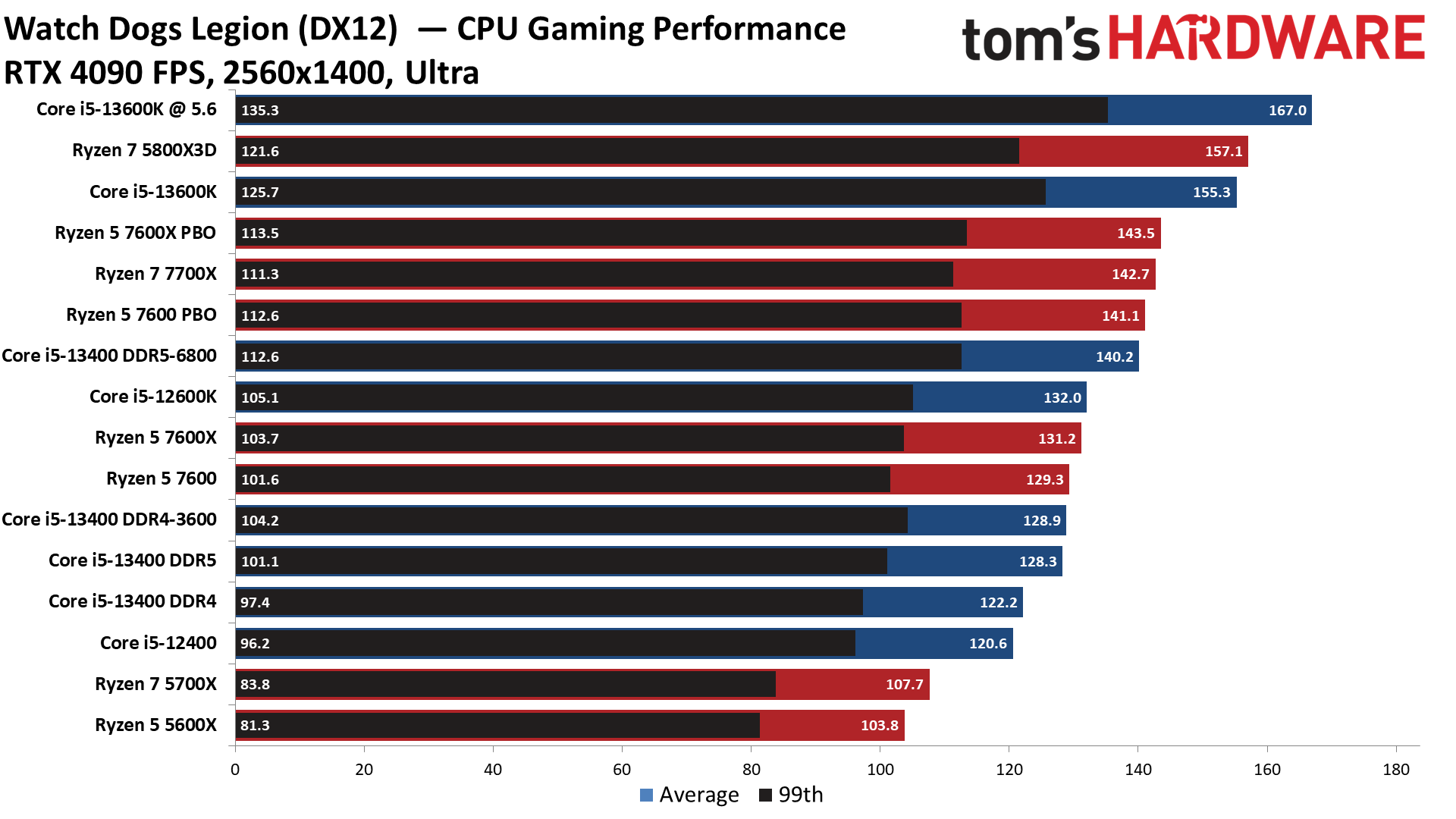
Flipping over to the 1440p charts shows us that higher resolutions are often the great equalizer that levels the playing field for chips with similar accommodations.
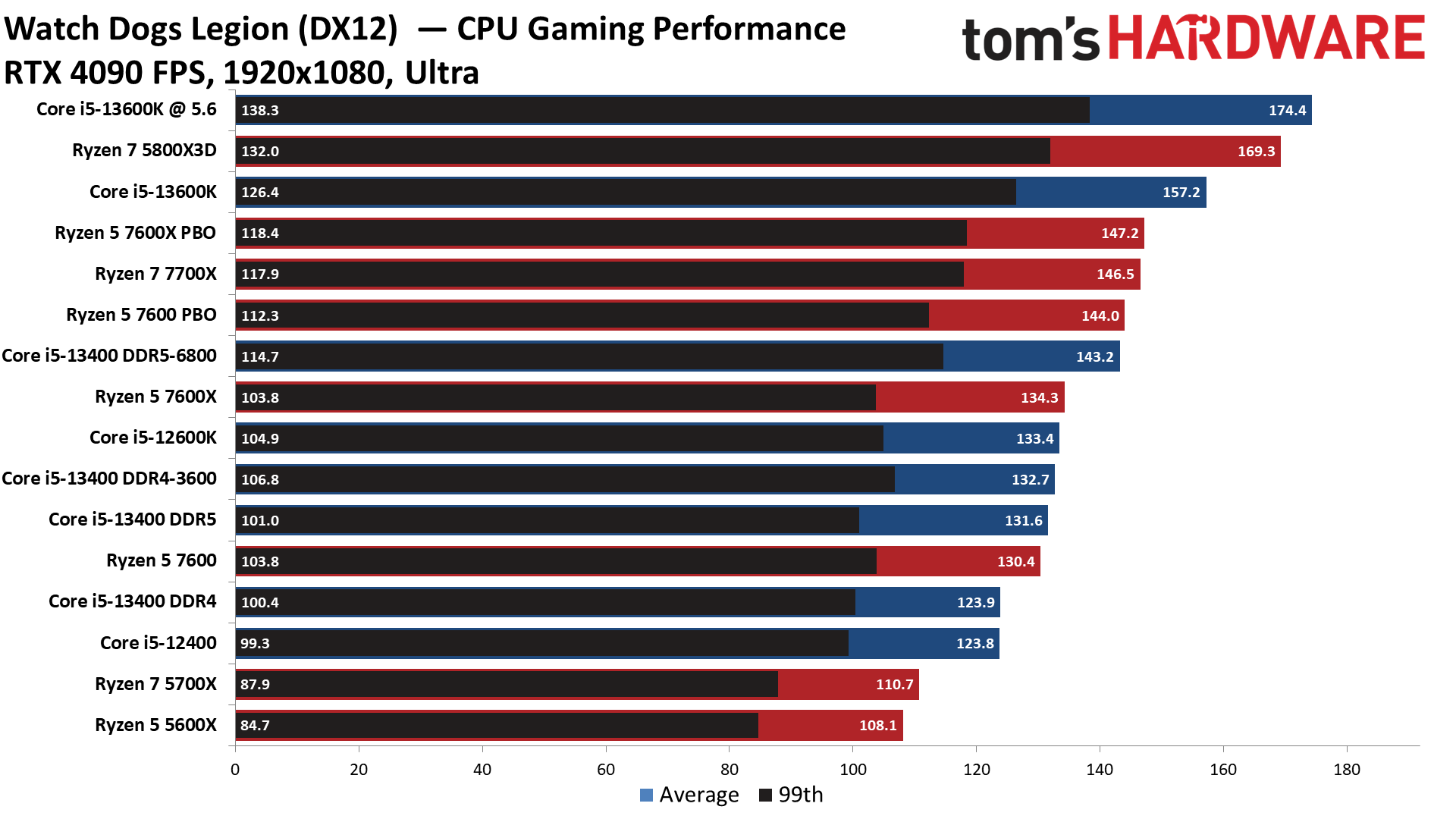
Watch Dogs Legion on Intel Core i5-13400 and Core i5-13400F
Productivity Benchmarks on Intel Core i5-13400 and 13400F — The TLDR:
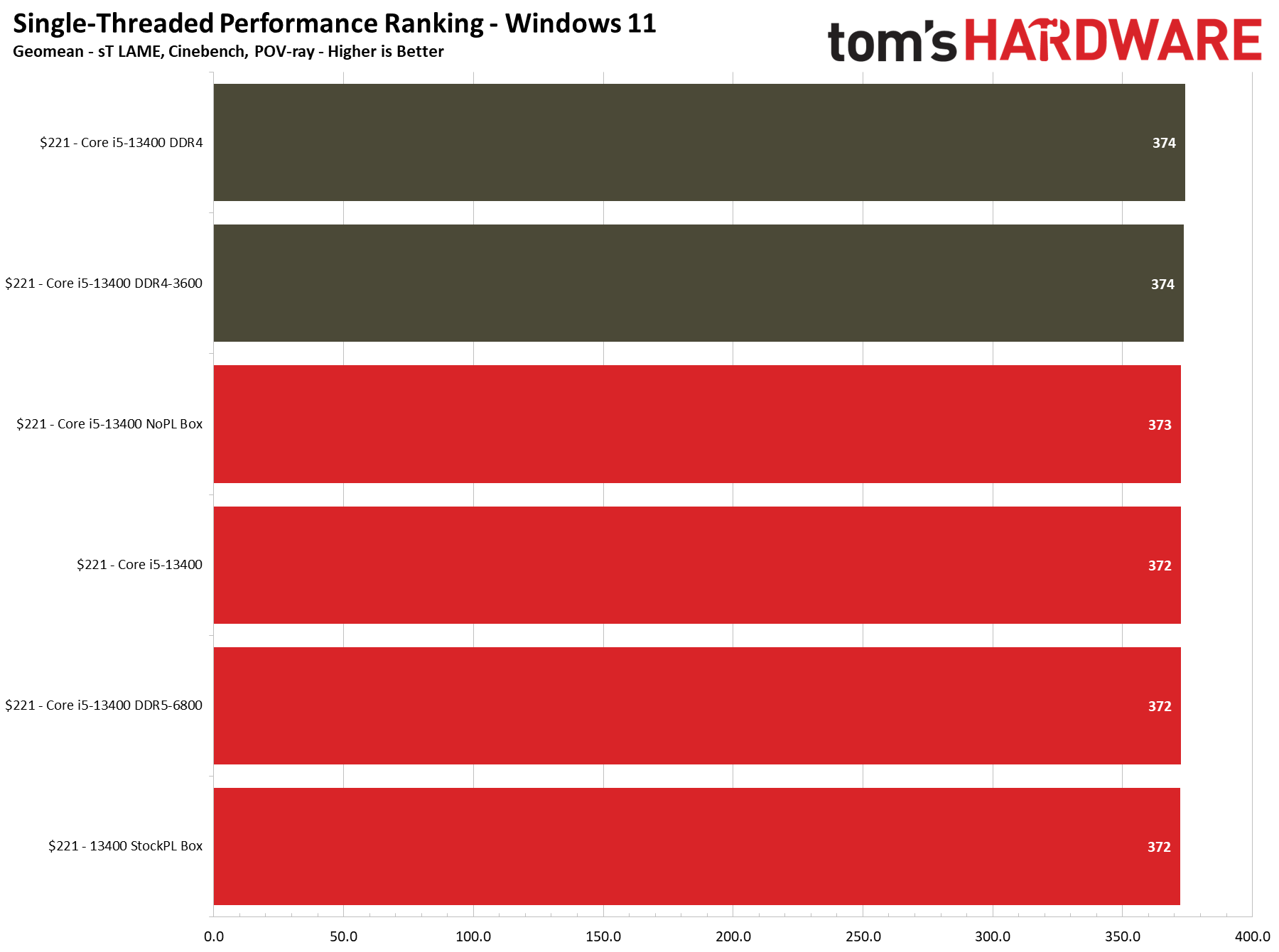
We can boil down productivity application performance into two broad categories: single- and multi-threaded. These slides show the geometric mean of performance in several of our most important tests in each category, but be sure to look at the expanded results below.
The Core i5-13400 with either DDR4 or DDR5 offers the same performance in our cumulative metrics for single- and multi-threaded work, though there will be certain applications that can take better advantage of DDR5's increased throughput. Conversely, some applications will prefer the lower latency of DDR4.
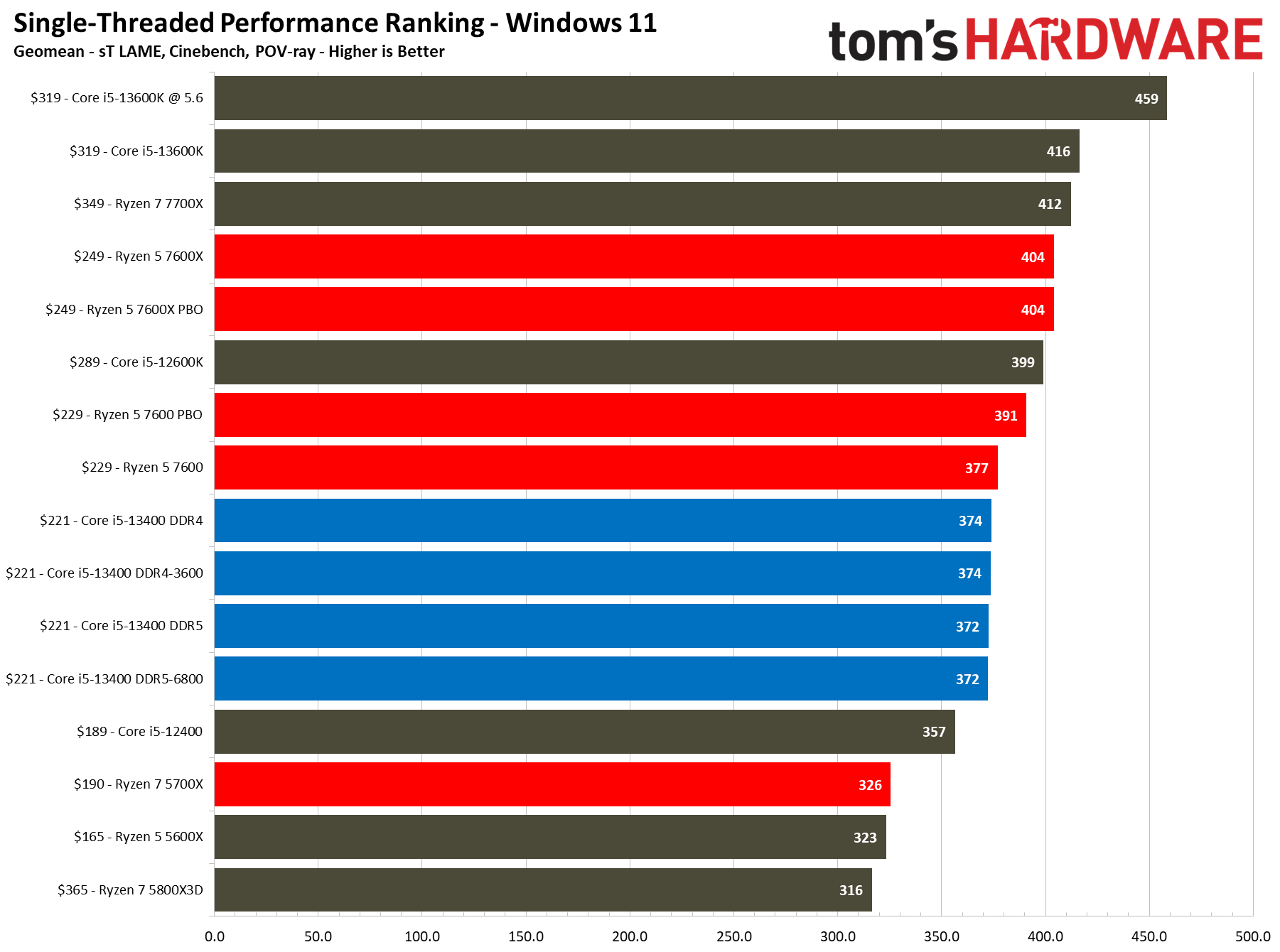
All configurations of the Core i5-13400 match the Ryzen 5 7600 in single-threaded work, but overclocking the 7600 gives it a 4.5% lead. Meanwhile, the Ryzen 5 7600X stretches its legs and leads by 8%, but that comes with a higher price tag.
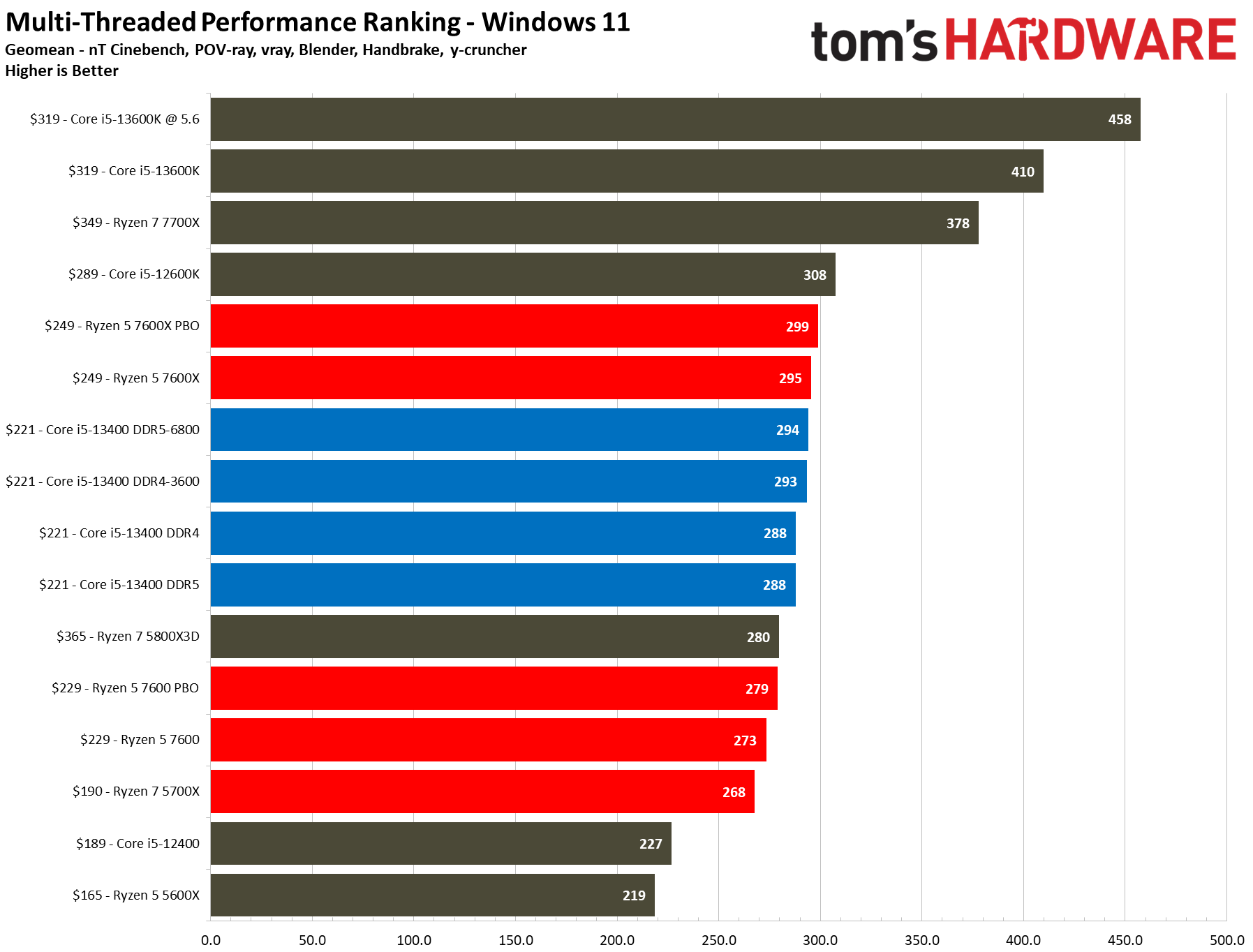
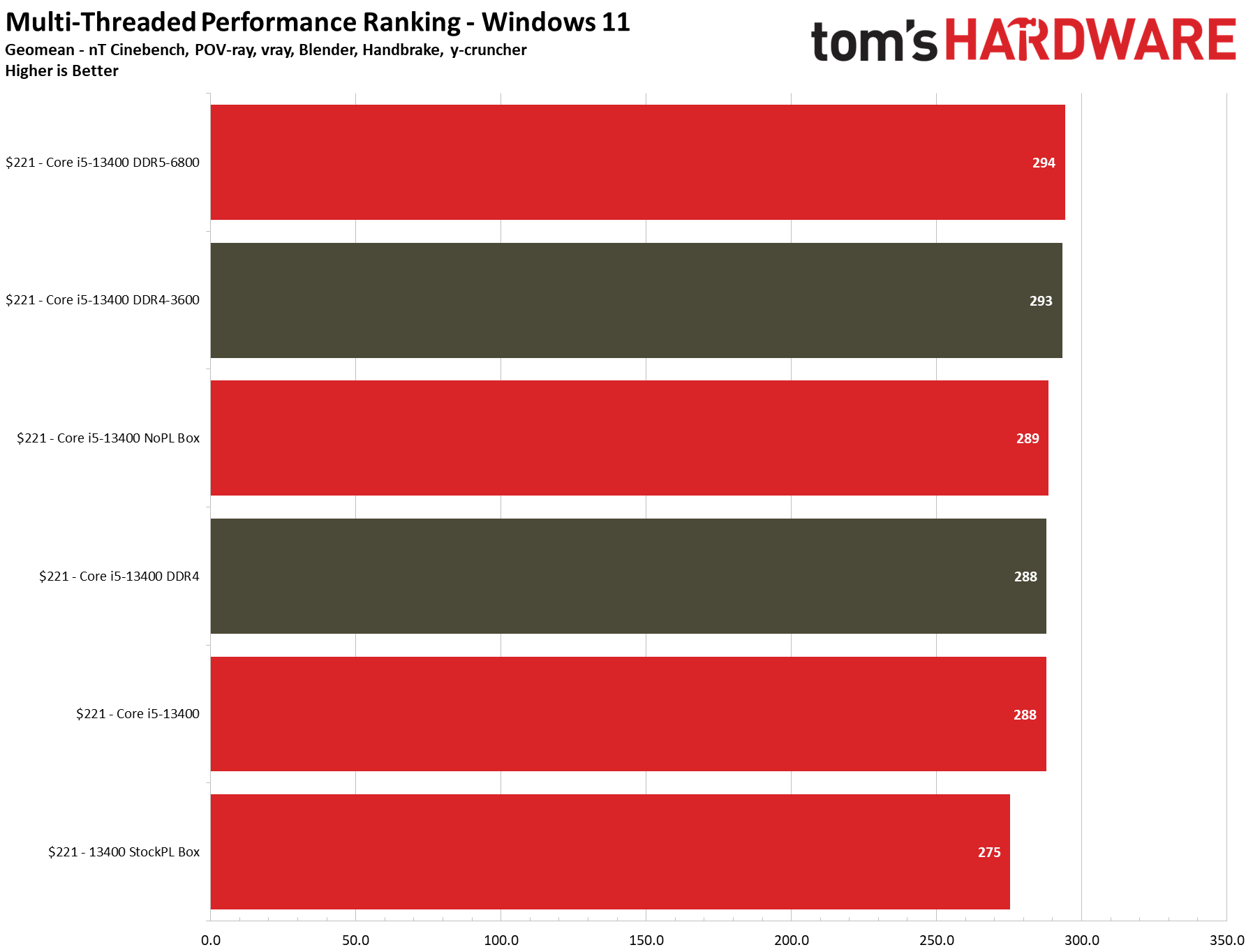
Turning to multi-threaded productivity applications, the 13400 with DDR4 and DDR5 is 5.5% faster than the Ryzen 5 7600 at stock settings and keeps a similar 5% lead after overclocking the 13400's memory and the Ryzen 5 7600. Meanwhile, the Ryzen 5 7600X is 2.5% faster than the Core i5-13400 in both stock and overclocked configs.
The Core i5-13400's e-cores deliver a solid 16% boost in threaded work and a 4% boost in single-threaded tasks over its predecessor, the Core i5-12400. However, the 13400's relatively tame clock speed improvements ensure that it doesn't beat the 12600K, which leads by 7% in both single- and multi-threaded applications.
We saw no decline in gaming performance or single-threaded apps with the 13400's bundled cooler when we limited the chip to the stock 65W/148W power limits, but we did see a difference in multi-threaded applications — the chip was 5% slower with the power limits and stock cooler than it was with the H115i 280mm water cooler.
However, removing the power limits while still using the boxed fan brought the performance in threaded apps back up to par with the watercooler. Naturally, there could be some long, extended rigorous workloads that might show more of a performance delta, but these will likely not have a meaningful impact on most users. Check our detailed benchmarks in the thermal section for more info.
| Tom's Hardware | Multi-Thread | Single-Thread |
| $699 — Core i9-13900KS | 100% | 100% |
| $319 - Core i5-13600K | 61.2% | 86.7% |
| $349 — Ryzen 7 7700X | 56.4% | 85.8% |
| $250 - Core i5-12600K | 45.9% | 83.1% |
| $249 - Ryzen 5 7600X / PBO | 44.1% / 44.6% | 84.1% / 84.1% |
| $221 - Core i5-13400 DDR4 / DDR4-3600 | 43.0% / 43.8% | 77.9% / 77.8% |
| $221 - Core i5-13400 DDR5 / DDR5-6800 | 42.9% / 43.0% | 77.5% / 77.5% |
| $365 — Ryzen 7 5800X3D | 41.7% | 65.9% |
| $229 - Ryzen 5 7600 / PBO | 40.8% / 41.6% | 78.5% / 81.4% |
| $185 - Core i5-12400 | 33.8% | 74.2% |
Rendering Benchmarks on Intel Core i5-13400 and Core i5-13400F
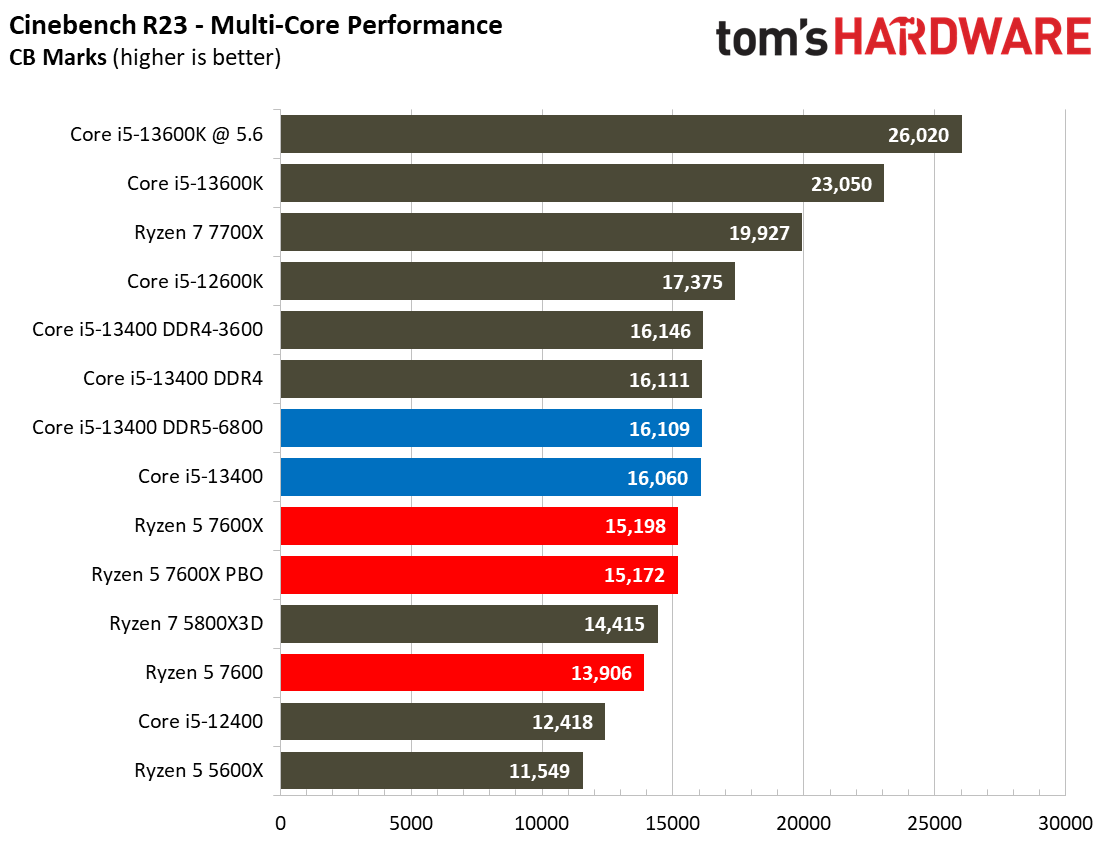
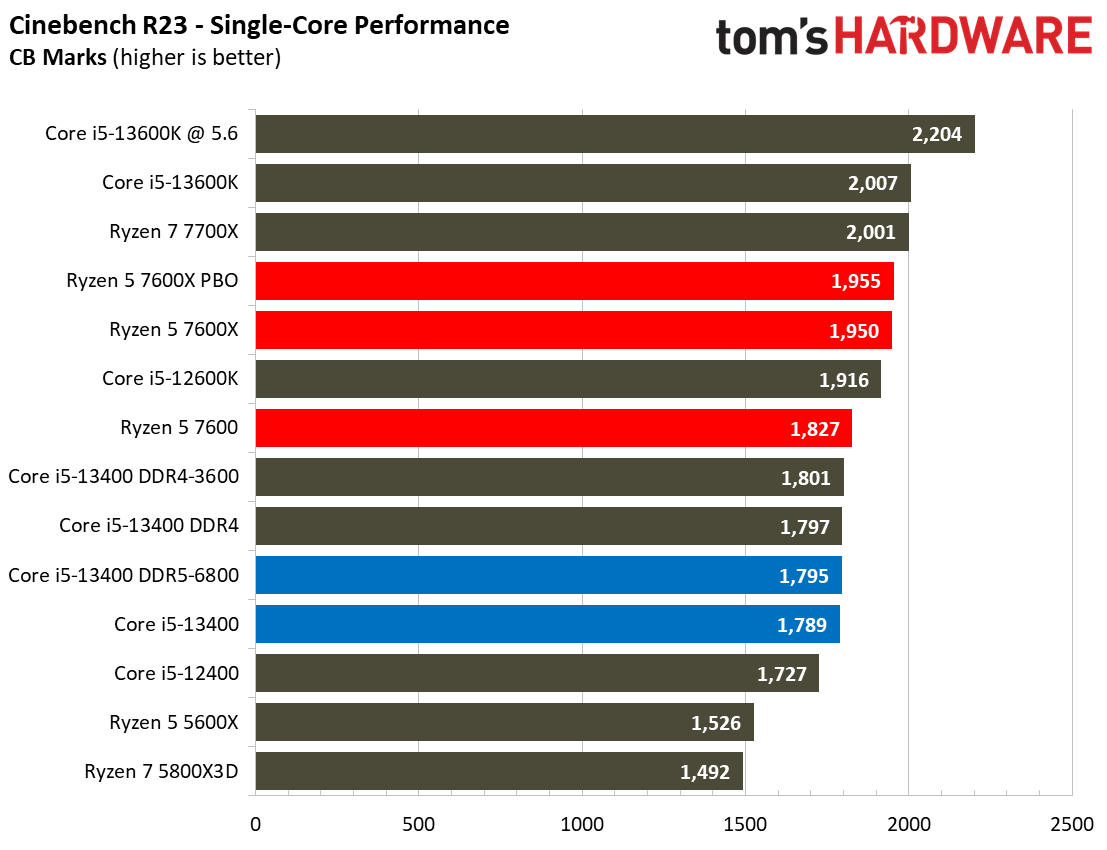
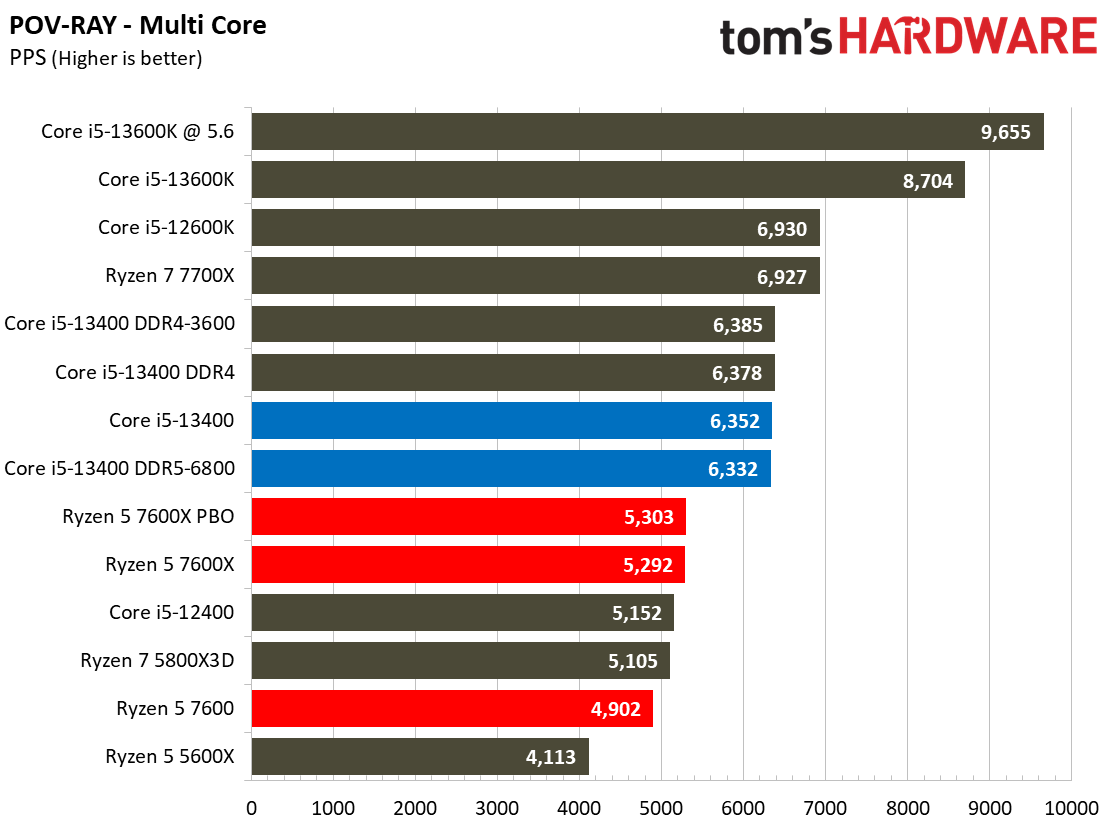
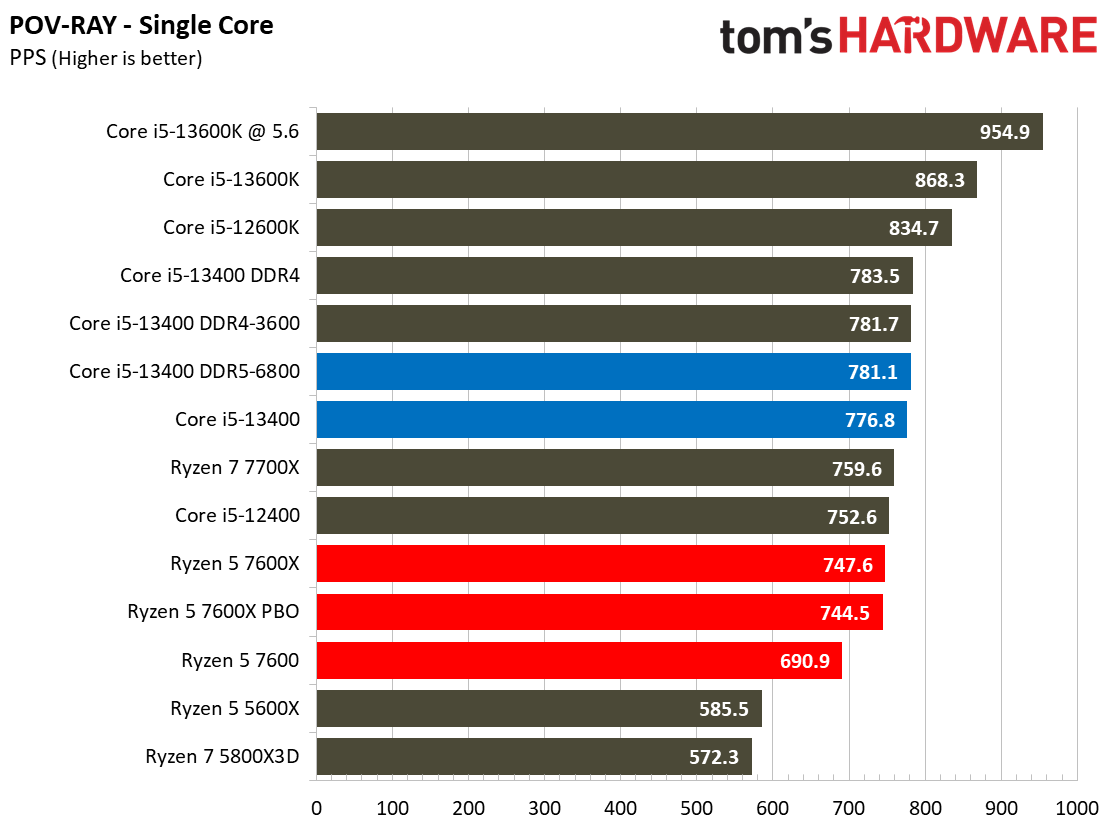
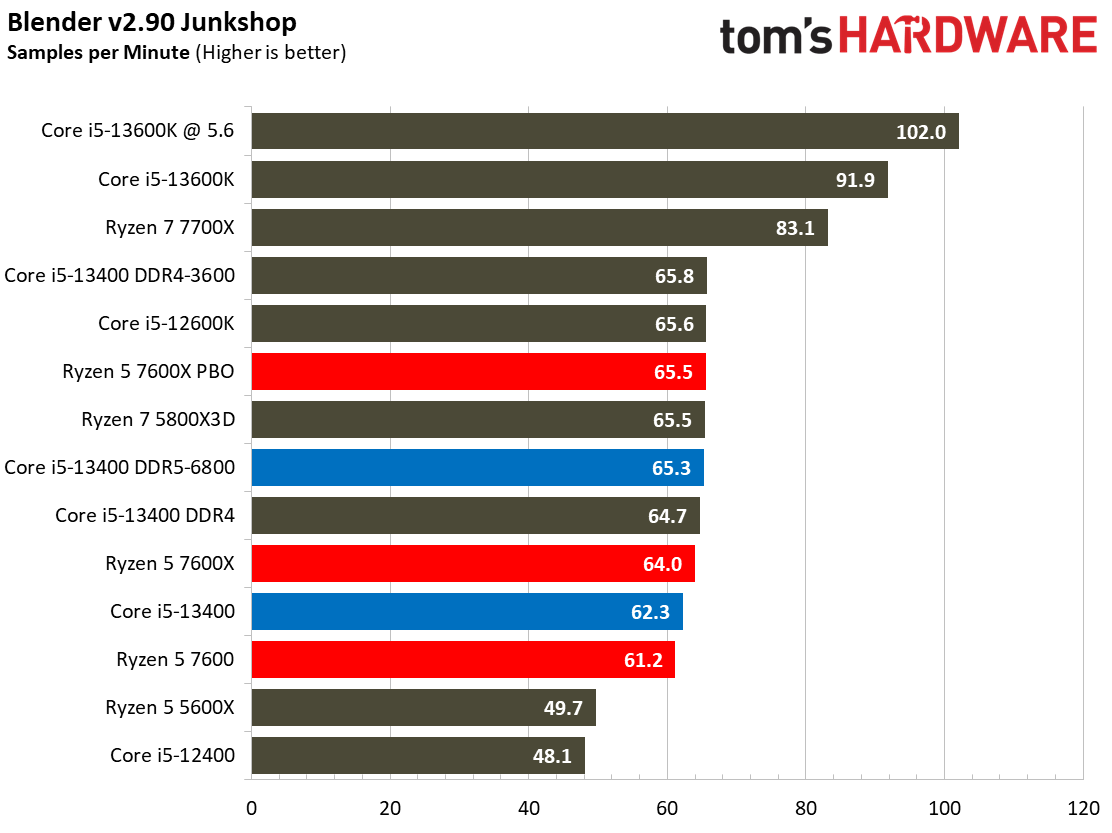
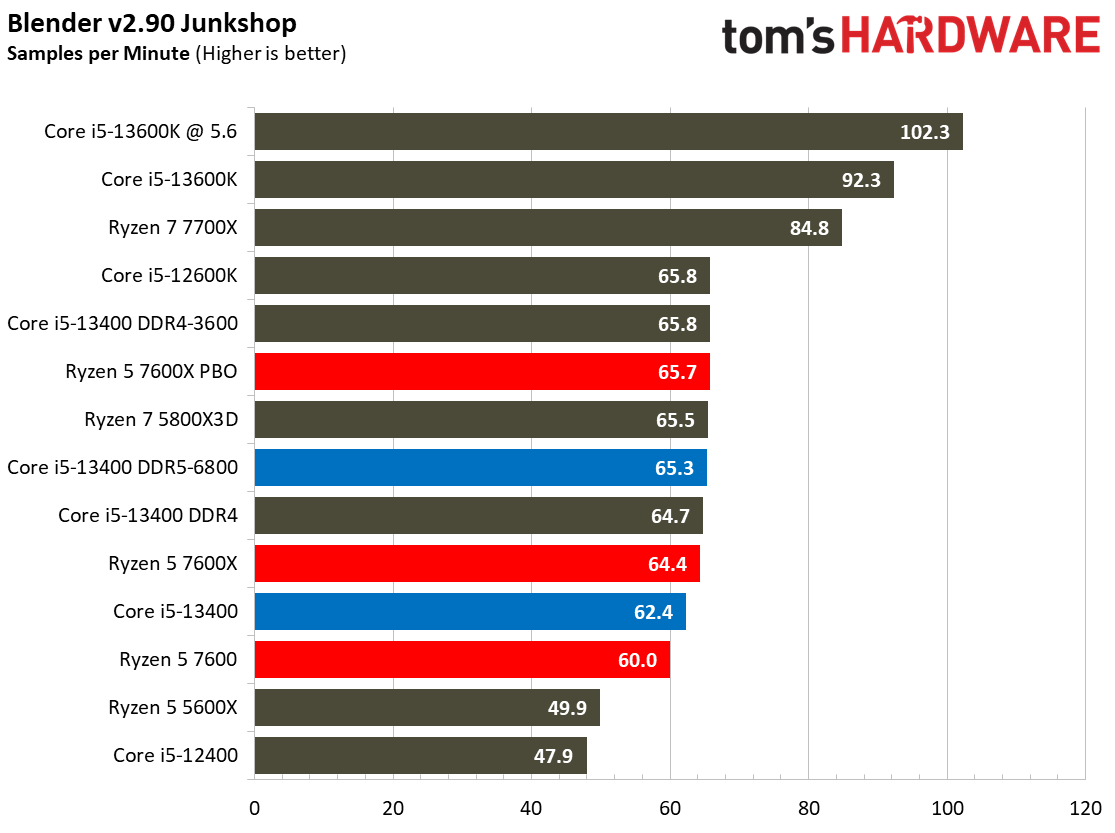
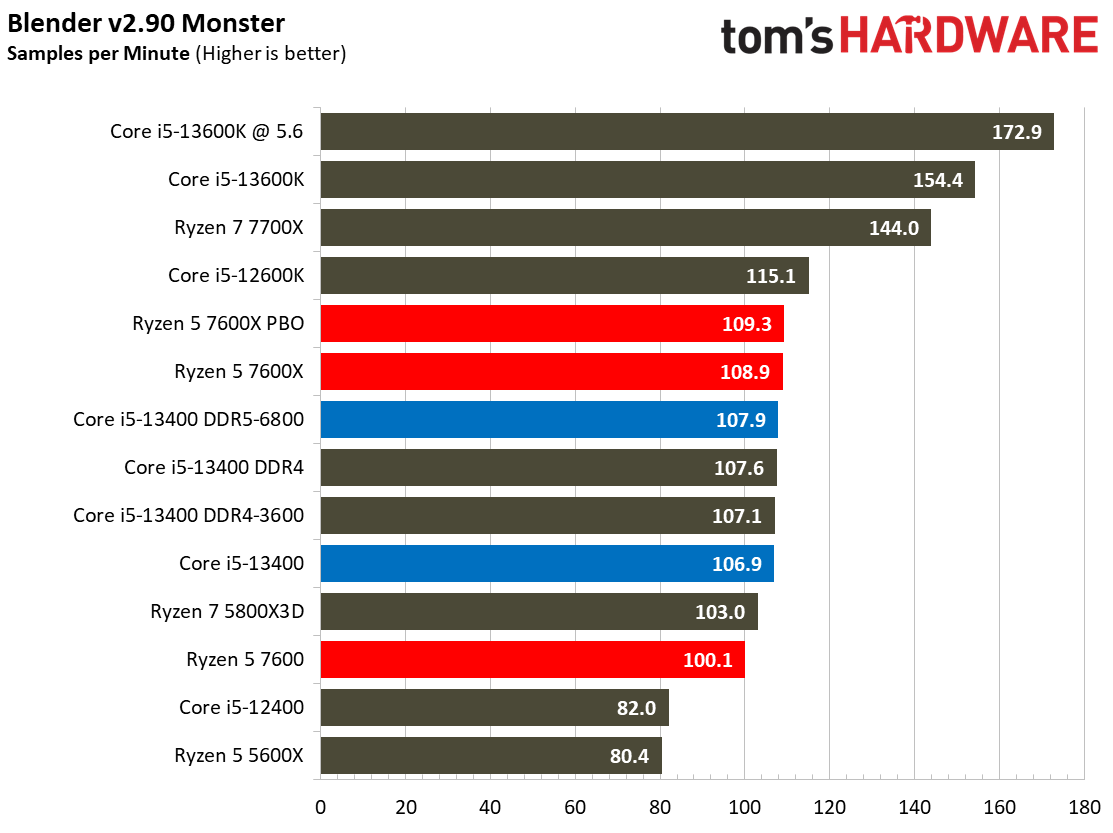
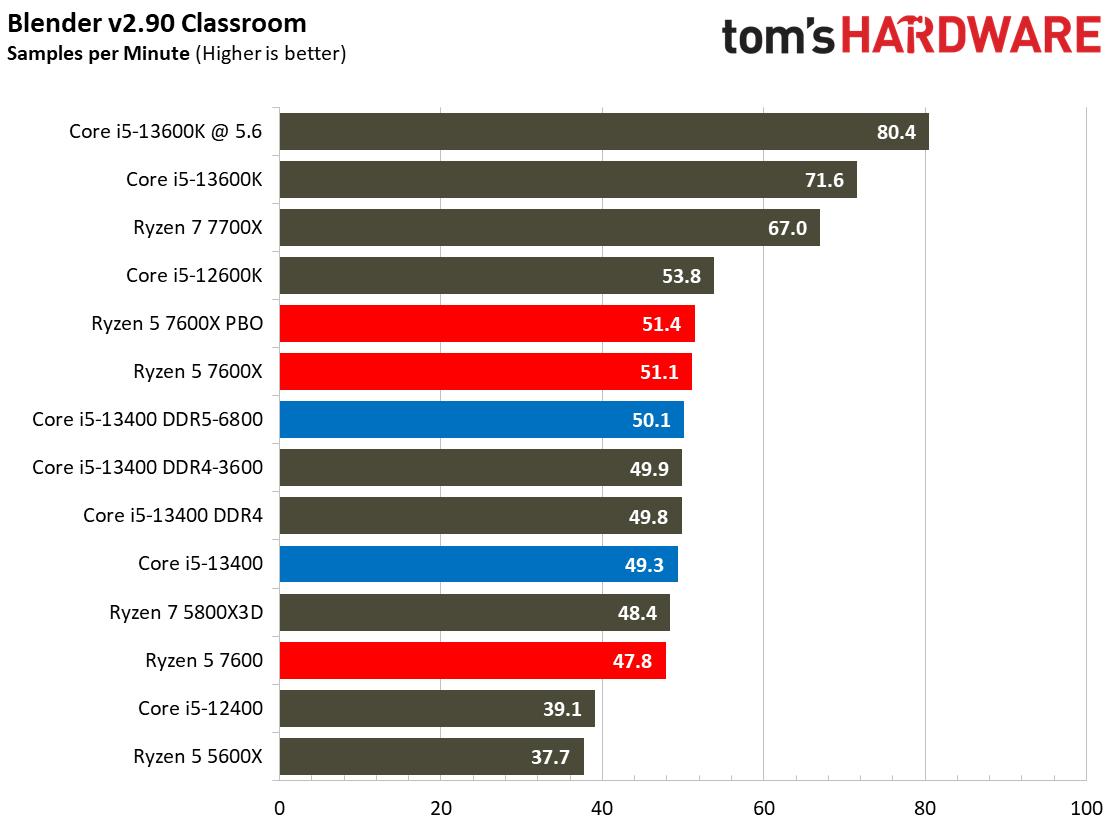
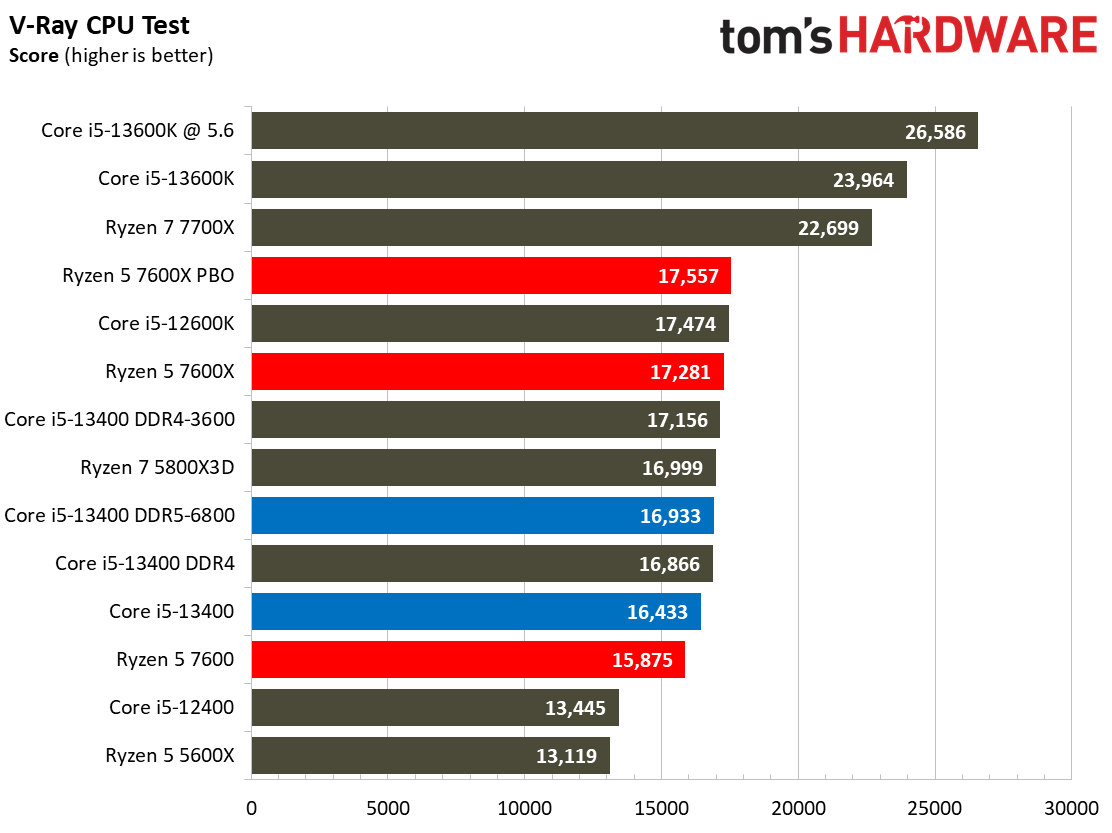
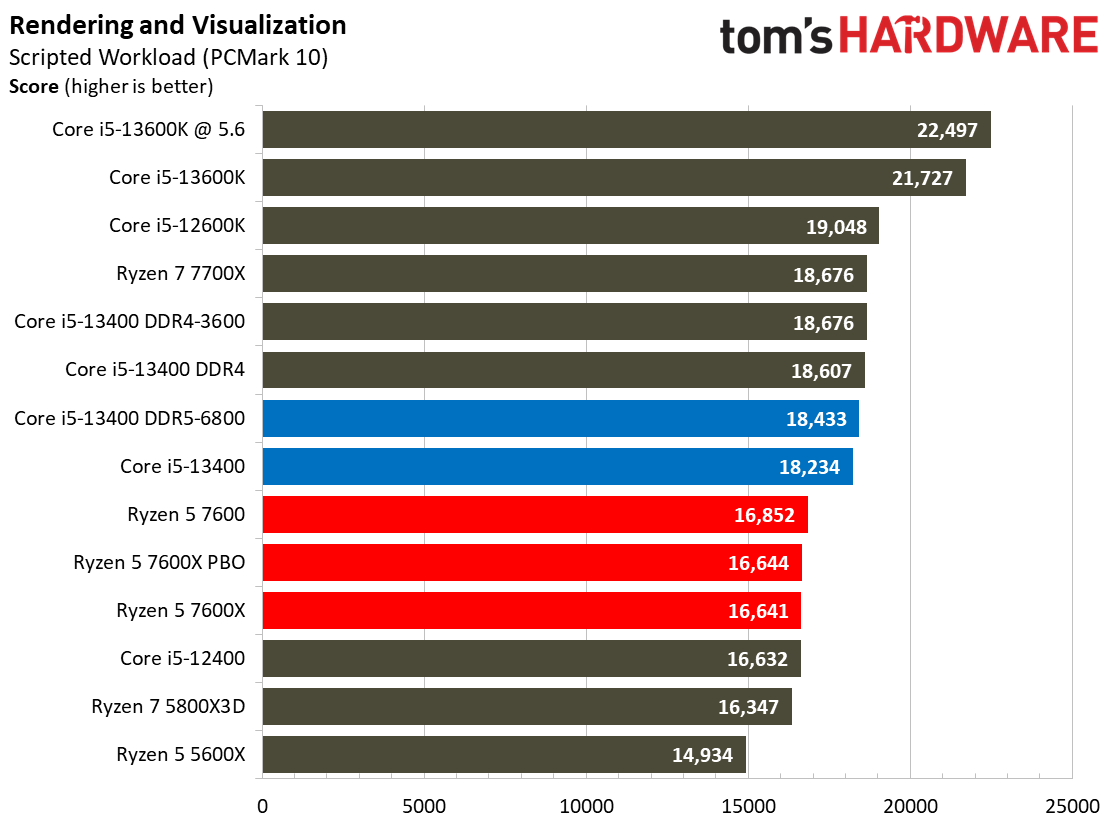
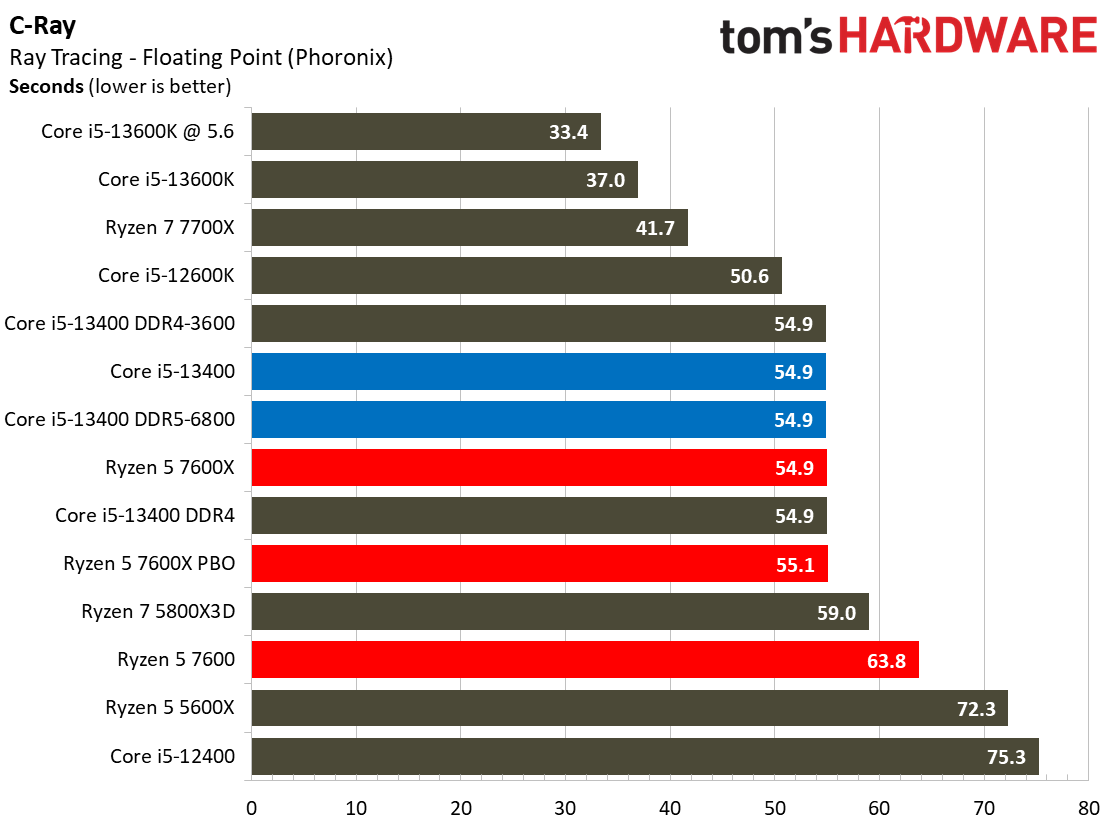
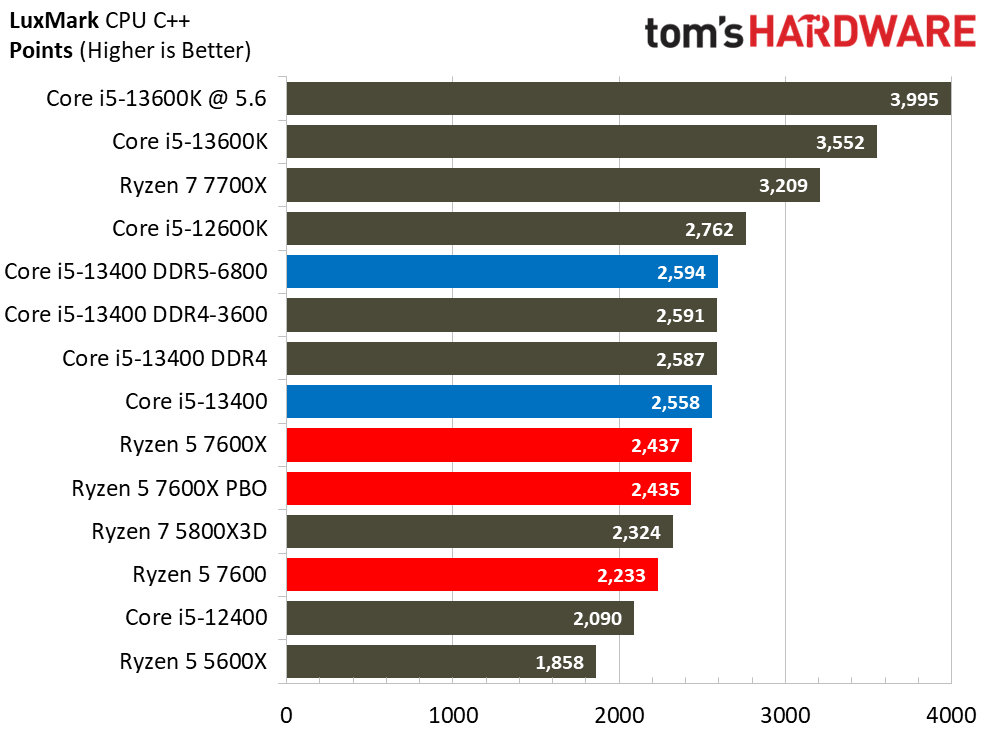
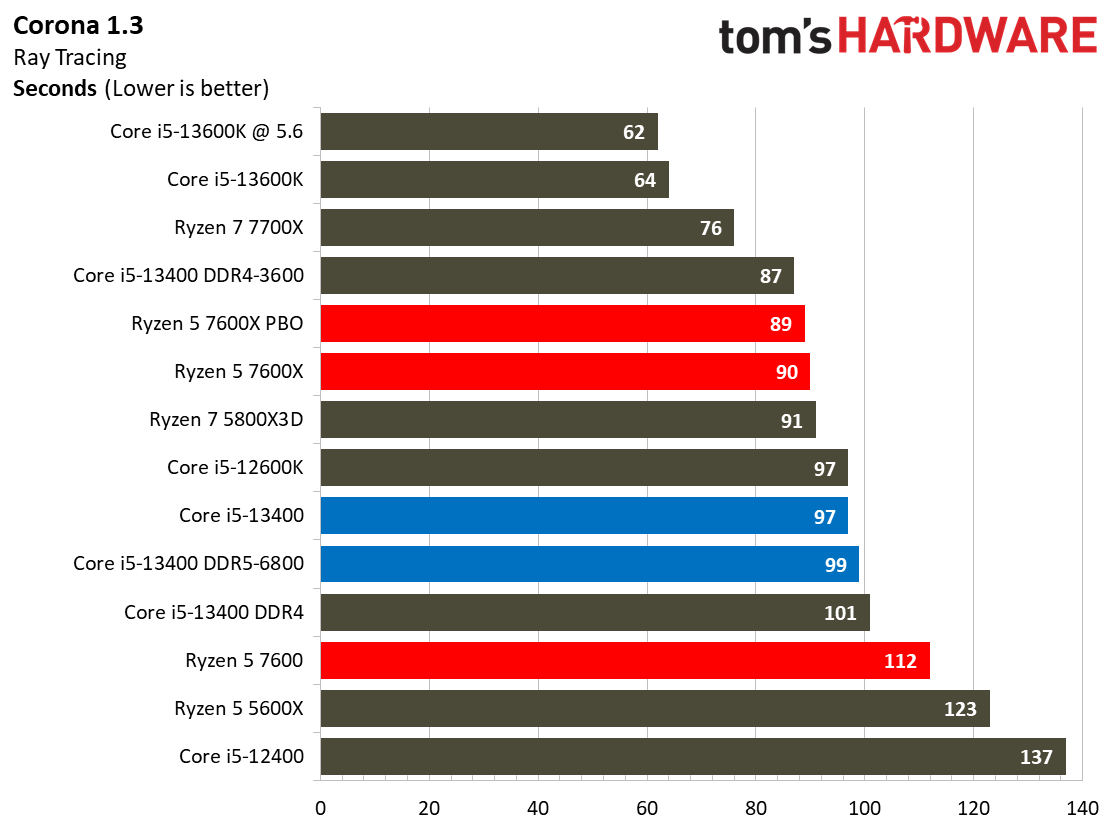
The Raptor Lake Core i5-13400 rivals or beats AMD's like-priced Ryzen 5 7600 in nearly all single- and multi-threaded rendering applications, with the single-threaded Cinebench R23 benchmark being the lone exception.
Encoding Benchmarks on Intel Core i5-13400 and Core i5-13400F
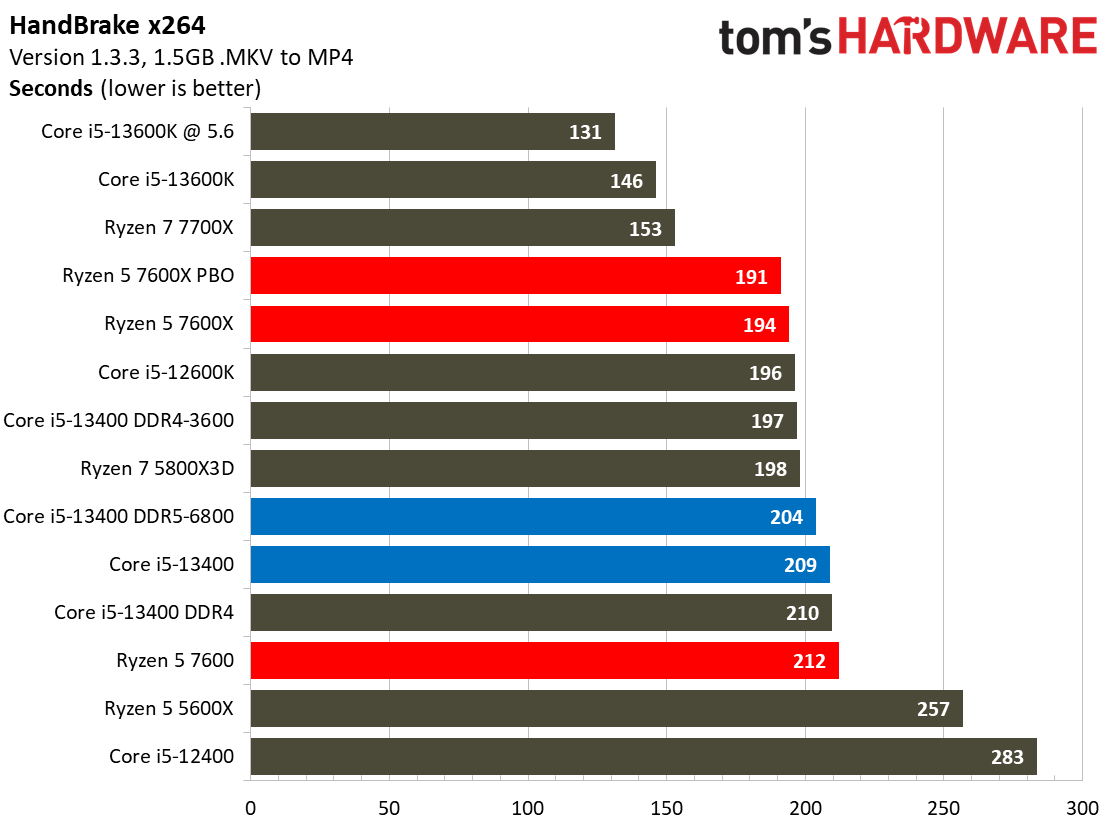
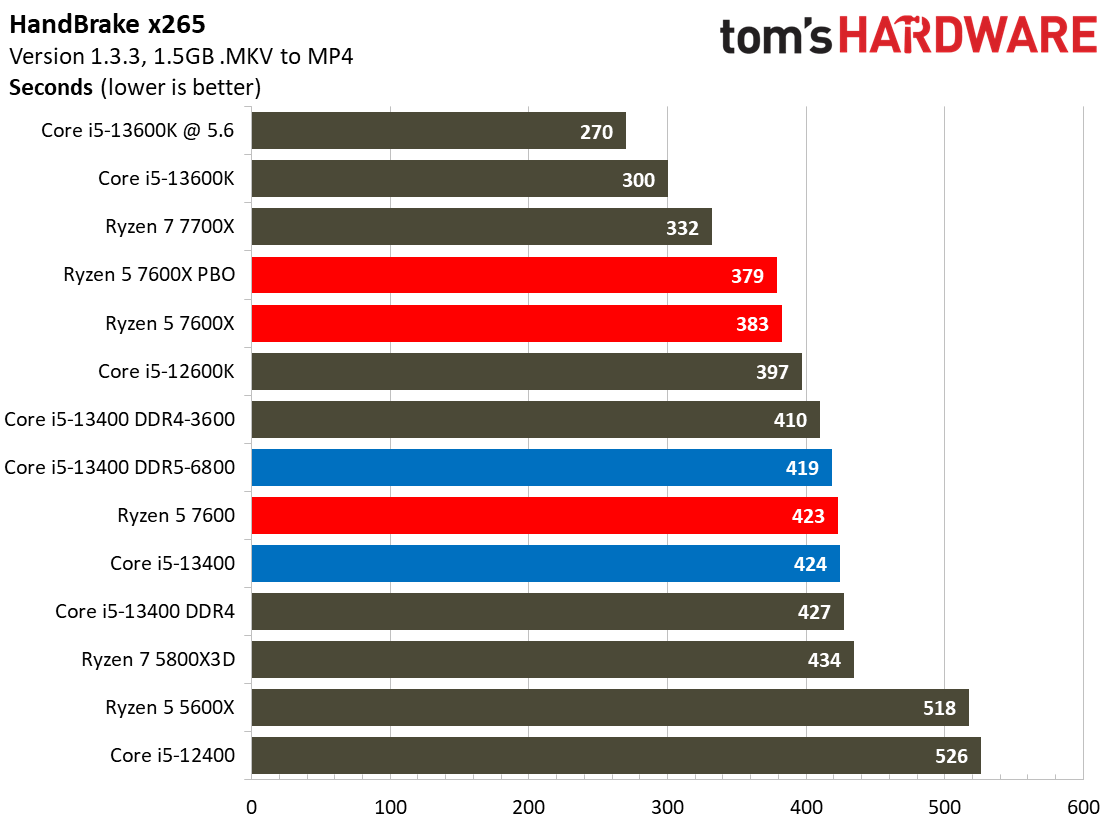
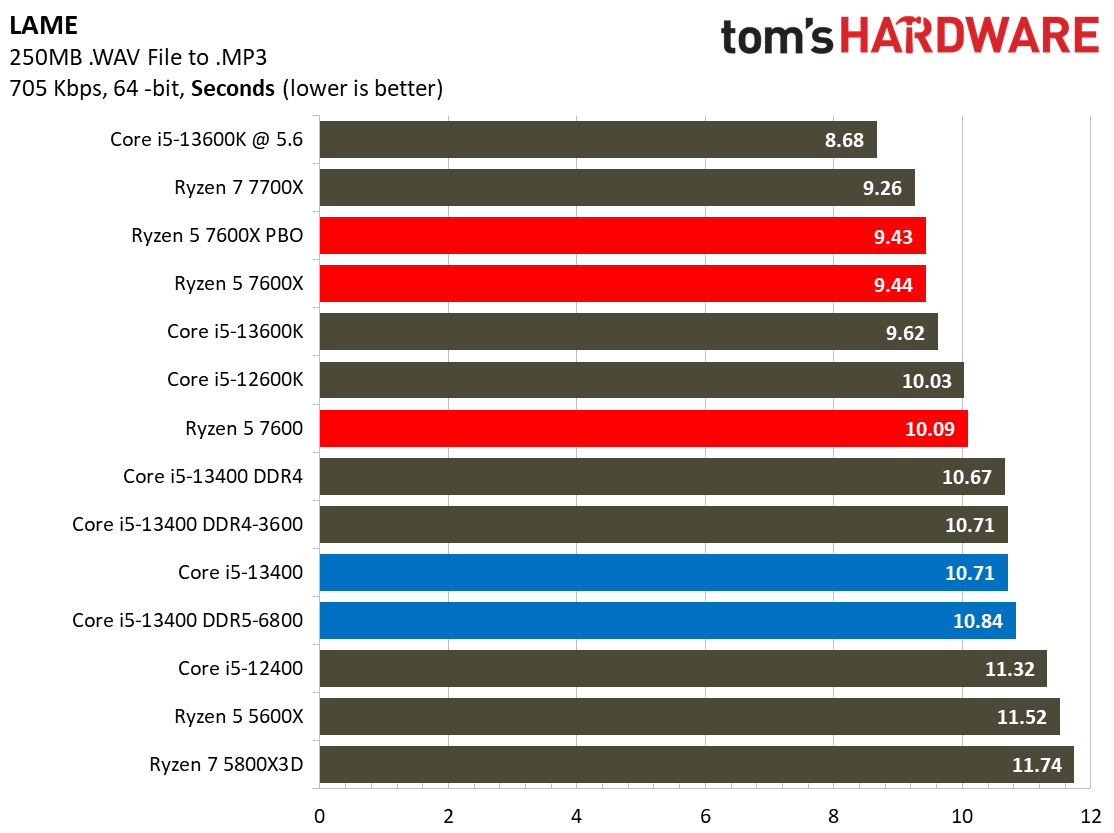
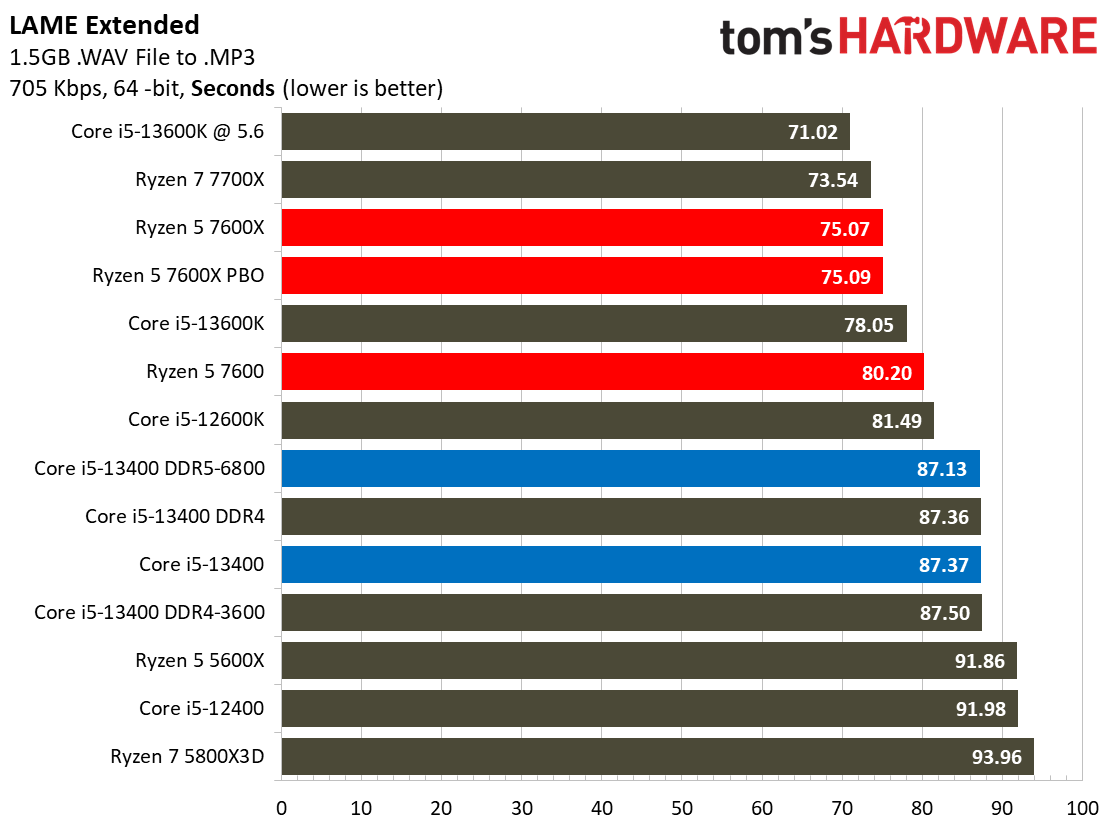
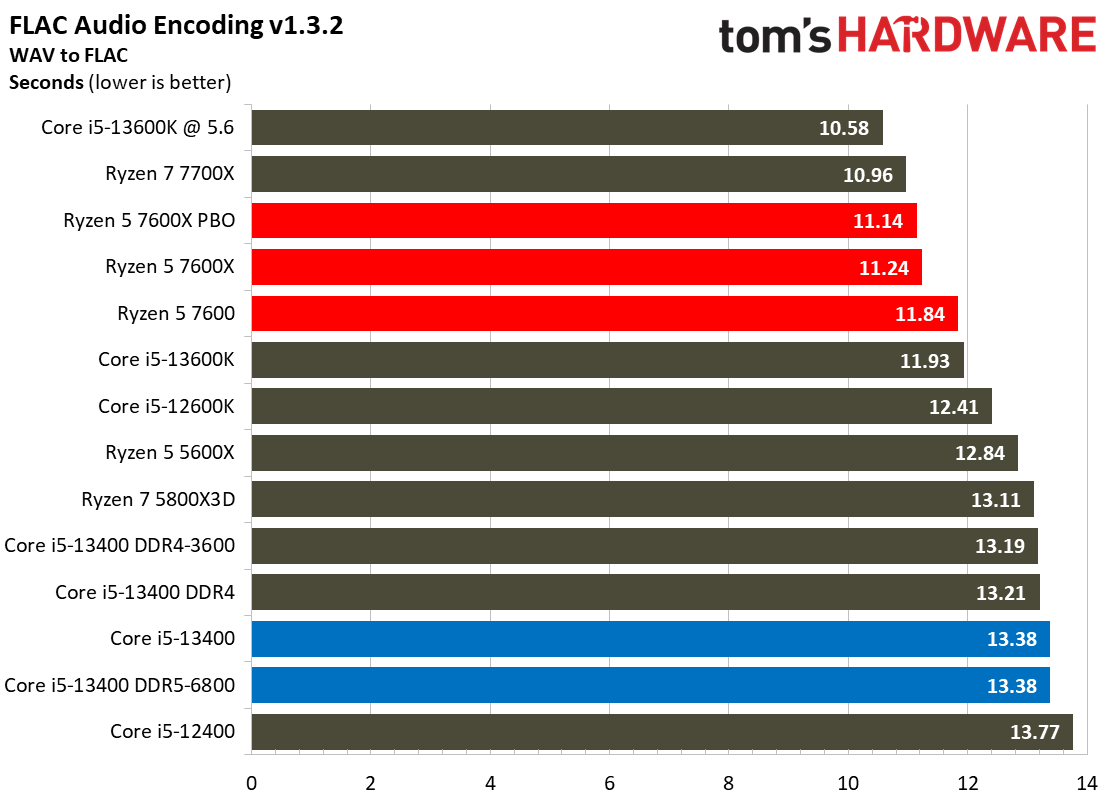
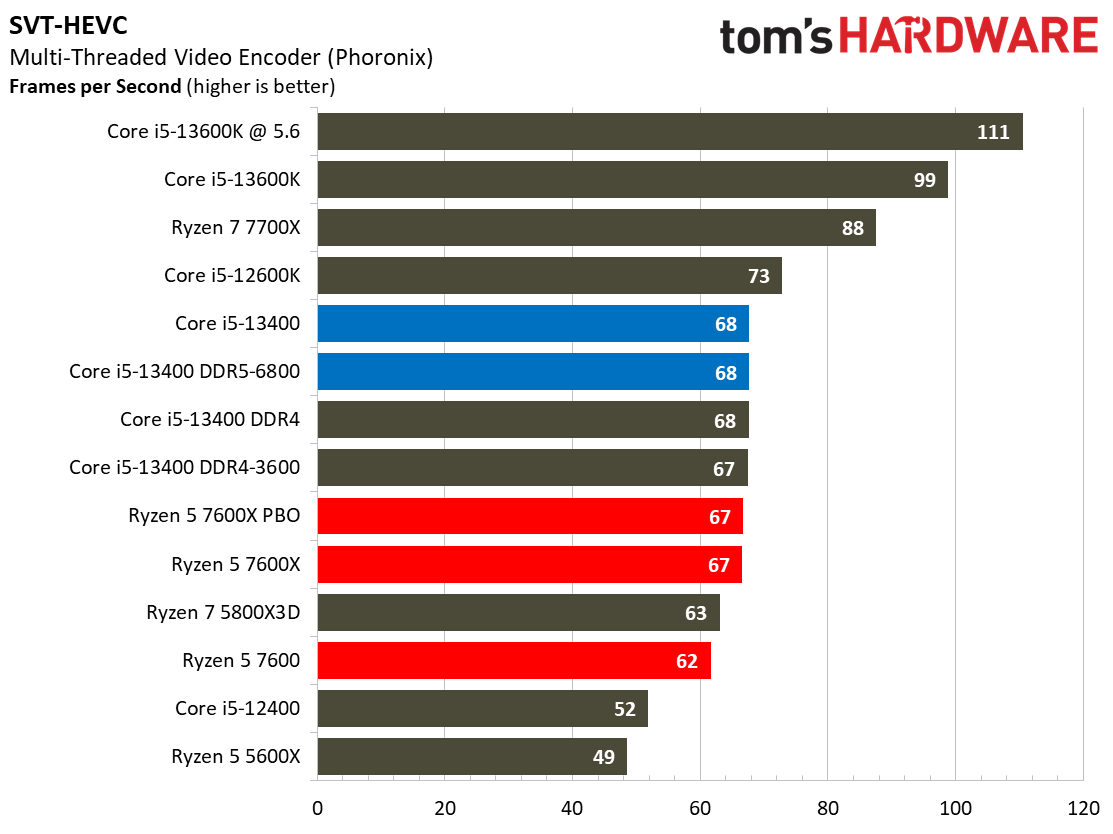
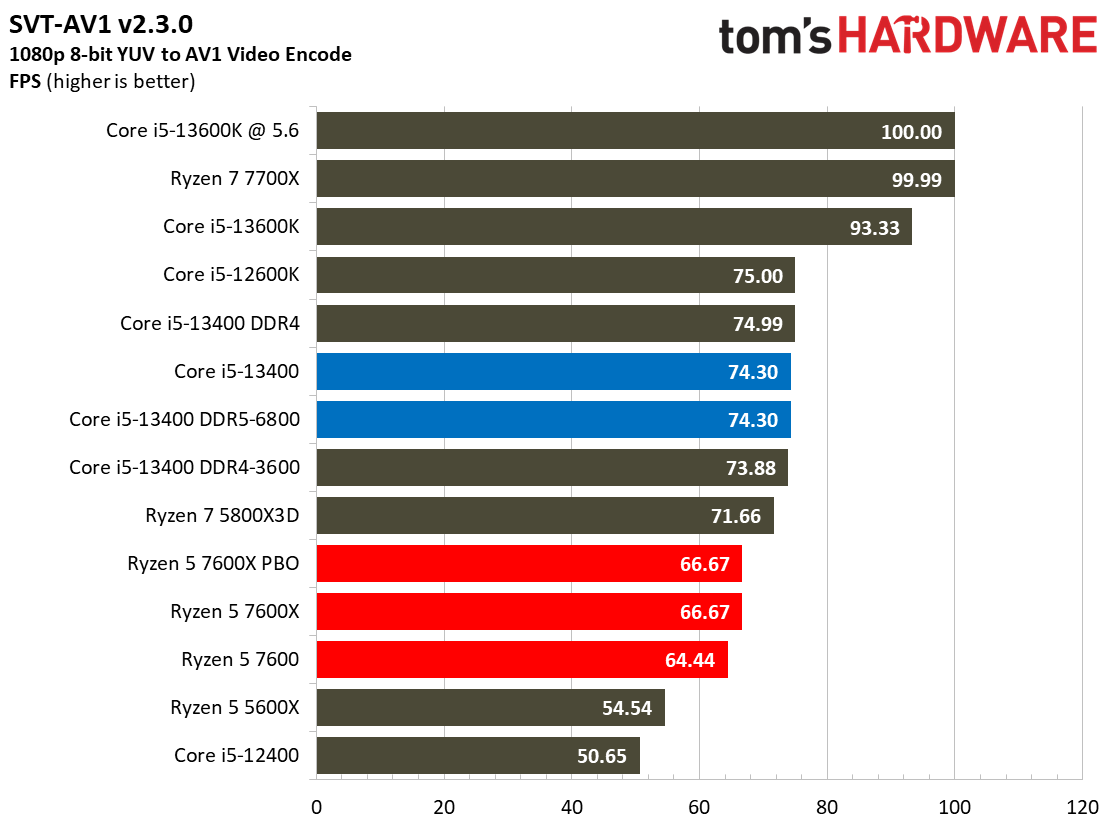
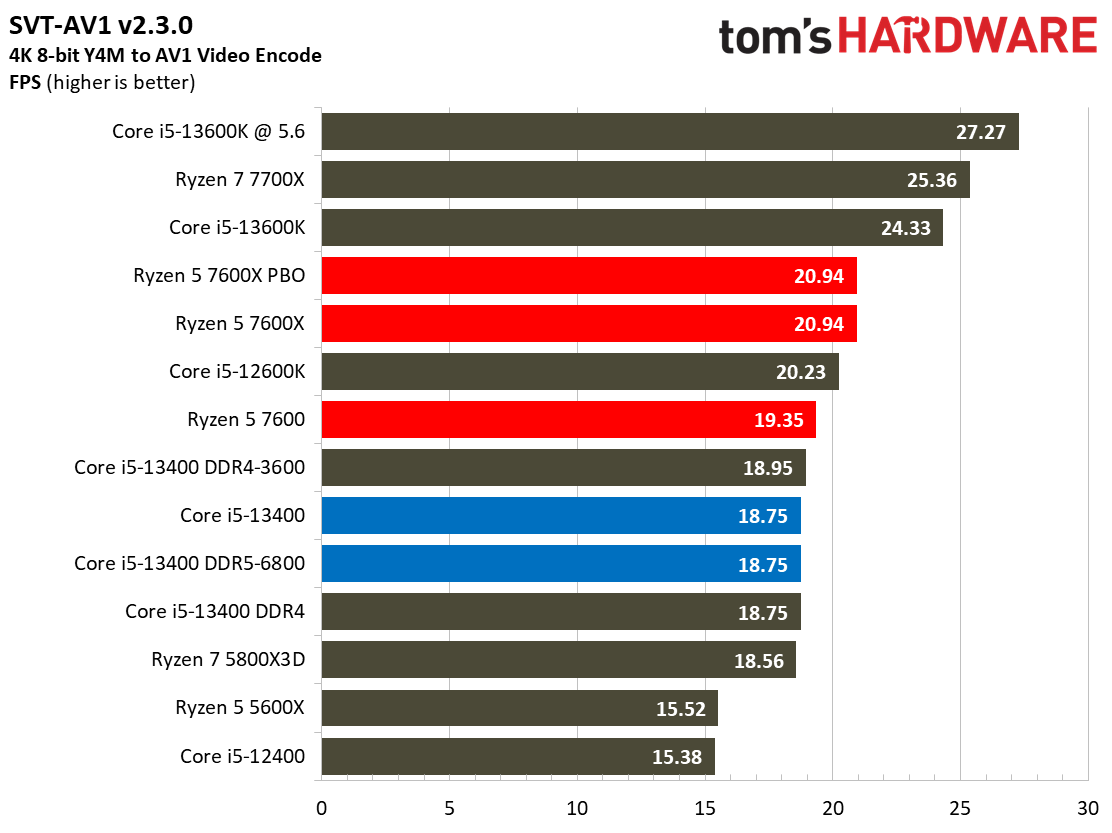
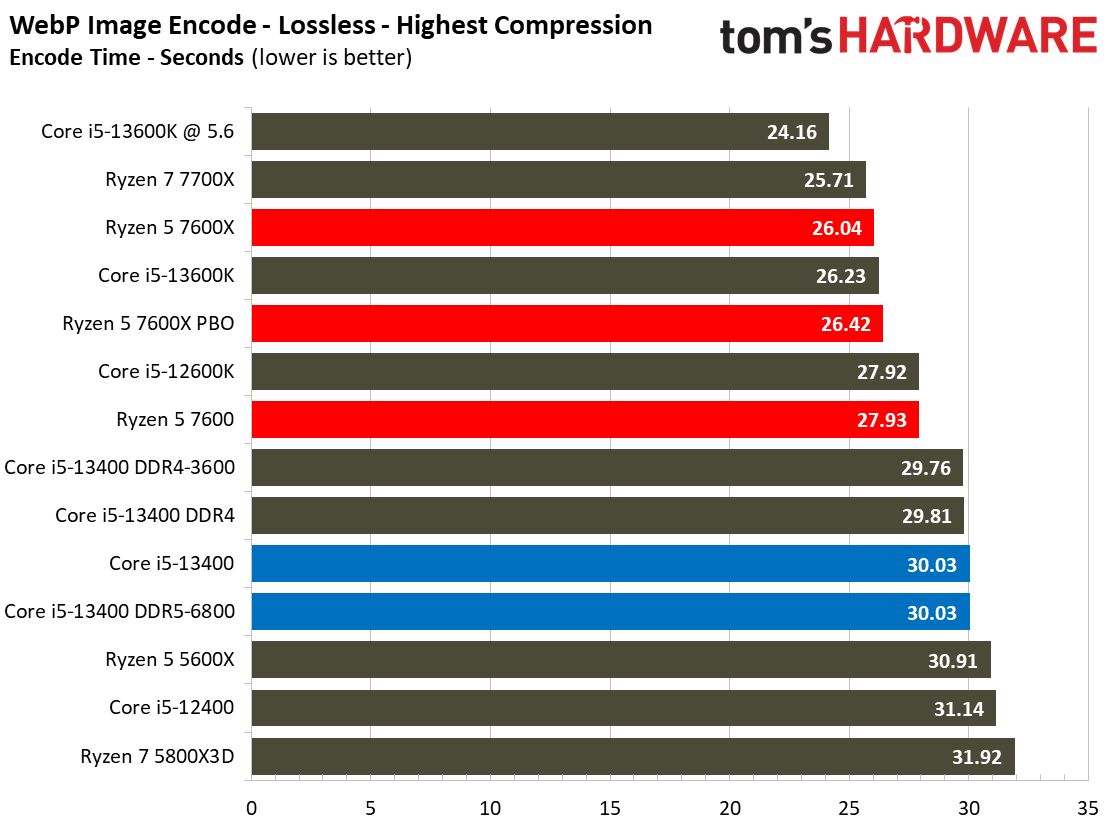
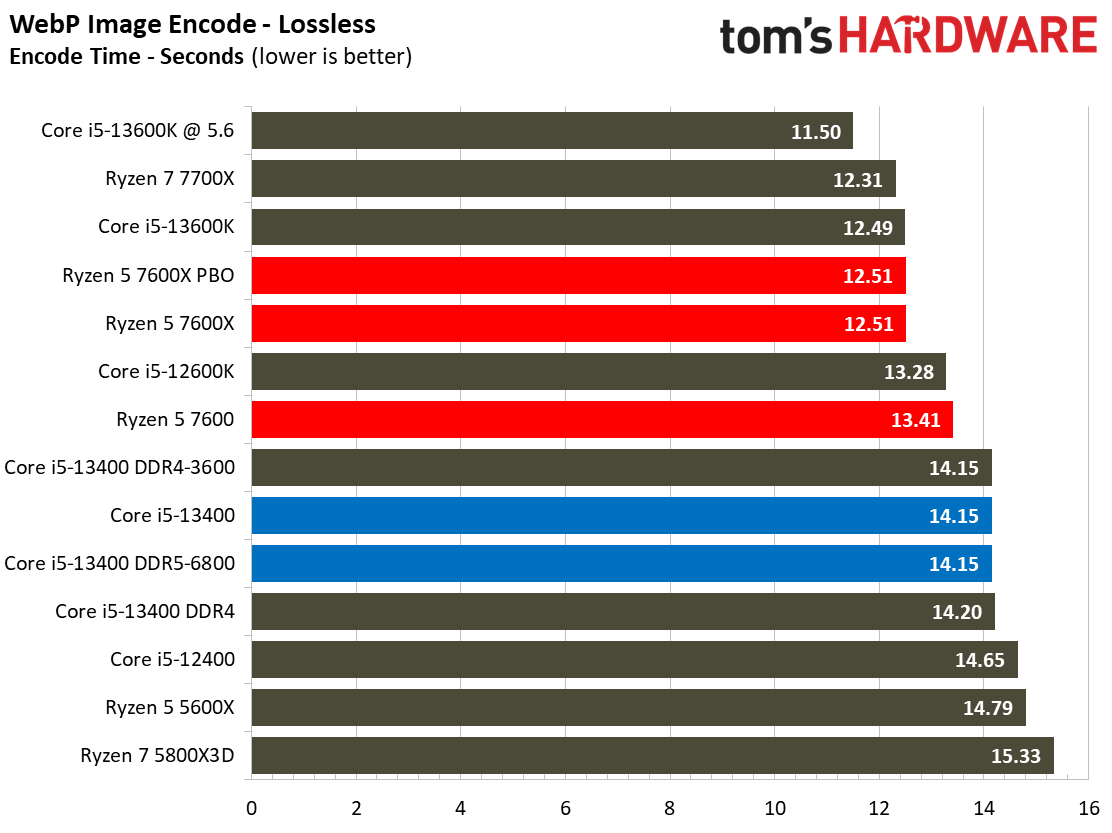
Most encoders tend to be either heavily threaded or almost exclusively single-threaded — it takes an agile chip to master both disciplines. Handbrake, SVT-HEVC, and SVT-AV1 serve as our threaded encoders, while LAME, FLAC, and WebP are indicative of how the chips handle lightly-threaded engines.
The Core i5-13400 navigates the threaded workloads well, but trails in many of the lightly-threaded encoders. Again, we have to take pricing into account, as the Ryzen competitors carry higher price tags.
Adobe, Web Browsing, Office, and Productivity on Intel Core i5-13400 and Core i5-13400F
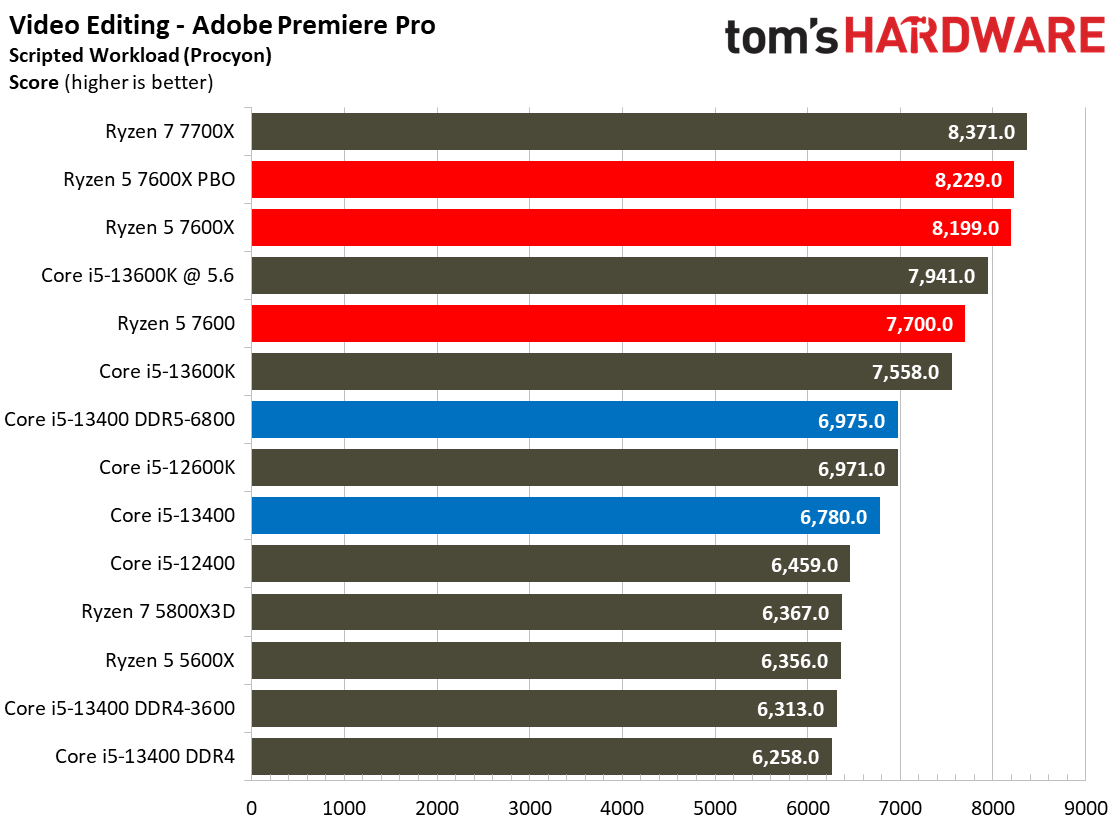
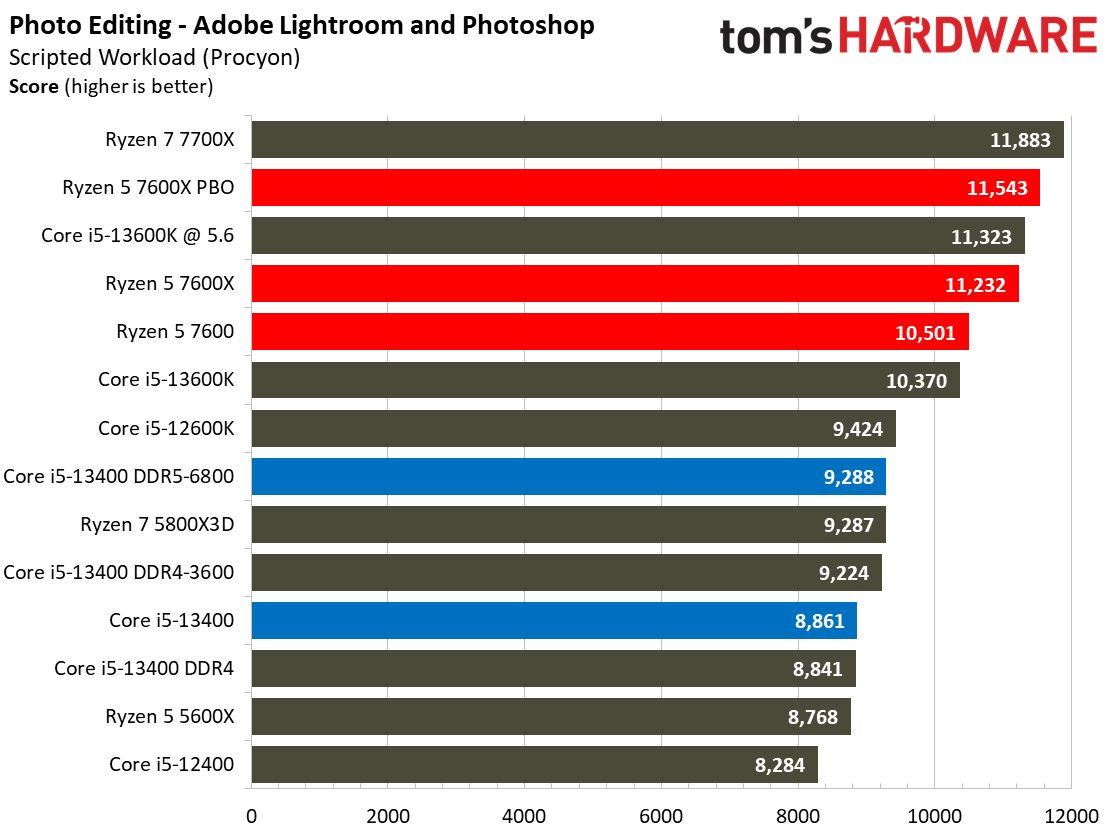
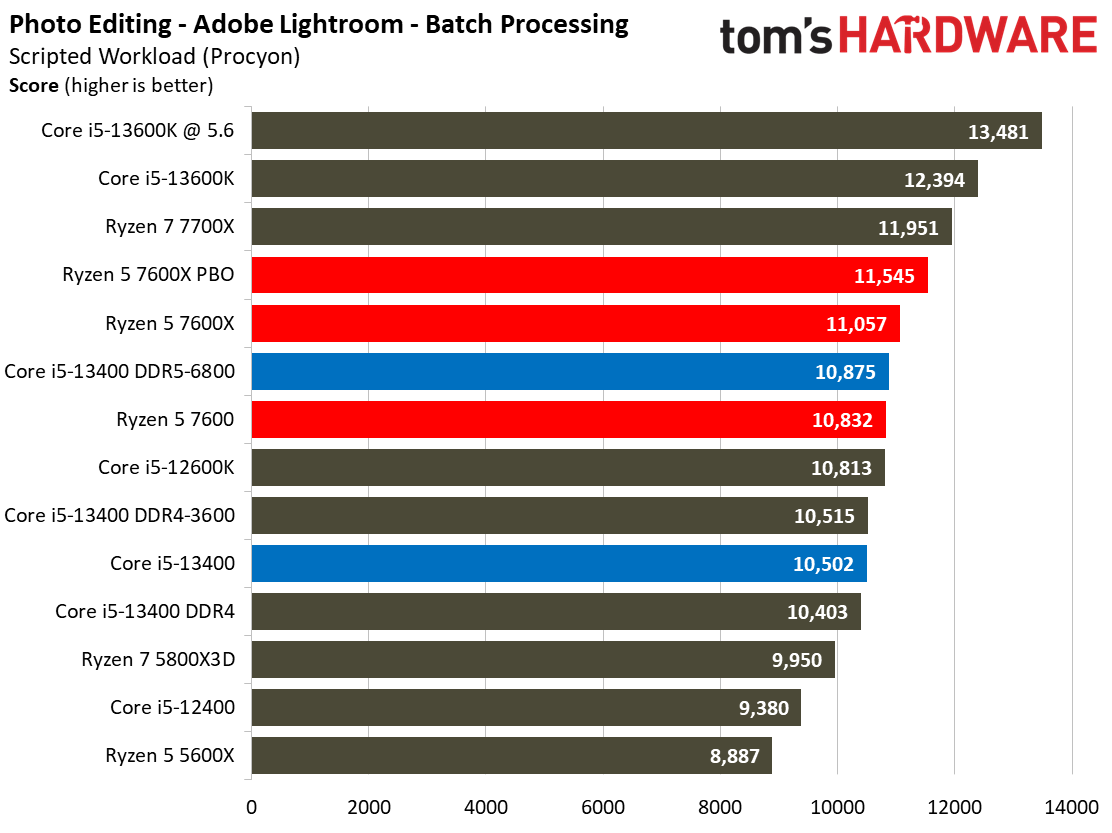
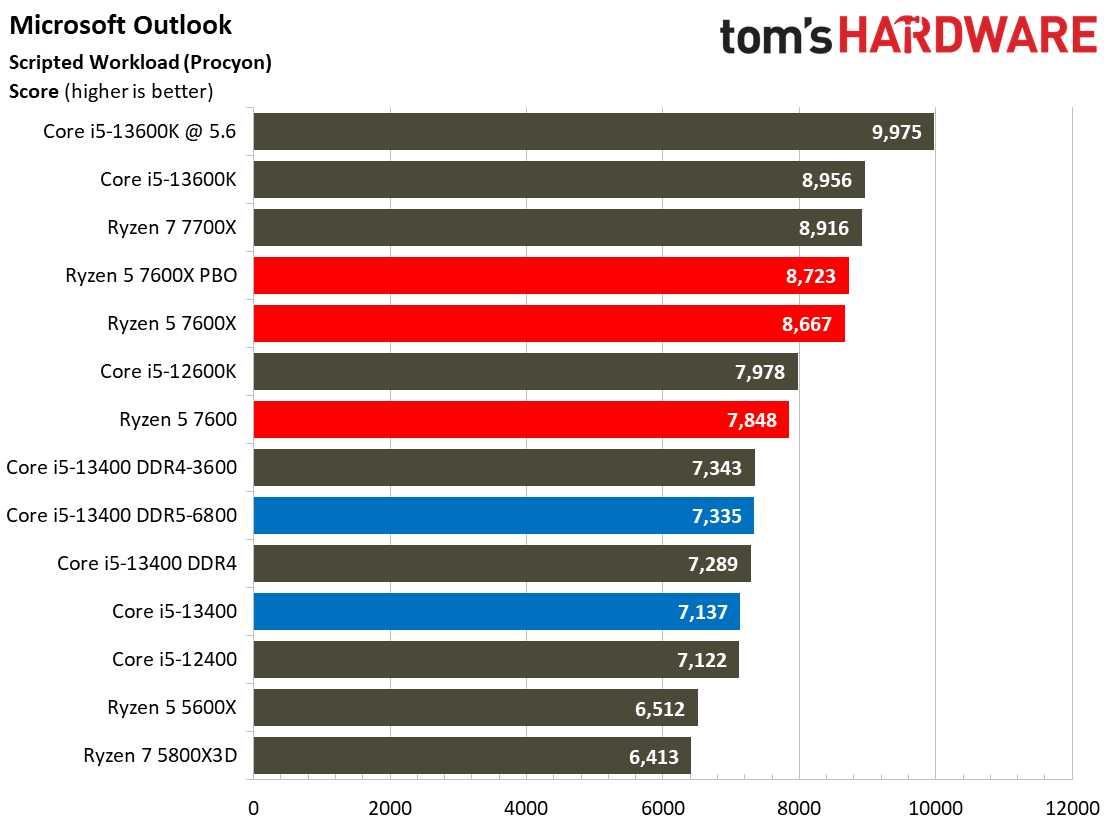
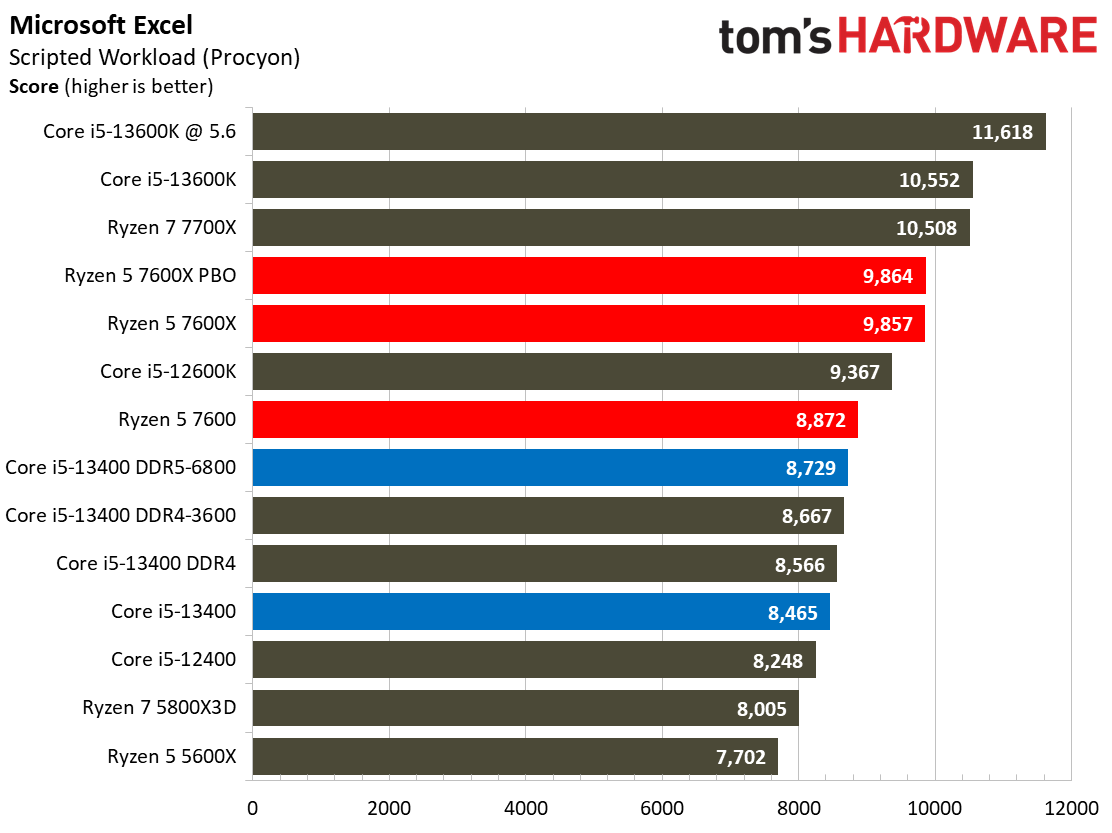
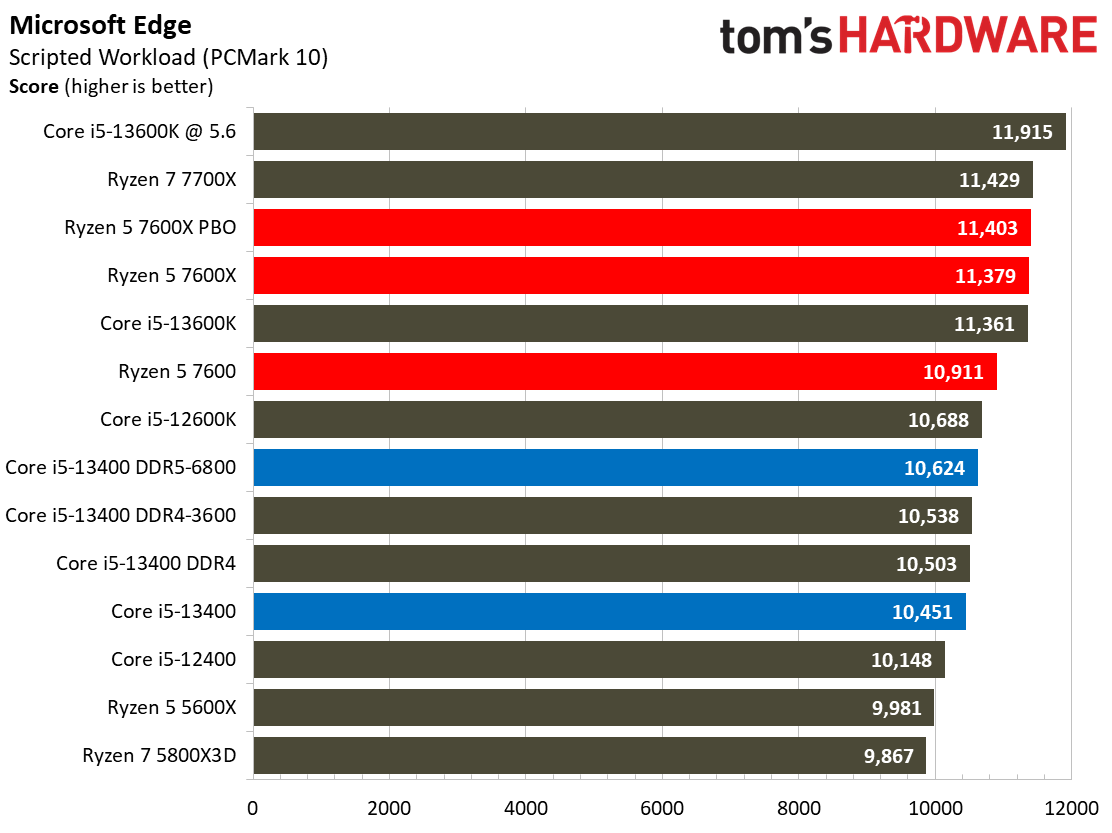
The Ryzen processors dominate in the Adobe and Office applications across the board.
Compilation, Compression, AI Chess Engines, AVX-512 Performance on Intel Core i5-13400 and Core i5-13400F
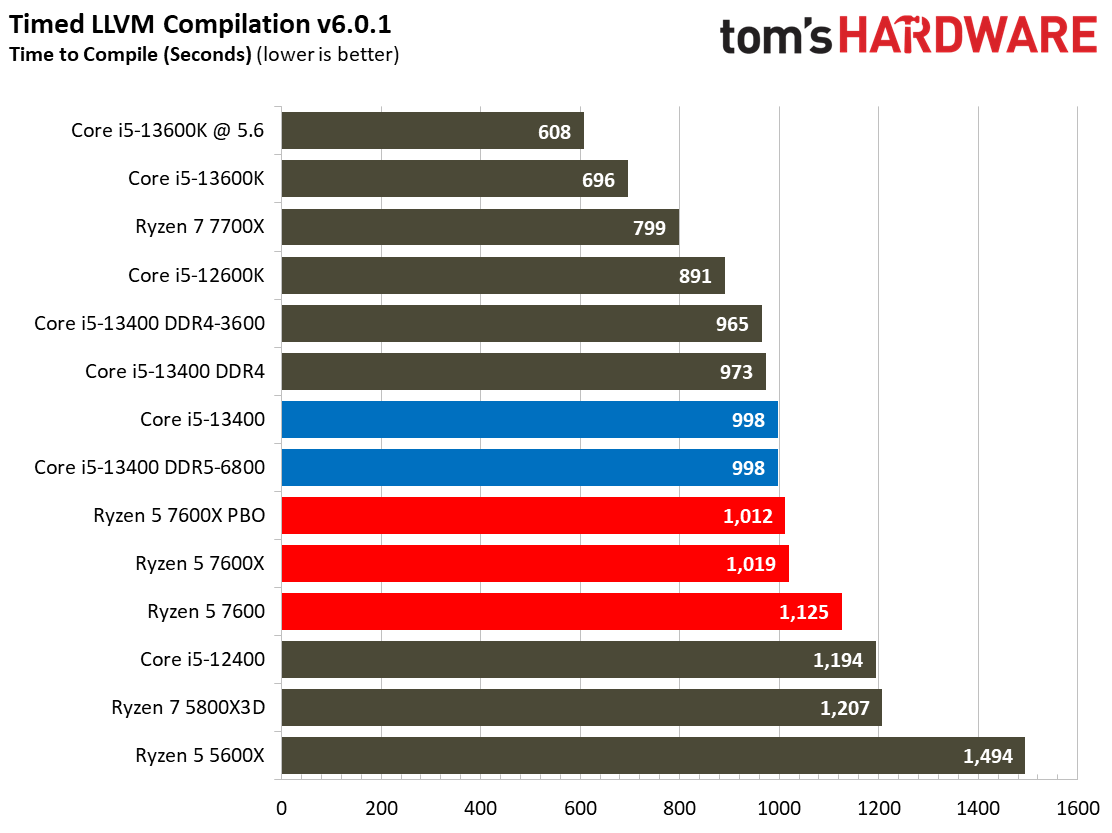
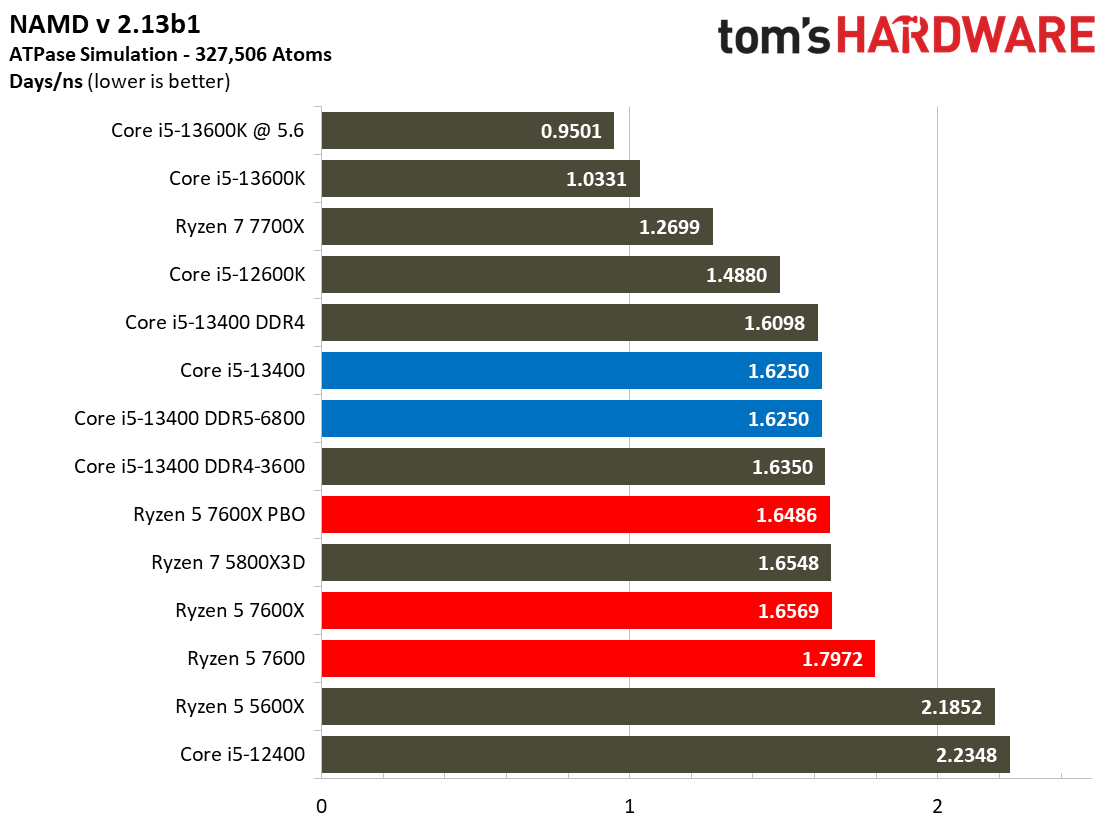
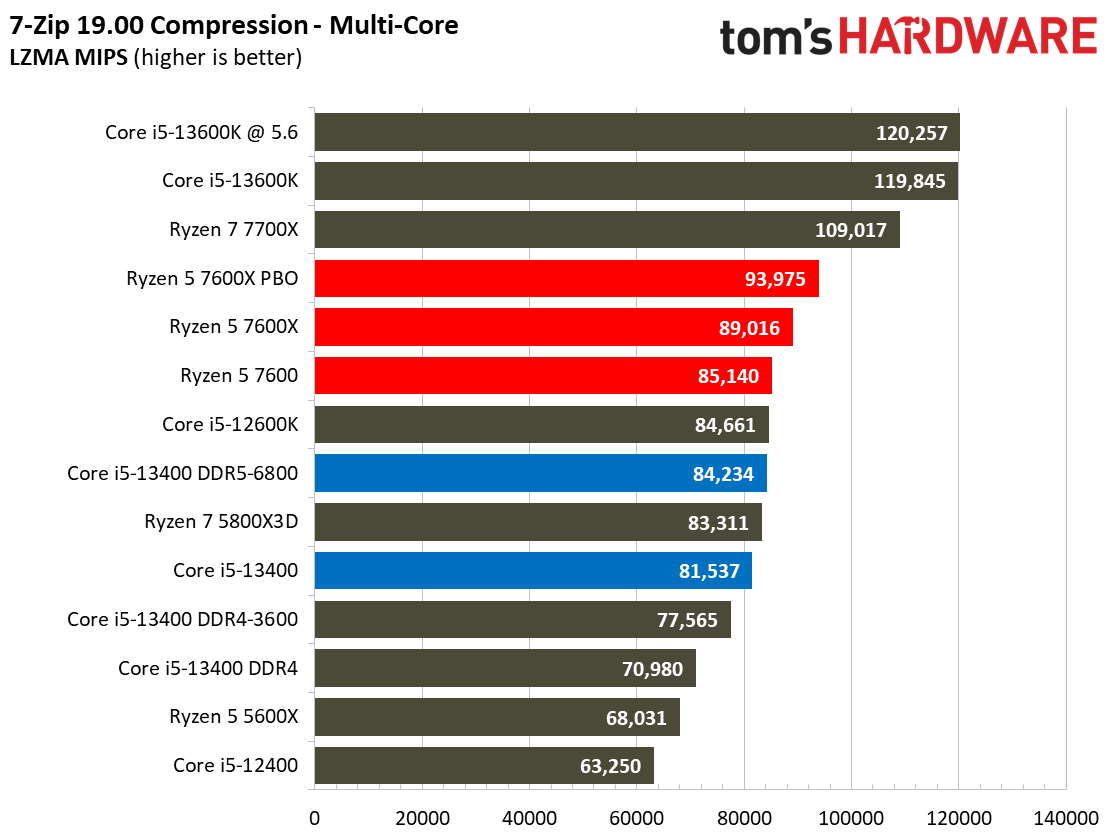
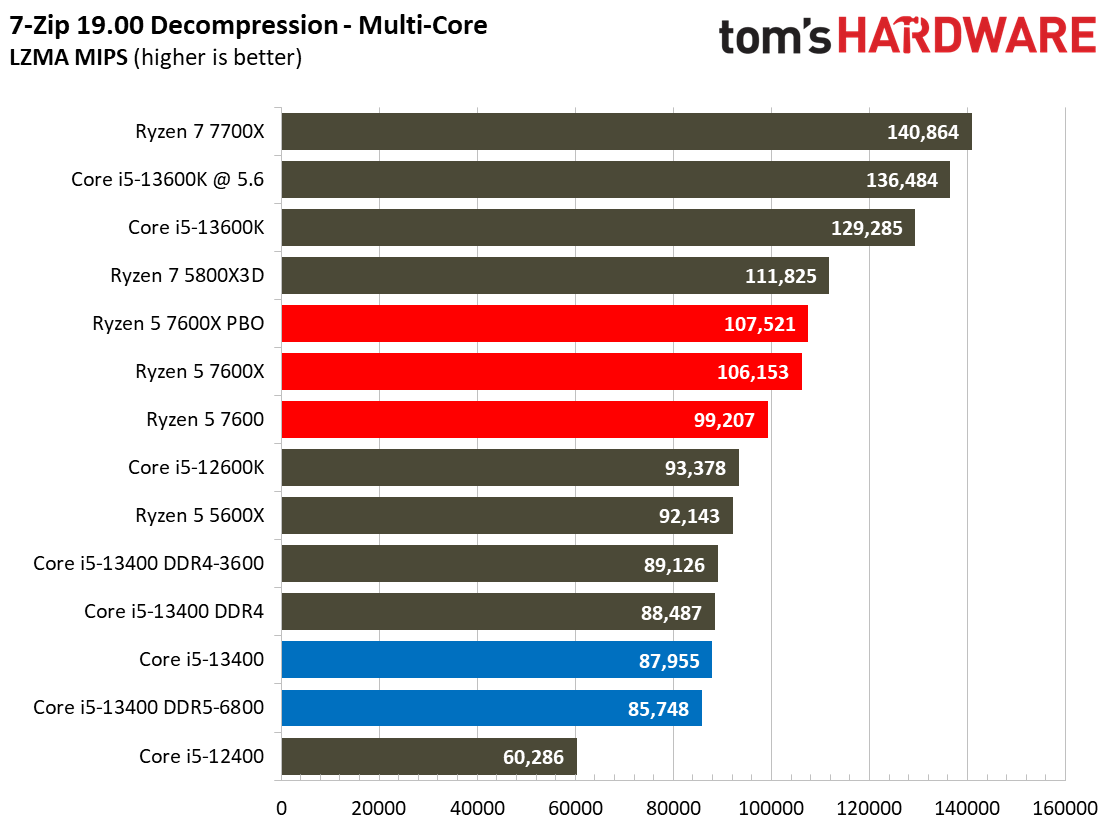
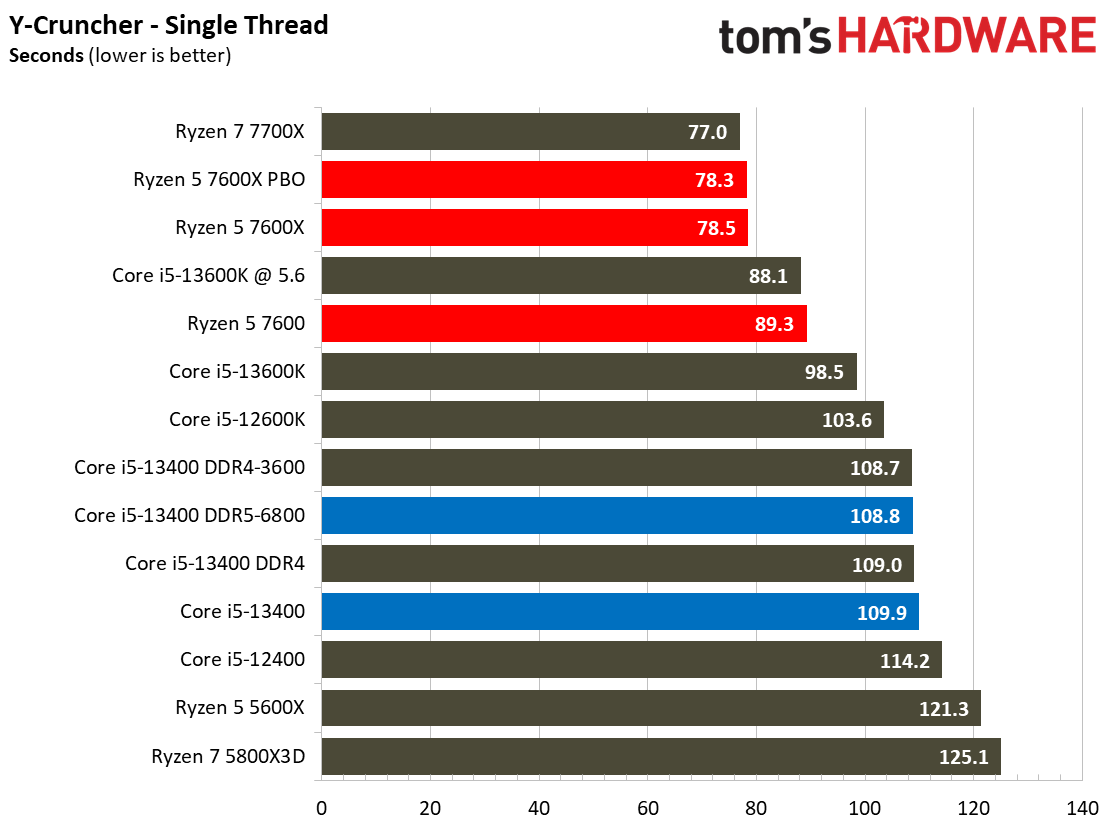
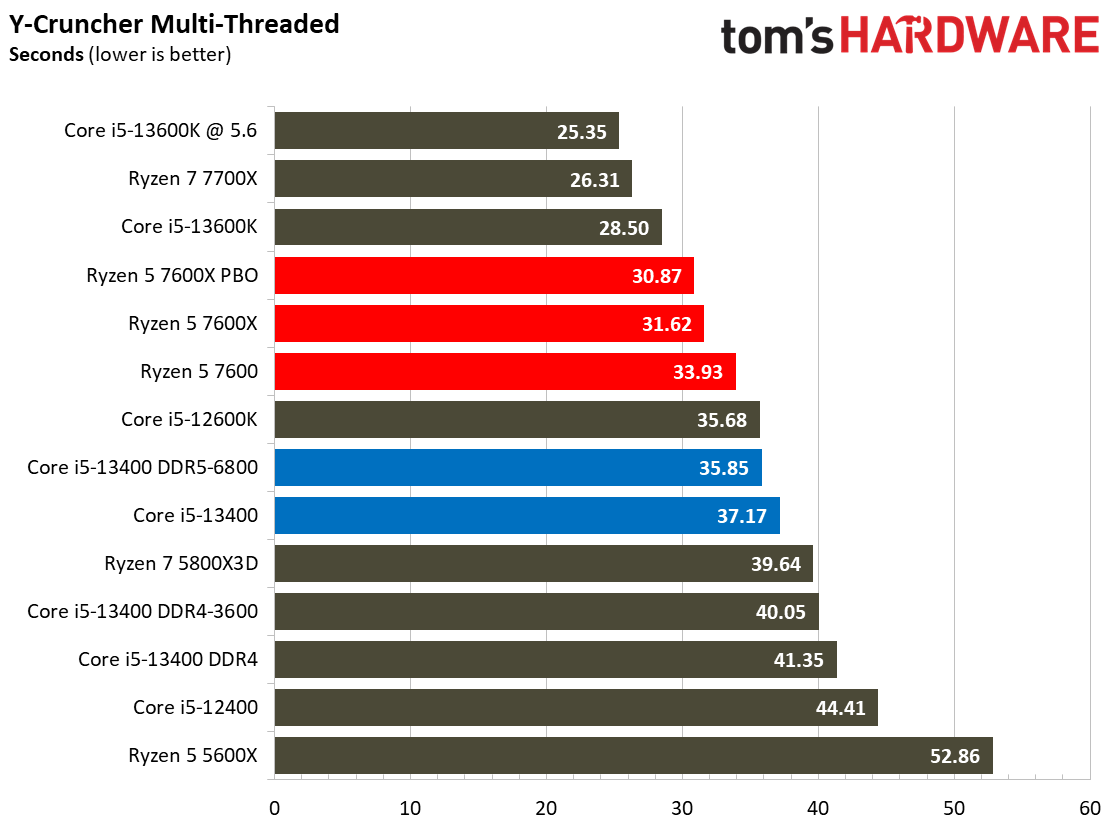
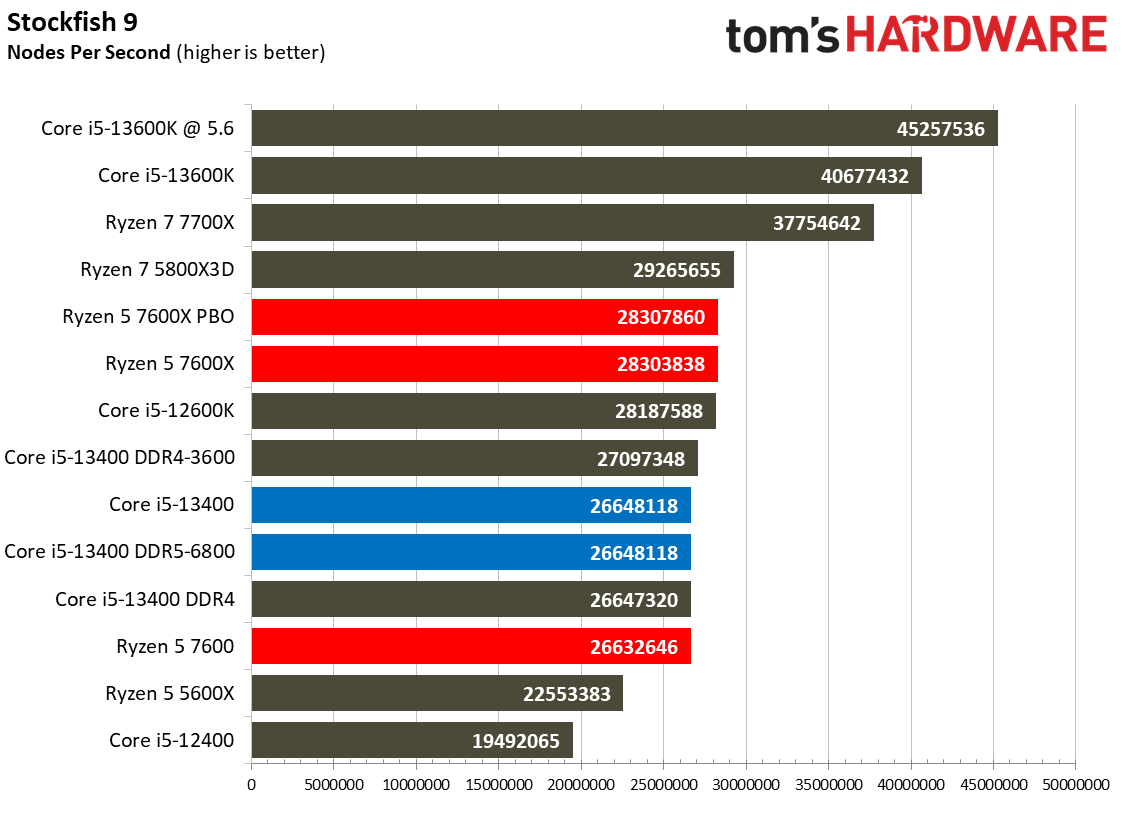
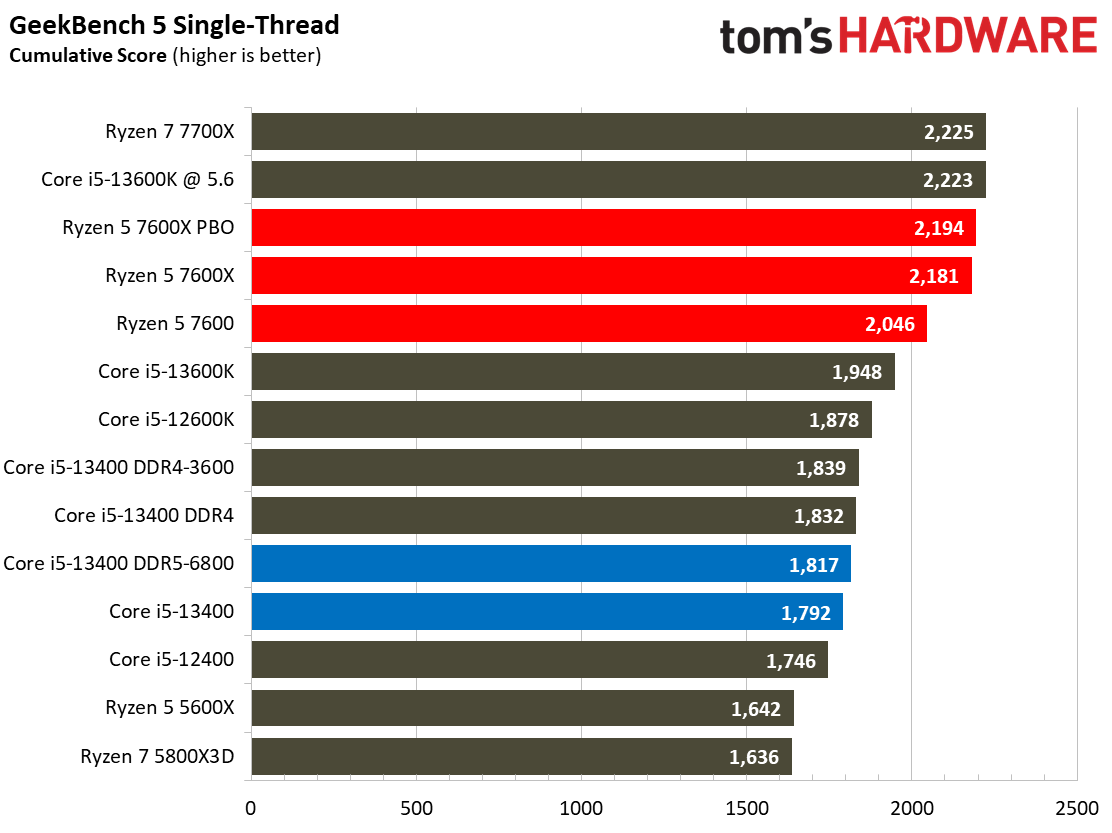
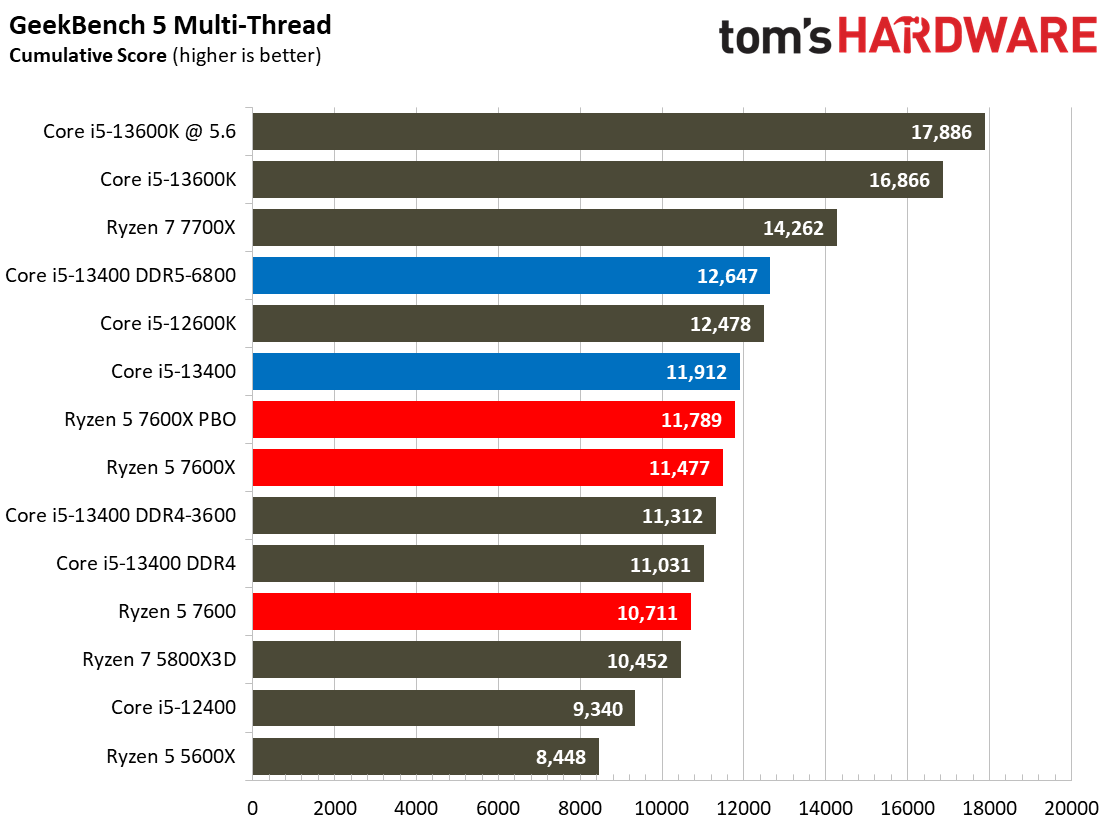
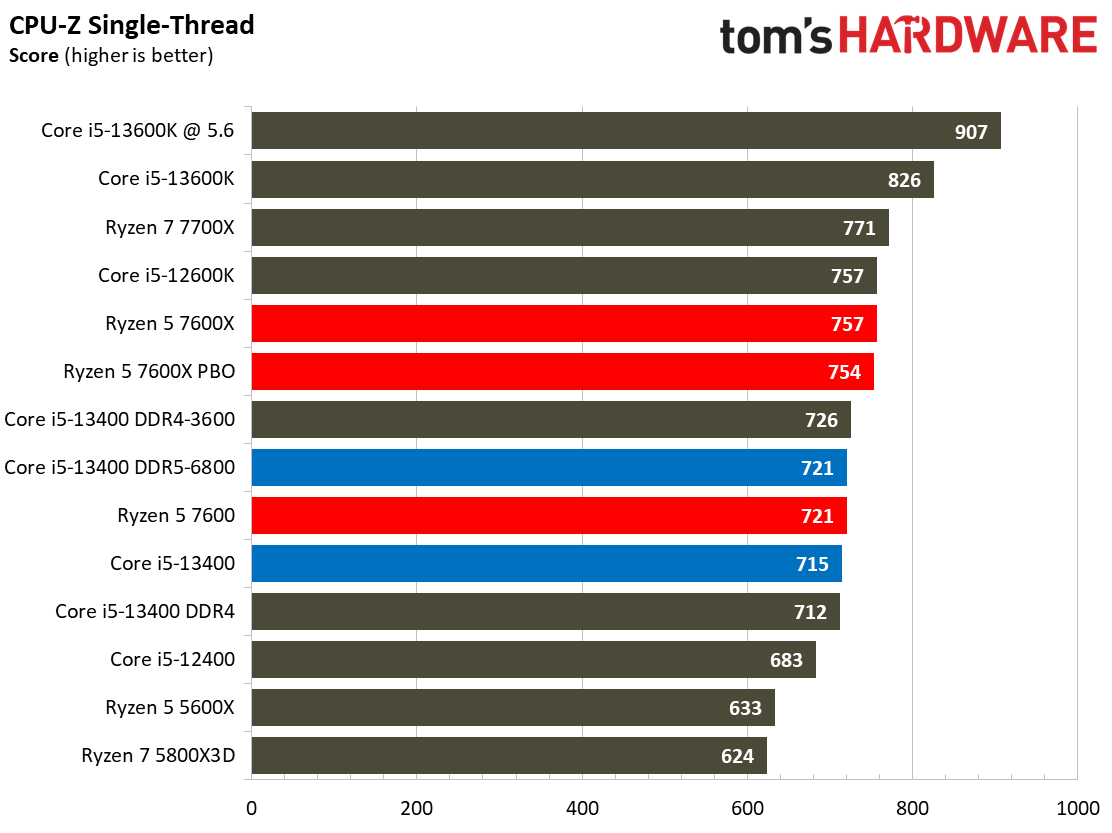
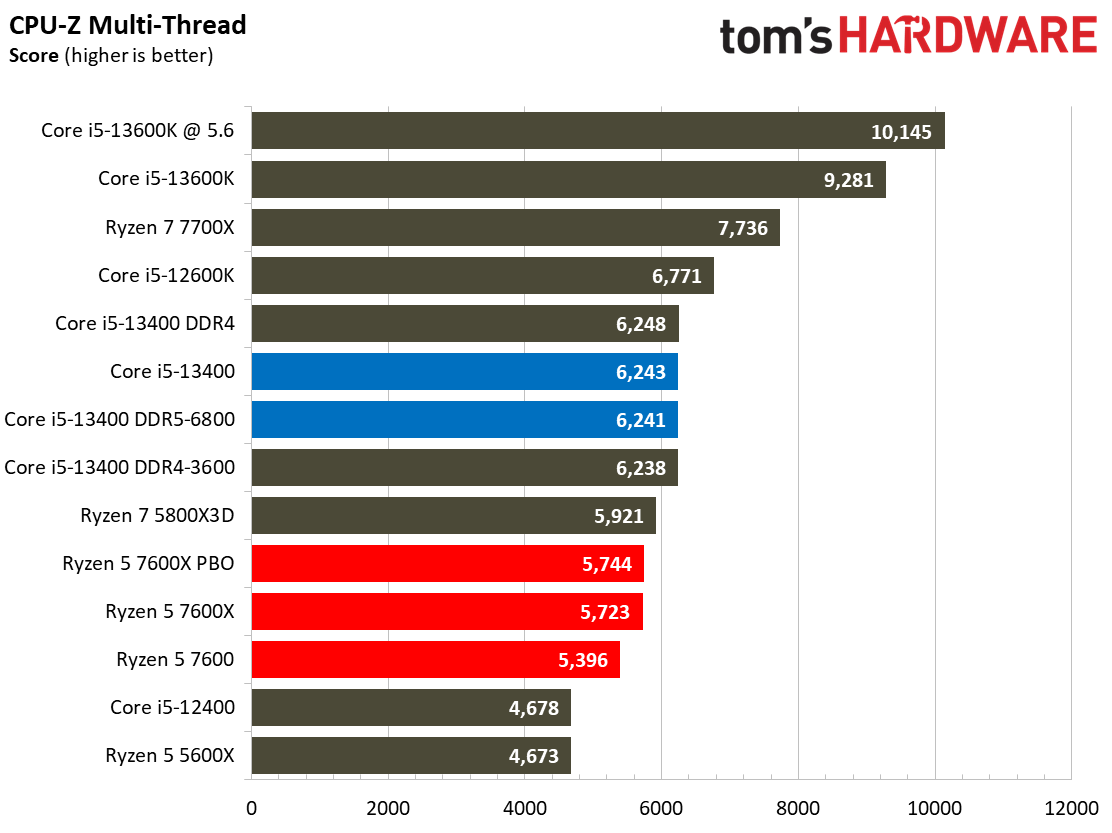
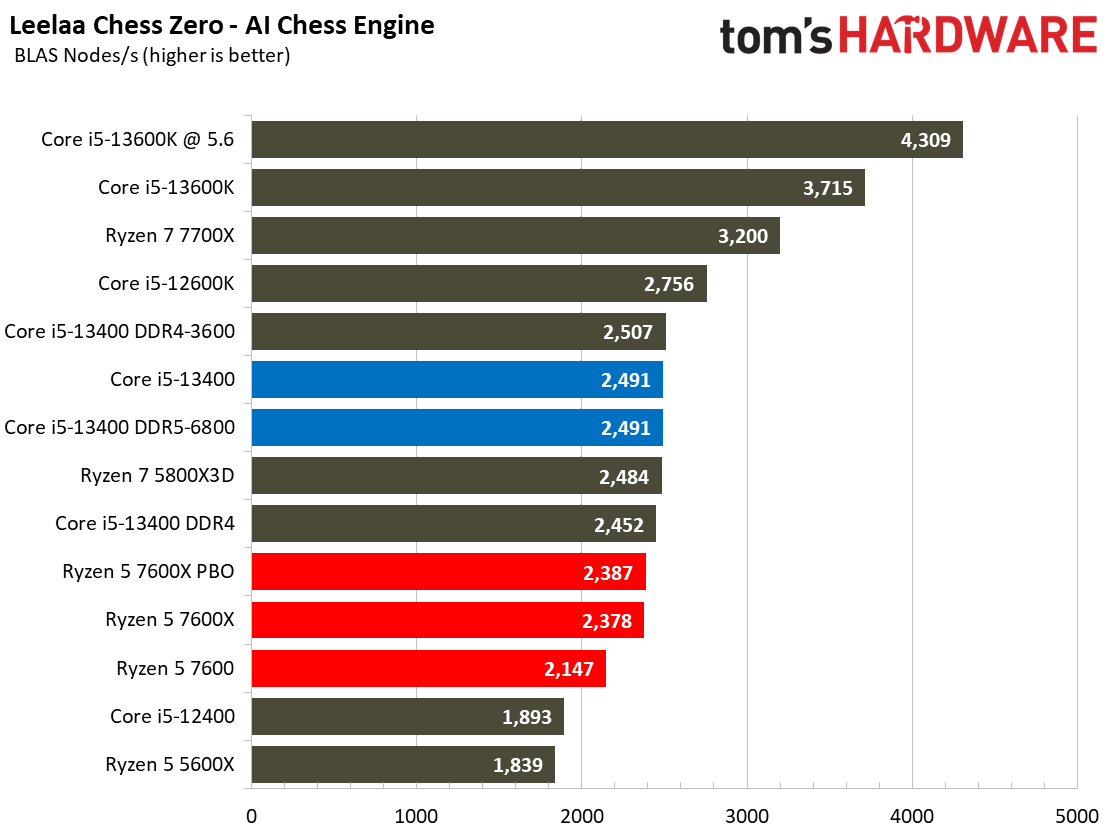
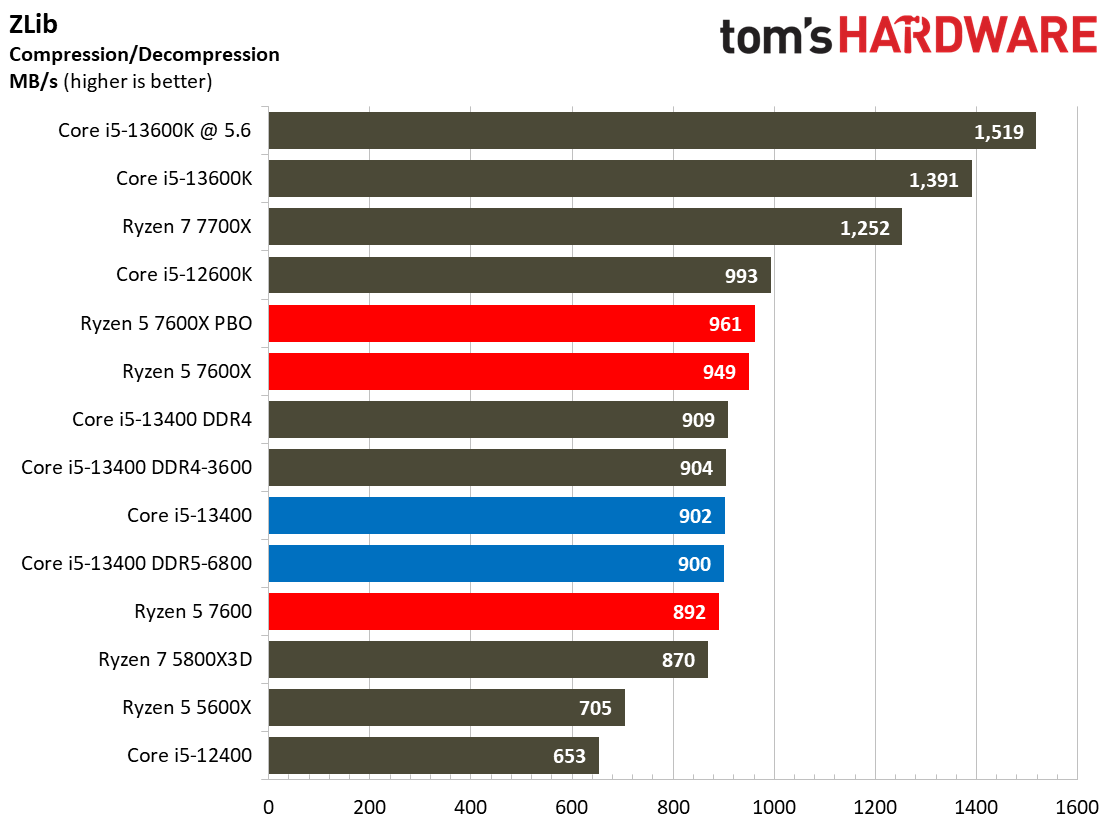
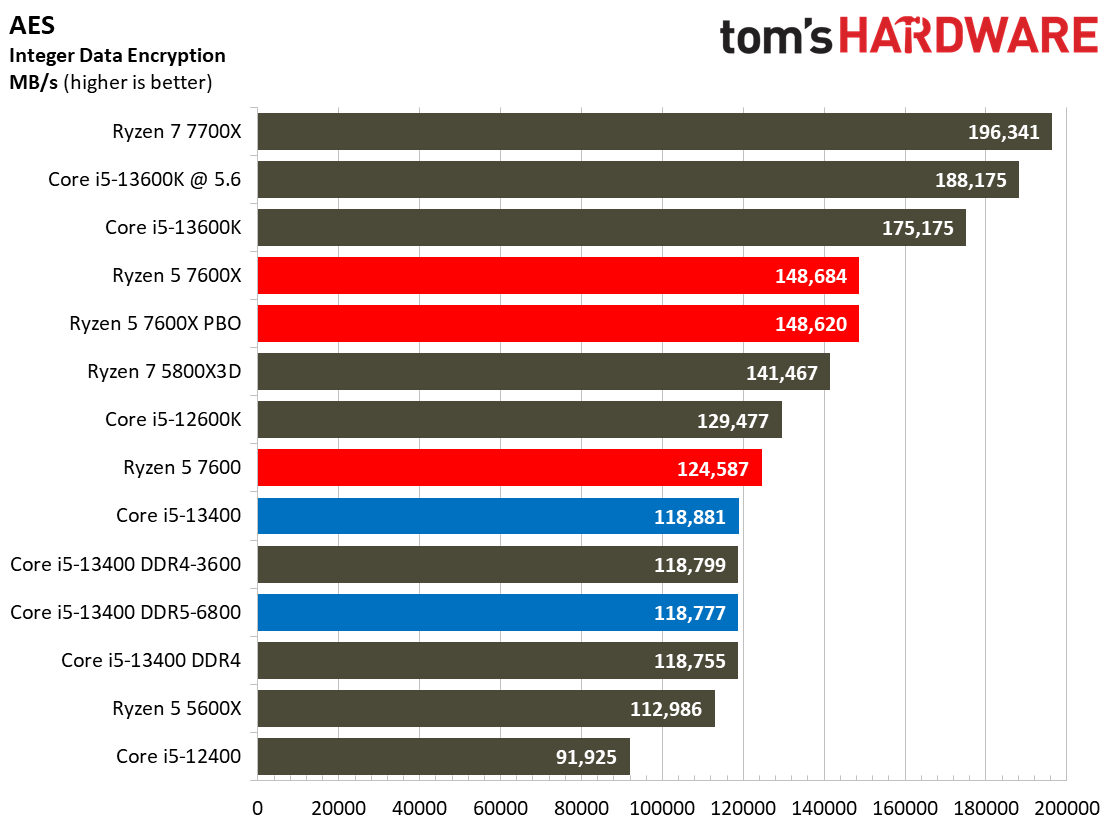
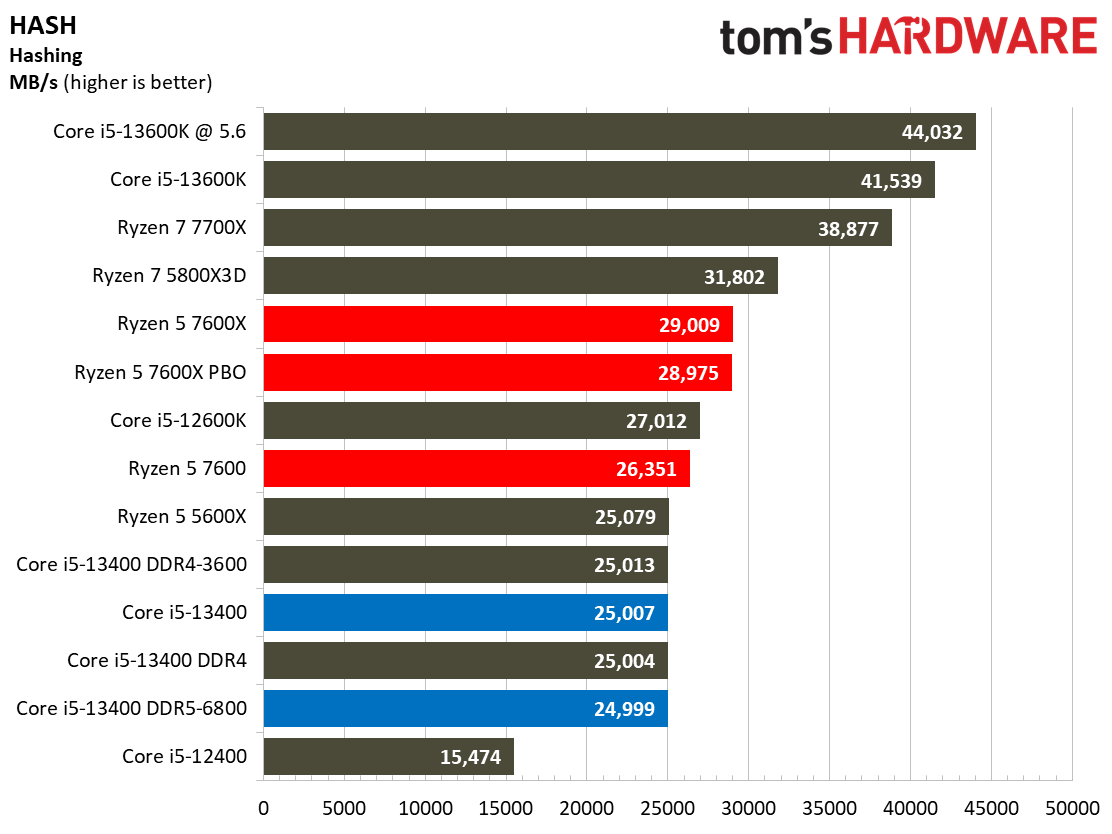
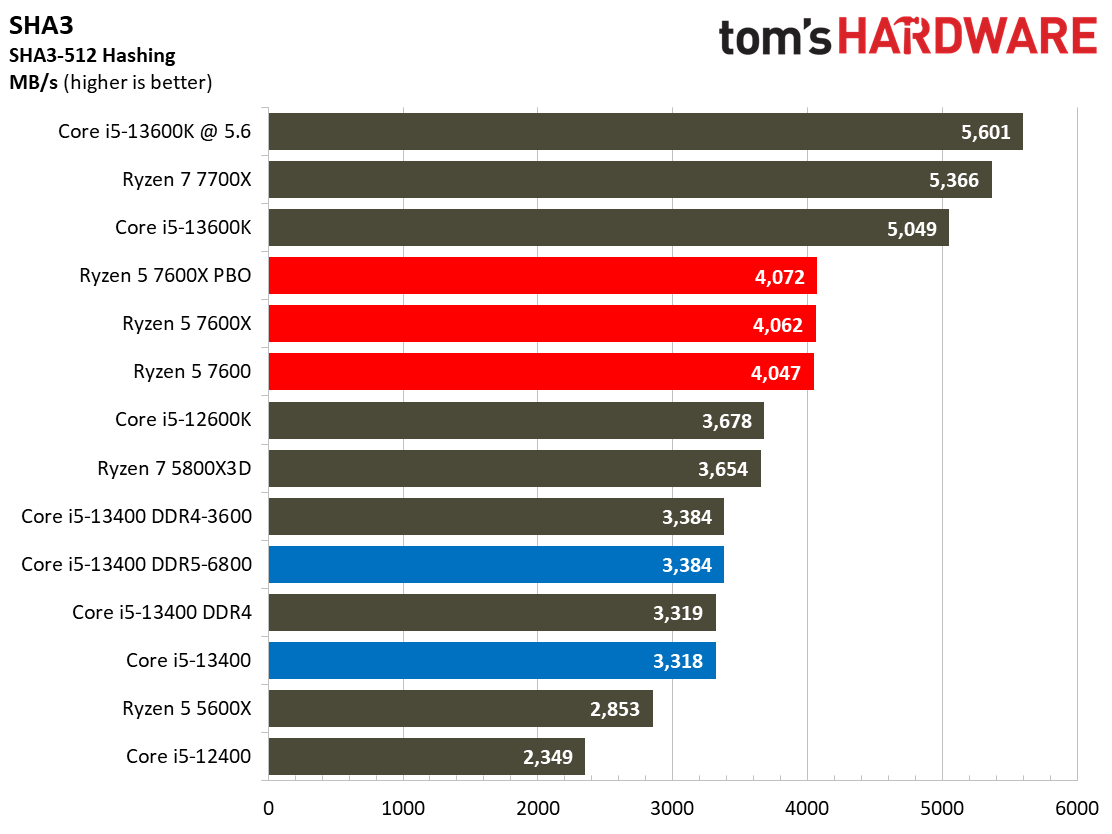
This selection of tests runs the gamut from the exceedingly branchy code in the LLVM compilation workload to the massively parallel molecular dynamics simulation code in NAMD to encryption and compression/decompression performance. Y-cruncher computes Pi with the AVX instruction set, making for an exceedingly demanding benchmark.
Intel Core i5-13400 and 13400F Thermals, Power Consumption, and Boost Clocks
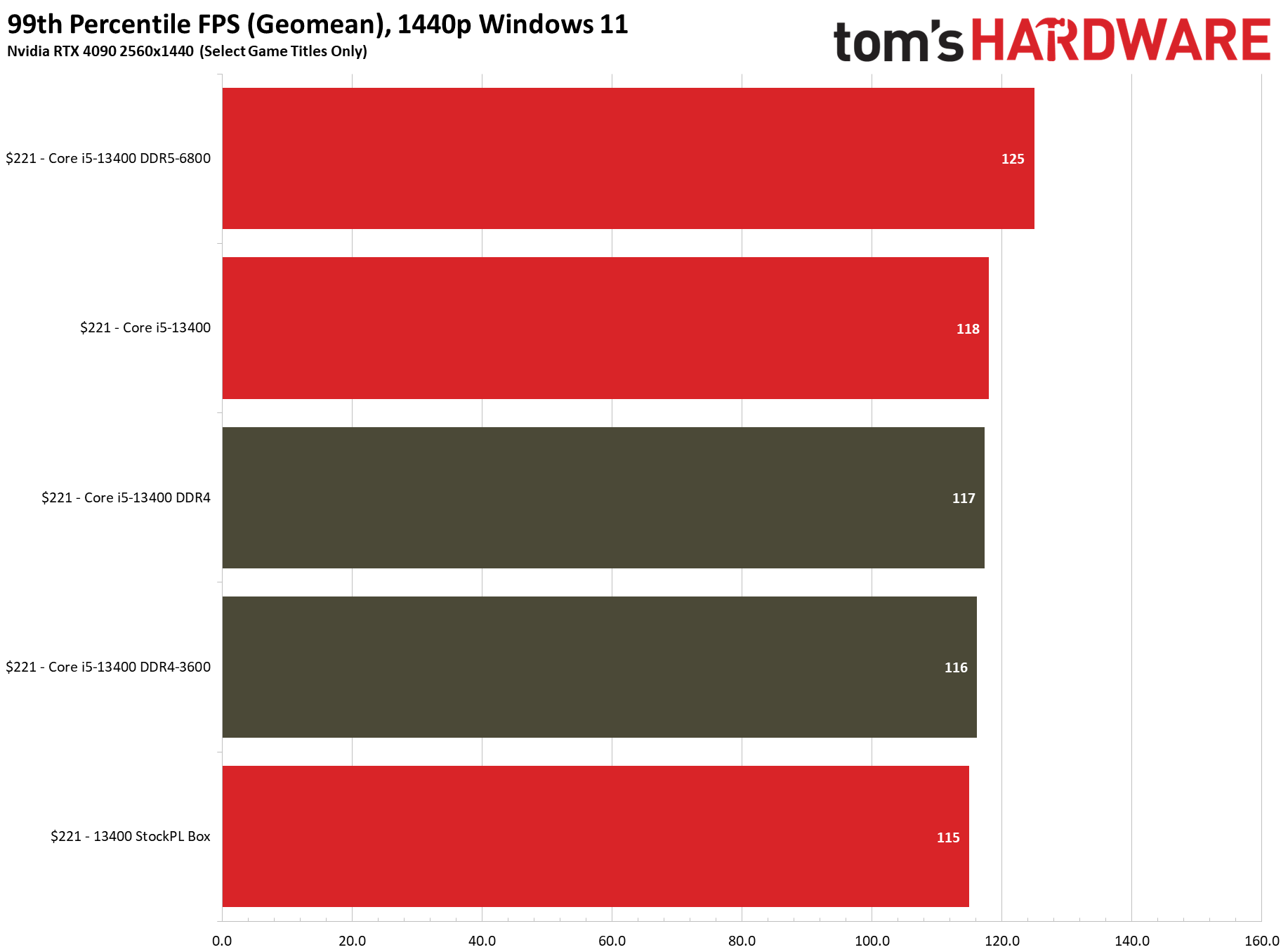
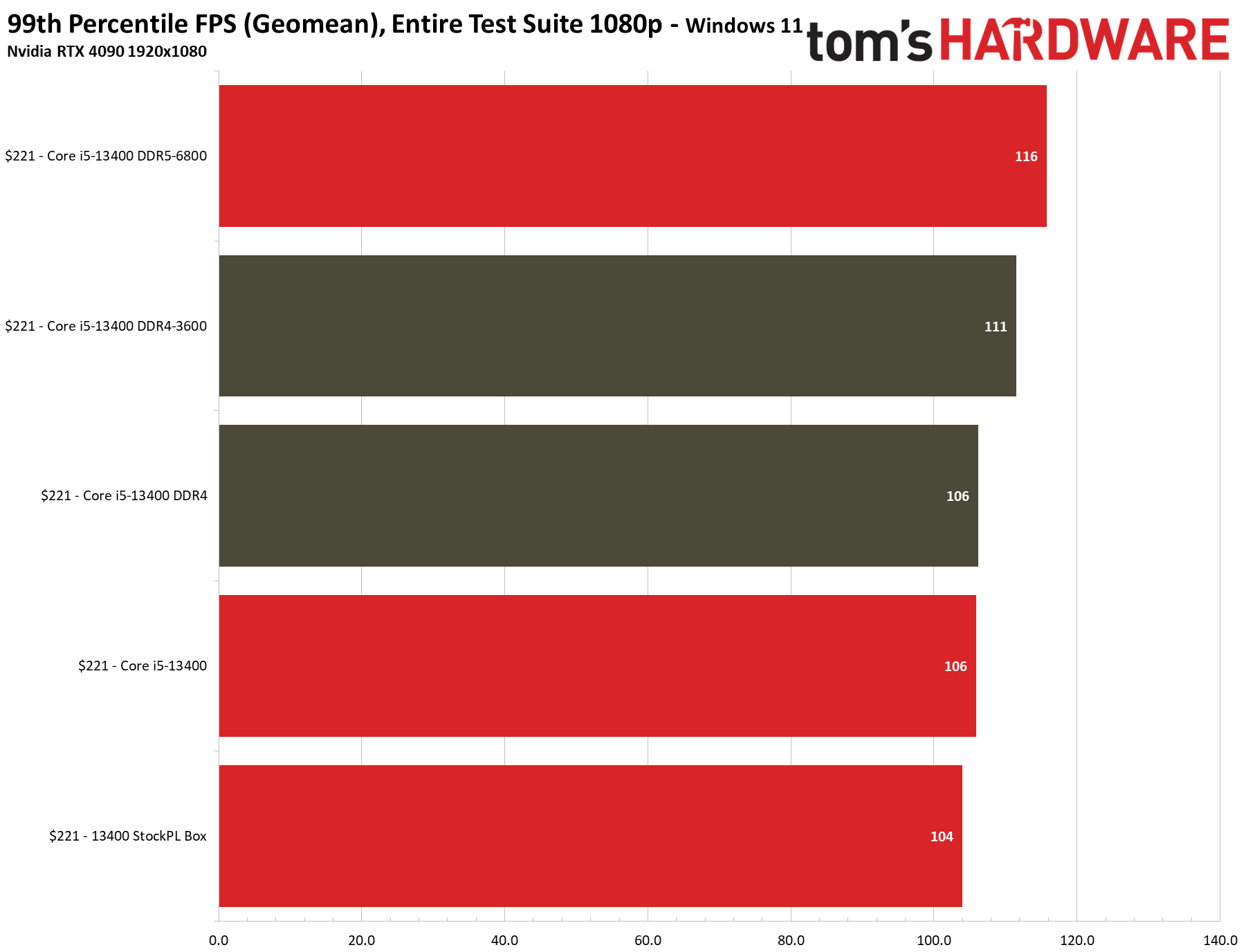
Our tests show that using the box cooler doesn't meaningfully impact gaming performance, even if you also lock the chip to the recommended 65W/148W power limit. The entry labeled "Core i5-13400" in the above charts represents the chip topped with a Corsair H115i 280mm liquid cooler and all power limits removed, while the "StockPL Box" setup measures performance with the bundled stock "box" cooler and fully-enforced 65W/148W power limits. We saw no difference with the box cooler in 1080p gaming, and the stock cooler was 1.2% slower at 1440p (close enough to call a tie).
We also measured the difference in productivity applications. Unsurprisingly, there isn't any difference in single-threaded work, regardless of configuration. However, enforcing the power limits with the boxed cooler produces roughly 5% less performance in multi-threaded work.
To determine the source of the disparity, we re-ran the same tests with the box cooler and no power limits (listed as "Core i5-13400 NoPL Box"). Removing the power limits while still using the box fan brought the performance in threaded apps back up to par with the watercooler, showing that the cooler has enough thermal headroom to run heavy threaded apps without power limits imposed. That's an interesting result, so we tested it further.
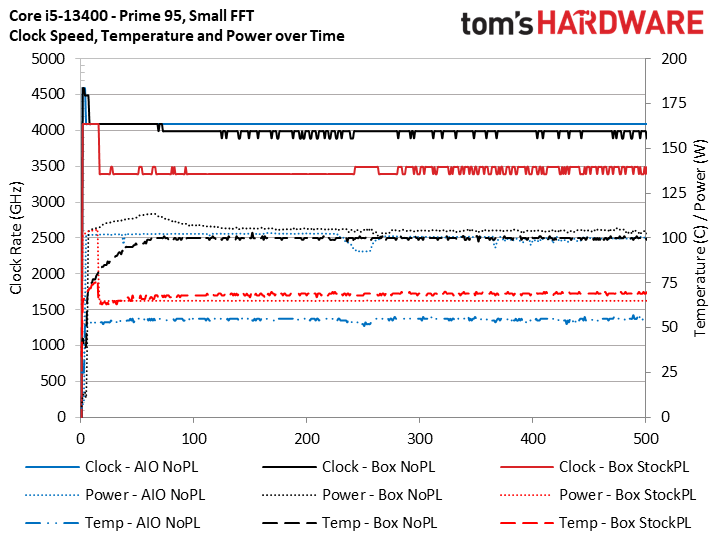
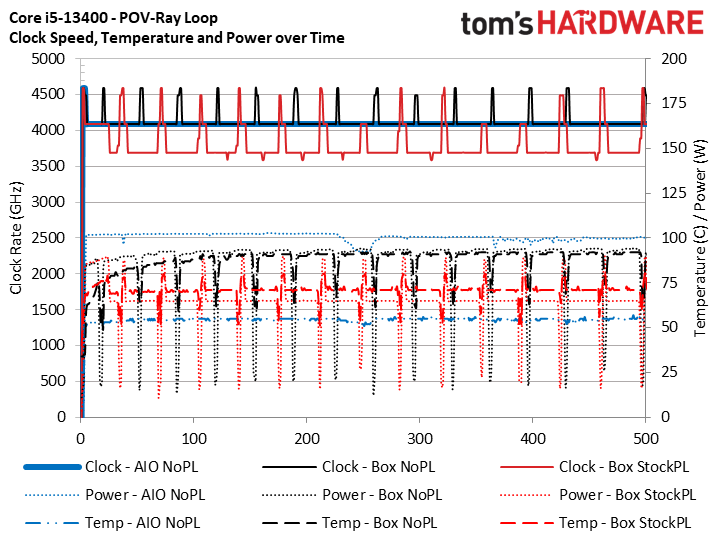
To remove thermals as a limitation, we always use the same 280mm Corsair H115i AIO cooler for all our test systems. This time we used the same three test configurations — the 280mm watercooler without power limits, the box fan without power limits (and its original pre-applied TIM), and the box fan with power limits — to measure performance in heavier work.
We ran Prime95 first, but be aware that this stress test serves as a power virus more than an actual representation of most threaded work; real-world apps simply do not consume as much power or generate as much heat. The chart is a bit of an eye sore, but the takeaway is that even though the box fan without power limits (Box NoPL) ran at the 100C limit during the test with the chip throttling, it only lost 100 MHz of frequency (2.5%) on the p-cores compared to the watercooled configuration. Meanwhile, imposing the 65W/148W power limits dropped clocks to 3.4 GHz, a whopping 21% decline from the results with the liquid cooler.
Prime95 is a stress test and not very indicative of normal use, so we then ran a looped series of POV-Ray benchmarks to see performance over time with a more realistic workload. Here we can see that the chip didn't exceed 90C with the power limits removed, and that clock rates between the watercooled and box cooler were the same. We then turned to even more standard productivity applications.
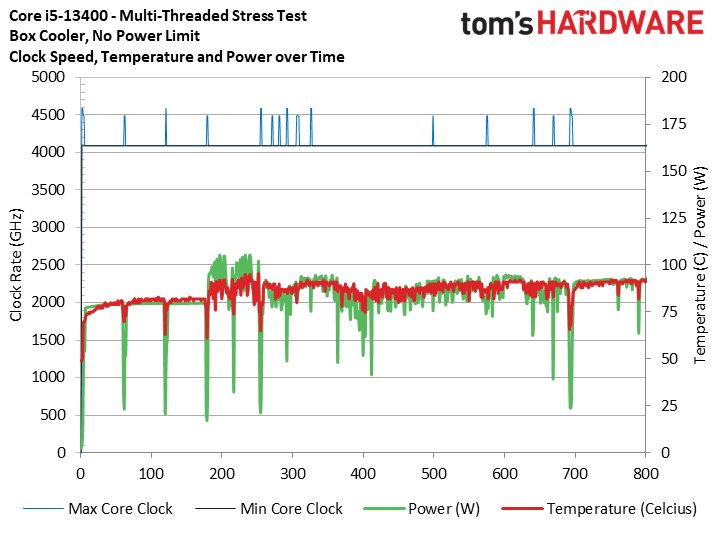
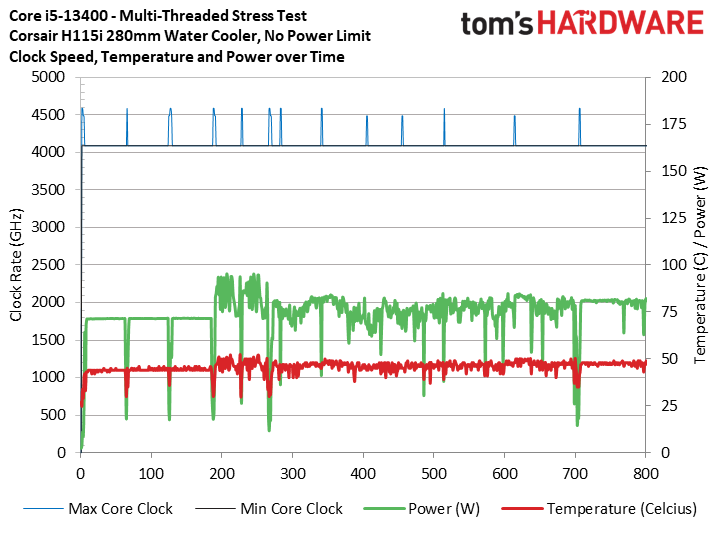
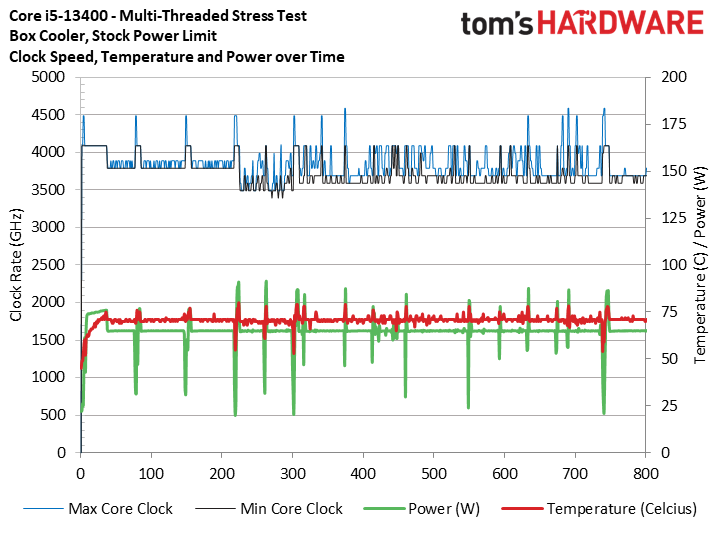
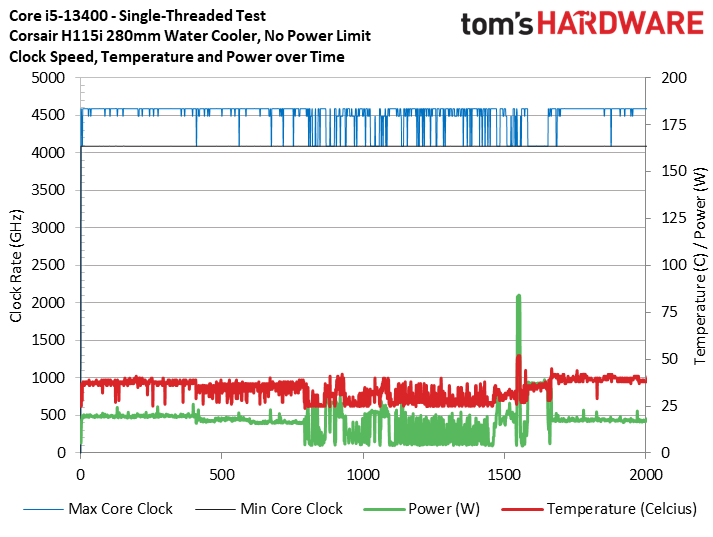
To reiterate the point with a broader selection of real-world benchmarks, we ran our standard series of heavily multi-threaded apps like y-cruncher, HandBrake, Cinebench, Blender, and POV-Ray.
The first slide shows that the box cooler with no power limits never exceeded 90C during these tests, showing that it is adequate to handle extended real-world workloads. This test shows the chip delivering the same 4.1 GHz all-core frequency as the 280mm AIO configuration. Meanwhile, imposing power limits is often 500 MHz slower.
The stock cooler isn't silent, so you'll have to accept the extra noise. However, the takeaway is that the box cooler is good enough to handle the chip at the lower 65W/148W power limits and adequate for multi-threaded real-world workloads with the power limits removed. Not that removing the power limits is too taxing — the Core i5-13400 peaked at 110W in our tests, which is far under the 148W official Maximum Turbo Power.
However, you could run into slightly more throttling if you run a heavy extended-duration heavy workload for an hour or more or have higher ambient temps (our tests were at ~74F ambient). However, the loss would be slight, and you would still come out ahead over running the chip at the recommended 65W power limits.
We would recommend investing in a $20 tower air cooler to reduce the noise level and ensure 100% operation, but it isn't a steadfast requirement if you're willing to accept the drawbacks.
Power Consumption on Intel Core i5-13400
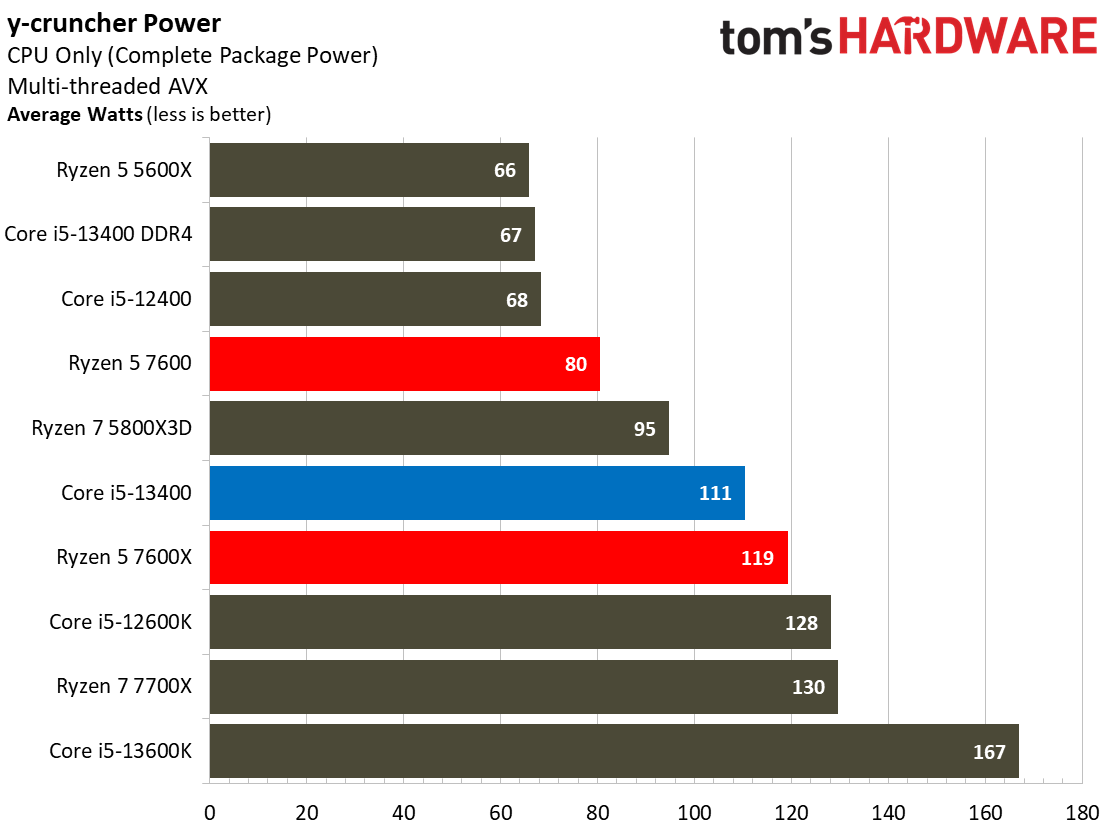
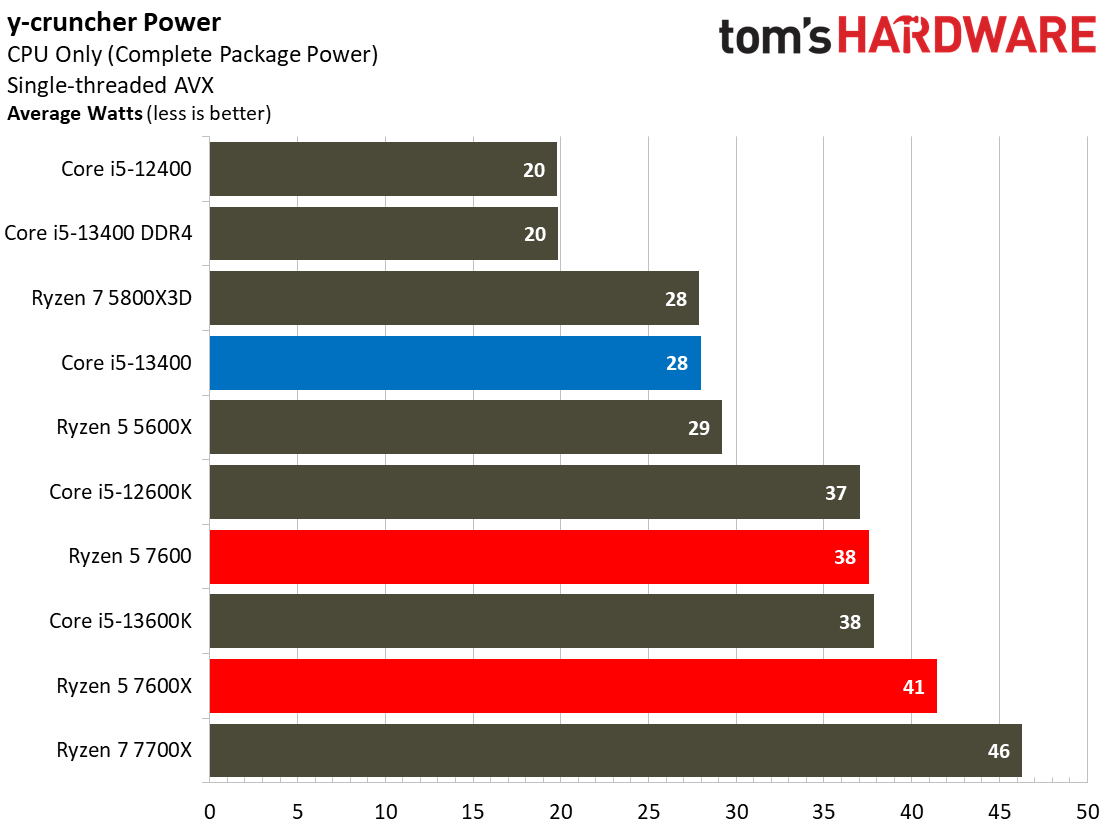
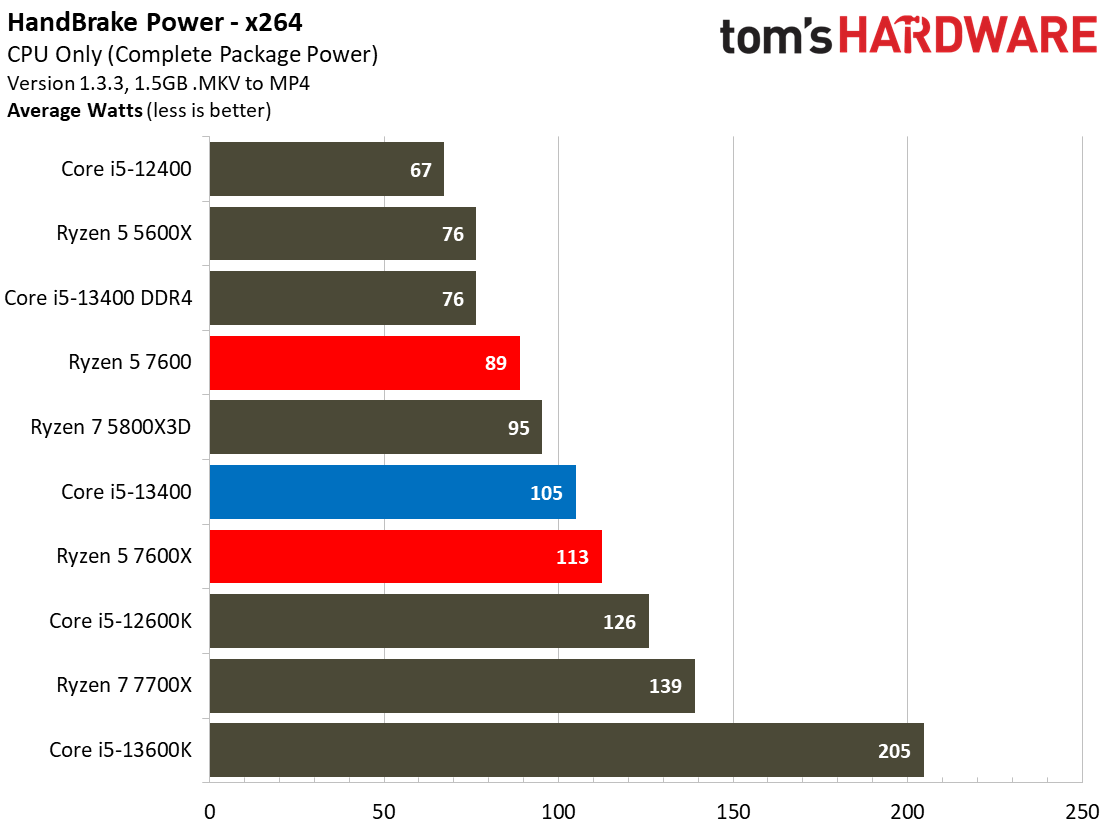
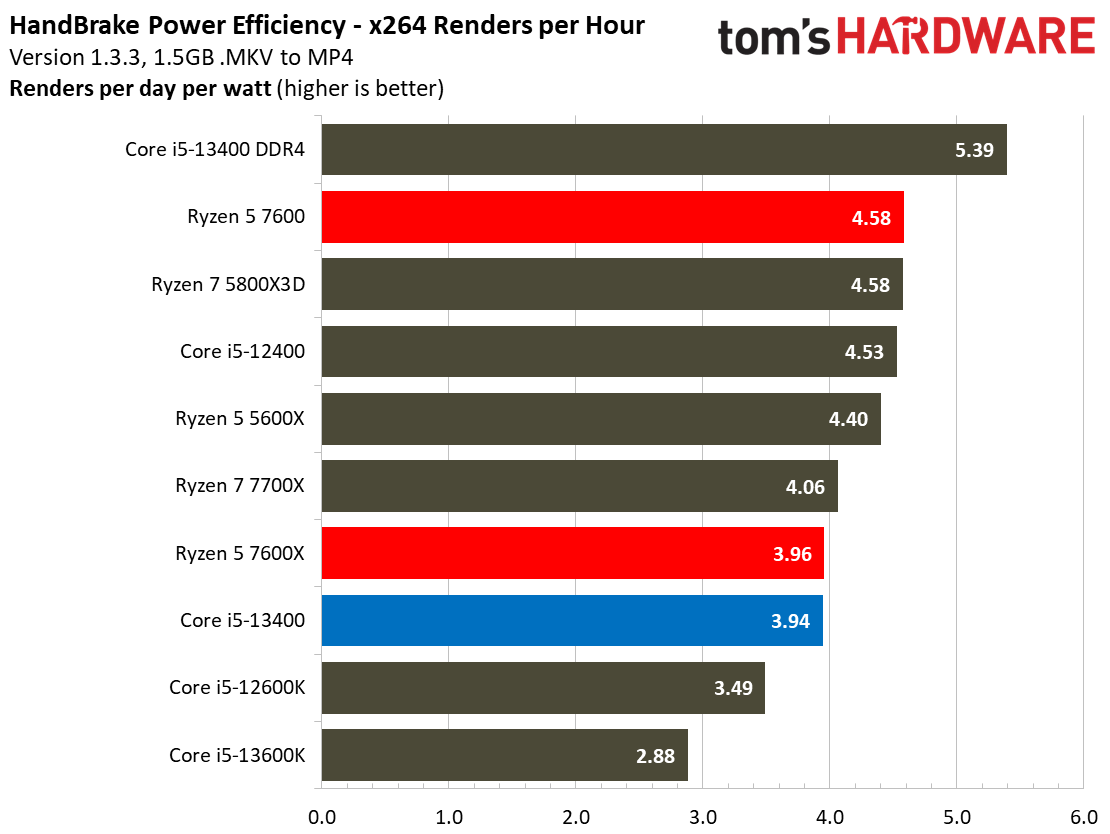
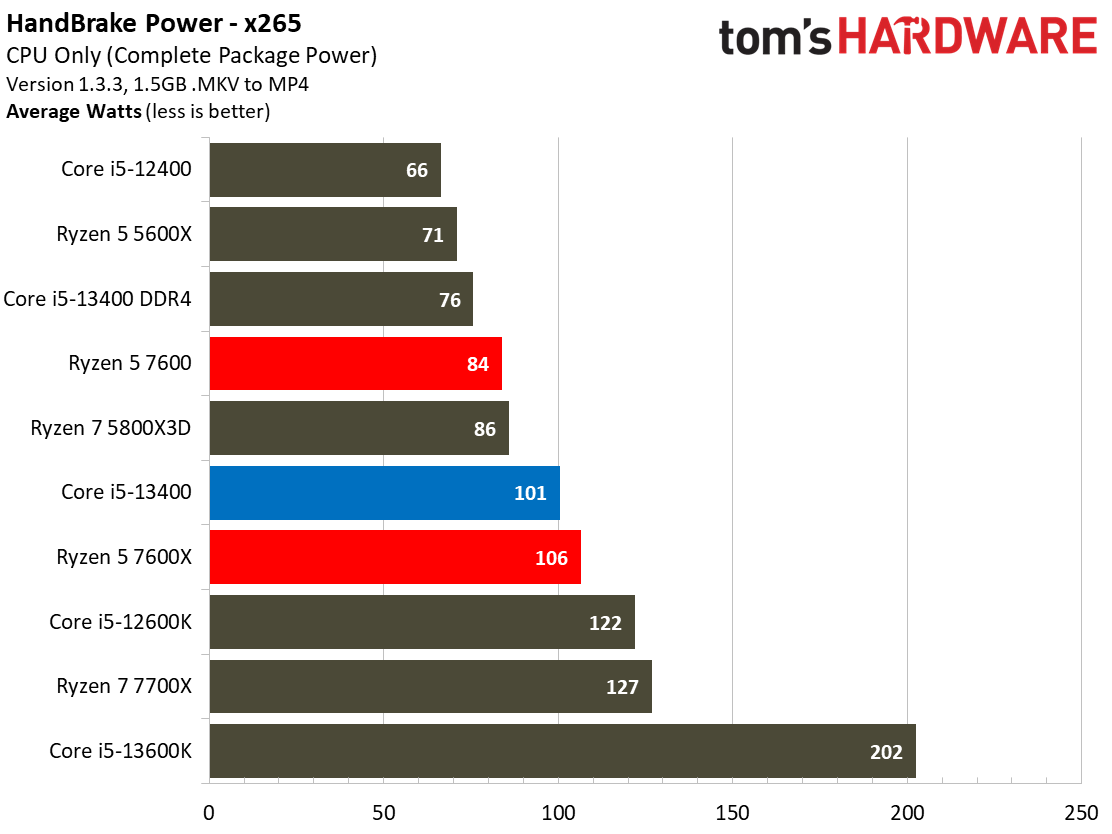
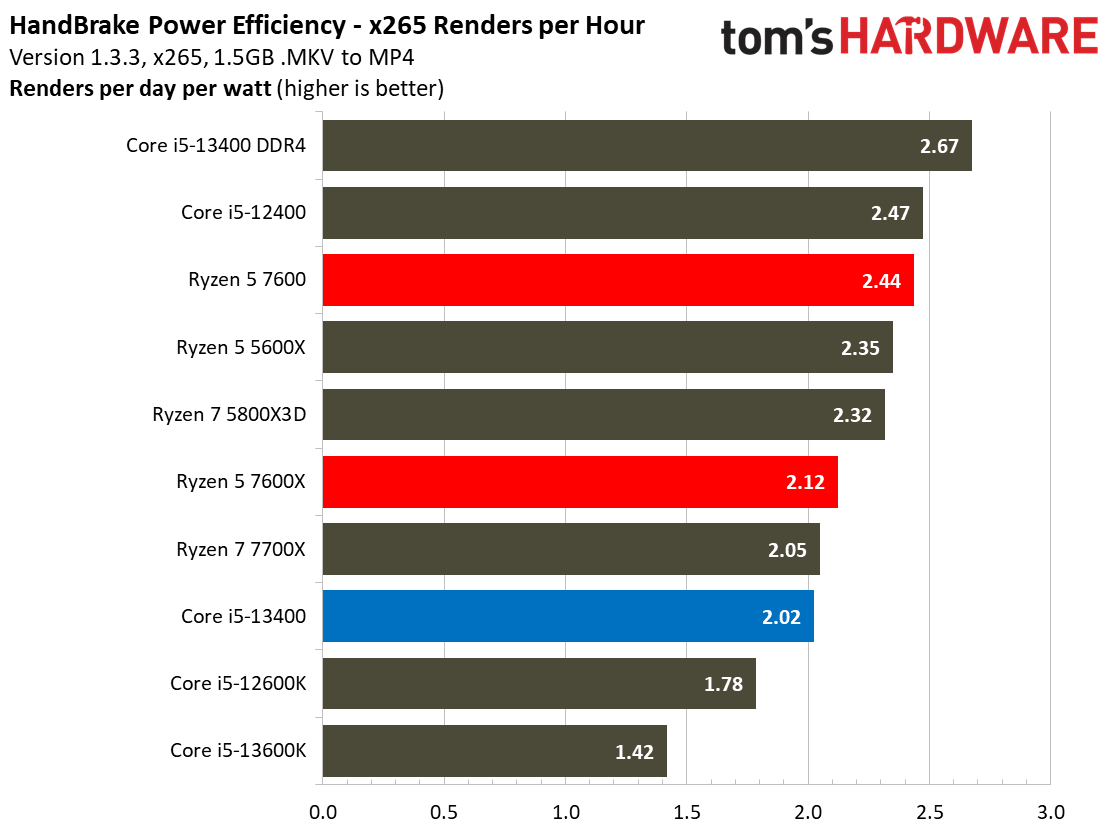
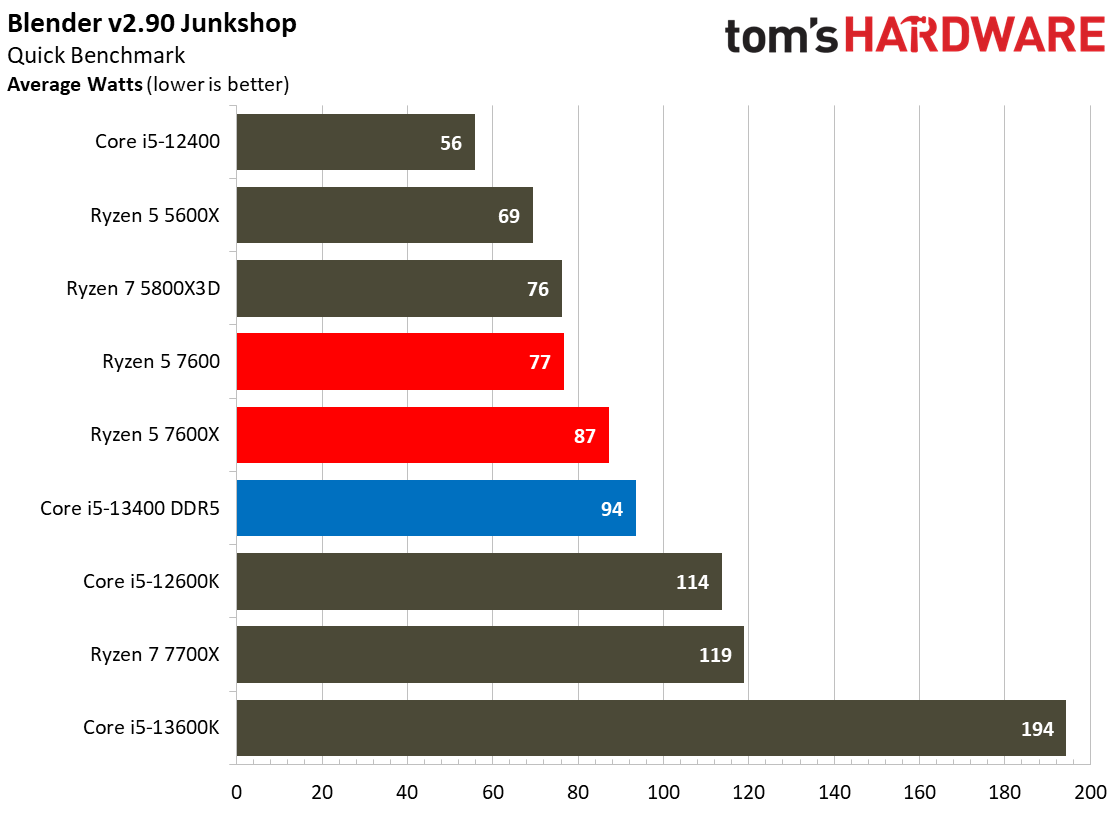
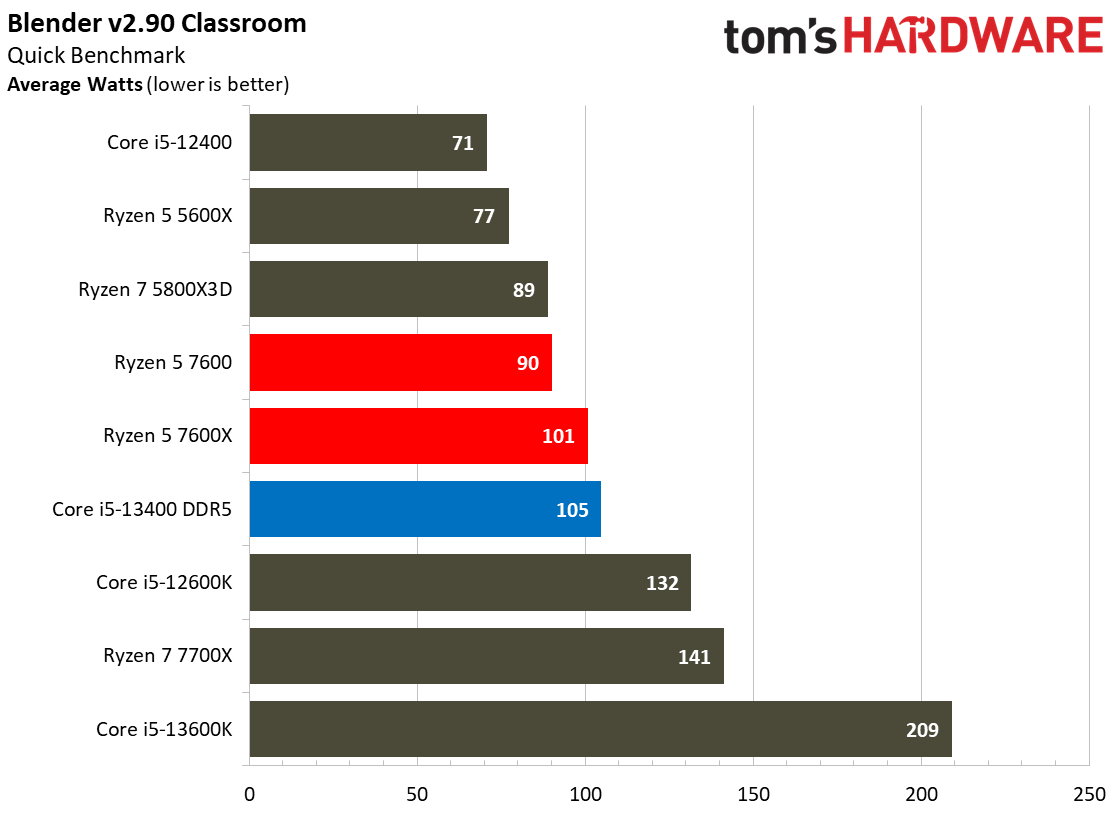
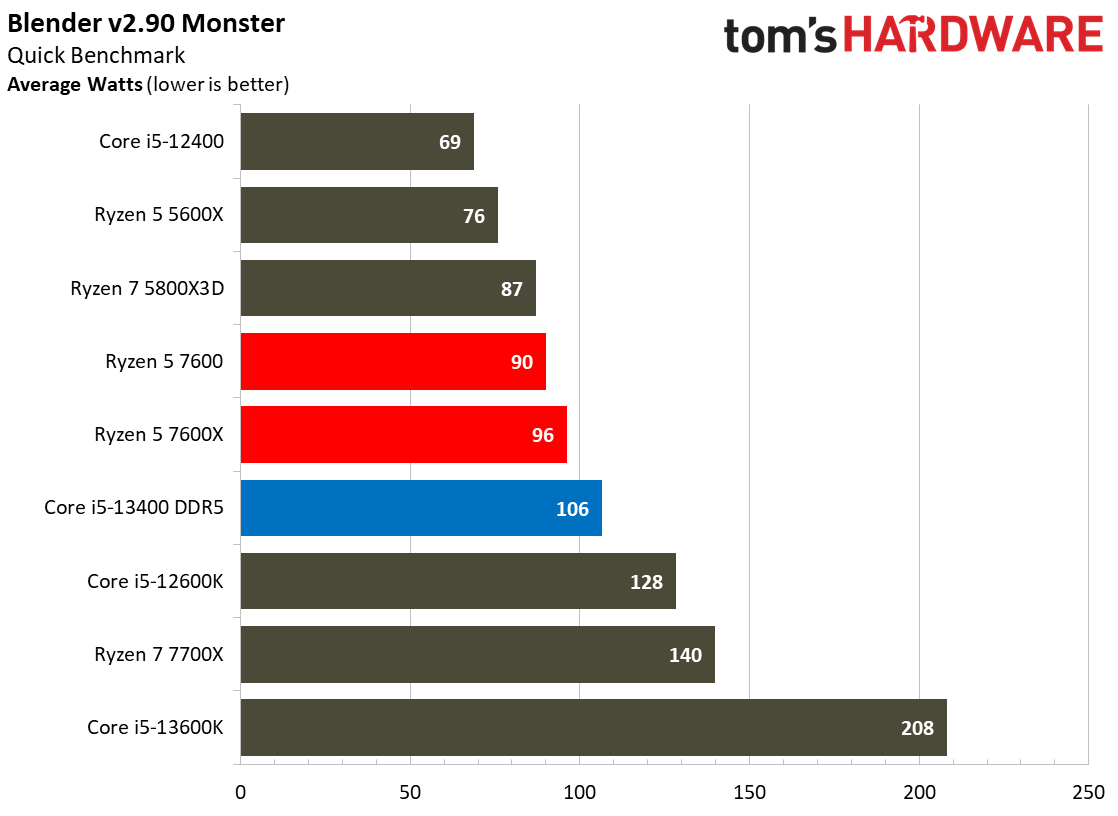
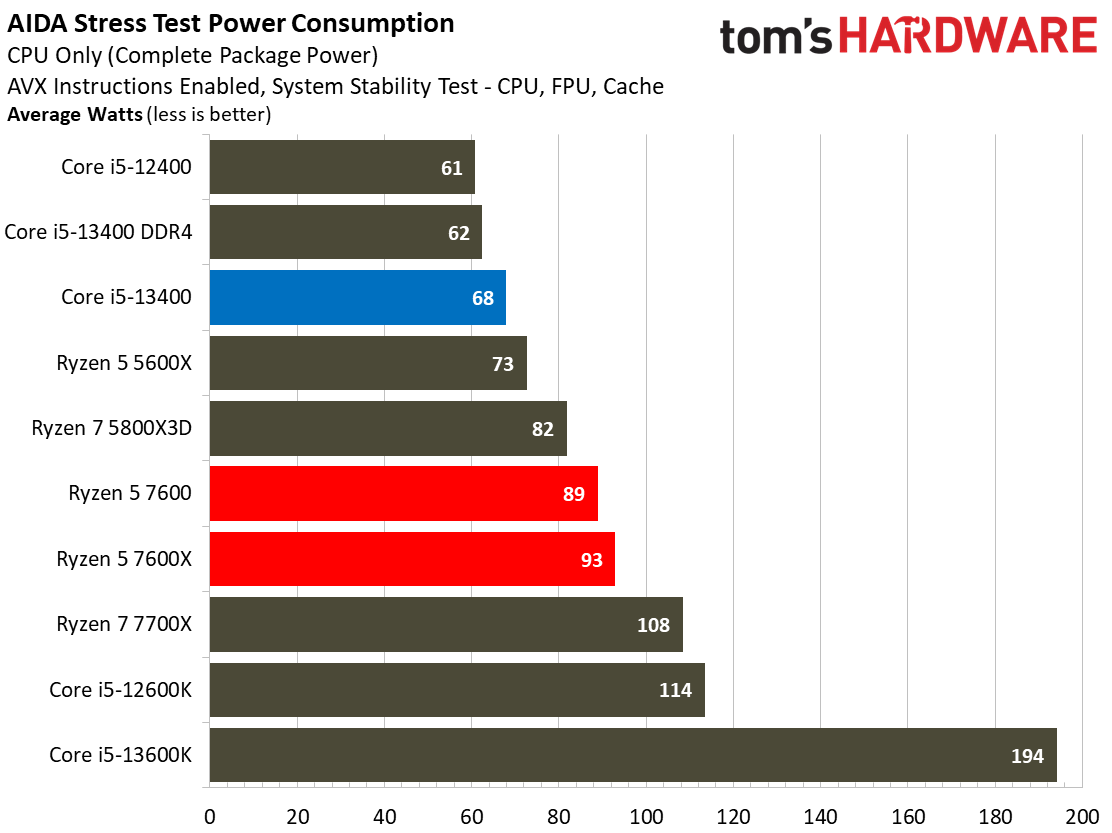
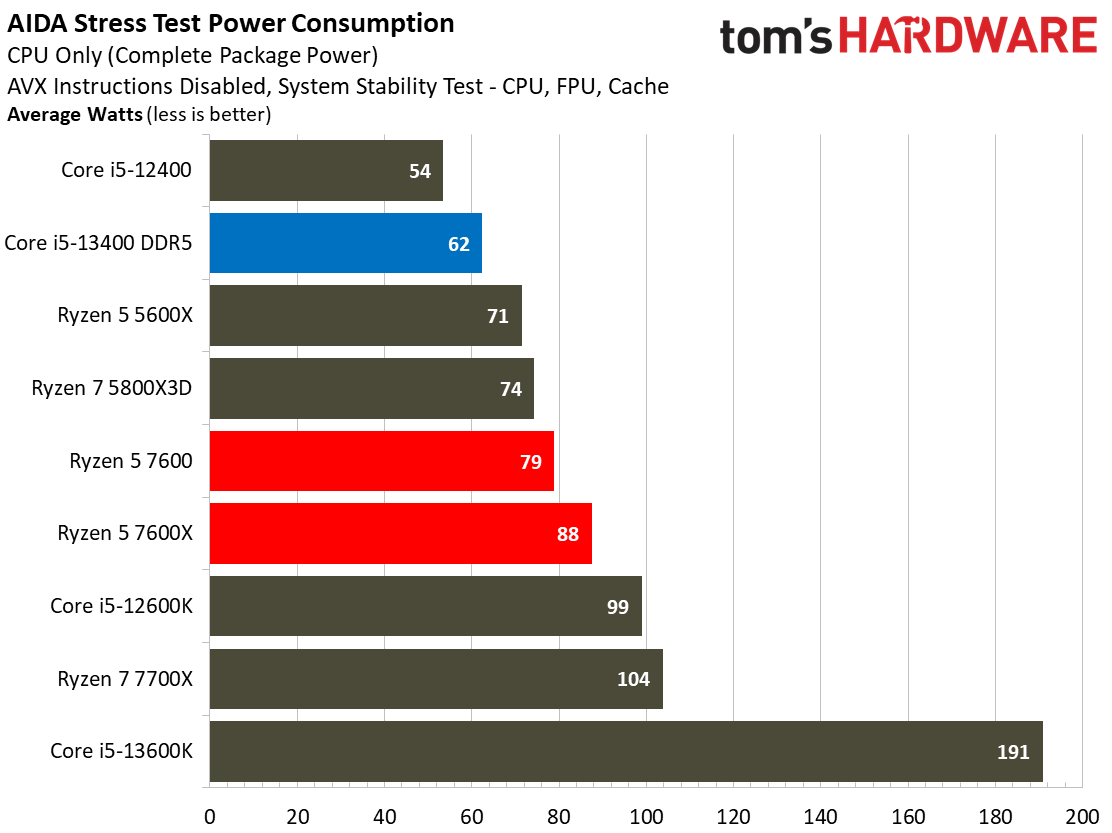
The Core i5-13400's power consumption is surprisingly good, especially given that our test chip uses the Alder Lake C0 die. The Ryzen 5 7600 is more power efficient in our renders-per-day metric and consumes less power in every workload, but the deltas aren't large enough to be of concern for most users. The Core i5-13400 is very power efficient in these workloads, largely due to the addition of four e-cores. That confers a generational improvement against the Core i5-12400 in both performance and power consumed.
Intel Core i5-13400 Overclocking and Test Setup
- Intel Core i5-13400 DDR5 or DDR4: Corsair H115i 280mm water cooler, power limits removed, Stock DDR5-4800 in Gear 2 / DDR4-3200 in Gear 1
- Intel Core i5-13400 DDR4-3600 / DDR5-6800: Corsair H115i 280mm water cooler, power limits removed, DDR4-3600 CL16, DDR5-6800 XMP 3.0
- AMD PBO Configs: Precision Boost Overdrive (Motherboard), Scalar 10X, DDR5-6000 EXPO
There isn't too much to say about overclocking — Intel doesn't allow overclocking the 13400's CPU cores, and a workaround created by the motherboard vendors for the previous-gen chips doesn't work with the new Raptor Lake models. That leaves us with lifting the power limits, which we did as described in the thermal section, and overclocking memory, which Intel allows on B-series motherboards.
We overclocked the DDR5 memory to DDR5-6800 using a single-click XMP 3.0 profile. With DDR4, we couldn't overclock beyond DDR4-3600 CL16 in Gear 1 (Gear 2 is slow) due to Intel's locked System Agent (SA) voltage. This is a small gain over the stock DDR4-3200 transfer rate.
We did receive decent performance gains in gaming from this overclock, and a cheap DDR4-3600 CL kit only costs about $10 more than a DDR4-3200 kit. Our sources tell us the SA voltage will be unlocked in the Raptor Lake Refresh models, but you'll be stuck with relatively low DDR4 overclocks for the 13400.
Microsoft recently advised gamers to disable several security features to boost gaming performance. As such, we disabled secure boot, virtualization support, and fTPM/PTT for maximum performance. You can find further hardware details in the table at the end of the article.
The Mid-Range Gaming Champ
The $221 Core i5-13400 and the graphics-less $196 Core i5-13400F build on the gaming performance of the previous-gen model that has long been the go-to mid-range gaming chip, but the addition of four e-cores drastically improves performance in threaded productivity workloads. The 13400's support for DDR4 memory gives it an unmatched value proposition in the $200 price range, making it the go-to chip for mid-range gaming PCs.
Below, we have the geometric mean of our gaming test suite at 1080p and 1440p and a cumulative measure of performance in single- and multi-threaded applications. We conducted our gaming tests with an Nvidia RTX 4090, so performance deltas will shrink with lesser cards and higher resolution and fidelity settings.
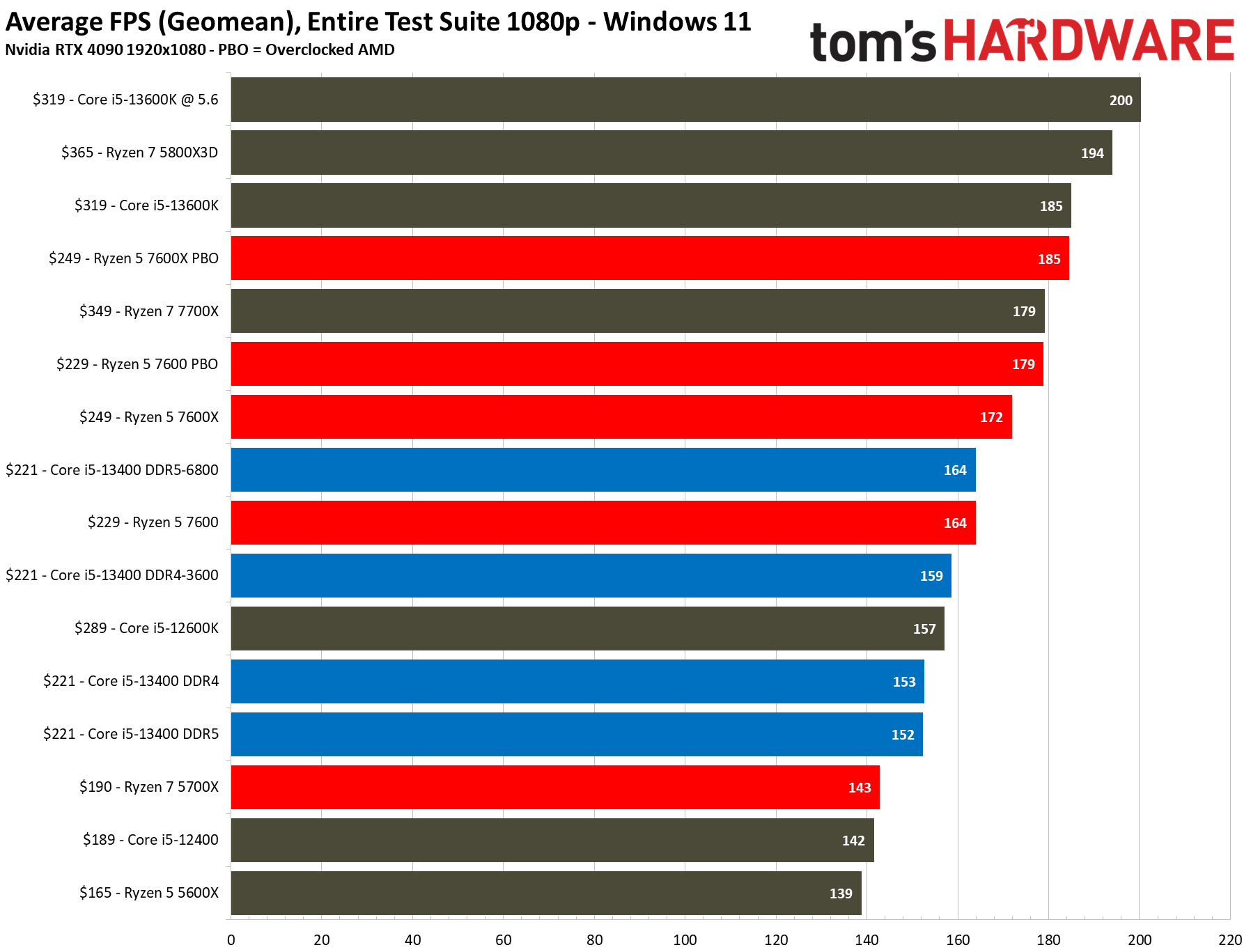
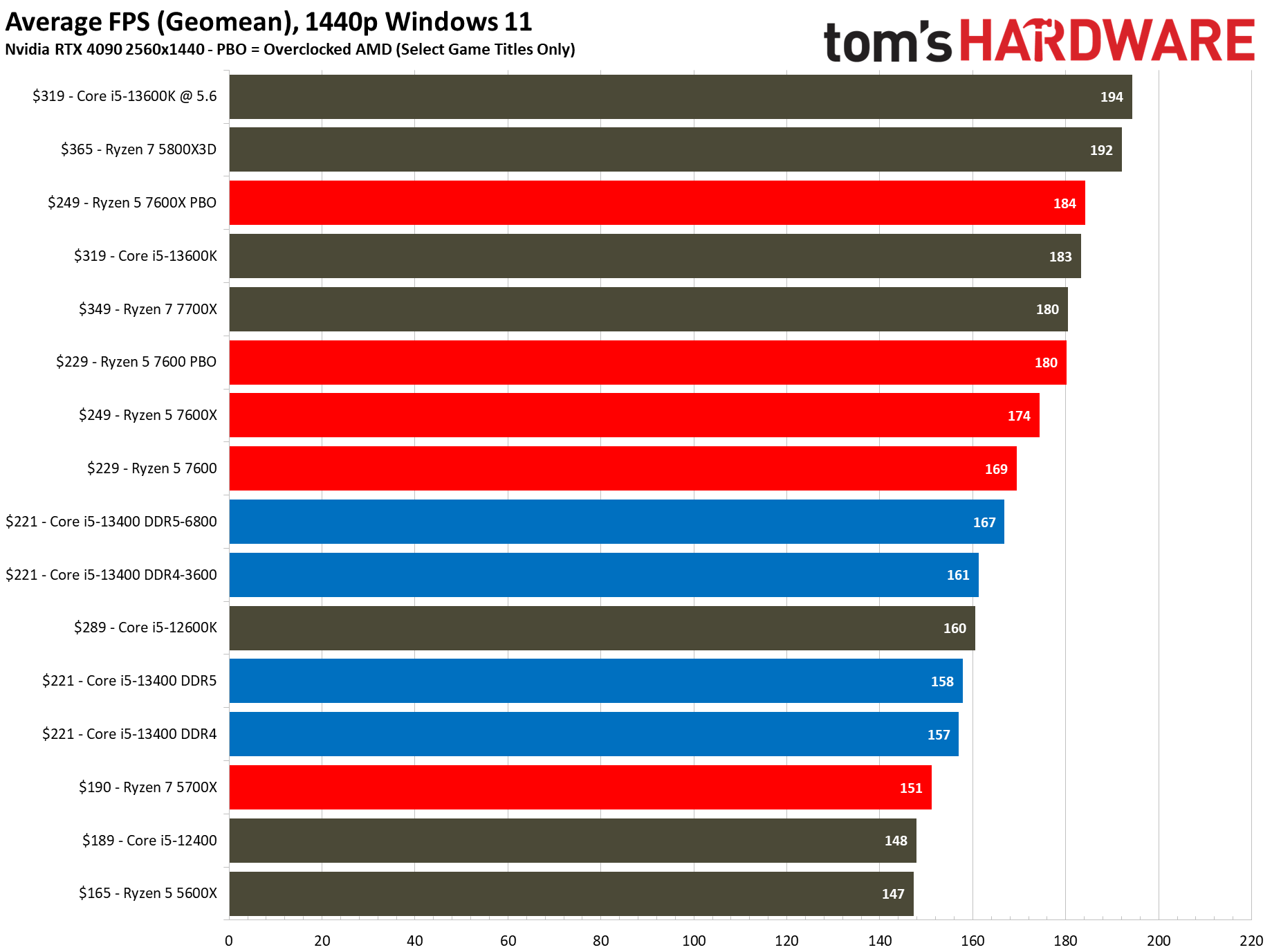
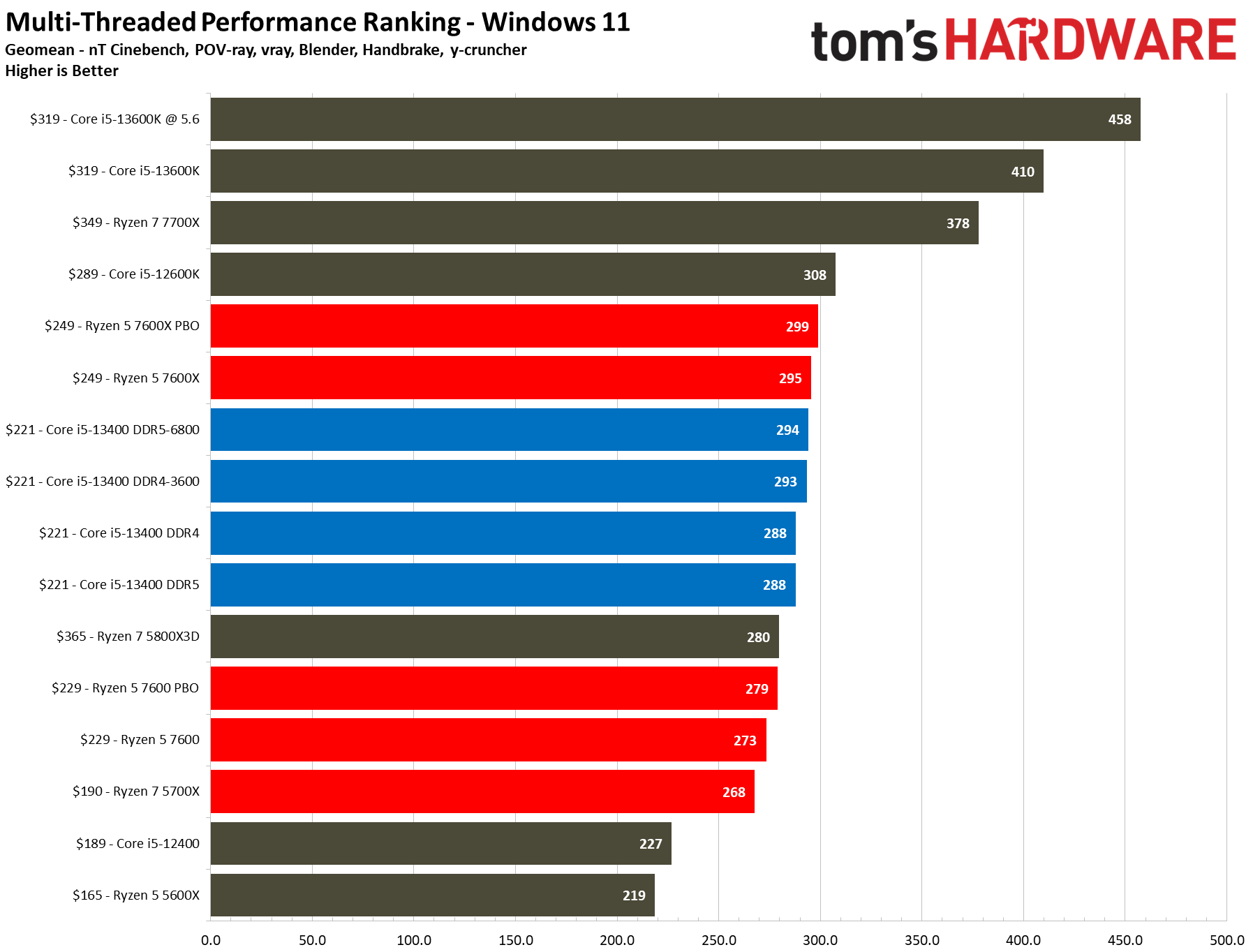
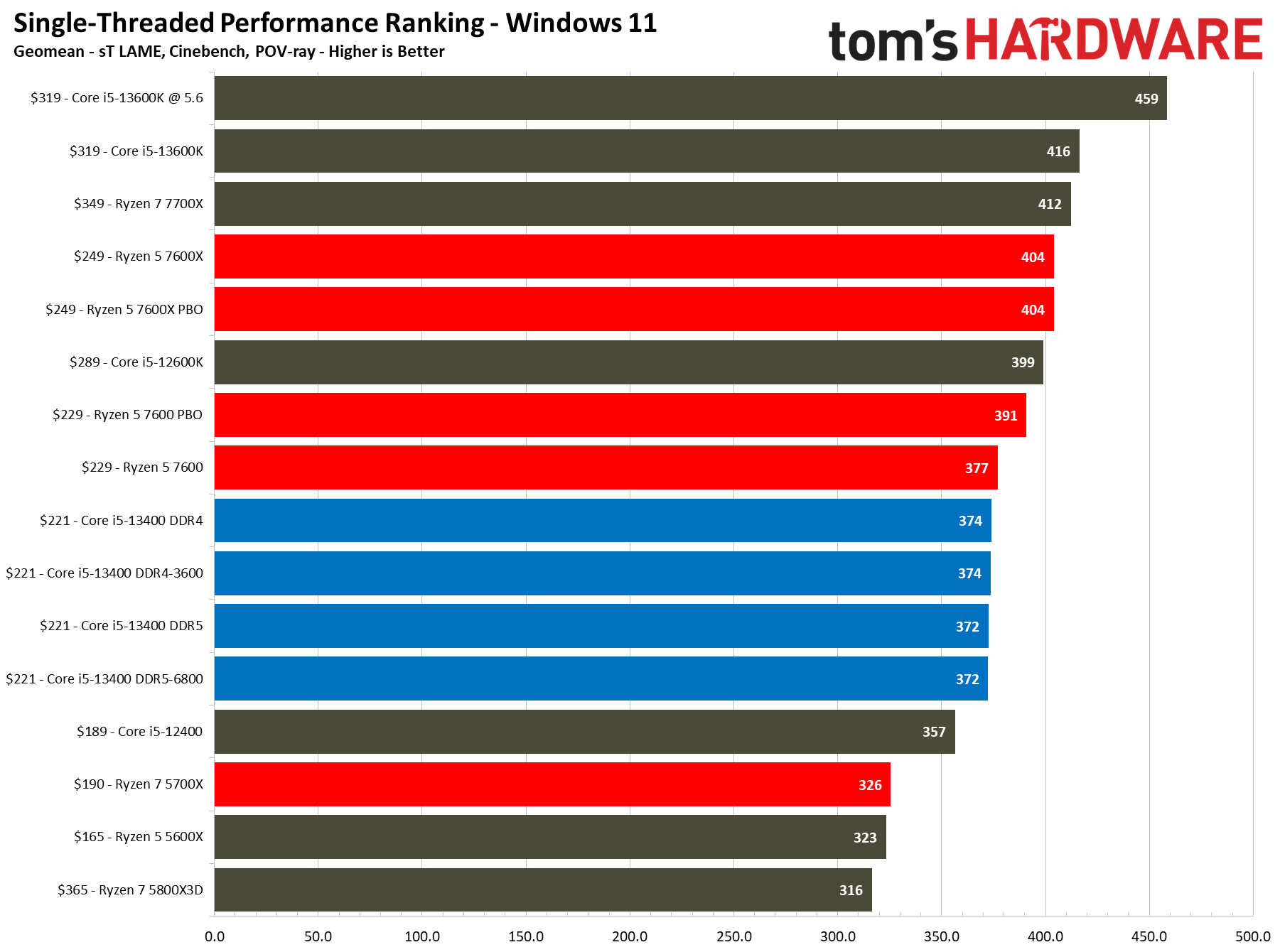
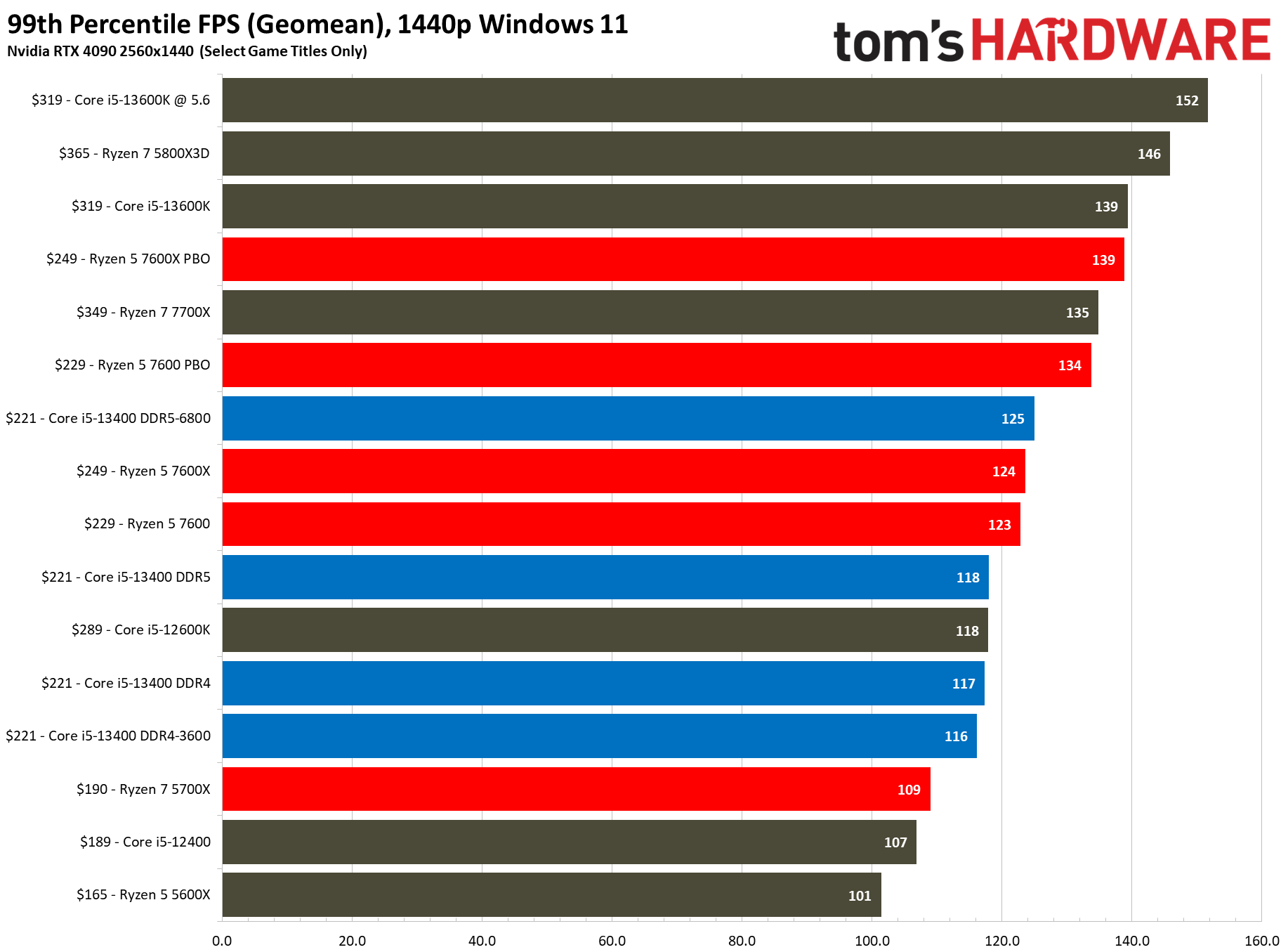
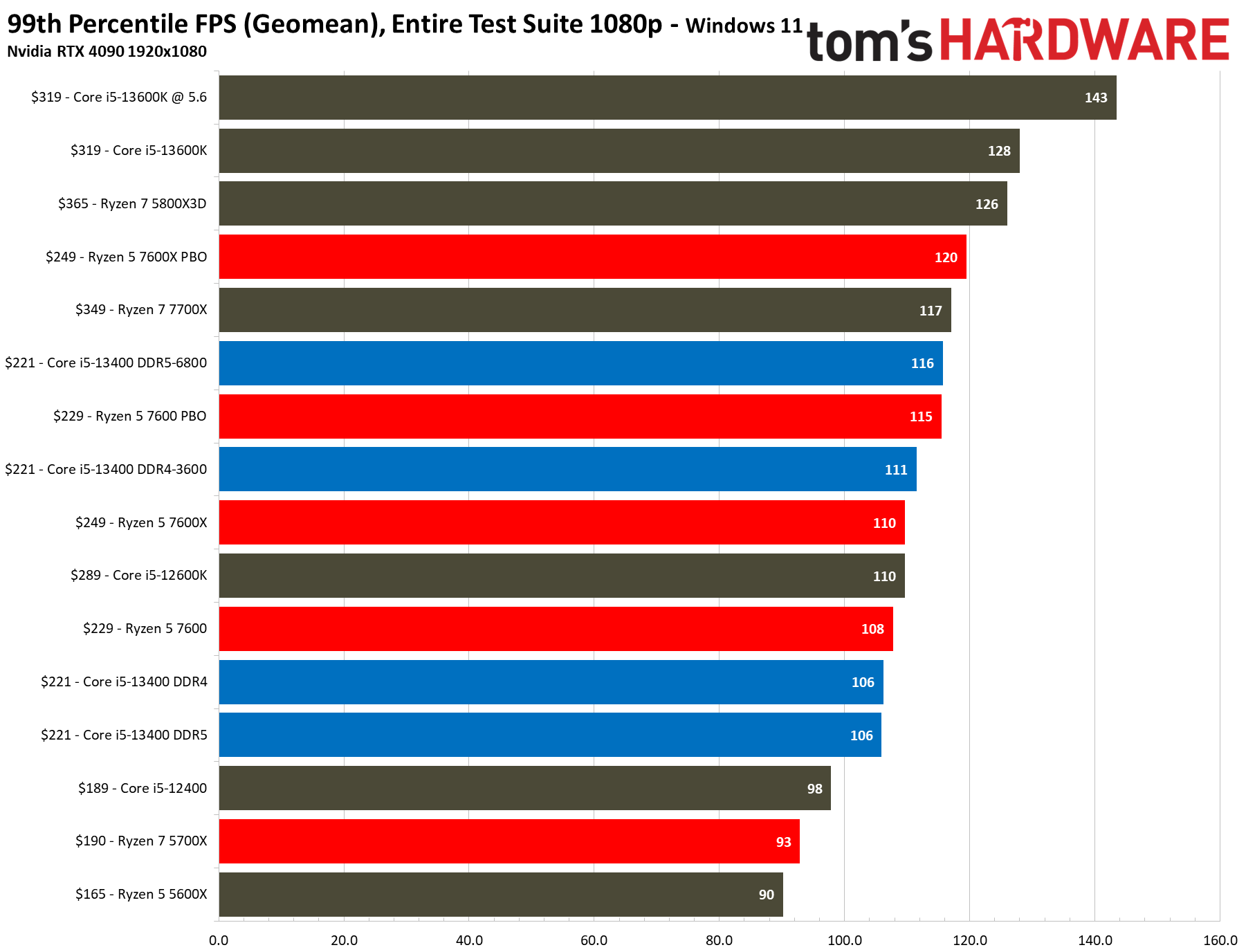
The $221 Core i5-13400 is 7% faster than the previous-gen Core i5-12400, a decent generational improvement. However, its main competitor comes in the form of the $229 Ryzen 5 7600, which is 7% faster than the Core i5-13400 at stock and overclocked settings in our 1080p tests. But the pricing between these two chips isn't as close as it appears.
The optimum low-cost build would also use the $196 graphics-less Core i5-13400F — it doesn't have an iGPU but offers the same performance as the normal model — to save another $25. You also have the option to stick with less expensive DDR4 memory with the Core i5-13400/F and get the same gaming performance as DDR5, albeit at the cost of some overclocking headroom with DDR5.
However, the last few percent of gaming performance from DDR5 overclocking is ridiculously expensive. With the Core i5-13400, we gained ~3% more gaming performance from the DDR5-6800 kit over the DDR4-3600 config, but the DDR5 kit costs nearly three times as much ($144 more). Stepping back to a DDR5-6000 kit that 'only' costs twice as much as the DDR4 kit doesn't make much sense in this price range, either. The AMD Ryzen 5 7600 profited more from overclocking with a 6% gain (some of this comes from PBO, though), and since there's no option for DDR4, you'll pay around 21% more over the already-pricey DDR5-5200 kit.
The Core i5-13400/F's DDR4 option combined with the generally much more forgiving Intel motherboard pricing can save ~$135 in total system costs compared to the Ryzen 5 7600.
| Header Cell - Column 0 | Core i5-13400 DDR4 | Core i5-13400 DDR5 | Ryzen 5 7600 DDR5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chip | $196 Core i5-13400F, $221 13400 | $196 Core i5-13400F, $221 13400 | $229 Ryzen 5 7600 |
| 32 GB Memory - Stock | $65 | $110 | $115 |
| Compatible Motherboards (Median starting price) | B660 $120, B760 $130 | B760 $160, B660 $180 | B650 - $170 |
| Minimum Total Cost / Cost per frame | $381 / $2.50 | $466 / $3.06 | $514 / $3.13 |
We typically don't include cost-per-frame analysis due to fickle component pricing, and including several components magnifies the pricing volatility. This won't be applicable after a month or so (be sure to check current pricing), but the above table gives us the needed nuance for the Core i5-13400 vs Ryzen 5 7600 debate.
The DDR4-powered Core i5-13400F system is the absolute lowest-cost solution at $381 compared to the 7600's $514 — you'll pay 35% more for the Ryzen system and ~25% more per frame to get the ~7% increase in 1080p gaming performance.
The $229 Ryzen 5 7600 isn't price-competitive with the Core i5-13400 DDR4 system at all, but it is more attractive if you already plan to shell out the extra cash for DDR5. However, there's a higher pricing bar for entry than with an Intel Core i5-13400 DDR5 system. The Ryzen system costs ~$50 (10%) more than the DDR5-powered Core i5-13400F system, or ~4% more per frame when we factor in performance. That's close enough to make the Ryzen 5 7600 a solid choice for a DDR5 gaming system, provided you have the extra $50 in the build budget.
Thus, DDR5 builders might turn to other factors, like the 7600's performance in applications (it's 5% slower than the 13400 in threaded work), or the fact that the AM5 platform is supported until 2025+ while the Raptor Lake platforms only have one more refresh gen in the cards. Intel's CPU cores also aren't overclockable (memory is), while Ryzen is fully unlocked. Naturally, personal preference also weighs in.
Both chips are evenly matched in single-threaded productivity applications, but the Core i5-13400 with DDR4 and DDR5 is 5.5% faster than the Ryzen 5 7600 in threaded workloads at both stock and overclocked settings. Again, DDR4 and DDR5 provide similar performance with the 13400 in productivity apps, both at stock and overclocked settings. DDR5 simply isn't worth it.
The 13400's four e-cores provide extra horsepower that helps with streaming — programs like OBS are designed to take advantage — and the additional cores don't add too much power consumption. If you're looking for a more productivity-focused chip, the Core i5-13500 looks very compelling with eight total e-cores; stay tuned for that review.
The Core i5-13400 does suck more power than the Ryzen 5 7600, but it is reasonable, which helps reduce heat output. Both the 13400 and the 7600 come with bundled 'box' coolers, and even though it is surprising, the Intel cooler is serviceable.
As always, we recommend upgrading to a $20 tower-style air cooler for this class of chip, but it isn't a requirement. The Intel cooler is more than adequate with the recommended power limits and can even handle strenuous work with the power limits fully removed. You could run into throttling if you run a heavy extended-duration heavy workload for an hour or more, but you would still come out ahead over running the chip at the recommended 65/148W power limits.
The Ryzen 5 7600 is a worthy alternative if you plan on upgrading to DDR5, but you will have to stomach the higher price of entry over Core i5-13400 systems that use both DDR4 and DDR5. That doesn't seem as reasonable in this price range.
With DDR5, the Core i5-13400 offers a lower price of entry and higher performance in threaded workloads. Even though it is 7% slower in gaming, it still has a competitive price-to-performance ratio with the competing AMD chips — but you don't need DDR5 to unlock the best performance.
When paired with DDR4, the Core i5-13400 generally provides the same performance as a DDR5 system but delivers a superior price-to-performance ratio in both gaming and productivity applications. Add in the unmatched entry-level platform pricing, and the Core i5-13400 is the best bang for your buck in the ~$200 price range, making it the mid-range gaming CPU leader.
| Intel Socket 1700 DDR5 (Z790) | Core i5-13600K, i5-13400, i5-12600K, i5-12400 |
| Motherboard | MSI MPG Z790 Carbon WiFi |
| RAM | G.Skill Trident Z5 RGB DDR5-6800 - Stock: DDR5-5600 | OC: XMP DDR5-6800 |
| Intel Socket 1700 DDR4 (Z790) | Core i5-13400 |
| Motherboard | MSI MAG Z790 Tomahawk WiFi |
| RAM | 2x 8GB Trident Z Royal DDR4-3600 - Stock: DDR4-3200 | OC: DDR4-3600 |
| AMD Socket AM5 (X670E) | Ryzen 7 7700X, Ryzen 5 7600X |
| Motherboard | ASRock X670E Taichi |
| RAM | G.Skill Trident Z5 Neo DDR5-6000 - Stock: DDR5-5200 | OC/PBO: DDR5-6000 |
| AMD Socket AM4 (X570) | Ryzen 5 5600X, 5800X3D |
| Motherboard | MSI MEG X570 Godlike |
| RAM | 2x 8GB Trident Z Royal DDR4-3600 - Stock: DDR4-3200 | OC/PBO: DDR4-3800 |
| All Systems | 2TB Sabrent Rocket 4 Plus, Silverstone ST1100-TI, Open Benchtable, Arctic MX-4 TIM, Windows 11 Pro |
| Gaming GPU | Asus RTX 4090 ROG Strix OC |
| Application GPU | Nvidia GeForce RTX 2080 Ti FE |
| Cooling | Corsair H150i, Stock Cooler |
| Overclocking note | All configurations with overclocked memory also have tuned core frequencies and/or lifted power limits. |
- MORE: AMD vs Intel
- MORE: Zen 4 Ryzen 7000 All We Know
- MORE: Raptor Lake All We Know

Paul Alcorn is the Editor-in-Chief for Tom's Hardware US. He also writes news and reviews on CPUs, storage, and enterprise hardware.
-
Elusive Ruse Why no mention of the 5700X? It's much cheaper and offers the same performance. And no 13400 cannot be found at $200 however the 5700x can be obtained as low as $179.Reply -
edzieba Removing the DDR4 pricing (because component level buyers will likely be replacing an existing system that is using DDR4, and the upgrade pricing already omits PSU, SSD, etc), and that puts the DDR4 13400 at a system buy-in cost of $316 and a cost/frame of $2.07.Reply -
Paul Alcorn ReplyElusive Ruse said:Why no mention of the 5700X? It's much cheaper and offers the same performance. And no 13400 cannot be found at $200 however the 5700x can be obtained as low as $179.
I see the 5700X at around $190. It is generally comparable to the previous-gen 12400 in terms of gaming performance, so it should be around 8% slower than the 13400F for similar pricing. It comes with an older platform and older architecture and we typically try to limit the number of chips in the charts. Besides, the 5700X only makes any kind of sense here if you completely ignore the 13400F... they have roughly the same pricing.
EDIT: We'll add the 5700X to the charts. Tale of the tape is that the 13400 is 7% faster at 1080p, 7.5% faster in multithreaded and 15% faster in single thread. Given the 5700X is only $10 less than the 13400F and comes on an old platform, it isn't a serious contender here. The 5700X also doesn't come with a stock cooler, so that adds cost. -
DRagor Reply
Well, the article clearly states that you can get F version below 200. And I had seen them at such price.Elusive Ruse said:And no 13400 cannot be found at $200 however -
horsemama Reply
Probably because they aren't actually comparing by price but by performance class , Ryzen 5, i5 etc.. Otherwise it would make more sense to suggest an R5 5500 or i3(making the 13400 less attractive) which are half the price and handle mid range gaming no problem.Elusive Ruse said:Why no mention of the 5700X? It's much cheaper and offers the same performance. And no 13400 cannot be found at $200 however the 5700x can be obtained as low as $179.
For the price of this CPU in Canada, I was able to get a 5500, B550 board, 16GB RAM and a cheapo Thermalright cooler. -
Paul Alcorn ReplyDRagor said:Well, the article clearly states that you can get F version below 200. And I had seen them at such price.
The 13400 launched about a month ago, and it will fall closer to that $196 over the next few months. Previous-gen 12400 was below Intel's recommended pricing even before 13400 launch, for instance. -
Paul Alcorn Replyhorsemama said:Probably because they aren't actually comparing by price but by performance class , Ryzen 5, i5 etc.. Otherwise it would make more sense to suggest an R5 5500 or i3(making the 13400 less attractive) which are half the price and handle mid range gaming no problem.
For the price of this CPU in Canada, I was able to get a 5500, B550 board, 16GB RAM and a cheapo Thermalright cooler.
The Ryzen 5 5500 is an APU, there are better options in that price class if you're looking to use a discrete gaming GPU. Additionally, the class of machines you're describing is a bit below the focus price range. -
logainofhades ReplyElusive Ruse said:Why no mention of the 5700X? It's much cheaper and offers the same performance. And no 13400 cannot be found at $200 however the 5700x can be obtained as low as $179.
Yes those of us lucky enough to have a Microcenter nearby, that $179 is doable. Not everyone has such a luxury though. -
Elusive Ruse Reply
And I see the 13400 at around $240 using the same platform as you used; the gaming performance comparison could go either way based on the games you review so it's not as straightforward. I understand the older gen argument; however, you mentioned the 5600X in your article that's why I was wondering at the omission of the 5700X.PaulAlcorn said:I see the 5700X at around $190. It is generally comparable to the previous-gen 12400 in terms of gaming performance, so it should be around 8% slower than the 13400F for similar pricing. It comes with an older platform and older architecture and we typically try to limit the number of chips in the charts.
OsA52DkP8WUView: https://youtu.be/OsA52DkP8WU -
Elusive Ruse Reply
The price gap is basically the same, on Newegg and Amazon e.g.logainofhades said:Yes those of us lucky enough to have a Microcenter nearby, that $179 is doable. Not everyone has such a luxury though.
