AMD A10-4600M Review: Mobile Trinity Gets Tested
AMD steps up to the plate with an all-new processor. Armed with the updated Piledriver CPU core and VLIW4 graphics architecture, the Trinity APU represents an impressive improvement over the Llano generation. But can it stand up to Intel's best efforts?
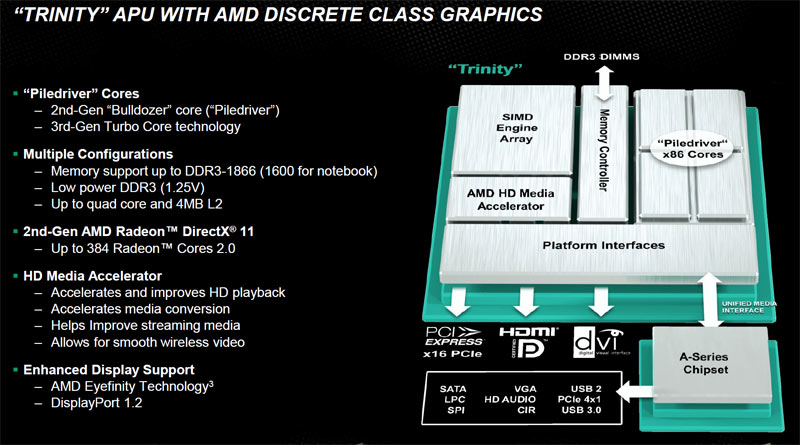
All Together Now: The Trinity APU
Now, how do the CPU and GPU fit together? You might want to read The AMD A8-3500M APU Review: Llano Is Unleashed for an explanation of how AMD plumbs its APUs, since the following covers Trinity specifically.
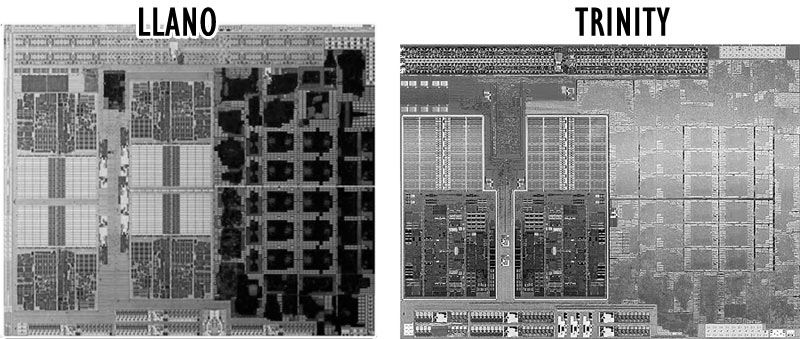
The new APU comes packaged on a 226 square-millimeter die with 1.303 billion transistors, which is almost exactly same size as Llano’s 228 mm2 die. Like Llano, Trinity is manufactured on GlobalFoundries’ 32 nm SOI process. Default frequencies scale much higher than Llano did, with 3.8 GHz CPU and 800 MHz GPU ceilings for the top-end desktop parts. TDPs on the low-power mobile models dip down as far as 17 W. We’ll delve more into the specific productization shortly, but it’s at least apparent right away that Trinity scales both higher and lower than Llano. As a side note, the new APU comes with either one or two modules, equaling two or four cores, so there won’t be any six- or eight-core APUs on their way to the market in this generation.
A quick peek at the die makes it clear that AMD is devoting more die space to graphics—an observation we made comparing Intel’s Ivy Bridge to Sandy Bridge. This isn’t much of a surprise, though, considering the Piledriver architecture makes generous use of resource-sharing.
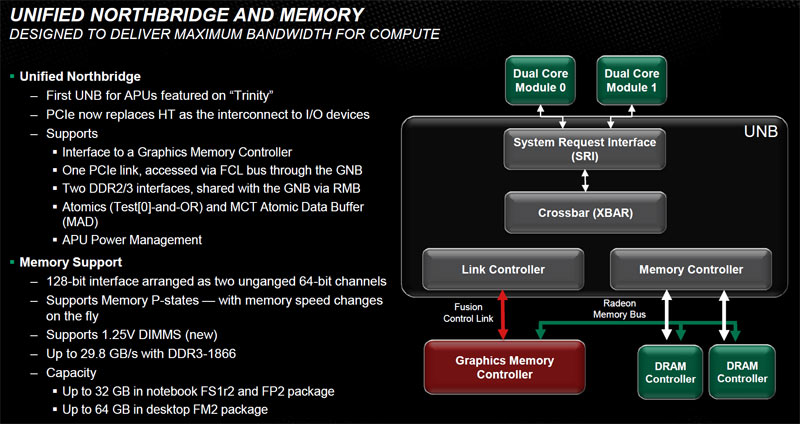
The New Unified Northbridge
Llano utilizes a somewhat standard CPU-to-Northbridge link and the Fusion Control Link for GPU-to-Northbridge memory exchange. In Trinity, a new Unified Northbridge (UNB) replaces the older hardware. This is AMD’s first application of a UNB outside of the server space; the company’s product CTO Bob Macri likens it to a traffic cop at the heart of the machine. It’s the component that ties everything to the memory and I/O subsystems. It must cope with various functional units, each making unique requests with specific attributes.
For example, the CPU hands relatively few requests to the UNB, but these are given a high priority since any added latency can have a significant impact. On the other hand, the GPU makes thousands of outstanding references and needs a lot of DRAM utilization to perform well. In this case, the UNB optimizes and reorders requests so the GPU can access the memory subsystem in the most efficient way possible. The UNB also has an important role in keeping the power down, and will modulate memory frequency depending on the load to get the optimal power usage per unit of work.
The New Memory Controller
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
An APU’s memory subsystem is especially important because so many functional units contend for bandwidth. Trinity’s memory controller is a new design with support for 1.25 V DIMMs that introduce potential power savings. As for data rates, DDR3 modules are limited to 1866 MT/s on the desktop and 1600 MT/s in mobile configurations, similar to Llano. The platform addresses up to 64 GB in desktop form, with peak system bandwidth as high as 29.8 GB/s. The mobile config accommodates up to 32 GB of memory and bandwidth as high as 25.6 GB/s.
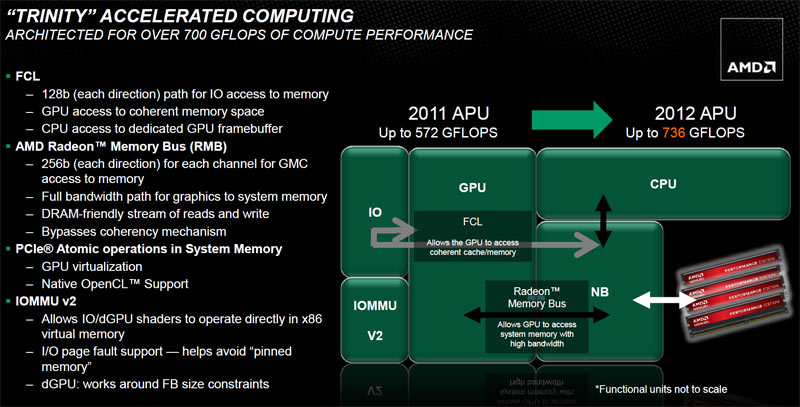
Accelerated Computing And The IOMMUv2
Llano is rated for up to 572 gigaflops of compute performance, but the top of the Trinity stack has the potential for 736. The increase is due mostly to improvements inherent to the Devastator GPU, but something that catches our eye is the new IOMMUv2 block.
This unit adds virtual address access discrete graphics, allowing an external GPU to directly access the same virtual address space as the CPU through page tables. As you can imagine, this is a key part of the programming model for AMD’s Heterogeneous Systems Architecture (HSA).
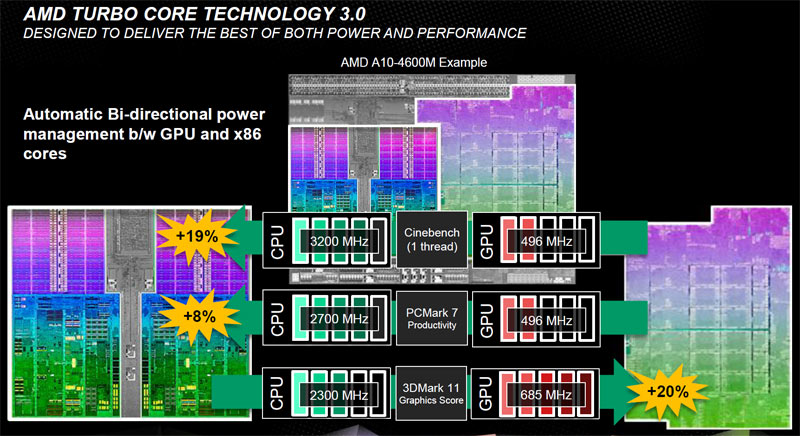
Turbo Core 3.0
Third-gen Turbo Core is the latest version of the feature first introduced in AMD’s Thuban-based Phenom II X6 CPUs, and it’s now purportedly dynamic in the way it balances CPU and GPU clock rates. The above slide from AMD’s presentation suggests that power and frequencies can be shifted from CPU to GPU on demand to meet the system load.
Unfortunately, this isn’t the behavior we witnessed in AMD’s system monitor utility, which reported CPU performance at a 2.3 GHz nominal rate, regardless of load. We did, however, see the GPU speed fluctuate and drop as low as 334 MHz during a single-threaded Cinebench run. We’re not sure if Turbo Core 3.0 isn’t working properly or if AMD’s system monitor is reporting the CPU clocks incorrectly. We asked AMD about it utility and were told that there’s currently no tool able to accurately monitor its chip’s Turbo rates. Incidentally, that’s the same answer we received a year ago when the company introduced Llano. You can be sure we’ll be diving into more depth on this in the days to come.
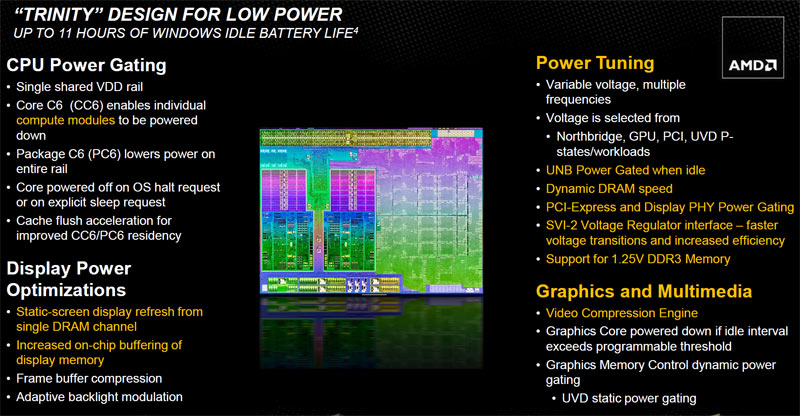
Power Management
As with Llano, Trinity is designed with low-power applications in mind. You can see the main power improvements AMD made to its APU in the diagram above, highlighted. This includes an improved CC6 power state able to turn off individual Piledriver modules when three or four execution cores aren’t needed. Both modules can be shut down on a package level.
Under normal use, the APU aggressively employs both DDR3 memory channels for graphics data. But when the screen is static, the APU detects more modest activity and remaps the output to a single memory channel. It can even put the unused channel to sleep and reduce the clock rate of the active channel to the minimum required for the display.
Engineers also increased the on-die buffering of memory so that DRAM isn’t queried as much, meaning power-hungry memory is left in a low-power state as long as possible.
Current page: All Together Now: The Trinity APU
Prev Page The GPU Side: VLIW4 > VLIW5 Next Page Products And PlatformsDon Woligroski was a former senior hardware editor for Tom's Hardware. He has covered a wide range of PC hardware topics, including CPUs, GPUs, system building, and emerging technologies.
-
Recently Charlie at semiaccurate (a massive amd fanboy) hinting an upcoming apple products, then I saw an article in thg that tells an upcoming mbp will using retina display... 15 inch retina will require huge gpu horsepower, my wild guess is mbp will use trinity as it's CPU.Reply
-
Based on this, gaming is much better than old i5, but everything else including application performance is still better on the old Sandy architecture. I'm not really sure why I would buy a Trinity other than for a casual gaming laptop. Unfortunately, budget says that my laptops have to be used for business first, play time later.Reply
-
beenthere Nice to see that Trinity and AMD have delivered the goods. I want a Trinity powered Ultrathin. Intel can stick their crap where the Sun don't shine.Reply
BTW, Charlie @ SemiAccurate is not an AMD fanbois IME. He just calls it like it is. Reality bites sometimes be it Nvidia, AMD or Intel's problems. Denial never changes reality. It is what it is. -
cleeve duckwithnukesWhere is the Intel HD 4000 vs. AMD Trinity comparison? Lazy reviewing at its finest.Reply
A10-4600M laptops will be int eh $600-$700 neighborhood, and we're still waiting for Ivy bridge Core i5 to arrive in this price range.
We go over this. We also talk about how we'll do a follow up as soon as an appropriate product is available.
You need to read for it to make sense.
-
FlippyFlap, Apple doesn't use AMD and an HD4000 can power a retina display. I'm sure Apple has worked with Intel engineers to get the drivers right for retina displays which is HD4000's problem. HD4000 is still lacking in terms of driver support (one can see that from the OpenCL benches around the net where only 1/2 get acclerated on HD4000). When the drivers work right, there isn't much difference between Ivy and Trinity.Reply
-
I agree with Cleeve and I personally hate comparing a reference system to a selling system anyway. Review 2 actual selling systems with similar parts and that gives you the benchmark.Reply
-
DRosencraft This looks like a very nice effort from AMD. I really, really need to replace my notebook. It's a six year old Toshiba Satelite with an AMD 1.9 GHz Turion 64 X2 with intergrated X2100 graphics.... yeah. Ancient now, I know. I've been trying to figure out a sweet spot in power since my needs are kind of complex. Typically I don't need it to do much more than handle MSOffice and web surfing. But I also tend to use it for video gaming when am interesting game comes around and some work in PaintShop when I'm out of the house, or don't feel like sitting at my desktop. This may be a little closer to what I'd like. It would be nice to get a notebook that combines this with a really good discrete card (sort of like how some MacBook Pros have their dual graphics setup). Nevertheless, Trinity looks to be just about enough power and performance, but the question is price. If tradition holds, it should be a good price competitor with Intel, which is the most important part, otherwise I'd just buy a core I7 already.Reply
In a related question, does Trinity's details and specs lead to any conclusions about what Piledriver desktop processors will be like? -
neoverdugo So this means that AMD can kick Intel's ass in the gpu department for the moment while AMD suffers greatly in the CPU portion of the apu battle. Didn't I said before that Intel is trying to make an (proprietary) Intel only PC with no third party strings attached? We all know that there is no competition in the CPU battle when it comes to Intel. Still, i would like to see that the morons of intel to drop the price of their hardware for once and for all and drop ridiculously low end hardware out of production.Reply -
dgingeri No WoW benchmarks this time? I was wondering if this might make a good laptop for WoW, but you guys failed me. :(Reply