AMD Raven Ridge Thermal/Power Analysis: Ryzen CPUs With Vega
Introduction & Test System
AMD Ryzen 5 2400G Review: Zen, Meet Vega went in-depth on the Raven Ridge architecture and explored the flagship processor's performance. Today, we're taking a closer look at the power consumption, clock rates, and temperatures of AMD's Ryzen 5 2400G and Ryzen 3 2200G. We're also pitting the stock thermal solution against our high-end chiller in order to find a temperature-independent power limit for the Ryzen 5 2400G.
It is also interesting that AMD uses heat-conducting paste instead of solder between its Raven Ridge dies and heat spreaders. However, with an average power dissipation of less than 100W, this cost-cutting measure is probably tolerable for everyday operation. Of course, we also ran a series of more demanding workloads to tax both processors. It comes as little surprise that we figured out how to get the 2400G to throttle. We weren't expecting, however, to get its Radeon Vega Graphics engine stuck that way.
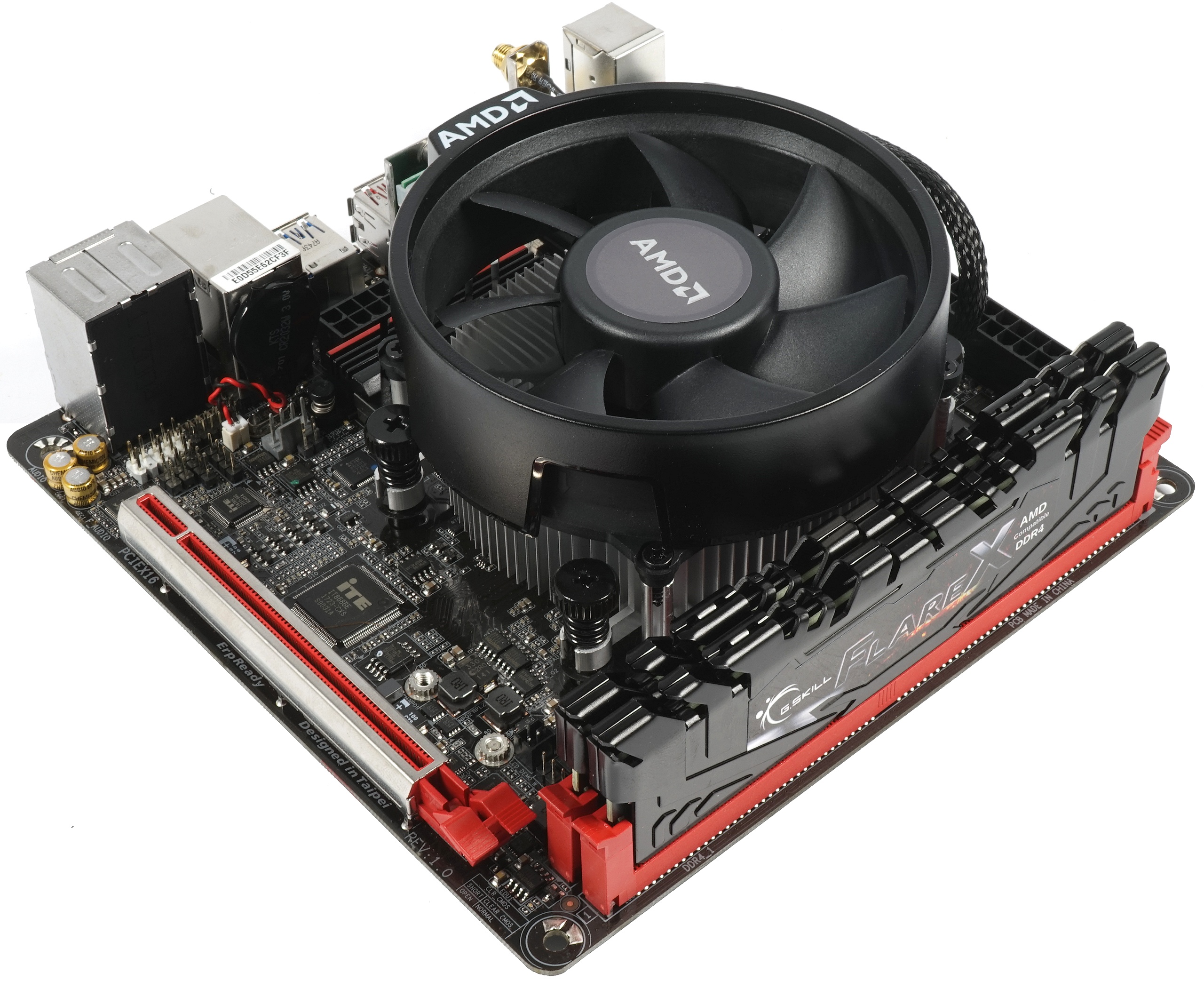
We’re using the same hardware for today's testing as what you saw yesterday: AMD's Ryzen 5 2400G and Ryzen 3 2200G, the Gigabyte AB350N Gaming WiFi with two 8GB G.Skill FlareX DDR4-3200 modules, and AMD’s Wraith Stealth cooler (an OEM part from AVC’s massive portfolio sporting an AMD label). Four screws hold the thermal solution in place, giving us a much more secure mounting mechanism than Intel's push-pin system.
In order to establish the limits of AMD's Raven Ridge-based processors, we need to push them as far as they can go. That's where Alphacool's powerful Eiszeit 2000 compression chiller comes into play. We combine it with the Alphacool Eisblock XPX, replacing AMD's Wraith Stealth heat sink. Motherboard components are cooled by 22°C air from a large fan blowing across them.
But before we dig into our findings, let's quickly recap the hardware used to test, the equipment in our lab responsible for our accurate measurements, and some of the software we run to monitor sensors:
| Test Equipment & Environment | |
|---|---|
| System | AMD Ryzen 5 2400GRyzen 3 2200GGigabyte AB350N-Gaming WiFiFlare X 16GB DDR4-3200MX300 SSD 1050GBDark Power Pro 10 (850W) |
| Cooling | AMD Stock CoolerAlphacool Eisblock XPXAlphacool Eiszeit 2000 ChillerThermal Grizzly Kryonaut (Used when Switching Coolers) |
| PC Case | Microcool Banchetto 101 |
| Monitor | Eizo EV3237-BK |
| Power Consumption Measurement | Motherboard Sensors, HWiNFO64, AIDA64, Custom Software (by Igor Wallossek)Contact-free DC Measurement at Eight-Pin EPS ConnectorDirect Voltage Measurement at Applicable Power Supplies and PSU1x Rohde & Schwarz HMO 3054, 500 MHz Digital Multi-Channel Oscilloscope with Storage Function 2x Rohde & Schwarz HZO50 Current Probe (1mA - 30A, 100 kHz, DC) 2x Rohde & Schwarz HZ355 (10:1 Probes, 500 MHz) |
| Thermal Measurement | 1x Optris PI640 80 Hz Infrared Camera + PI Connect Real-Time Infrared Monitoring and Recording |
| Operating System | Windows 10 Pro (1709, All Updates) |
MORE: Best CPUs
MORE: Intel & AMD Processor Hierarchy
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
MORE: All CPUs Content

Igor Wallossek wrote a wide variety of hardware articles for Tom's Hardware, with a strong focus on technical analysis and in-depth reviews. His contributions have spanned a broad spectrum of PC components, including GPUs, CPUs, workstations, and PC builds. His insightful articles provide readers with detailed knowledge to make informed decisions in the ever-evolving tech landscape
-
Combat_Medic The prices you chose to use here are bogus - the $99 and $169 MSRP are what they're actually going for.Reply -
AgentLozen ReplyCombat_Medic said:The prices you chose to use here are bogus - the $99 and $169 MSRP are what they're actually going for.
The prices from Amazon or NewEgg (or whatever) are usually inaccurate. I think Tom's should provide us with the MSRP and the internet price. That way, if the internet price is malfunctioning and showing a +50% markup, at least we know what it's SUPPOSED to sell for.
edit: minor fix -
FormatC When I wrote this review, we had only the official MSRP from AMD. The availability in Germany looks ok and the prices in EUR with VAT are lower :)Reply -
Ninjawithagun The prices (provided via direct link to Amazon.com) are now correct. Unfortunately, they are all sold out...lol.Reply -
JamesSneed These seem to be very efficient for the CPU and GPU performance they deliver. Nifty more options for budget PC's.Reply
I am left wondering if the 14nm process AMD is using, is having issues scaling to higher frequencies as it appears you keep Zen and Vega at lower clocks and they are very efficient. -
FormatC I really like the new power management and it is finally nothing else as efficiency-orientated mobile technology for the desktop.Reply -
nuclearpowerofattorney Maybe the 2400G is so smart and powerful, that when it reaches critical computational capacity, it evolves to become sentient, and thus unruly. Only after it is rebooted, to have the sentience removed, will the system cease its rebellious behavior. (Actually, I don't think this..but it's all I've got).Reply -
Rookie_MIB For the 2400G, bundling the better Wraith Spire could probably avoid the throttling bouncing around by preventing it from hitting the thermal limits under the more taxing loads.Reply
Eventually though they're going to have to find out what's causing it to get stuck in that loop. -
7angrytangerines Obviously 2400G wants to protect itself from some poor saps trying to use it for cryptocurrency mining.Reply