Six-Core Analysis, Part 2: Intel Core i7-980X Scaling
Intel's Turbo Boost technology provides a mechanism for improving system performance most significantly in lightly-threaded apps, even at peak loads. But what is the feature's impact on a Gulftown-based Core i7-980X processor with different core counts?
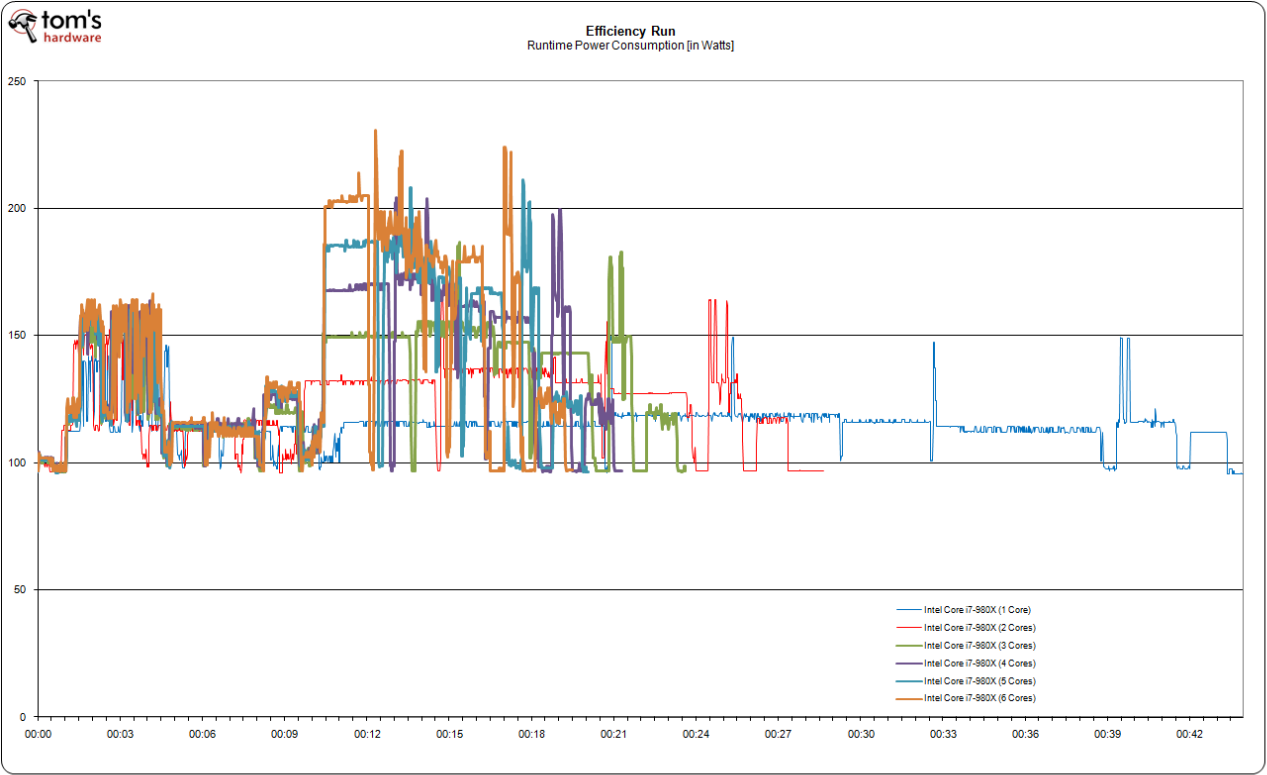
Benchmark Results: Efficiency
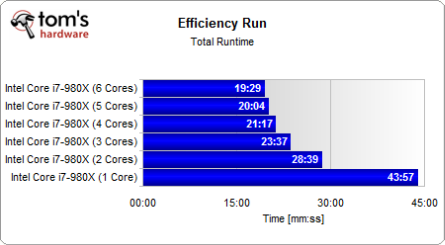
The total runtime tells us how long the systems took to complete our full efficiency workload, including most of the applications mentioned previously. Clearly, the difference between one, two, and four cores is significant, while adding cores five and six don't yield the same performance jumps. This is very applicable to real life and typical applications.
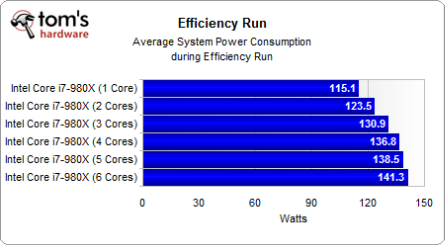
The average power consumption during this efficiency run increases with every core we switch on, but look at how the bars create a curve that flattens out. Average power may increase, but so does performance, and probably to a larger extent.
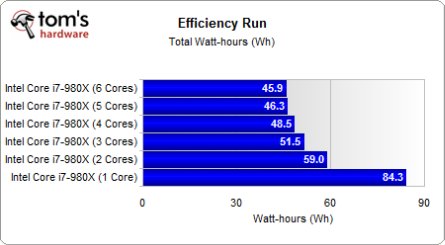
These results are similar to what we found on our AMD system. The total power required to complete our efficiency workload is lowest with a maximum number of cores.
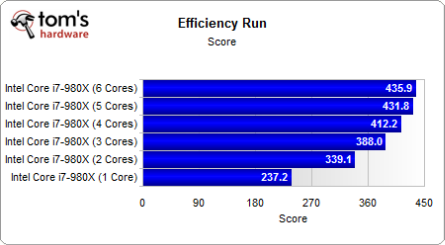
These results clearly show how performance increases significantly with additional cores while power consumption increases more moderately. If we relate performance to power used, we get confirmation that 5- and 6-core operation is most efficient.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Benchmark Results: Efficiency
Prev Page Benchmark Results: Power Consumption Next Page Normalized Power And Efficiency Results